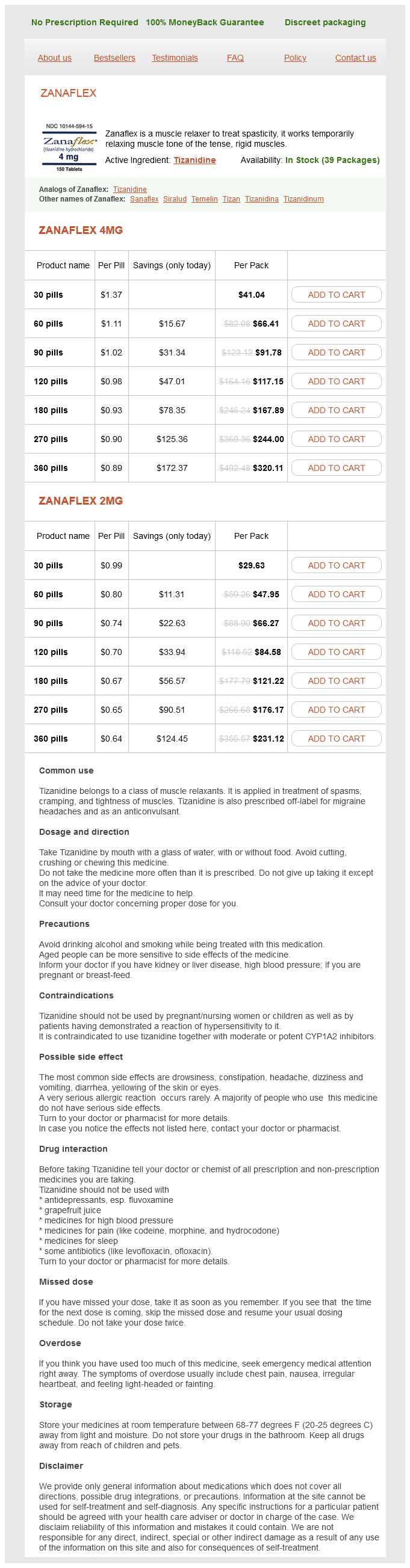
Tizanidine
Discount tizanidine 4 mg amex
Factors affecting dengue fever knowledge muscle relaxant generic names purchase tizanidine 4mg amex, attitudes and practices among selected urban, semi-urban and rural communities in Malaysia. The impact of preventive fogging on entomological parameters in a university campus in Malaysia. Epidemiology and new initiatives in the prevention and control of dengue in Malaysia. An epidemiological cluster pattern of dengue outbreak amongst close contacts in Selangor, Peninsular Malaysia. Male-female differences in the number of reported incident dengue fever cases in six Asian countries. Cross-reactive T-cell responses the nonstructural regions of dengue viruses among dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever patients in Malaysia. Cytokine factors present in dengue patient sera induces alterations of junctional proteins in human endothelial cells. Sharing experiences: towards an evidence based model of dengue surveillance and outbreak response in Latin America and Asia. Antibodies against prM protein distinguish between previous infection with dengue and Japanese encephalitis viruses. Spatial, environmental and entomological risk factors analysis on a rural dengue outbreak in Lundu District in Sarawak, Malaysia. A comparative evaluation of dengue diagnostic tests based on single-acute serum samples for laboratory confirmation of acute dengue. Developing a vulnerability mapping methodology: applying the water-associated disease index dengue in Malaysia. Neurovirulence of four encephalitogenic dengue 3 virus strains isolated in Malaysia (1992-1994) is not attributed their envelope protein. The diagnostic sensitivity of dengue rapid test assays is significantly enhanced by using a combined antigen and antibody testing approach. Importation and co-circulation of multiple serotypes of dengue virus in Sarawak, Malaysia. Non-invasive diagnosis of risk in dengue patients using bioelectrical impedance analysis and artificial neural network. Modeling of hemoglobin in dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever using bioelectrical impedance. Prevalence of dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever in Hospital Tengku Ampuan Rahimah, Klang, Selangor, Malaysia. Localization of dengue virus in naturally infected human tissues, by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Evaluation of a capture screening enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for combined determination of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies produced during Dengue infection. Nonsubstrate based inhibitors of dengue virus serine protease: a molecular docking approach study binding interactions between protease and inhibitors. Asia Pacific Journal of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 2007;15(2):53-9. Transovarial transmission of dengue virus in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in relation dengue outbreak in an urban area in Malaysia. Structure-based and ligand-based virtual screening of novel methyltransferase inhibitors of the dengue virus. Community vulnerability on dengue and its association with climate variability in Malaysia: a public health approach. Application of geographical information system for spatial-temporal mapping: a case study of dengue cases in Seremban, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Chikungunya infection in Malaysia: comparison with dengue infection in adults and predictors of persistent arthralgia. The place of health and the health of place: dengue fever and urban governance in Putrajaya, Malaysia. Epidemiological and clinical features of dengue versus other acute febrile illnesses amongst patients seen at government polyclinics. Awareness of dengue and practice of dengue control among the semi-urban community: a cross sectional survey. A review of dengue fever incidence in Kota Bharu, Kelantan, Malaysia during the years 1998-2003. The role of an emergency department short-stay ward in the management of dengue fever: a case-control study in a university hospital. Co-infection of dengue virus and chikungunya virus in two patients with acute febrile illness. Measurement of dengue epidemic spreading pattern using density analysis method: retrospective spatial statistical study of dengue in Subang Jaya, Malaysia, 2006-2010. A case-control study on factors affecting the incidence of dengue fever in Johor Bahru. Audit of haemorrhagic manifestations in dengue infection and its correlation with bleeding profile. Serial tourniquet testing in dengue haemorrhagic fever-How clinically useful is it? Asian Oceanian Journal of Pediatrics and Child Health 2004;3(1):16-25. Field evaluation on the effectiveness of a modified approach of chemical fogging against the conventional fogging in controlling dengue outbreak. The role of virological surveillance of dengue serotypes for the prediction of dengue outbreak. Review of dengue hemorrhagic fever fatal cases seen among adults: a retrospective study. Antigenic cell associated dengue 2 virus proteins detected in vitro using dengue fever patients sera. Use of multiple data sources estimate the economic cost of dengue illness in Malaysia. Carica papaya leaves juice significantly accelerates the rate of increase in platelet count among patients with dengue fever and dengue haemorrhagic fever. Dengue infection in pregnancy: prevalence, vertical transmission, and pregnancy outcome. The clinical features and outcomes of acute liver failure associated with dengue infection in adults: a case series. Risk factors associated with development of dengue haemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome in adults in Hospital Tengku Ampuan Afzan Kuantan. Differential expression of aldolase, alpha tubulin and thioredoxin peroxidase in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever patients. The use of two-dimension electrophoresis identify serum biomarkers from patients with dengue haemorrhagic fever. Predictive value of thrombocytopaenia in the diagnosis of dengue infection in outpatient settings. Prevalence of non-dengue thrombocytopaenia among adult patients presenting with acute febrile illness in primary outpatient clinics. Clinical features of acute febrile thrombocytopaenia among patients attending primary care clinics. Evolutionary history of Dengue virus type 4: insights into genotype phylodynamics. Molecular typing of dengue viruses circulating on the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia from 2005 2009. Antibody neutralization and viral virulence in recurring dengue virus type 2 outbreaks. Behavioural factors influencing the dengue infection: the study among students in the higher learning institution. Sensitivity of Aedes albopictus C6/36 cells line for the detection and infectivity titration of dengue virus. International Proceedings of Economics Development & Research 2011;1:345-9. Atrial fibrillation as a complication of dengue hemorrhagic fever: non-self-limiting manifestation. A case of mixed infections in a patient presenting with acute febrile illness in the tropics. The mosquitoes are genetically engineered die at the larval stage in the absence of the antibiotic tetracycline, which acts as a chemical switch allow breeding in the laboratory.
Order tizanidine toronto
It is water and alcohol soluble quetiapine muscle relaxer buy tizanidine 2mg online, Mucolytic Agent environmentally friendly and extremely economical. Following air drying, the cell spreads should be for use as a general collection fuid for cytology specimens. Plus, it helps immersed for ten minutes in 95% ethanol thoroughly remove the prevent cell loss and distortion in order maintain specimen integrity, polyethylene glycol. Sed-Fix is available in a liquid concentrate make which is necessary for accurate diagnosis. S7444-70B 76160 120 mL preflled container 72/cs L3802950 3802950 Concentrate 384 mL bottle 1/ea S7444-71B 76161 1 gal. Each kit comes with a selection of components and S7783-16 231060 1-slide kit with fxative spray 25/bx, 500/cs instructions for performing a single test. All test kit components are S7783-17 241050 2-slide kit with fxative spray 25/bx, 500/cs packaged inside a patented no-touch folder pack designed protect fragile specimens. Folder packs utilize a folder perforation hold slides securely in place, eliminating the use of adhesives that can damage specimens. After specimen collection, simply tear away the courier portion of the folder pack provide reliable protection for your samples Plastic Cervical Scraper during transport. S7783-9 890076-C500 Scraper 500/cs Each no-touch pack withstands a minimum of 2 lbs. The reinforced design of the pack helps prevent slide breakage, and no-touch packaging helps prevent the specimen from rubbing of onto transport folder. Cervical Scrapers All Pap smear test kits come with detailed instructions for collecting specimens using a swab, scraper and cytology brush. The Elongated Tip Scraper allows deeper penetration into S7783-23 230080 With wooden scraper, brush and 500/cs the endocervical area. The Duo-End Scraper enables the clinician use fxative pump bottle either the Ayres Tip or modifed Elongated Tip, providing cell samples S7783-3 230100 With swab, spatula, cytology brush 500/cs from both cervix and endocervix in one step. Ayres-style wooden scraper is sterile and constructed of straight grain and white birch. VisionTek is the only system which enables simultaneous live review of multiple slides and/or multiple areas of the same slide with time-to-view under 17 seconds. The ability focus through diferent planes on live and scanned images eliminates soft focus issues associated with scanners. Efcient fow through slots maximize fuid exchange and help ensure proper drainage. Three writing Assembled Biopsy Cassettes areas, including the anterior side at a 45 angle. Cassette features a recessed cover, resistant chemical actions of histological solvents. Flow-through slots maximize fuid exchange and help ensure proper Histology Tissue Cassettes drainage. They have excellent adherence for all inks; optimal polymer technology resistant chemicals and are secure and safe. Available in 10 colors, these biopsy cassettes come attached lid and an improved rounded thumb-tab for comfort and easy pre-taped for easy dispensing into Thermo, R. The chemical-resistant ridged materials provide a stable platform for embedding and cutting. Enhanced perforation allows proper fuid transfer and efective drainage, which produces greater infltration and reduces carryover during processing. The rigidly constructed cassettes are made of solvent and acid-resistant plastic featuring a textured writing surface on three sides. Biopsy cassettes also feature 1 x 1 mm square holes permit complete fuid exchange and thorough parafn infltration and a stay-shut closure design. The cassettes also feature sloped walls, creating a basket for small tissue management. The pre-packaged cassettes feature a seamless tube, providing a smooth internal surface through which the cassettes can slide without obstruction. The pre-packaged cassettes feature a seamless tube, providing 3802775 3802775 Aqua 1,000/cs a smooth internal surface through which the cassettes can slide without 3802755 3802755 Blue 1,000/cs obstruction. The increase in fuid exchange results in less incidence of unfxed or under-processed tissues and faster fxation/processing of tissue specimens. They feature a unique hinge and are precision molded from using solvent-resistant plastic. Processing Cassettes are textured writing surface, parallel fow vents, thick wall stability, rounded compatible with most metal lids and base molds. Cassette ofers a thumb tab, a stay-shut latch closure, nibs providing separation between 50 writing surface. Sure-locking lids and closure guides prevent cassettes, the proper angle of the premature separation of lid and base during processing. Plastic cassettes required strike the printer disposable lids, easily removable with a twist, eliminate the need for head is maintained. Histo-Tek Cassettes are resistant solvent and decalcifying when the column is fed into the printer head for ink application. A rear locking mechanism, M7321-68 9228 Tan 1,000/cs coupled with an enlarged front M7321-69 9229 White 1,000/cs latch-type lock, combine ofer M7321-70 9230 Yellow 1,000/cs the ultimate in tissue security. The opening tab is enlarged Bulk packed biopsy cassettes with lid detached and rounded, making it S9350 9350 Blue 1,000/cs easier open. Raised nibs 9351 9351 Gray 1,000/cs on all four corners of each S9352 9352 Green 1,000/cs lid help keep cassettes S9353 9353 Lilac 1,000/cs apart during processing, ensuring S9354 9354 Orange 1,000/cs thorough fuid exchange. An They have detached lids, making etched surface for positive identifcation eliminates the need for labels. M7615-1 4102 Standard 38 x 8 mm 1,000/cs Note: Not compatible with Tissue-Tek SmartWrite Cassette Printer. The cassette has a disposable plastic lid with a latch hinge-lock and three textured writing surfaces. Histo-Tek Standard Cassettes Note: Not compatible with Tissue-Tek SmartWrite Cassette Printer. They are resistant M7321-34 4166 Reusable base mold 6/cs solvent and decalcifying solution. Cassettes are Tissue-Tek Processing packaged with separate compartments for lids and bases. Embedding Cassette Covers Note: Not compatible with Tissue-Tek SmartWrite Cassette Printer. This unique system consists of an outer frame that is M7322-48 7078 Red 400/cs compatible with most commercially available microtome chucks, and M7322-49 7079 Tan 400/cs an inner cassette is made of Paraform material. The Paraform Cassette is compatible with all existing laboratory methods and manual embedding processes. In addition, it can accommodate a variety of specimens, even those requiring special orientation. Available in 11 colors including clear M7321-86 7032 Gray 500/cs M7321-88 7034 Green 500/cs. M7321-89 7035 Lilac 500/cs M7321-90 7036 Orange 500/cs Note: Not compatible with Tissue-Tek SmartWrite Cassette Printer. M7037 7037 Pink 500/cs Please order Stainless Steel Process Cover M7321-2 separately. M7321-93 7039 Tan 500/cs M7321-16 4129 Aqua 3 x 500/cs M7321-94 7040 White 500/cs M7321-9 4184 Blue 3 x 500/cs M7321-95 7041 Yellow 500/cs M7321-13 4126 Burnt orange 3 x 500/cs Tissue-Tek Paraform Base Molds M7321-1 4191 Clear 3 x 500/cs M7321-98 7056 Biopsy/Orientation, 30 x 19 mm 12/bx M7321-15 4128 Gold 3 x 500/cs M7321-97 7055 Standard, 32 x 28 mm 12/bx M7321-8 4183 Green 3 x 500/cs M7322-50 7057 Biopsy, 13 x 13 mm 12/bx M7321-14 4127 Lilac 3 x 500/cs Tissue-Tek Paraform accessories M7321-7 4182 Pink 3 x 500/cs M7321-82 7015 Cassette tamper 1/ea M7321-12 4125 Tan 3 x 500/cs S7089 7089 Low-profle blade 1/cs M7321-5 4187 White 3 x 500/cs M7321-6 4179 Yellow 3 x 500/cs 24 Cardinal Health Anatomic Pathology Products cardinalhealth. The cassettes are bound by premature separation of lid and base during the processing of small adhesive tape that can easily be removed after the cassettes are inserted biopsy specimens. All cassettes are chemical resistant and ofer textured writing surfaces for clear printing. M7321-33Y 8088 Yellow 400/cs Tissue-Tek Processing/Embedding Stacked Cassettes Use our online services help simplify your ordering M7321-35A 8129 Aqua 400/cs process. Just load the stack in the hopper, cut and remove the holding tie and you are ready for printing.
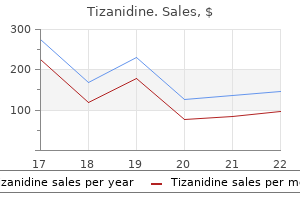
Purchase 4 mg tizanidine with amex
Conclusion this is the first prospective randomized trial worldwide evaluating the impact of three different endocrine treatments in male breast cancer spasms from dehydration buy generic tizanidine 4mg on line. At the meeting, final results of the primary and secondary endpoints will be present. While breast cancer has been documented in men with pathogenic variants in a number of other breast cancer susceptibility genes. Results: the clinical histories and test results of 381 men with breast cancer were reviewed, of whom 12. Therefore, it is reasonable utilize a panel that is inclusive of these genes when testing male breast cancer patients. Unsupervised clustering identified subgroups and within subgroups differentially expressed genes were identified. All identified subgroups were related outcome using logistic regression (p-value using Wald test). Profound tumor infiltrate gene expression was present in 5% of cases and one third of cases expressed proliferation markers. Body: Background: Limited data exist on the molecular biology, treatment, and outcomes of breast cancer in men and much of our understanding in this area remains largely an extrapolation from data in women with breast cancer. Patients with negative nodes, micrometastasis, and 1-3 positive nodes were included. Conclusion: this large genomic study reveals some distinctive biologic features of breast cancer in men and an important prognostic role for 21-gene testing in both men and women, regardless of nodal status. Body: Background: the majority of deaths from breast cancer are due distant metastatic disease. Results: Using Bayesian approaches, we find that cancers fit one of two patterns: canonical linear evolution (whereby the metastatic tumor arises from one or more advanced primary tumor subclones) vs. In cases where tumors show evidence of branched evolution or small subclone dissemination, we expect that a large proportion of mutations may not be represented in both the primary and corresponding metastatic tumors. Furthermore, we find that metastatic tumors have decreased clonal heterogeneity, suggesting a history of selection. Body: Background: Oncology research increasingly involves biospecimen collection and data-sharing. Methods: We administered a cross-sectional self administered anonymous paper survey among patients at the Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center. Mean age was 59 (range 2 91), 81% were women, 86% were white, and 81% were college educated. The vast majority of participants (94%) expected both that donated tissue would be used help as many patients as possible and (92%) that privacy of a donors health information would be carefully protected. We did not detect significant differences in responses on the basis of sociodemographic characteristics, cancer type, disease stage, or research experience. Conclusion: Patients with cancer are highly supportive of tissue donation for research and expect that donated tissue will be used to maximize scientific results. Eligible patients must have received at least 6 months of adjuvant endocrine therapy with biopsy-proven diagnosis of metastatic or locally recurrent disease. Despite the small sample size, there is a trend that patients with mutations in both genes may have worse survival. IncuCyte real-time image system and boyden chamber transwell assays were used monitor the cell migration and chemotaxis. Tail vein injection were performed on nude mice, and immunofluorescent staining of lung tissues with human specific cytokeratin 19 were utilized evaluate in vivo metastatic capacities of the mutant cell models. Materials and Methods Targeted whole exome sequencing (Illumina, 2x50bp) of a 434 gene panel was performed on a set of 297 primary and metastatic breast tumor samples. Tissue of origin included breast (56%), liver (15%), lymph node (10%), lung (3%) and others (16%). Results We identified a total of 26 signatures from the set of 30 known signatures in our patient samples. Body: Breast cancer results in large part from the accumulation of multiple mutations in premalignant cells, which provide a molecular basis for genetic diversity. This genetic diversity in premalignant cells allows selection for increased proliferation and survival and ultimately leads invasion, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Its overexpression and aberrant activation lead unexpected clusters of mutations in the majority of breast cancers. This phenomenon of clustered mutations, termed kataegis (shower in Greek) forms a unique mutation signature in breast cancer. Interestingly, A3G expression is strongly associated with immune response signature genes in all breast tumors. Consequently, A3G is highly associated with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast and several other disease types. This acquisition of an hypermutator genotype was confirmed in five paired primary-metastatic samples. We hypothesize that these agents may synergize induce responses with long term clinical benefit (ClinicalTrials. As exploratory objectives, immunological biomarkers are analyzed in tumor biopsies and blood samples and correlated with (1) clinical efficacy and (2) disease outcomes. Blood samples are drawn at baseline, cycle 3, and cycle 6, or at post-treatment visit (whatever occurs first). If 5 or fewer responses are observed in up 28 patients, the trial will be terminated in favor of the null for futility. If 11 or more responses are observed, then the trial will be stopped in favor of the alternative for demonstration of activity. If 6 10 patients have an observed response then a further 28 patients may be evaluated. A fixed dose of 200 mg pembrolizumab will be given by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 3 weeks. Though effective, response rates are typically limited (~15-30% of pts depending on tumor type) and therapy fails benefit the majority of pts. Imprime drives a cascade of immune activating events activating tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells. Imprime treatment elicits repolarization of the immunosuppressive microenvironment while activating the maturation of antigen presenting cells. Body: Objective: the primary purpose of the study is determine the local and systemic antitumor efficacy of talimogene laherparepvec in locally recurrent breast cancer patients with or without distant metastases, as evidenced by improved overall response rates. Patients with breast cancer who have recurrence of chest wall disease with or without distant metastasis, have at least 1 injectable lesion? The trial will be conducted using a two-stage design and the overall response rate will be estimated accordingly. A response rate of 5% or lower will be considered treatment failure and the regimen will be rejected under this circumstance. Sponsor: Amgen State of Texas appropriation for rare and aggressive breast cancer research. The primary endpoint is disease control rate at the end of 4 months after receiving the treatment. After patients achieving a clinical response systemic therapy, the maintenance of disease control is not guaranteed. Chemotherapies can debulk the disease volume but cannot be used for maintenance due their toxicities. A disease control rate of 10% or lower will be considered treatment failure and the regimen will be rejected under this circumstance. Statistical Methods: Using the Simons optimal method, in the first stage, 8 patients will be enrolled. If there is at least 1 response, accrual will continue the second stage where up 19 additional patients will be enrolled. With this design, the probability of stopping the trial early is 78% if the true response rate is 3%. If the true response rate is 20% the chance that the regimen is declared worthy of further study is 80%. Patients may have had prior surgery, prior chest wall radiation is not required, and other sites of distant metastases are allowed. An interim analysis for futility will be performed after 18 patients are enrolled into Arm B allow early closure of that arm for lack of efficacy.
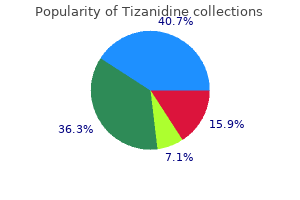
Order tizanidine canada
Eye conditions and vision impairment Substantial progress has been made in addressing specifc eye conditions and vision impairment spasms liver discount tizanidine 2mg overnight delivery. The number of children and adults with eye infections and blindness due vitamin A defciency (6), onchocerciasis (7) and trachoma (8, 9) has decreased in all regions during the past 30 years (10). This is due the implementation of large-scale public health initiatives that have led improvements in hygiene measures, nutrition and immunization coverage, as well as the distribution of antibiotics, ivermectin, and vitamin A. In addition the successes of the preventive interventions for active trachoma, the number of people worldwide who need operations for trachomatous trichiasis has decreased substantially during the past decade: from 8. Cataract is the leading cause of blindness globally and has been a primary focus of many programmes aimed at meeting the Vision 2020 objectives. As a result, many low and middle-income countries have seen substantial increases in rates of cataract surgery (12, 13). For example, India was successful in increasing its cataract surgery rate by almost nine-fold between 1981 and 2012 (14). These endeavours have resulted in modest reductions in the global proportion of cases of vision impairment and blindness attributable cataract between 1990 and 2015 (15). Furthermore, modest reductions have been achieved in the proportion of adults with vision impairment or blindness specifcally due preventable or treatable causes (5). It is important note, however, that reductions in prevalence are not keeping pace with population ageing and growth, thus, the number of adults affected by vision impairment is increasing. Scientifc and technological advances Scientifc and technological advances have also opened a wide range of clinical and research opportunities in the feld of eye care. For example, optical coherence tomography has signifcantly shaped the clinical practice of eye care during the past 15 years (16), assisting diagnosis of a range of eye conditions and guiding treatment regimens for glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration. The adoption of telehealth solutions has been effective in improving access a range of eye care services, particularly for those living in rural and remote areas of many countries (17?19). Several emerging technologies in the feld of eye care, including the use of mobile-based software applications for vision assessment (20, 21) and cataract surgery benchmarking (22), and artifcial intelligence technologies for the detection of a range of eye conditions including diabetic retinopathy (23?26), offer further hope for enhancing access and quality of health care the most neglected communities. However, further research is required in real-world settings prior widespread adoption of these technologies. The use of big data analytics also has the potential improve knowledge of service use and the surveillance and aetiology of eye conditions (27), and for the monitoring surgery outcomes (28). In the context of treatment, advances in surgical techniques for cataract, coupled with improvements in intraocular lens design and the increased availability of low-cost, high-quality intraocular lenses (29), has led signifcant improvements (in terms of the quality of visual outcome of patients, safety and surgical volume) in cataract surgical service delivery (30, 31). Further scientifc advances in the felds of nanomedicine and tissue engineering 75 offer hope for improvements in treatment of glaucoma and age related macular degeneration, and surgery for corneal opacities (37?39). The development of smart phones, voice recognition, and accessibility features in computer operating systems, have dramatically enhanced access information and communication for individuals with vision impairment and blindness (40). Digital audio books are widely available in increasing numbers for those with print-reading disability. Although further research is required, retinal implants could potentially offer an innovative solution restoring sight those with little functional vision (42). It is important recognize that the examples provided here are by no means exhaustive, and as a result of the rapid pace of innovation in the feld of eye care, there are likely be further noteworthy technological advances during the coming decades. As outlined in Chapter 2, at least 1 billion people worldwide1 have vision impairment that could have been prevented or has yet be addressed. Furthermore, global eye care needs will increase substantially due increasing urbanization, demographic and behavioural and lifestyle trends. Changing population demographics As described in Chapter 2, the number of people aged 60 years and over is estimated increase by 54%: from 962 million in 2017, 1. An increase in life Challenges remain expectancy and population growth will compound the situation. Despite being more feasibly addressed, cataract and uncorrected refractive error remain major items on the unfnished agenda of public health (44, 45). Close 200 million people worldwide currently have moderate severe presenting distance vision impairment or blindness caused by cataract or uncorrected refractive error, while an estimated 826 million have near vision impairment caused by unaddressed presbyopia. This fgure is expected increase substantially since cataract and presbyopia development are an inevitable part of ageing. Projected increases in myopia, however, are believed be driven largely by environmental factors. It is clear that there is a growing need expand the coverage of interventions for cataract and refractive error in order meet the current and future demand for these conditions; a report from the United States of America estimated that in order maintain the current surgical coverage, an additional 4. The main challenges in meeting these 1 Population eye care needs describes the volume and type of need for eye care from all individuals within a given population. It includes the need for eye care across all health strategies, health promotion, prevention, treatment and rehabilitation. The need for eye care can arise from eye conditions that can or do not commonly cause vision impairment, as well as other health conditions that can impact vision function, such as diabetes. Although increases in cataract surgical rates have been documented in many countries (12, 13), recent evidence suggests that post-operative vision results are, at times, suboptimal (47). New strategies are also needed address the challenges related the rapid emergence of noncommunicable chronic eye conditions, such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, complications of high myopia and retinopathy of prematurity. In contrast the single or short-term interventions required for cataract (48), these conditions require a comprehensive range of interventions for their management as well as long-term care which will have a profound impact on an already strained health system and eye care workforce. Based on the projected burden of diabetes alone, it is estimated that, by In many low 2040, there will be a 50% increase in the number of people worldwide income countries requiring access routine. The change in population demographics, blindness in young and subsequent rise in the number of people with vision impairment that cannot be treated, will see an increasing demand for such services. Changing priorities among child populations Of importance is the shift in eye care priorities observed among child populations in low and middle-income countries during the past couple of decades (10). In many, but not all, low-income countries where blindness from corneal scarring has declined due the successful implementation of public health initiatives, cataract is now the leading cause of addressable blindness in young children. Despite this, due slower progress in some countries, corneal scarring remains the most common cause of blindness (52). Early detection and referral is essential, and tertiary eye care services for children, which are inadequate in many low-income countries, are required for the surgical management and follow up. Due an increase in the number of preterm births, and survival of premature babies, retinopathy of prematurity has also become a leading cause of blindness among children in many middle-income countries (53), and is a newly emerging challenge in several African countries (54). As a result, there is greater need for high-quality neonatal care, and for integrated retinopathy of prematurity screening and treatment services with long-term follow up. A recent global systematic review and meta-analysis reported that the number of children and adolescents with myopia is expected increase by 200 million between the years 2000 and 2050. This increase is likely be more marked in populations undergoing rapid economic transitions. East Asia) (55, 56) and has important implications for planning eye care services. Data challenges this section focuses on the current data challenges in the context of population-based surveys (only). However, it must be acknowledged that the paucity of health services research and implementation research in the feld of eye care also hampers the evidence-based the measure of planning of eye care programmes and services (57). Moreover, of those countries that have conducted surveys, many of their fndings remain unpublished (59), and be calculated. Thus, smaller regional surveys are often used as a proxy report the prevalence of vision impairment and blindness for the entire country. As outlined in chapters 1 and 2, there are also a number of gaps in the global epidemiology of eye conditions and vision impairment. Some of these include a lack of reliable global estimates of the prevalence of (i) eye conditions that do not typically cause vision impairment; (ii) having at least one eye condition; and (iii) unilateral vision impairment and blindness. Furthermore, and importantly, the measure of presenting visual acuity in most population-based surveys does not allow for the total number of people with vision impairment. As a result, the important indicator of effective coverage of refractive error correction cannot be reported. Thus, these data are valuable assess the accessibility and quality of of refractive error services within a country and should be reported by population-based surveys on a regular basis (47). However, as the feld progresses, it is possible for these procedures be integrated within the calculation.
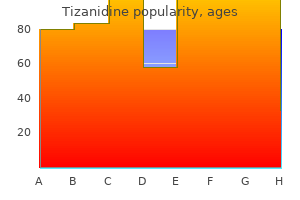
Purchase tizanidine 2mg without prescription
If a contact who has received Rifampicin develops symptoms of meningitis or septicaemia they will still require treatment with intravenous antibiotics spasms pelvic floor generic tizanidine 2 mg. Public Health Investigation of single cases of meningococcal disease should start immediately Response find other cases and manage contacts (see below). Signs & symptoms Fever and generalised maculopapular rash are the most common symptoms. Swollen glands (lymph nodes) in the neck are Communicable Disease Surveillance & Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 119 common, and occur 5 10 days before the rash. Problems include cataracts, congenital heart disease, hearing impairment, and developmental delay. Pathogen(s): Rubella virus Sources of infection Humans Mode of Airborne transmission via breathing, coughing, and sneezing. Period of For about 1 week before and at least 4 days after the appearance of rash. Clinical Rubella is highly infectious until four days after appearance of rash and patients should management of be isolated. Management of Anyone who has been in the same room as a case during the period of infectiousness is contacts: considered a contact. Ask contacts be alert for acute fever and rash and advise those who develop symptoms call ahead, if possible, before seeking medical advice (so as avoid common waiting areas in health centres or hospitals and spreading the infection). Communicable Disease Surveillance & Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 120 Response Actively search for other cases that were in contact with the case this should Investigation, continue for at least 2 incubation periods (about 1 month). Communicable Disease Surveillance & Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 122 Incubation period the most common causes of severe acute respiratory illness have an incubation period of 1?3 days. Provide information about contacts preventing infection, symptoms and what do if they develop symptoms. They should be educated Control about hand hygiene, respiratory hygiene (not coughing/sneezing on others and avoiding Communicable Disease Surveillance & Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 123 other peoples coughs/sneezes) and social distancing. Immunisation is the most effective measure against seasonal influenza and pneumococcus. Signs & symptoms Clinical presentations range from mild gastroenteritis and low-grade fever severe life threatening complications, and can be difficult distinguish from other infections. Most common symptoms are prolonged fever (lasting several days), severe headache, weakness, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. Less common symptoms include bradycardia, enlarged liver and/or spleen, dry cough, rose spots (rash on the trunk), mental dullness or confusion, mild deafness, parotitis, myocarditis, encephalitis, meningitis, chronic osteomyelitis, and suppurative arthritis. Communicable Disease Surveillance & Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 125 Most common causes of death are intestinal haemorrhage or perforation (in about 1% of cases), which are more likely occur in untreated cases. The majority of cases are reported in iTaukei, but outbreaks have also occurred in the Indo-Fijian population. Pathogen(s): Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (Salmonella Typhi) (Salmonella Paratyphi is the cause of paratyphoid, which produces a similar but milder illness) Sources of infection Humans, including asymptomatic carriers (reservoir) Mode of Ingestion of food and water contaminated by stool or urine of cases or asymptomatic transmission carriers. For example: River and streams may become contaminated by sewage during flooding and public health emergencies, or if people upstream use it as their toilet. Period of Stools of typhoid patients are infectious while the person has symptoms. Up 5% of infectiousness infected people become carriers, who can shed bacteria in their stool for weeks or months. People are more likely become carriers if they were not treated with antibiotics, or if the full course of antibiotics was not completed. Laboratory See Typhoid Clinical Guidelines for detailed information on collection and investigations transport of samples. Patients with suspected typhoid should therefore be treated with antibiotics regardless of the results of laboratory tests. Collect blood samples before starting antibiotics, and transport Communicable Disease Surveillance & Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 126 promptly the laboratory. Stool samples should be processed within 2 hours of collection, or o stored and transported at 4 C. Stool culture is also used monitor carrier status, but often produce false-negatives because carriers only shed intermittently. See Typhoid Clinical Guidelines for detailed description of general laboratory tests and findings. All suspected cases should therefore be treated with antibiotics, and the entire course should be completed even if laboratory tests are negative. Ciprofloxacin is the antibiotic of choice in Fiji for all ages, and should be given twice daily for 5 days. Depending on the antibiotic used, 15-20% may experience a relapse within 1 6 weeks. Management of Contacts should be advised about hand hygiene, safe drinking water, and proper food contacts: hygiene. Healthy household contacts should have stool cultures (3 samples with at least 24 hours between samples) if positive, they should be treated with Ciprofloxacin for 28 days. Public Health See Typhoid Clinical Guidelines for detailed information on management of Response typhoid outbreaks, case investigation, environmental investigation, and control Communicable Disease Surveillance & Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 127 Investigation, measures. Prevention & Case investigations should be conducted on all probable and confirmed cases. Two or Control more linked cases should be investigated urgently identify any common sources of infection. If positive, they should be excluded from work until they have been treated with antibiotics and stool samples x3 are clear. If the child is not breastfed, ensure that all milk and drinking water are boiled, and wash hands before preparing milk and food for the child Vaccination. The parenteral typhoid vaccine (polysaccharide Vi) is available in Fiji, and can be used from age 2 years. Zika virus disease Zika is an emerging virus that has not yet been fully characterized. The most updated information about Zika virus and related complications is available at. There have been reports of serious neurological disorders related Zika virus outbreaks. Communicable Disease Surveillance & Outbreak Response Guidelines 2016 129 Microcephaly and other foetal malformations, in the presence of Zika virus, have been reported from a number of countries. Although the link between Zika virus and these neurological conditions has not been proven, there is mounting evidence that Zika virus is the cause. Pathogen(s): Zika virus Sources of infection the exact nature of the reservoir of Zika virus in the Pacific has not been documented. Mode of Zika virus is transmitted by the bite of infected mosquitoes of the Aedes genus. They bite transmission during the whole day, but mostly during the early morning and evening. People with Zika infection should be cared for under bed nets so that a mosquito cannot bite them and then carry the infection another person. Non-mosquito transmission is possible, including by sexual intercourse and blood transfusion. Incubation period the exact incubation period has not been definitively determined but is likely be similar other flaviruses such as dengue (2-14 days). Period of the infectious period has not been established but is believed be short. It is likely that infectiousness humans are infectious mosquitoes for up 5 days after onset of illness. There are number of reports of sexually transmitted Zika infection and transmission through transfused blood products has been reported. Pregnant women: Should be advised not travel areas of ongoing Zika virus outbreaks. Serological cross-reactions with other flaviviruses such as dengue may occur and IgM results should be interpreted with caution in areas where multiple flaviviruses are circulating. Not all reference laboratories will test all biological sample types, so verify with your specific laboratory before collection and shipment.
Order tizanidine 4 mg with visa
Personalized prevention strategies have proven spasms while eating discount tizanidine 2mg mastercard be effective for individuals at very high risk because of inherited mutations that predispose them breast cancer [17,18]. On the opposite, 87 breast cancers are expected in women for whom only 4-yearly mammogram will be planned (low risk), but for 41 of these women, the standard is an absence of mammogram since they are aged 50 or less. Only 46 cancers are expected in low risk women for whom the current standard would be do bi-yearly mammogram, and who will get 4-yearly mammogram instead (light orange). Submission the competent authorities will be done as early as possible after obtaining the grant agreement, at latest on January 2018 so that accrual can start at month 10. A quality assemment chart will be proposed all participating screening centers. This algorithm uses the following variables: age, family history, previous history of benign breast biopsy, breast density, and genotyping results. If no baseline breast mammography is available (women under 50y), the maximum risk will be applied. The information will be introduced in the risk-evaluation software and the final risk score will be produced and send the inclusion center. Genotyping will be carried out using the Illumina Global Screening Array, with over 600,000 variants selected maximise the capacity capture genetic variability across the genome either directly or through imputation using the 1000 Genomes data. Furthermore, it will allow re-evaluate risk as new variants are validated in the literature by re-analyzing the mature trial data, as opposed carrying out additional genotyping. Both scores will be adjusted for national breast cancer incidences and will incorporate genotyping results for all patients. Screening procedures will be scheduled accordingly, based on the pre defined screening decision tree (see below). Breast Cancer Screening in the risk-based arm: In the risk-based arm, women are screened in a risk-based fashion: Screening recommendations in each risk category are as described in the Table below. The whole recommendations have been elaborated by the steering committee of the trial. Risk level Low risk Average risk High risk Very high risk Numerical < 1% at 5 years 1? A quality assessment chart will be proposed all participating screening centers. Risk level assignment modification in risk-based arm these risk-based screening recommendations might be subject evolution during the trial, both at a personal participant level and at a general trial level. At personal level, a web-based yearly update will be organized for all women in this risk-based arm better adapt their risk profile if required. This advice will be part of the recommendations produced by the risk assessment tool. Such women will of course remain within the trial, and be assigned high or very high risk categories, with the adequate proposed follow-up. Upon risk calculation, they will receive a printed + online document summarizing all their personal information, risk category assignment, proposed screening strategy, but also suggested personalized risk reduction measures (such as avoidance of certain endocrine therapies, dietary and exercise recommendations, etc). These measures will be predefined by the trial steering committee and detailed in the full study protocol. All data available will be totally anonymous, participants being identified by a unique code number. Module 2 is the randomization module, developed under the responsibility of Patrick Arveux, as an external module linked server 1 and server 2 3. It will be able integrate genotyping data limited the relevant results of the target 120-150 polymorphisms. Module 3 will allow automated recalculations of risk in case of new validated snps or new relevant clinical data. This interface will allow participants fill and change their personal data, fill questionnaires, and receive invitations or reminders for their personal surveillance program. They also will be able enter data on their screening exams or results, as well as events. It will be based on server 2 and is dedicated the interface with the screening centers. It will allow direct entry of data (images, results, events) and images from the screening centers, as well as inverse communication with the screening centers on randomization allocation for a given participant, surveillance program, dates of invitations, reminders, etc. For secondary end-point (economic analysis) additional data will be collected from national insurance system. Long-term breast cancer specific mortality data will be retrieved in each country through regularly crossing with national databases (national health insurance databases and national epidemiological and statistical databases) in concerted, pre-planned, anonymous fashion. Image collection: image collection is not mandatory for the trial but will be organized as much as possible, in some regions/countries. The Database will be hosted by the data management centre Centre Georgaes Francois Leclerc, Dijon, France (Unicancer). A data validation plan will be developed and will describe in detail the checks be performed for each significant variable and a list of obvious authorized corrections. The essential data necessary for monitoring the primary and secondary endpoints will be identified and managed at regular intervals throughout this work in collaboration with the coordinator and the clinical trial project management. The database will be frozen after final quality control, and then exported for the statistical analysis of the primary and secondary objectives. This centralized full database will need have interrelation with the screening structures and national security insurance. For the purpose of long term follow-up and economic analyses respectively, individual records will be linked national health security systems in the different countries. The trial will be conducted in accordance with all relevant aspects of the Data Protection Act and the Health Research Authority Confidentiality Advisory Group (and previously, the National Information Governance Board) requirements. The data will be treated with appropriate confidentiality, and used only for medical research. Quality controls, mechanisms ensure security of data collected Patient will be identified by a numeric code, the first letter of the last name, the first letter of the first name and the date of birth in case of homonymy. All women will receive a unique patient identification number when signing the informed consent form and before any trial procedure is performed. This number will be used identify the woman throughout the trial and will be used on all trial documentation related this woman. Indeed, once the genotyping result will be available, the remaining samples will be automatically destroyed. Furthermore, we will be able re-evaluate risk as new variants could be identified by re analyzing the mature trial data, as opposed carrying out additional genotyping. In all countries, coordination centers will centralize data retrieval and pseudonimization for transmission the database. Clinical trial Steering Committee In the framework of this study, a Clinical trial Steering Committee will be constituted oversee all question regarding the clinical trial as well as the exploitation of the common database (ancillary studies and industrial partnerships). Meeting schedule will be reduced once accrual is going as planned and during the follow-up phase. Data Monitoring and Ethics Committee the data monitoring and ethics committee, which is independent of the trial team, will oversee the progress of the study, safety of the participants, and ethical issues, including any that arise from new information from other sources. It will confer no less than about once a year, and can request extra meetings at any times it considers appropriate. Progress reports and data will be provided when it confers, and it can demand any analyses or information it considers appropriate inform its decisions. The recruiting centers will be either community of general practitioners, radiologists and gynecologists in the 15 participating areas. Regarding the gynecologists or radiologists participating in the National Screening program, they were already approached and they agreed participate. When the project will be approved, we will contact them again select and finalize a list for each participating area. He was correct; there was nothing represent evidence and most, if not this is a commonly used and abused new about the idea. The world test in experimental studies and peer doctors have always tried manage literature cannot reassure us on the review. A famous example of harm, patients based on the best available value of published expert evidence, in a case involving thousands, oc evidence. They show how one can hijack a entifc objectivity and understand the edge in terms of clinical outcomes. We do our best be objec References taining clinical treatments in which tive, but it is vital that we recognize 1. That the defciencies that exist in the pro acid supplementation in the treatment particular group lists nonclinical self cess. Lancet 1974;2:(7880): proclaimed experts who offer expert Medical Journal sent an article con 544-546.
Diseases
- Reductional transverse limb defects
- Nakamura Osame syndrome
- Weaver Williams syndrome
- Ethylmalonic adipic aciduria
- Progressive kinking of the hair, acquired
- Short stature dysmorphic face pelvic scapula dysplasia
Purchase 2mg tizanidine mastercard
Body: Background: Due spasms right before falling asleep generic tizanidine 2mg without prescription early detection and improved treatments, women with breast cancer are living longer. Less is known about the association between cardiac risk factors and long-term cardiac events among the patients enrolled in breast cancer trials, as most trials fail collect this information. This analysis included patients with 6+ months of Medicare coverage prior baseline and 12+ months of Medicare coverage at any point after baseline. The comorbidities investigated at baseline were diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, coronary artery/ischemic heart disease and obesity. She developed spreadsheets assist in tracking patients and measuring compliance. Assessments for further supportive services are performed, and appropriate referrals made. Results are tracked and reported Cancer Service Line Leadership and the Breast Steering and Cancer Committees. The monitoring of new patients through this process has enabled this center go from estimates of analytic cases, a current real-time numbers. This is necessary provide a comprehensive review of care and survivorship guidelines cancer survivors and meeting accreditation standards. The median age was 61, 5/11 women had received prior chemotherapy, and 7/11 were currently taking aromatase inhibitors. All but one lost weight with an overall median of 8% total mass loss, which was associated with 13% total fat mass loss and 21% visceral fat mass loss. It is feasible design a clinical trial for such breast cancer survivors examine biomarker modulation as a function of level of physical activity. It is essential identify factors that influence the development of sexual symptoms and understand their trajectory over time in order guide potential interventions treat sexual dysfunction. Validated questionnaires on sexual health and function were administered patients after they were diagnosed with breast cancer, but before they initiated cancer treatment and at one-year follow-up after initiation of primary breast cancer therapy. Results: 127 women were eligible for analysis at the time of this abstract and had a median age of 41. Similarly, women engaging in sexual activity more than once a week increased from 9. Controlling for baseline score, younger age and treatment with tamoxifen were associated with better 12-month scores (p < 0. Patients are being followed see if sexual function continues improve over time, better understand the factors causing sexual dysfunction in these patients and determine the best time intervene in order improve symptoms. Therapeutic ultrasound applied the vaginal introitus is safe and was shown increase vaginal temperature and blood flow in our phase I study. We now report results from a twelve-week trial of daily, self-applied therapeutic ultrasound the vaginal introitus. Methods: Breast cancer survivors and post-menopausal women with symptomatic vaginal atrophy were enrolled. Patient-reported outcomes for vaginal dryness and personal lubrication were recorded on a Likert-type scale (0-3). Of the 15 women who completed the treatment according protocol, 93% reported an improvement in at least one of their symptoms. Conclusions: Self-application of therapeutic ultrasound the vaginal introitus decreased symptoms of vaginal atrophy in the majority of users. Significantly fewer Group2 patients and more Group3 patients were unable work (p<0. Body: Background: Surgery is an integral component of comprehensive breast cancer therapy, but leaves physical scars that may have psychosocial consequences in survivorship. As overall survival from early staged breast cancer approaches 99%, more data is needed on the late and long term consequences of breast cancer treatment and quality of life in survivorship. Methods: A nationwide internet survey was conducted among women who reported being surgically treated by lumpectomy only (n=215), mastectomy only (n=140), or both procedures (n=132) for breast cancer. The majority of women in each of the three study groups also felt self-conscious some or all of the time due the surgical scars and avoided certain pieces of clothing some or all of the time because they revealed the scars. Conclusion: Consistent with previous literature, this survey shows that surgical scars from lumpectomy and mastectomy are not merely cosmetic but have a substantial impact on the lives and well-being of women in survivorship. Efforts minimize the iatrogenic impact of surgery and provide comprehensive care may ensure good psychosocial survivorship. Body: Objectives: Breast cancer-related lymphoedema involves chronic, progressive, and incurable swelling in the treated breast or ipsilateral arm, hand, and/or trunk. The traditional referall-based model of care involves women being referred a lymphoedema therapist after the onset of symptoms. Clinical guidelines from the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia have urged that lymphoedema surveillance and early intervention be implemented routinely after breast cancer treatment. Swelling within 90 days of surgery or 270 days of commencing taxane-based chemotherapy was not defined as lymphoedema. Conclusion: Prospective surveillance may result in earlier intervention with L-Dex measurements, earlier diagnosis of lymphoedema and lower L-Dex values. Ongoing statistical analyses will inform the clinical risk factors leading increased lymphoedema incidence. This study has important implications for breast cancer clinical practice guidelines. We found a particularly high risk among non-Hispanic white patients with hypertension. Patients with hypertension may require closer blood pressure monitoring and treatment with anti-hypertensives in order reduce risk of developing cardiotoxicity. Pts are assessed at diagnosis, 3-6, 12, 36, 48 and 60 months after treatment completion. In the current study, we focus on the first set of data available from the trial (1st database lock, n=6090). Body: Background: Nipple-areola tattoos can provide restoration of a natural looking breast that more closely resembles its pre-surgical appearance while avoiding additional surgeries. To date, the majority of nipple-areola tattoo procedures are performed by healthcare providers with minimal training in tattoo procedures. Substandard results explain the high rates of dissatisfaction among women who receive nipple-areola tattoos. In response, professional tattoo artists have emerged as an alternative provider for women seeking reconstruction. Methods: In-depth interviews were conducted with a racially/ethnically diverse group of 30 women who had undergone nipple-areola tattooing in the past 0-2 years. Interviews were conducted in English, Spanish, Chinese, and Arabic, recorded, and translated and transcribed into English for analysis. A team of three researchers conducted iterative reviews of the data which included closely reading each transcript, coding, running queries of codes, and developing summary documents highlight recurrent concepts and patterns which were shared and discussed in group meetings. Women described their decision-making processes as weighing concern about the needle, the pain, and uncertainty about the tattoo artist, setting for the procedure, and outcome with the opportunity return a more normal appearance without further surgeries. Participants noted the integral role the tattoo artist played in their positive experiences, describing her as both an artist and caregiver. Our results indicate that women should be informed of nipple-areola tattooing as an alternative more invasive, surgical reconstruction options. Results also illustrate how the healthcare system can extend beyond the traditional healthcare setting include and leverage non-clinical and non-traditional specialists provide appropriate care and positive breast health outcomes for women. In order increase access and legitimacy these services, additional research is needed understand how bring tattoo artists in-house. Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Medicas y Nutricion Dr Salvador Zubiran, Mexico City, Tlalpan, Mexico. Results: Median age at diagnosis and at the time of the questionnaire application was 50 and 56 years, respectively. Patients received the following treatment: 26 (48%) underwent conservative surgery, 28 (52%) mastectomy; 40 (74%) chemotherapy, 34 (63%) radiotherapy, and 41 (76%) hormonal therapy. Ongoing studies are identifying optimal target populations, appropriate timing of such interventions, and informative measures of patient-centered outcomes. Vasomotor, gynecological and bladder symptoms were scored using the Menopausal Symptom Scale (scale ranges 0-4) based on the Breast Cancer Prevention Trial Symptom Checklist.
Order discount tizanidine line
This section the doctors were expecting before your is the short description of all the important tissue sample was tested spasms upper back buy tizanidine from india. Usually the abnormal lump or spot may be found breast cancer begins either in the cells using mammography or other testing of the lobules, which are milk-producing methods. A procedure called a biopsy glands, or the ducts, the passages that removes a piece of tissue from the lump or drain milk from the lobules the nipple. Breast cancers have many characteristics the pathology report will tell you what that help determine the best treatment. There can know whether the cancer has spread also be cells that fall somewhere between outside the milk ducts or lobules of the normal and cancerous (?atypical cells). Cancer cells are cells that grow in an Non-invasive cancers stay within the milk uncontrolled way. They place where they started grow, or they do not grow into or invade normal tissues this is what the inside within or beyond the breast. The real size of a normal If the cancer has grown into normal duct or lobule rib cage fat tissues, it is called invasive. When muscle lobule cancer cells spread other parts of the duct body, it is called metastatic breast cancer. Based on these fnd their names in the word list that begins comparisons, they give a grade the on page 34 of this booklet. Grade 2 has grown into the surrounding normal cancer cells do not look like normal cells. This is the most They are growing a little faster than common kind of breast cancer. Grade 3 cancer cells look making glands (called lobules), but very different from normal cells. Ki-67 is a protein in cells that for synthesis phase, happens just increases as they prepare divide before a cell divides into two new cells. Tumor size: 1 cm the pathologist also measures the distance between the cancer cells and the margin. More surgery pathways remove used blood and waste is usually needed remove any products. Cancer cells are close the edge coming back when cancer cells are found of the tissue, but not right at the edge. If lymphatic or blood vessel (vascular) invasion is found, your pathology report will say present. So doctors use the under your arm is associated with an number of involved lymph nodes increased risk of the cancer spreading. The lymph nodes try How much cancer is in each catch and trap cancer cells before they lymph node? You may see these words describing When lymph nodes are free, or clear, how much cancer is in each lymph node: of cancer, the test results are called Microscopic. To learn more about tests for receptors may respond hormonal various genes, please see page 20. Some help control how a breast cell grows, genes and the proteins they make divides, and repairs itself. If the genetic recipe mistake (abnormality) or repeated instruction For more information, go to: (amplifcation) calls for too much protein Your Inherited cases of breast cancer are pathology report may also contain likely associated with abnormal genes. This 60% risk of being diagnosed with breast analysis can help decide if a person is cancer during their lifetimes (compared likely beneft from chemotherapy to about 12% for women overall). Their reduce the risk of the cancer coming risk of ovarian cancer is also increased. Changes in other genes are also If the breast cancer is early-stage and associated with breast cancer, though hormone-receptor-positive, you and they are less common and don?t seem your doctor may decide that a genomic increase risk as much as abnormal assay is appropriate for your situation. Many of the cancer traits you surrounding breast tissue) in which: reviewed in this booklet are not included. To qualify evidence of cancer cells or non-cancerous as microscopic invasion, the cells that abnormal cells breaking out of the part have begun invade the tissue cannot of the breast in which they started, or measure more than 1 millimeter. The cells have increased Comedo refers areas of dead cancer in number and fll almost the entire cells that build up inside the tumor?a lobule. Also called tissues of the breast and features holes triple-negative breast cancer. Hormone receptors: Proteins on and in cells that respond signals from Grade: How different the cancer cells hormones. In situ: A cancer within the part of the Locoregional recurrence: A breast breast where it started, such as in the cancer that comes back in the lymph ducts, without signs of spread. Menopause: the time when a woman Papillary carcinoma of the breast: A completely stops getting her period rare type of invasive breast cancer (menstruating). Poorly differentiated: Cancer cells that Sentinel lymph node: the frst lymph look very different from normal cells. Triple-negative breast cancer: Breast Pre-cancerous: An overgrowth of cancer that tests negative for estrogen abnormal cells that shows no signs receptors, progesterone receptors, and of invasion. Tubular carcinoma of the breast: A rare Progesterone can cause some cancers type of invasive breast cancer that is grow. Regional recurrence: A breast cancer Well differentiated: Cancer cells that that comes back in the lymph nodes look a little bit different from normal in the armpit or collarbone area near cells. Are any lymph nodes involved j positive (amplifed) j negative (not amplifed) with this cancer? What other lab tests were done on the j positive (amplifed) j negative (not amplifed) cancer tissue? Is any further surgery recommended j positive (cancer found in lymph node[s]) number of lymph nodes involved: based on these results? Our mission is help people affected by breast cancer make sense of complex medical and personal information so they can make the best decisions for their lives. Our goal is empower everyone face breast cancer with knowledge, clarity, and confdence. This booklet was made possible by an unrestricted educational grant from Breastcancer. Real-time imaging delivers a wealth An intuitive user interface, real-time Fast, accurate and streamlined of information the point of care imaging, and automated specimen procedures mean less time under so you can make informed clinical collection and separation work compression and can result in a decisions with confdence. Technical Specifcations Biopsy Device Components Console Control Display Reusable driver dimensions 7. Intuitive Interface Real-time Core Imaging Dedicated Technologist Screen Flexible Dual Monitors System-guided Setup Min 53. We integrate the Science of Sure into everything we do help healthcare professionals discover, diagnose and treat their patients with progressive certainty deliver ever-greater peace of mind. Because Hologic materials are distributed through websites, eBroadcasts and tradeshows, it is not always possible control where such materials appear. InterventIonal Breast solutIons In addition speed, Eviva provides physicians a high level of both consistency and control in every procedure. Physicians have found that total procedure time with the eviva breast biopsy system is greatly reduced, largely due. Providing you a fast and easy way order ateC, eviva and Celero breast biopsy devices, time perform the procedure is reduced by at least ffty percent, biopsy drapes, and the MammoPad breast cushion thus reducing patient time on the biopsy table, streamlining the workfow, supplies online. Approach)* Eviva 0913-12 Device Type Eviva 0910-20 *eviva adapter Kits for Ge systems include two(2) reusable needle guide bushings Outer Cannula (incision size) Eviva 1210-20 Needle Gauge (g) 09: 9g, 12: 12g Eviva 0910-12T Needle Length (cm) Eviva 0910-12 10: 10 cm long, 13: 13 cm long Aperture Size (mm) (core length) 12: 12 mm aperture, 20: 20 mm aperture Suf? Hologic provides a wide array of biopsy site marking options for the eviva system, with a total of seven clearly distinct shapes. Titanium Stainless steel TriMark for Eviva biopsy site markers securMark Biopsy site Markers triMark Biopsy site Markers. Hologic Biopsy Devices Eviva Eviva Eviva Eviva Eviva Eviva Eviva Eviva 0913-20 0913-12 0913-12T 0910-20 0910-12 0910-12T 1213-20 1210-20 sMark-eviva-13 4 4 4 sMark-eviva-2s-13 4 4 4 sMark-e-13-ss1 4 4 4 sMark-e-13-ss2 4 4 4 sMark-e-13-ss3 4 4 4 sMark-eviva-10 4 4 4 sMark-eviva-2s-10 4 4 4 sMark-e-10-ss1 4 4 4 sMark-e-10-ss2 4 4 4 sMark-e-10-ss3 4 4 4 triMark-eviva-13 4 4 4 4 securMark biopsy site marker in stainless steel shape one (1) securMark biopsy site marker in stainless steel shape two (2) under mammography triMark-eviva-10 4 4 4 4 note: secondary images are side views triMark-eviva-2s-13 4 4 4 4 triMark-eviva-2s-10 4 4 4 4 note: shapes appear larger than actual size. All other trademarks, registered trademarks, and product names are the property of their respective owners.
Purchase tizanidine in united states online
Digital rectal exam is not include that screening was done only once back spasms 40 weeks pregnant purchase tizanidine 4mg mastercard, that protection recommended for screening because fewer than 10% of was limited distal colorectal cancer, and that the first study cancers are within digital reach. Observational studies immunohistochemical fecal occult blood tests) having polyp have been fairly consistent in showing reductions in sensitivity of about 23-25%, much improved over prior colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. False positive rates are on the studies have shown that, similar sigmoidoscopy, order of 5-8% with the newer tests, but were only about 2% colonoscopy may not produce a benefit for proximal lesions. In 3 studies, advocated colonoscopy as their strongly-preferred test, the colorectal cancer mortality reductions ranged from 15-33%, possible lack of protection against proximal cancers has with differences most likely due differences in screening raised some doubt about whether it is a more effective test intervals and in how the tests were performed. Two randomized controlled trials sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy in adults, beginning at age of flexible sigmoidoscopy screening have been published 50 years. Both trials were based on once-only screening, and follow-up ranged from 7 11 years. In the first, population the frequency of screening depends on the screening was randomized screening or not; at 7 years, there were modality. Men with a first-degree relative with prostate cancer preparation, may outweigh the benefits. Poverty Individualizing the choice of screening method for the increases the risk of advanced-stage prostate cancer. Some highest likelihood of compliance and the least intrusive studies show that taking 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. Studies of the effects of diet and supplements on prostate cancer risk show inconsistent results. Screening People at Higher Risk Prostate cancer has a remarkably heterogeneous natural Screening people at higher risk of colorectal cancer is likely history, ranging from a symptom-free cancer with a slow be more effective and cost-effective than screening the course and no morbidity or effect on life, a virulent cancer general population. High-risk individuals can be classified with rapid progression bone metastases and death. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer for screening high-risk people Rationale for Recommendation are presented in Table 5. Clinical Background Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among men in the United States, excluding skin cancers, and among men it ranks second lung cancer in the number of cancer-related deaths. In 2012, an estimated 241,740 new cases will be diagnosed nationwide and about 28,170 men will die from the disease. Colorectal Cancer Screening for People at Higher Risk Risk Category Screening Recommendation Familial Risk One second-degree a or any third-degree relative b with Same as average risk colorectal cancer First-degree relative c affected with colorectal cancer or Same as average risk, but starting at age 40 years adenomatous polyp at age? Personal Risk History of adenomatous polyps, for example: Manage according the findings and clinical judgment. History of colorectal cancer After colonoscopy rule out synchronous neoplasms and resection with curative intent, first follow-up colonoscopy at 1 year, then after 3 years, and then, if normal, every 5 years. By detecting some prostate cancers that would never cause Considering the evidence and the recommendations of these significant clinical problems, screening leads both over groups: diagnosis and over-treatment. For average-risk men ages 55-69 with a life expectancy > volume prostate cancers may be candidates for less 10 years, clinicians may choose initiate or not initiate aggressive approaches, such as Active Surveillance, where a shared decision-making discussion about routine curative treatment is delayed pending evidence of disease screening with patients. African-American men, and men with a information about the uncertainties, risks, and potential father, brother or son with prostate cancer (especially if onset benefits of screening. Earlier discussion and Screening for Prostate Cancer initiation of screening, starting at age 40, may be indicated for these groups, although a benefit has not been proven. It is not known whether screening will reduce the number of deaths from prostate cancer. An abnormal screening result requires a prostate guideline were conducted prospectively on Medline. When prostate cancer is detected, it is difficult guideline the guideline team learned of the ongoing literature predict who will benefit from treatment. We requested and clinicians not offering routine screening and many patients received from the Editorial Board Manager a copy of the not wanting it. The following information addresses search strategies they use for cancer screening literature. These terms are used for choose consider prostate cancer screening for a man at the specific topics of breast neoplasms, cervix neoplasms, average risk for prostate cancer who is age 50-74 and has a colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer. Screening should not occur without an informed summaries, we accepted their strategy and results as the decision-making process. Informed decision making tools literature search we would use update our guideline. The are available on-line from the Centers for Disease Control results available in the online summaries as of June 2010 and Prevention at the site: were used. Our conclusions were based on prospective randomized controlled trials if available, the exclusion of other data; if Terminating screening. If no such data were available for have chronic medical problems and a life expectancy of less a given link in the problem formulation, expert opinion was than 10 years. Both age and overall health status should be considered when making decisions about screening. When programs have Breast Cancer Screening measures, the measures are generally similar, although specific details vary. Screening sigmoidoscopy during the measurement year or the four prior and surveillance for early detection of colorectal cancer years, colonoscopy during the measurement year or the nine and adenomatous polyps, 2008. The University of Michigan Health System endorses the Guidelines of the Association of American Medical Colleges and the Standards of the Accreditation Council for Measures of Clinical Performance Continuing Medical Education that the individuals who present educational activities disclose significant National programs that have clinical performance measures relationships with commercial companies whose products or of cancer screening include the following. Screening for and by distribution for comment within departments and Breast Cancer, 2009. General Medicine, General Obstetrics & Gynecology, Breast Oncology, Breast Radiology, Gastroenterology, Gynecology Cervical cancer screening Oncology, and Urology. Society, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and American Society for Clinical Pathology screening guidelines for the prevention and early detection Acknowledgments of cervical cancer. American Urological Association, Prostate-Specific Antigen Both available at Best Practice Statement: 2009 Update. Yet, cytokinetic modelling suggests that increasing the dose density of cytotoxic therapy by shortening the intervals between courses, or by using sequential rather than concurrent treatment schedules may enhance efficacy. Methods: Individual patient data were provided for 98% (21,537/21,944) of women randomised in relevant trials: 7 randomised trials (10,004 women, 2240 breast cancer recurrences, 1481 breast cancer deaths) that compared 2-weekly dose-dense chemotherapy versus the same chemotherapy given 3-weekly, and 9 trials (11,533 women, 2773 breast cancer recurrences, 1711 breast cancer deaths) that compared sequential with concurrent anthracycline and taxane-based chemotherapy. Similarly, for sequential versus concurrent taxane plus anthracycline chemotherapy the rate ratio for disease recurrence was 0. Trial publications also indicate that, with haematopoietic growth factor support, dose-dense chemotherapy does not substantially increase toxicity. The correlations between differents parameters were assessed using Spearman correlations (? University Hospital Ulm, Ulm, 2 3 Germany; University Hospital Duesseldorf, Heinrich-Heine University, Duesseldorf, Germany; University Hamburg-Eppendorf, 4 5 Hamburg, Germany; Charite University Hospital Campus Virchow, Berlin, Berlin, Germany; Charite University Hospital Campus 6 Virchow, Berlin, Berlin, Germany; Gynecologic Practice Dres Lorenz, Hecker, Wesche, Braunschweig, Germany; 7 8 Hemato-Oncological Practice Dres Forstbauer and Ziske, Troisdorf, Germany; Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, Munich, 9 10 Germany; National Center for Tumor Diseases, University Hospital Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany; Onkologie Bethanien, 11 12 Frankfurt, Germany; University Hospital Tubingen, Tubingen, Germany; Schwerpunktpraxis fur Onkologische Gynakologie, 13 Furstenwalde, Germany; University Hospital Erlangen, Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Nuremberg, 14 Germany and Sheffield Cancer Research Centre, Weston Park Hospital, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom. After chemotherapy, patients were subject a second randomization of 5 years of zoledronate treatment (4 mg i. As of data cutoff on 6/30/2017, 71 are deceased, 23 in long-term follow-up, and 16 still on treatment. Treatment was well tolerated, with no treatment-related deaths, 2 treatment discontinuations for toxicity, and no anti-drug antibodies detected. Results of the independent central blinded review along with sensitivity analyses of prior treatment regimens, including checkpoint inhibitor use, and exploratory biomarker analysis of Trop-2 expression will be presented at the meeting. Characterizing more advanced tumors has borne valuable insight into cancer progression, yet studies of longitudinally collected breast cancer specimens are scarce given lengthy periods of cancer dormancy. The primary analysis was conducted after 318 events had occurred; median time from randomization data cut-off date was 19. Of these, neutropenia (61% vs 4%) and leukopenia (14% vs 1%) were the only Grade 3/4 events reported in? Febrile neutropenia (ribociclib vs placebo arm) occurred in 2% vs <1% of patients. Phase Ib was a 3+3 dose-escalation of 2 pembrolizumab doses (2mg/kg, 10mg/kg) Q3W. Clinically stable pts with progression were allowed continue pembrolizumab until confirmation on subsequent assessment. Secondary objectives included objective response, clinical benefit rate, duration of response and clinical benefit, overall survival and safety. In the celecoxib and placebo groups there were 17 and 8 deaths respectively in patients who had not relapsed.
Order tizanidine 2mg with visa
Medical care providers must include health education activities such as disease prevention in their daily work spasms of the heart cheap 4 mg tizanidine free shipping. Physical examination the physical examination should include: assessment of mental state; assessment of hydration status; assessment of haemodynamic status (Textbox D); checking for tachypnoea/acidotic breathing/pleural effusion; checking for abdominal tenderness/hepatomegaly/ascites; examination for rash and bleeding manifestations; tourniquet test (repeat if previously negative or if there is no bleeding manifestation). A rapid decrease in platelet count in parallel with 32 a rising haematocrit compared the baseline is suggestive of progress the plasma Chapter 2: Clinical management and delivery of clinical services leakage/critical phase of the disease. However, it is not necessary for the acute management of patients, except in cases with unusual manifestations (Chapter 4). Laboratory confrmation is not necessary before notifcation, but should be obtained. Suggested criteria for early notifcation of suspected cases are that the patient lives in or has travelled a dengue-endemic area, has fever for three days or more, has low or decreasing white cell counts, and/or has thrombocytopaenia positive tourniquet test. In dengue-endemic countries, the later the notifcation, the more diffcult it is prevent dengue transmission. Management decisions Depending on the clinical manifestations and other circumstances, patients may (12) be sent home (Group A), be referred for in-hospital management (Group B), or require emergency treatment and urgent referral (Group C). Adequate oral fuid intake may be able reduce the number of hospitalizations (13). Patients who are sent home should be monitored daily by health care providers for temperature pattern, volume of fuid intake and losses, urine output (volume and frequency), warning signs, signs of plasma leakage and bleeding, haematocrit, and white blood cell and platelet counts (see group B). These include patients with warning signs, those with co-existing conditions that may make dengue or its management more complicated (such as pregnancy, infancy, old age, obesity, diabetes mellitus, renal failure, chronic haemolytic diseases), and those with certain social circumstances (such as living alone, or living far from a health facility without reliable means of transport). If the patient has dengue with warning signs, the action plan should be as follows. Start with 5?7 ml/ kg/hour for 1?2 hours, then reduce 3?5 ml/kg/hr for 2?4 hours, and then reduce 2?3 ml/kg/hr or less according the clinical response (Textboxes H, J and K). If the haematocrit remains the same or rises only minimally, continue with the same rate (2?3 ml/kg/hr) for another 2?4 hours. If the vital signs are worsening and haematocrit is rising 34 rapidly, increase the rate 5?10 ml/kg/hour for 1?2 hours. Reassess the clinical status, repeat the haematocrit and review fuid infusion rates accordingly. Give the minimum intravenous fuid volume required maintain good perfusion and urine output of about 0. Reduce intravenous fuids gradually when the rate of plasma leakage decreases towards the end of the critical phase. This is indicated by urine output and/or oral fuid intake that is/are adequate, or haematocrit decreasing below the baseline value in a stable patient. Parameters that should be monitored include vital signs and peripheral perfusion (1?4 hourly until the patient is out of the critical phase), urine output (4?6 hourly), haematocrit (before and after fuid replacement, then 6?12 hourly), blood glucose, and other organ functions (such as renal profle, liver profle, coagulation profle, as indicated). If the patient has dengue without warning signs, the action plan should be as follows. For obese and overweight patients, use the ideal body weight for calculation of fuid infusion (Textboxes J and K). Patients may be able take oral fuids after a few hours of intravenous fuid therapy. Other laboratory tests (such as liver and renal functions tests) can be done, depending on the clinical picture and the facilities of the hospital or health centre. All patients with severe dengue should be admitted a hospital with access intensive care facilities and blood transfusion. Judicious intravenous fuid resuscitation is the essential and usually sole intervention required. The crystalloid solution should be isotonic and the volume just suffcient maintain an effective circulation during the period of plasma leakage. Plasma losses should be replaced immediately and rapidly with isotonic crystalloid solution or, in the case of hypotensive shock, colloid solutions (Textbox M). For overweight or obese patients, the ideal body weight should be used for calculating fuid infusion rates (textboxes J and K). Input is typically much greater than output, and the input/ output ratio is of no utility for judging fuid resuscitation needs during this period. If the haematocrit increases or is still high (>50%), repeat a second bolus of crystalloid solution at 10?20 ml/kg/hr for one hour. After this second bolus, if there is improvement, reduce the rate 7?10 ml/ kg/hr for 1?2 hours, and then continue reduce as above. If haematocrit decreases compared the initial reference haematocrit (<40% in children and adult females, <45% in adult males), this indicates bleeding and the need cross-match and transfuse blood as soon as possible (see treatment for haemorrhagic complications). The action plan for treating patients with hypotensive shock is as follows (Textboxes D and N, Figure 2. Then continue with crystalloid infusion and gradually reduce 5?7 ml/kg/hr for 1?2 hours, then 3?5 ml/kg/hr for 2?4 hours, and then 37 Dengue: Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control 2?3 ml/kg/hr or less, which can be maintained for up 24?48 hours (textbox H). If the haematocrit was low (<40% in children and adult females, <45% in adult males), this indicates bleeding and the need cross match and transfuse blood as soon as possible (see treatment for haemorrhagic complications). If the condition is still unstable, repeat the Crystalloid/colloid 10 ml/kg/hr for haematocrit after the second bolus. If the haematocrit increases compared the If patient continues improve, fuid can be previous value or remains very high (>50%), continue colloid solutions at 10?20 further reduced. Patients with dengue shock should be frequently monitored until the danger period is over. Parameters that should be monitored include vital signs and peripheral perfusion (every 15?30 minutes until the patient is out of shock, then 1?2 hourly). In general, the higher the fuid infusion rate, the more frequently the patient should be monitored and reviewed in order avoid fuid overload while ensuring adequate volume replacement. If resources are available, a patient with severe dengue should have an arterial line placed as soon as practical. The reason for this is that in shock states, estimation of blood pressure using a cuff is commonly inaccurate. The use of an indwelling arterial catheter allows for continuous and reproducible blood pressure measurements and frequent blood sampling on which decisions regarding therapy can be based. Urine output should be checked regularly (hourly till the patient is out of shock, then 1?2 hourly). Haematocrit should be monitored (before and after fuid boluses until stable, then 4?6 hourly). In addition, there should be monitoring of arterial or venous blood gases, lactate, total carbon dioxide/bicarbonate (every 30 minutes one hour until stable, then as indicated), 38 blood glucose (before fuid resuscitation and repeat as indicated), and other organ Chapter 2: Clinical management and delivery of clinical services Figure 2. However, changes must be interpreted in parallel with the haemodynamic status, the clinical response fuid therapy and the acid-base balance. For instance, a rising or persistently high haematocrit together with unstable vital signs (particularly narrowing of the pulse pressure) indicates active plasma leakage and the need for a further bolus of fuid replacement. However, a rising or persistently high haematocrit together with stable haemodynamic status and adequate urine output does not require extra intravenous fuid. In the latter case, continue monitor closely and it is likely that the haematocrit will start fall within the next 24 hours as the plasma leakage stops. A decrease in haematocrit together with unstable vital signs (particularly narrowing of the pulse pressure, tachycardia, metabolic acidosis, poor urine output) indicates major haemorrhage and the need for urgent blood transfusion. Yet a decrease in haematocrit together with stable haemodynamic status and adequate urine output indicates haemodilution and/or reabsorption of extravasated fuids, so in this case intravenous fuids must be discontinued immediately avoid pulmonary oedema. Treatment of haemorrhagic complications Mucosal bleeding may occur in any patient with dengue but, if the patient remains stable with fuid resuscitation/replacement, it should be considered as minor. In patients with profound thrombocytopaenia, ensure strict bed rest and protect from trauma reduce the risk of bleeding. It should be noted that prophylactic platelet transfusions for severe thrombocytopaenia in otherwise haemodynamically stable patients have not been shown be effective and are not necessary (14). If major bleeding occurs it is usually from the gastrointestinal tract, and/or vagina in adult females. Internal bleeding may not become apparent for many hours until the frst black stool is passed. Patients at risk of major bleeding are those who: have prolonged/refractory shock; have hypotensive shock and renal or liver failure and/or severe and persistent metabolic acidosis; are given non-steroidal anti-infammatory agents; have pre-existing peptic ulcer disease; are on anticoagulant therapy; have any form of trauma, including intramuscular injection.