Female Viagra
Purchase female viagra 50 mg line
The apoptotic cells are round to oval shrunken masses Physiologic Processes: of intensely eosinophilic cytoplasm (mummified cell) 1 women's health issues today proven 50mg female viagra. Organised cell destruction in sculpting of tissues during containing shrunken or almost-normal organelles development of embryo. Normal cell destruction followed by replacement proliferation such as in intestinal epithelium. Cell death by cytotoxic T cells in immune mechanisms such as in graft-versus-host disease and rejection reactions. The nuclear chromatin is condensed or fragmented on the outer surface of apoptotic cell facilitates early (pyknosis or karyorrehexis). The cell membrane may show convolutions or projections appearance of inflammatory cells. Triggers for signalling program or loosely floating apoptotic cells after losing contact, with med cell death act at the cell membrane, either intra each other and basement membrane as single cells, or may cellularly or extracellularly. These include the following: result in major cell loss in the tissue without significant i) Withdrawal of signals required for normal cell survival change in the overall tissue structure. Staining of chromatin condensation (haematoxylin, initiated into self-destruct mode, the programme inbuilt in Feulgen, acridine orange). Biochemical processes get activated either by coming in contact with some etiologic underlying the morphologic changes are as under: agent of cell injury agent or by unknown mechanism. Appearance of phosphatidylserine on the outer surface appropriately called a death receptor because on coming in of cell membrane. Definition Programmed and coordinated cell death Cell death along with degradation of tissue by hydrolytic enzymes 2. Morphology i) No Inflammatory reaction i) Inflammatory reaction always present ii) Death of single cells ii) Death of many adjacent cells iii) Cell shrinkage iii) Cell swelling initially iv) Cytoplasmic blebs on membrane iv) Membrane disruption v) Apoptotic bodies v) Damaged organelles vi) Chromatin condensation vi) Nuclear disruption vii) Phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies by macrophages vii) Phagocytosis of cell debris by macrophages 4. Thus, it may regulate the apoptotic examples of necrotising inflammation are: gangrenous process by binding to some related proteins. The net effect on the mitochondrial membrane is variant form of wet gangrene called gas gangrene. The above mechanisms lead to proteolytic this form of gangrene begins in the distal part of a limb due actions on nucleus, chromatin clumping, cytoskeletal to ischaemia. The typical example is the dry gangrene in the damage, disruption of endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondrial toes and feet of an old patient due to arteriosclerosis. It is usually initiated in one of the toes which membrane changes which promote their phagocytosis. The gangrene spreads slowly upwards until appear on the outer surface of the cells in apoptosis, which it reaches a point where the blood supply is adequate to keep facilitate their identification by adjacent phagocytes and the tissue viable. The phagocytosis is unaccompanied between the gangrenous part and the viable part. The type of necrosis is usually coagulative due usually brings about complete separation with eventual to ischaemia. The gangrenous area is dry, shrunken and dark and is separated from the viable tissue by clear line of separation. Histologically, there is necrosis with smudging of the venous, and less commonly, arterial blood flow from tissue. The toxic products formed by bacteria are absorbed Wet Gangrene causing profound systemic manifestations of septicaemia, and finally death. The spreading wet gangrene generally Wet gangrene occurs in naturally moist tissues and organs lacks clear-cut line of demarcation and may spread to such as the mouth, bowel, lung, cervix, vulva etc. Bed sores occurring in a bed-ridden patient due to is soft, swollen, putrid, rotten and dark. The classic pressure on sites like the sacrum, buttocks and heels are the example is gangrene of bowel, commonly due to other important clinical conditions included in wet gangrene. The part Wet gangrene usually develops rapidly due to blockage of is stained dark due to the same mechanism as in dry gangrene (. Histologically, there is coagulative necrosis with stuffing of affected part with blood. The line of demarcation between gangrenous segment and viable bowel is generally not clear-cut (. It is a special form of wet gangrene caused by gas-forming clostridia (gram-positive anaerobic bacteria) which gain entry into the tissues through open contaminated wounds, especially in the muscles, or as a complication of operation on colon which normally contains clostridia. Clostridia produce various toxins which produce necrosis and oedema locally and are also absorbed producing profound systemic manifestations. Grossly, the affected area is swollen, oedematous, painful and crepitant due to Figure 3. Line of demarcation between gangrenous segment and the viable bowel is not clear-cut. Subsequently, the affected tissue becomes dark black and Metastatic calcification, on the other hand, occurs in foul smelling. Microscopically, the muscle fibres undergo coagulative Etiology and pathogenesis of the two are different but necrosis with liquefaction. Large number of gram-positive morphologically the deposits in both resemble normal bacilli can be identified. Histologically, in routine H and E stained sections, calcium salts appear as deeply basophilic, irregular and granular clumps. Occasionally, hetero Deposition of calcium salts in tissues other than osteoid or topic bone formation (ossification) may occur. Two deposits can be confirmed by special stains like silver distinct types of pathologic calcification are recognised: impregnation method of von-Kossa producing black colour, Dystrophic calcification, which is characterised by and alizarin red S that produces red staining. Pathologic deposition of calcium salts in dead or degenerated tissues calcification is often accompanied by diffuse or granular with normal calcium metabolism and normal serum calcium deposits of iron giving positive Prussian blue reaction in levels. Mechanisms Arterial occlusion More commonly venous obstruction, less often arterial occlusion 3. Macroscopy Organ dry, shrunken and black Part moist, soft, swollen, rotten and dark 4. Putrefaction Limited due to very little blood Marked due to stuffing of organ with blood supply 5. Line of demarcation Present at the junction between No clear line of demarcation healthy and gangrenous part 6. Prognosis Generally better due to little septicaemia Generally poor due to profound toxaemia 52 Figure 3. Microscopy shows coagulative necrosis of the affected bowel wall and thrombosed vessels while the junction with normal intestine is indistinct and shows an inflammatory infiltrate. Stroma of tumours such as uterine fibroids, breast cancer, different etiologies and mechanisms. Some tumours show characteristic spherules of calci definition, dystrophic calcification may occur due to 2 types fication called psammoma bodies or calcospherites such as in of causes: meningioma, papillary serous cystadenocarcinoma of the Calcification in dead tissue ovary and papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. Cysts which have been present for a long time may show Calcification in dead tissue calcification of their walls. Calcinosis cutis is a condition of unknown cause in which for dystrophic calcification. Living bacilli may be present there are irregular nodular deposits of calcium salts in the even in calcified tuberculous lesions, lymph nodes, lungs, skin and subcutaneous tissue. Fat necrosis following acute pancreatitis or traumatic fat or bronchial cartilages, and pineal gland in the brain etc. Dead parasites like in hydatid cyst, Schistosoma eggs, and cysticercosis are some of the examples showing dystrophic calcification. Congenital toxoplasmosis involving the central nervous system visualised by calcification in the infant brain. Milk-alkali syndrome caused by excessive oral intake of as to how dystrophic calcification takes place. Since serum calcium in the form of milk and administration of calcium calcium levels are within normal limits, the denatured carbonate in the treatment of peptic ulcer.
Discount female viagra online amex
Superficial thyroid vein is closely related with external branch of superficial laryngeal nerve 17 contemporary women's health issues for today and the future 4th edition buy female viagra 50mg visa. Most common tumor to have metastatic involvement of upper deep cervical lymph nodes is 1. A patient presented with unilateral ptosis and diplopia and on examination was found to have decreased movement of eyeball in all directions. Corneal involvement is always associated with tip of nasal involvement and ulcers 4. All the following are true regarding acute anterior uveitis in Ankylosing spondylitis except 1. Which of the following helps in diagnosis, in biopsy of brain specimen in Rabies 1. In a splenectomized patient there is increased chances of infection by all the following organisms except 1. In India which of the following is true regarding the cause of travelers diarrhea 1. In adult rhabdomyosarcomas are resistant to radiotherapy and spread to lymphnodes Ans. Dermatofibrosarcoma protruberance is a malignant tumor and often presents with metastasis 4. Deficiency of which of the following factors does not cause an abnormality of the. Which of the following muscles are used in the action involved in sucking of a straw 1. The serosal lining of the rectum is tough and prevents spread of tumor to surrounding pelvis 145. It is difficult to treat Diaphyseal aclasis when it causes which of the following 1. In the management of a case of fracture mandible, importance must be given most to 1. It contains Kulchitzky cells in the mucosa which may give rise to Carcinoid tumor 174. All the following are true about Ischemic heart disease in India as compared to other more developed countries 1. A 6 year old child complains of difficulty in swallowing and on examination there is a sublingual swelling, which is suspected to be Lingual thyroid. In a patient with history of blood loss, brought to casualty must be treated initially with 1. Lieomyoma uterus is least susceptible to undergo which of the following changes 1. Most common cause of ocular morbidity in our country as found by the 86-89 national survey for blindness was 1. Which of the following requires emergency operation in setting without tertiary care facilities. Nephrocalcinosis can be diagnosed in x-ray as caused by all the following except 1. Gall stone causes intestinal obstruction when it gets impacted in which part of the intestine commonly 1. A patient with hyperparathyroidism with pheochromocytoma develops a thyroid swelling. An adult male with history of regurgitation of food taken 3-4 days back, and halitosis, also complains of dysphagia to solid food. All the following are true about Hyperkinetic attention deficit disorder except 1. On examination of a patient there was a double peaked pulse in his peripheral artery. Which of the following types of human papiloma viruses is implicated in causation of carcinoma cervix a. The ratio of number of essential amino acids present in the given diet to reference protein b. The ratio of number of limiting amino acids present in given diet to the reference protein c. The difference between use of a selective alpha1 blocker to using a non selective alpha blocker is a. The increased production of vitamin D induced transport protein increases absorption of a. Loss of speech with inability to read, understand in a patient is referred to as a. Deep tranverse arrest is commonly associated with which of the following types of pelvis a. The weight of the body is transmitted through the axis of the vertebrae passing through a. All of the following are common uses of beta blockers and calcium channel blockers except a. All of the following are physiological cysts in the ovary except one which is a tumor a. Current modes of investigation for infertility to check functioning of tubes are all of the following except a. During surgery involving abdomen ligation of a small vein can cause death of the patient a. Rotation of radius occurring without extension and flexion at the elbow joint is caused by a. Which of the following amino acids undergoes hydroxylation and is involved in the formation of collagen a. Chronic exposure with which of the following particle size causes chronic lung disease a. A 17 yr nonsmoking man presents with deep venous thrombosis and a pulmonary embolus. All of the following are responsible for internal rotation of shoulder joint except a. In a patient presenting with hoarseness of voice, inability to turn head to left against resistance was on examination found to have a swelling in the cervical region. Propranolol 11 the first step on priority basis required in the management of status epilepticus is a. Supracondylar fracture is associated most commonly with which of the following nerve lesions a. On examination the abdomen is soft and there is no tenderness, with bowel sounds being normal. Long tubes used to treat obstruction are now outdated and not used in modern practice c. A delay in operation in a patient with partial loop obstruction is not beneficial as compared to an early operation d. The pathology report suggested that the adenoma was found to extend upto the muscularis mucosae. If properly cultured then bacteroides account for 20% of cases causing peritonitis c. A patient was operated 2 months back and at that time a midline inscicion was used. Now he requires a second operation and this the ideal incision to be used now is. Behavioral therapy is required 31 Most common complication in colles fracture is a. A child suffered through trauma and had to undergo splenectomy for splenic injury and blood loss. A patient came with history of fall and on examination there was tenderness between the extensor pollicis longus and brevis. Early tracheostomy is indicated because it is difficult to to pass tube through inflamed pharynx c.
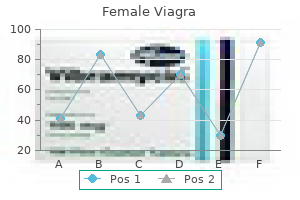
| Comparative prices of Female Viagra | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | McDonald's | 326 |
| 2 | Albertsons | 295 |
| 3 | Nordstrom | 492 |
| 4 | Save Mart | 361 |
| 5 | Apple Stores / iTunes | 402 |
Purchase female viagra 50 mg overnight delivery
Note the absence of any enhancing or soft tissue components within this splenic cyst breast cancer grade 3 generic female viagra 100mg with visa. The patient was symptomatic with pain and early satiety and consequently underwent surgical cyst deroofing. While the typical nodular, centripetal enhancement seen with hepatic hemangiomas is less common in the spleen, splenic hemangiomas often demonstrate avid enhancement. While the mass in the liver superficially resembles a hemangioma, the liver lesion was one of multiple metastases in this patient. Although they resemble hemangiomas with nodular enhancement, these were found to represent metastatic angiosarcoma. The size of the mass raised concern for malignancy and precipitated splenectomy, where the lesion was found to be sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation. The cystic components within the mass are unusual prior to treatment, as lymphoma usually appears as a solid hypodense mass. Diffuse involvement of spleen (or liver) may be difficult to recognize on imaging, often appearing as nonspecific organomegaly. Note the lymphomatous infiltration in the adrenal gland and nodes throughout the abdomen. Melanoma is one of several tumors which can appear cystic, as in this case, and be misinterpreted as a splenic abscess. In most published reports, breast cancer is the most common primary source for splenic metastases. Segmental Anatomy of the Liver Several newer contrast agents have been introduced into the Couinaud system of defining liver segmental anatomy clinical imaging that include a heterogeneous group of divides the liver into 8 segments by vertical planes that extend paramagnetic agents that are taken up in hepatocytes and through the course of the hepatic veins and by a horizontal excreted in bile; these are referred to collectively as plane that extends through the right and left portal veins. This phase, however, is usually not effective in detecting liver with an enlarged caudate and small right lobe indicates focal masses, even those that are hypervascular. Late arterial phase (35-45 sec): this is usually the optimal Hepatic vein occlusion is usually the result of Budd-Chiari phase for depiction of hypervascular hepatic masses, such as syndrome, hypercoagulable state, or tumor encasement. The falciform ligament plane separates the medial (segment 4) from the lateral (segments 2 and 3) left lobe. This coronal reformation shows both hepatic arteries arising from the proper hepatic artery, which in turn arises from the common hepatic artery. Some of the intravenously injected contrast medium is still circulating through the arteries, resulting in enhancement of the aorta. This, along with the presence of a capsule in a young, otherwise healthy woman is essentially diagnostic of hepatic adenoma. In addition there are spherical and oval lesions in other segments of the liver. The hepatic vessels course through the low-density lesions without being displaced or occluded. While a neoplastic mass could not be excluded by imaging characteristics alone, the appearance is more suggestive of infection. Metastases could have an identical appearance but are rare within a cirrhotic liver. While cholangiocarcinoma could have a similar appearance, the diagnosis of focal confluent fibrosis is much more likely given the clinical and radiographic evidence of alcoholic cirrhosis. The lobular architecture in adjacent parenchyma is well maintained with normal central veins. This patient had biopsy-proven congenital hepatic fibrosis, which results in hepatic failure and accounts for splenomegaly. Vajro P et al: Management of adults with paediatric-onset chronic liver disease: strategic issues for transition care. Venkatanarasimha N et al: Imaging features of ductal plate malformations in Demographics adults. Note the innumerable small hypodense lesions as well, probably representing biliary hamartomas. There are innumerable tiny bright cystic lesions in the liver, which are biliary hamartomas. The cysts ranged in size from microscopic to 5 cm in greatest dimension and contained clear fluid. This liver, which weighed 9 kg, was resected due to intractable patient discomfort and pressure on other organs. Note the compression of the stomach by a dominant cyst from the left hepatic lobe, which was subsequently marsupialized at surgery with resolution of symptoms. Abu-Wasel B et al: Pathophysiology, epidemiology, classification and treatment options for polycystic liver diseases. Venkatanarasimha N et al: Imaging features of ductal plate malformations in adults. Expert 0 Isolated polycystic liver disease is distinct genetic disease Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. The right kidney was displaced caudally and was hydronephrotic due to compression of the renal pelvis (not shown). Some cysts have higher than water density contents and others have peripheral calcification in cyst walls due to prior episodes of intracystic hemorrhage. Some are nearly black, as one would expect for simple fluid content, while others are of intermediate intensity. Note a clip from a prior cholecystectomy; the gallbladder normally lies in the interlobar plane. There is a collection of gas and fluid at the center of the mass that was aspirated and proved to be an infected, necrotic tumor. Two weeks later, the patient was clinically well and required no further treatment, though a residual liver mass was still present. On needle aspiration, blood-tinged purulent material was found and drained via pigtail catheter. Lymphomatous parenchymal involvement is rarely detected as such small discrete lesions. Also seen are multiple small lesions with hypodense centers and hyperenhancing rims or capsules. As in this case, most (85%) amebic abscesses are solitary and in the right hepatic lobe. Gunther J et al: Short report: Amebiasis-related mortality among United States residents, 1990-2007. The contents are very heterogeneous and echogenic, with little apparent posterior acoustic enhancement. Most amebic abscesses are single or few in number, while pyogenic abscesses are clustered and multiple. Fungal abscesses are even more numerous and usually appear as innumerable "microabscesses" in the liver &/or spleen. At surgery, the appendix appeared to be thickened and chronically inflamed; an appendectomy was performed. Note the thick, fibrotic wall (pericyst) and the presence of peripheral "daughter" cysts within the larger cyst. Hydatid disease can affect any abdominal organ, though involvement of retroperitoneal organs is unusual. A curvilinear echogenic scolex and highly echogenic debris attest to the complex nature of the cyst contents. This woman came from a sheep-raising area of Italy where hydatid disease is endemic. Note the presence of numerous septa within the mass, representing scolices or "daughter" cysts within the larger "mother" or exocyst.
Generic 50 mg female viagra fast delivery
Although rarely inflamed women's health of pasco buy discount female viagra, there is edema of the nail folds and separation of the folds from the nail plate. A bacterial culture may reveal a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. A healthy 7-year-old child who develops progressive yellowing and increasing friability of all nails over a period of 12 months likely has what condition The progressive development of rough nails with longitudinal grooves, pitting, chipping, ridges, and discoloration occurring in isolation in school-aged children has been given this name, although not all nails need be involved. The etiology remains unclear, and most cases resolve spontaneously without scarring. The nail changes, however, may herald other conditions, such as alopecia areata, lichen planus, and psoriasis. Spread occurs directly by contact with an infected individual or indirectly through the use of shared combs, brushes, or hats. For unknown reasons, infestation is nearly 35 times more likely among whites than blacks. It can be a vector for other diseases, such as epidemic typhus, trench fever, and relapsing fever. A search for lice should be made in any school-aged child presenting with scalp itching. Nits (lice eggs) are found in greatest density on the parietal and occipital areas. On physical examination, an actual louse (wingless, grayish insects about 3 to 4 mm) may be difficult to find, although one should easily be able to find nits. The nits are first attached to the hair close to the surface of the scalp and are oval and flesh colored (. When the louse emerges, the empty egg case, or nit, appears white in color and remains firmly attached to the hair shaft as the hair grows out (see. Malathion, aweakorganophosphatecholinesteraseinhibitor, iscurrentlyanapprovedprescription topical treatment for resistant head lice and their eggs. It should be used in a well-ventilated area given its odor and precautions also include increased absorption through open sores. Once an infestation of lice has been properly treated, the nits are not viable or contagious. Despite this, many schools will not allow children with nits to attend, although this nit-free policy has not been shown to be of benefit for controlling outbreaks. Increasing resistance to therapy may make removal more important to avoid diagnostic confusion. Manual removal (nit picking) is the most effective method, although it is time consuming and tedious. Fine-toothed combs, such as the LiceMeister comb (available through the National Pediculosis Association [. Because the highest percentage of mites are usually concentrated on the hands and feet, the web spaces between digits are the best places to look for the characteristic linear burrows. Moisten the skin with alcohol or mineral oil, scrape across the area of the burrow with a small, rounded scalpel blade. Burrows, if unseen, can be more precisely localized by rubbing a washable felt-tip marker across the web space and removing the ink with alcohol (called the burrow ink test). If burrows are present, ink will penetrate through the stratum corneum and outline the site. It is more effective than Lindane (the previously accepted treatment for scabies), and it has a much lower risk for neurotoxicity. The cream is applied from the neck to the toes at night with removal after 8 to 14 hours by bathing or showering. Physicians must make patients aware of the fact that lesions and pruritus may linger for 1 to 2 weeks after effective therapy. One must be supportive during this time to prevent unnecessary retreatment by parents. It must be stressed that all family members and close contacts should be treated simultaneously. It is often considered for patients with a significant dermatitis that precludes the application of topical permethrin. Ivermectin is not recommended for children younger than 5 years or weighing less than 15 kg because it may cross the immature blood-brain barrier. A series of linear or cluster formation erythematous or urticarial papules (often 3 or more in a row indicative of multiple meals), each with a central pinpoint punctum that occur in response to the bite of a bed bug (Cimex lactularius) or other crawling insect. Other furniture, clutter in the room, and cracks and crevices in the wall or floor may also harbor bedbugs. They are then attracted to the warm moist carbon dioxide around the sleeping child in the dark of night. Usually fade, but may persist indefinitely, becoming more prominent during crying. Seen in 80% to 90% of newborns with darker skin types but only 10% or less of fair-skinned infants. It is important to rule out infectious etiologies because some may be life-threatening. A Wright stain will reveal the presence of neutrophils or eosinophils (Table 4-3). Cutis marmorata is the bluish mottling of the skin often seen in infants and young children who have been exposed to low temperatures or chilling. The reticulated marbling effect is the result of dilated capillaries and venules causing darkened areas on the skin; this disappears with warming. However, persistent cutis marmorata is associated with trisomy 21, trisomy 18, and Cornelia de Lange syndromes. There is also a congenital vascular anomaly called cutis marmorata telangiectatic congenita that has persistent purple reticulate mottling of the skin. In addition, capillary malformations (port wine stains) may have a reticulated appearance and be mistaken for cutis marmorata. A healthy infant with scattered reddish nodules on the back skin most likely has what condition Subcutaneous fat necrosis, which consists of sharply circumscribed, indurated nodular lesions usually seen in healthy, term newborns and infants during the first few days to weeks of life. The stony hard areas of panniculitis, which are reddish to violaceous in color, are most often found on the cheeks, back, buttocks, arms, and thighs. However, occasionally they may extensively calcify and spontaneously drain with subsequent scarring. Remember that significant hypercalcemia may be present in a small number of patients. Therefore, a serum calcium level should be ordered whenever the disorder is suspected; it should be rechecked periodically until the condition resolves and for several months thereafter. What should the family of a newborn with a yellow, hairless patch with a cobblestone texture be advised to do This hamartomatous neoplasm usually presents as a yellow-pink hairless plaque on the scalp or face at the time of birth and is composed primarily of malformed sebaceous glands. Under the influence of androgens at puberty, the glands may hypertrophy and lead to the development of other neoplasms. Careful monitoring of the lesion for new growths or nonhealing ulcerations at all ages is advised, especially during adolescence. Aplasia cutis congenita (congenital absence of the skin) presents on the scalp as solitary or multiple well-demarcated ulcerations or atrophic scars. Of variable depth, the lesions may be limited to epidermis and upper dermis or occasionally extend into the skull and dura. Although most children with this lesion are normal without multiple anomalies, other associations include epidermolysis bullosa, placental infarcts, teratogens, sebaceous nevi, and limb anomalies.
Generic female viagra 100 mg
Thickness women's health big book of abs 4-week exercise plan cheap female viagra online master card, cross-sectional area and depth of invasion in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. The histogenesis and biologic behavior of primary human malignant melanomas of the skin. Randomized, surgical adjuvant clinical trial of recombinant interferon alfa-2a in selected patients with malignant melanoma. Combination of surgery, irradiation, and hyperthermia in treatment of recurrences of malignant tumors. Intraoperative radiolocalization of the sentinel node in patients with vulvar cancer. The use of locally mobilized skin (Z-plasty and rhomboid flaps) for large defects. Surgical-pathologic variables predictive of local recurrence in squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva. Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia: a long term follow up of treated and untreated women. Use of local flaps for primary anal reconstruction following perianal resection for neoplasia. N-ras mutations are common in melanomas from sun exposed skin of humans but rare in mucosal membranes or unexposed skin. Alternate reconstructive techniques for repair of large vulvar and vaginal defects. Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant therapy of high risk resected cutaneous melanoma: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trial. Vulvar reconstruction using a pedicle flap based on the superficial external pudendal artery. The application of immunoperoxidase techniques in the evaluation of vulvar and vaginal disease. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of metastatic melanoma: a morphological analysis of 174 cases. Malignant melanoma of the vulva: report of six cases and review of the literature. Malignant melanoma of the vulva in a nationwide, 25 year study of 219 Swedish females. The anatomic and biophysical principles permitting accurate control over the depth of dermal destruction with the carbon dioxide laser. Pelvic exenteration for treatment of locally advanced primary or recurrent vulvar carcinoma. Lymphadenectomy in the management of stage I malignant melanoma, a prospective randomized study. Delayed regional lymph node dissection in stage I malignant melanoma of the skin of the lower extremities. Body weight 20% below ideal (Ideal =100 lbs for 60" height + 5 lbs for each additional inch) B. Increased nutritional needs: burns, trauma, surgery, fever, sepsis, wounds, pregnancy G. Nutritional losses: malabsorption, short bowel syndrome, dialysis, effusions, chronic bleeding or diarrhea H. Protein Store Assessment Normal Mild Moderate Severe Weight loss, 1 month, % 3 4 5 > 5 3 months, % 6 7 7. Keep infusion less than 4 mg/kg-min in stressed individuals (surgery, trauma, burns, steroids) D. Essential fatty acids are linoleic and linolenic acids: absolute requirements for essential fatty acids is 3-5% of total caloric intake. Wt 10 kg 100 mL/kg-day 10 kg <Wt 20 kg (+)50 mL/kg-day Wt >20 kg (+)20 mL/kg-day F. Metabolic function Zinc Metabolism of protein, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids Copper Cofactor for oxidative enzymes, collagen synthesis, iron interactions Manganese Muccopolysaccharide metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation Chromium Potentiation of insulin effects via glucose tolerance factor Selenium Cofactor for glutathione peroxidase Also: Iron, Molybdenum, Iodine, Fluoride Patients with high output fistulas are usually deficient in zinc and copper. Duodenum: vitamins A & B, iron, calcium, glycerol and fatty acids, monoglycerides, amino acids, mono and disaccharides 3. Entire: glucose, galactose, vitamin C, amino acids, glycerol and fatty acids, monoglycerides, folic acid, biotin, copper, zinc, potassium, pantothenic acid b. Jejunum and ileum: vitamins D, E, K, B1, B2, B3, B6, iodine, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus Gyn Onc Overview, Page 69 R. University of Michigan Standard Formulation: Amino Acids (5%) 50 g Total Volume 1050 mL Dextrose (20%) 200 g Ca2+ 4. Lipids: Liposyn 20%, contains soybean and safflower oil, egg phospholipids, and glycerin in 500 mL bottles. Minimum essential fatty acid requirements met with two 300 mL bottles of Liposyn weekly. Hypophosphatemia: "Refeeding Syndrome" results in respiratory failure, cardiomyopathy. Standard protein (<20% kcal as protein): (This list is not comprehensive and formulations change frequently. When planned infusion rate reached, advance concentration to 3/4 strength formula for 24 hours, then to full strength b. Dobhoff tubes should be irrigated after each bolus feeding, or q6h if on continuous infusion d. Energy attenuates proportional to the inverse square of the distance from the source. Absorption proportional to cube of atomic number, a useful property for diagnostic X-rays. Isodose Curves Penumbra: lateral spread, a function of source size as well as beam energy. Radiation causes delay of cell cycle by blocking progression from G1 > S and G2 > M. Multiple hit kinetics: N=N {1-[1-exp(-D/D)]n}, n=number of targets per cell 0 0 c. Linear quadratic kinetics: N=N exp(-D-D2), and describe probability of 0 interacting lesions caused by single and double tracks, respectively. The more time a cell has before entering S phase, the more likely it is that successful repair will occur. Oxygen Enhancement Ratio: oxygenated cells are about 3x more sensitive to radiation than hypoxic cells. X-rays: manufactured by electron beam striking tungsten target, no mass or charge 3. Two implants, spaced 1-2 weeks apart near conclusion of teletherapy, and removed after 24-48h. Chemosensitization administered concurrently with radiation using cisplatin, 5fluorouracil, or both. Post-op: Benefit of adjuvant therapy after surgical staging with negative nodes not yet demonstrated (See endometrial cancer chapter). Dose: 45-50 Gy, followed by optional vaginal brachytherapy if vaginal apex recurrence risk is significant. Historically reported for Stage Ib-Ic epithelial tumors with no residual disease and no significant adhesions. Post-operative therapy: Indicated for >1 positive inguinofemoral node, any positive pelvic nodes, and for residual disease of the vulva. Treatment ports customized, electrons commonly used for vulva/groins to maximize surface dose 2. Pre-operative therapy: Indicated for bulky T3-4 lesions to reduce tumor size, allowing less radical surgery. Concurrent chemotherapy using 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, and/or mitomycin C improves likelihood of remission 3. Acute: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, myelosuppression, ovarian failure, skin burns B. A: Tumor hypoxia decreases efficacy of radiation by reducing oxygen free radical mediated cell damage. A: Electrons have mass and charge causing them to slow when they encounter tissue.
Syndromes
- Loss of color from the skin (pallor)
- One child is born with two abnormal genes (at risk for the disease)
- Gas released when mixing bleach with some of the powdered cleansing products and ammonia (chloramine gas)
- Scleroderma
- Convulsions
- Intercourse also may be less pleasurable because the man must pull out his penis right after ejaculation.
- You are a heavy smoker
- Vandalizing or destroying property
- Glass thermometers
Purchase female viagra on line
The chemicals in Visine directly lower the concentrations of the cannabinoids in the urine women's health clinic blacktown order female viagra 50 mg visa. In addition, it is metabolized to oxalic acid, which can cause renal damage by the precipitation of calcium oxalate crystals in the renal parenchyma and can lead to hypocalcemia. It is the formic acid that causes the refractory metabolic acidosis and ocular symptoms. Both methanol and ethylene glycol require the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase to create their toxic metabolites. Ethanol competitively inhibits the formation of these metabolites by serving as a substrate for the enzyme. However, it is inebriating, it may cause hypoglycemia, and its kinetics are widely variable. The osmolar gap is the difference between the measured osmolarity (obtained from freezing point depression) and the calculated osmolarity (calculated 2 [serum Na] blood urea nitrogen/2. A significant osmolar gap suggests an alcohol poisoning, which typically produces exogenous osmoles. If a child has ingested an acetaminophen-containing product, when should the first acetaminophen level be obtained A plasma level obtained 4 hours after ingestion is a good indicator of the potential for hepatic toxicity. It should be used for any acetaminophen overdose with a toxic serum acetaminophen level within the first 24 hours after ingestion. Normally, 94% of acetaminophen is metabolized to glucuronide or sulfate form, and 2% is excreted unchanged in urine, both of which are nontoxic. The remaining 4% is conjugated with glutathione (with the help of cytochrome P-450) to form mercaptopuric acid, which is also not hepatotoxic. When a significant acetaminophen overdose occurs, cytochrome P-450 becomes the major system for metabolizing the acetaminophen, leading to depletion of hepatic stores of glutathione. When the glutathione is depleted to less than 70% of normal, a highly reactive intermediate metabolite binds to hepatic macromolecules, causing hepatocellular necrosis. They also cause lactic acidosis and ketoacidosis by inhibiting Krebs cycle enzymes, uncoupling oxidation phosphorylation, and inhibiting amino acid metabolism (metabolic acidosis). These are salicylates that are found in over-the-counter products, such as Pepto-Bismol (bismuth salicylate). Salicylate absorption can be substantial, and in the setting of influenza or chickenpox, Pepto-Bismol use has been discouraged because of the potential for complications such as the development of Reye syndrome. Tricyclic antidepressants interfere with myocardial conduction and can precipitate ventricular tachycardias or complete heart block. If these findings are noted, treatment with sodium bicarbonate should be initiated. Sodium bicarbonate helps prevent the sodium channel blockade that is caused by these medications. Which clinical and laboratory features correlate with an acutely elevated serum iron Serum iron levels obtained 4 to 6 hours after ingestion correlate with severity of toxicity. Other laboratory tests that correlate with an elevated iron level include leukocytosis (>15, 000/mm3) and hyperglycemia (>150 mg/dL). What are the four clinical stages of iron toxicity and the correlating pathophysiology The toxic dose of iron ingestion is at least 20 mg/kg of elemental iron, and the lethal dose of iron reported is in the range of 60 to 180 mg/kg of elemental iron. In a small child, a toxic dose is about 300 mg of elemental iron, which is the equivalent of 20 tablets of multivitamins containing 15 mg/tab of elemental iron. Because iron can initially cause nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain, a child with a suspected but unknown amount of iron poisoning can be observed, and an iron level may be obtained. A child who has no complaints and has a normal physical examination after 4 to 6 hours of observation can be safely discharged home. You are better off with the toilet bowl cleaner, although both acid (toilet bowl cleaner) and alkali (dishwashing detergent) ingestions may cause severe esophageal burns. Alkalis cause injury by liquefaction necrosis, dissolving proteins and lipids, thereby allowing deeper penetration of the caustic substance and greater local tissue injury. This results in the formation of an eschar that limits the penetration of the toxin into deeper tissues. Compared with acids, alkalis are more typically in solid and paste form, which increases tissue contact time and tissue injury. The household hydrocarbons with low viscosities pose the greatest aspiration hazard. These include furniture polishes, gasoline and kerosene, turpentine and other paint thinners, and lighter fuels. What is the differential diagnosis in a child who presents with confusion and lethargy This dystonic reaction is classically seen as an adverse side effect of antidopaminergic agents such as neuroleptics, antiemetics, or metoclopramide. Organophosphates inhibit cholinesterase and cause all the signs and symptoms of acetylcholine excess. Acrodynia is the term applied to one form of mercury salt intoxication that results in a constellation of signs and symptoms very similar to that currently recognized as Kawasaki disease. The classic presentation of acrodynia was described in children exposed to calomel, a substance used in teething powders, which was essentially mercurous chloride. The symptom complex included swelling and redness of the hands and feet, skin rashes, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypertension, photophobia, and an intense irritability with anorexia and insomnia. Infants were often very limp, lying in a frog-like position, with impressive weakness of the hip and shoulder girdle muscles. Similar symptoms have been described in children exposed to other forms of mercury, including broken fluorescent lightbulbs or diapers rinsed in mercuric chloride. Cyanide ion binds to the heme-containing cytochrome a3 enzyme in the electron transport chain of mitochondria, which is the final common pathway in oxidative metabolism. Thus, with a significant exposure, virtually every cell in the body becomes starved of oxygen at the mitochondrial level and is unable to function. The body does have minor routes of cyanide detoxification, including excretion by the lungs and liver through rhodanese, a hepatic enzyme that combines cyanide with thiosulfate to form the less toxic thiocyanate for renal excretion. However, these mechanisms are inadequate in the face of a significant cyanide exposure. As with carbon monoxide poisoning, symptoms tend to be most prominent among the metabolically active organ systems. Less severe ingestions may be noted initially by burning of the tongue and mucous membranes, with tachypnea and dyspnea due to cyanide stimulation of chemoreceptors. What kinds of plants account for the greatest percentage of deaths due to plant poisonings The most dreaded variety is the Amanita species, which initially causes intestinal symptoms by one toxin (phallotoxin) and then hepatic and renal failure by a separate toxin (amatoxin). Other mushroom classes can cause a variety of early-onset (<6 hours) symptoms, including muscarinic effects. Rarely, large ingestions have resulted in seizures, hypertension, and even cardiac arrest. In some countries, extracts of mistletoe have been used for illegal abortifacients, brewed in teas that are particularly toxic. In the United States, the typical call to a poison center concerns a child who eats one or two mistletoe berries, which in general is unlikely to produce significant signs or symptoms. Otherwise, if the battery is in the stomach or beyond and the patient remains asymptomatic, watchful waiting is appropriate with follow-up imaging if the battery is not seen in the stool.
100mg female viagra amex
It is not the intent of this section to claim rights or contest your rights to work written entirely by you; rather breast cancer diet purchase discount female viagra, the intent is to exercise the right to control the distribution of derivative or collective works based on the Database. You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the Database except as expressly provided under this License. Any attempt otherwise to copy, modify, sublicense or distribute the Database will automatically terminate your rights under this License. However, parties who have received copies, or rights, from you under this License will not have their licenses terminated so long as such parties remain in full compliance. However, nothing else grants you permission to copy, modify or distribute the Database or its derivative works. Therefore, by copying, modifying or distributing the Database (or any work based on the Database), you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so, and all its terms and conditions for copying, distributing or modifying the Database or works based on it. Each time you redistribute the Database (or any work based on the Database), the recipient automatically receives a license from Multum to copy, distribute or modify the Database subject to these terms and conditions. You are not responsible for enforcing compliance by third parties to this License. You acknowledge that updates to the Database are at the sole discretion of Multum. Multum makes no representations or warranties whatsoever, express or implied, with respect to the compatibility of the Database, or future releases thereof, with any computer hardware or software, nor does Multum represent or warrant the continuity of the features or the facilities provided by or through the Database as between various releases thereof. Any warranties expressly provided herein do not apply if: (i) the end-user alters, mishandles or improperly uses, stores or installs all, or any part, of the Database, (ii) the end-user uses, stores or installs the Database on a computer system which fails to meet the specifications provided by Multum, or (iii) the breach of warranty arises out of or in connection with acts or omissions of persons other than Multum. You warrant that you have authority within the organization you identified during registration for the Database to enter into license agreements with other organizations including Multum. You also agree that Multum may issue, if it desires, a press release stating that you and/or your organization have licensed the Database. If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot distribute so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this License and any other obligations, then as a consequence you may not distribute the Database at all. If any portion of this License is held invalid or unenforceable under any particular circumstance, the balance of this License is intended to apply and the License as a whole is intended to apply in other circumstances. If the distribution and/or use of the Database is or becomes restricted in certain countries either by patents or by copyrighted interfaces, Multum may add an explicit geographical distribution limitation excluding those countries, so that distribution is permitted only in or among countries not thus excluded. In such case, this License incorporates the limitation as if written in the body of this License. Multum Lexicon Copyright (c) 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2008 Cerner Multum, Inc. Vincent Road Kochi 682 018, Kerala Phones: +91-484-4036109, +91-484-2395739, +91-484-2395740 e-mail: kochi@jaypeebrothers. No part of this publication should be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means: electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the author and the publisher. This book has been published in good faith that the material provided by author is original. Every effort is made to ensure accuracy of material, but the publisher, printer and author will not be held responsible for any inadvertent error(s). In case of any dispute, all legal matters are to be settled under Delhi jurisdiction only. My positive reaction to the previous Edition probably gives some clues on why I accepted the second invitation, this time to introduce the Sixth Edition to new students of Pathology and other potential readers. Up to now, it has been used by thousands of students and I am sure that it will continue to be read and cherished in the new Edition as well. For the Sixth Edition, Dr Mohan has partially restructured the book, substantially revised it, and updated the text wherever it was necessary. Following the advances of basic sciences and clinical pathology, the revisions and addition are most evident in portions pertaining to molecular biology and genetics. Other aspects of modern pathology have not been neglected either and contain numerous novelties; even the seasoned specialists will learn something new from each and every chapter. Furthermore, the author has dramatically increased the number of illustrations, which are so essential for understanding Pathology. The distribution of illustrations has also been changed so that they are now much closer to the text to which they relate. For the new generation of modern students who have grown up next to the computers, the author has placed all the images and tables on the website with facility for downloading them. These images will serve the twin purpose of quick review and self-assessment for students and will appeal to Pathology teachers who could use them for their lectures, being assured that their students will have access to the same material for review and study. The Quick Review Book, the ever popular companion to the previous two Editions, was also updated, succinctly supplementing the main text. It will provide a helpful study material to many a student and help them review the subject for examinations. In summary, it is my distinct pleasure and honour to most enthusiastically endorse the new edition of an established textbook and salute its publication. Dr Mohan deserves kudos for the job well done and for providing the medical students with such an attractive, modern, up-to-date and useful Textbook of Pathology. These books are sent to my office from publishers, with a standard request for a potential review in the Journal. I acknowledged the receipt of the books by email, and also congratulated the Publisher on a job well done. A brief electronic exchange between Kansas City and New Delhi ensued, whereupon Mr Vij asked me to write a foreword for the Reprint of 5th Edition of the Textbook. Even though there were no specific instructions attached to the request, I assumed that I should address my notes primarily to undergraduate and graduate students of Pathology. Furthermore, I decided to write the Foreword in the form of answers to the questions that I would have had if I were a medical student entering the field of Pathology. I hope that these hypothetical questions and answers of mine will be of interest to the readers of this Textbook. This is a modern Textbook written by an expert who knows his pathology; an experienced teacher who knows what is important and what is not, and who has obviously taught pathology for many years; a well informed academician who is with modern trends in medical education, and knows how to present pathology as a preparatory step for future clinical education of medical students. This Indian Textbook covers more or less the same topics as the equivalent Textbooks currently used in the Western Hemisphere. Like the Western textbooks it covers the traditional fields of General and Systemic Pathology: one-third of the book viii is devoted to General Pathology, whereas the remaining two-thirds cover Systemic Pathology. In that respect the Indian textbook resembles more the European than the American textbooks, which have become more clinically-oriented. In my opinion this approach gives excellent results, but only if the students have enough time to devote to Pathology. Histopathology has been deleted from most curricula, and most American medical students do not know to use efficiently the microscope, which is unfortunate. Question 3: Answer: the material is presented in a systematic manner in the best tradition of classical British textbooks, a tradition that can be traced to the classical writers of ancient Greece and Rome. This time tested teaching will be most appreciated by students who are methodical and do not take shortcuts in their effort to acquire encyclopedic knowledge of pathology. As we all know clear writing reflects clear thinking, and clear thinking in my opinion, is an absolute prerequisite for good teaching. Judging from the book at hand, Professor Mohan (whom I do not know personally) is not only a clear thinker, but he must be also an exceptionally talented teacher. Each chapter is subdivided into smaller entities, which are further divided into paragraphs, ideally suited for easy reading. Color coded headings and the added emphasis in form of words printed in bold or capital letters are additional attractions that facilitate learning. Unique to this Textbook are the numerous hand-drawn color illustrations, including many renditions of histopathologic slides.
100mg female viagra otc
In general menopause mondays purchase 100mg female viagra with mastercard, the growth rate of neoplasms correlate with their level of differentiation and thus, most malignant neoplasms grow more rapidly than do benign neoplasms. On occasions, cancers have been observed to decrease in size and even spontaneously disappear. Local invasion Nearly all benign neoplasms grow as cohesive expansile masses that remains localized to their site of origin and do not have the capacity to invade or metastasize to distant sites, as do malignant neoplasms. Thus, such encapsulations tend to contain the 192 benign neoplasms as a discrete, rapidly palpable and easily movable mass that can easily surgically enucleated. Generally, they are poorly demarcated from the surrounding normal tissue (and a well-defined cleavage plane is lacking). Several matrix-degrading enzymes including glycosidase may be associated with tumour invasion. Cartilage is probably the most resistant of all tissues to invasions and this is may be due to the biologic stability and slow turnover of cartilage. Malignant cell surface receptors bind to basement membrane components (ex laminin). Metastasis 193 Most carcinomas begin as localized growth confined to the epithelium in which they arise. As long as this early cancers do not penetrate the basement membrane on which the epithelium rests such tumours are called carcinoma in-situ. In those situations in which cancers arise from cell that are not confined by a basement membrane, such as connective tissue cells, lymphoid elements and hepatocytes, an in-situ stage is not defined. Metastasis It is defined as a transfer of malignant cells from one site to another not directly connected with it (as it is described in the above steps). The invasiveness of cancers permits them to penetrate in to the blood vessel, lymphatic and body cavities providing the opportunity for spread. Pathways of spread: Dissemination of malignant neoplasm may occur through one of the following pathways. Most often involved is the peritoneal cavity, but any other cavities such as pleural, pericardial, sub-arachnoid and joint spaces-may be affected. These carcinomas fill the peritoneal cavity with a 194 gelatinous soft, translucent neoplastic mass. Lymphatic spread Lymphatic route is the most common pathway for the initial dissemination of carcinomas the pattern of lymph node involvement follows the natural routes of drainage. Lymph nodes involvement in cancers is in direct proportion to the number of tumour cell reaching the nodes. The cut surface of this enlarged lymph node usually resembles that of the primary tumour in colour and consistency. The best examples of lymphatic spread of malignant neoplasm can be exemplified by breast carcinoma. Skip metastasis happen to occur because of venous lymphatic anastomoses or because inflammation or radiation has obliterated the lymphatic channels for example abdominal cancer (gastric cancer) may be initially signaled by supra clavicular (sentinel node). Conversely, the absence of tumour cells in reseated lymph nodes does not guarantee that there is no underlying cancer. Hematogenous spread Typical for all sarcomas and certain carcinomas the spread appears to be selective with seed and soil phenomenon. Lung & liver are common sites of metastasis because they receive the systemic and venous out flow respectively. Cancer Epidemiology the only certain way to avoid cancer is not to be born, to live is to incur the risk. Over the years cancer incidence increased in males while it slightly decreased in females (due to largely screening Procedures-cervical, breast etc. In the studied populations the most common cancer in males is broncogenic carcinoma while breast carcinoma in females. Acute leukemias and neoplasms of the central nervous system accounts for about 60% of the deaths. Geographic factors (geographic pathology): Specific differences in incidence rates of cancers are seen worldwide. Inherited cancer syndromes (Autosomal dominant) with strong familial history include Familial retinoblastomas usually bilateral, and a second cancer risk particularly osteogenic sarcoma. Oncosupressor gene is the basis for this carcinogenesis 196 Familial adenomatous polyps of the colon. Endometrial hyperplasia endometrial carcinoma Cervical dysplasia cervical cancer Bronchial dysplasia bronchogenic carcinoma Regenerative nodules liver cancer Certain non-neoplastic disorders may predispose to cancers. Chronic atrophic gastritis gastric cancer Solar keratosis of skin skin cancer Chronic ulcerative colitis colonic cancer Leukoplakia of the oral cavity, vulva and penis squamous cell carcinoma Certain types of benign neoplasms Large cumulative experiences indicate that most benign neoplasms do not become malignant. Molecular Basis of Cancer (Carcinogenesis) Basic principles of carcinogenesis: the fundamental principles in carcinogenesis include 1) Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis. Such genetic damage (mutation) may be acquired by the action of environmental agents such as chemicals, radiation or viruses or it may be inherited in the germ line. However, initiation alone is not sufficient for tumour formation and thus, promoters can induce tumours in initiated cells, but they are non-tumourogenic by themselves. Furthermore, tumours do not result when a promoting agent applied before, the initiating agent. Directly acting compound these are ultimate carcinogens and have one property in common: They are highly reactive electrophiles (have electron deficient atoms) that can react with nucleophilic (electron-rich) sites in the cell. Indirect acting compounds (or pro-carcinogens) Requires metabolic conversion in vivo to produce ultimate carcinogens capable of transforming cells. Miners for radioactive elements--lung cancer Therapeutic irradiations have been documented to be carcinogenic. Thyroid cancer may result from childhood & infancy irradiation (9%), and by the same taken radiation therapy for spondylitis may lead to a possible acute leukemia year later. In intermediate category are cancers of the breast, lungs, and salivary glands In contrast, skin, bone and gastrointestinal tract are relatively resistant to radiation induced neoplasia. The infection of B cell is latent and the latently infected B-cell is immortalized. The actively dividing B cells are at increased risk of mutations (t 8; 14) translocation that juxta pose C myc with one of Immuno globuline gene loci. Helicobacter pylori There is an association between gastric infections with helicobacter pylori as a cause of gastric lymphoma. The lymphoid cells reside in the marginal zones of lymphoid follicles and hence alternatively named as mantle zone lymphoma. Although cancer evaluation may suggest one or the other, the only unequivocal benign mass is the excised and histopathologically diagnosed one. Effects of tumour on the host: Both benigin and malignant neoplasms may cause problems because of 1. For example a benign B cell adenoma of pancreatic islets less than 1 cm in diameter may produce sufficient insulin to cause fatal hypoglycemia the erosive destructive growth of cancers or expansile pressure on benign tumour of any natural surface may cause ulceration secondary infection and bleeding. Cancer cachexia Cachexia is a progressive loss of body fat and lean body mass accompanied by profound weakness, anorexia and anemia. The origin of cancer cachexia are obscure Clinically anorexia is a common problem in patients with cancer. Reduced food intake has been related to abnormalities in taste and central control of appetite. In patents with cancer, calorie expenditure often remains high and basal metabolic rate is increased despite reduced food intake. Paraneoplastic syndromes Paraneoplastic syndrome is an aggregate of symptom complexes in cancer bearing patients that can not readily be explained either by the local or distant spread of the tumour or by the elaboration of hormones indigenous to the tissue from which the tumour arose Paraneoplastic syndrome occurs in about 10% of patients with malignant disease Despite its infrequency, the syndrome is important for three reasons: 1. In affected patients, they may represent significant clinical problems and may even be lethal. Laboratory Diagnosis of Cancer Every year approach to laboratory diagnosis of cancer becomes more complex more sophisticated and more specialized with time.

Cheap generic female viagra uk
While on adult fluoroscopy menopause 2 week period buy generic female viagra 50mg on-line, pediatric fluoroscopy rotations, and on-call, residents may wear personal scrubs with white lab coats. Residents or faculty who are not appropriately dressed will be counseled in proper dress for the hospital workplace at the first occurrence. At the second occurrence they will be sent home to obtain proper dress, with the time charged to vacation leave. Telephone Protocol Local calls can be made from most phones in the Radiology Department. Phone calls from all extensions in the department are reported to the Business Manager on a monthly basis. Long distance personal calls should not be made on hospital phones without authorization by Radiology Business Manager. Monday and Friday physics from 7:30 to 8:30, case conference Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday from 7:30 to 8:30; categorical course daily from 12:00 (noon) to 1:00 pm. Residents are individually responsible for scheduling and attending these training sessions to insure their certification. R Level-Specific Overall Roles, Responsibilities and Functions the roles, responsibilities and functions of the diagnostic radiology resident per training year are based on the following objectives, as follows: I. Clarify any questions regarding duties with expected attending at start of rotation. Get exposed to the broad spectrum of patient examinations and/or procedures as assigned by attending or senior resident with an emphasis on quality of patient evaluation and patient care. In-depth discussion of all cases with the attending prior to initiation of all but the most basic diagnostic studies or therapeutic interventions. Take no supervisory role or direction of decisions of other residents or medical students, but ensure active medical student involvement. All procedures must be done under direct approval and supervision of attending radiologist. Prepare for and pass Freshman plain film examination in order to begin supervised plain film call beginning in January. Prepare for and pass Freshman complex imaging examination in order to begin solo call July of their R2 year. By completion of the first 12 months of residency and the minimum required training in core rotations, residents should be judged by the faculty to be capable of serving as the Short Call Resident, providing immediate plain film consultation to Emergency Room and Hospital physicians. Review rotation goals and objectives prior to beginning the rotation and clarify any questions regarding duties and expectations at start of rotation. Emphasis on gaining experience with full spectrum of diagnostic and invasive radiology procedures and increasing proficiency on skills already acquired. All decisions regarding invasive radiology procedures and specialized diagnostic procedures are discussed in depth with the attending. By completion of the second year of training, residents should show increased ability in interpretation of plain films, computed tomography, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and nuclear radiology studies. All radiology residents are required to take the Resident In-Training examination each February. Residents are expected to pass this examination with a global score of 30% or more. Percentile scores will be included in the yearly performance criteria required for promotion to the next year of radiology residency training. Must discuss all cases with attending prior to performance of vascular/interventional procedures and complex diagnostic studies. By completion of the third year of training, residents should demonstrate advanced skills in interpretation of routine and complicated imaging studies in all areas of radiology. All residents are required to take the Resident In-Training examination each February. Senior residents play a supervisory role of junior residents, with increased teaching responsibilities 3. Senior residents play increased role in consultation with other residents or attending physicians from other clinical services. All radiology residents are required to take the Resident In-Training examination each th February. Residents are expected to pass this examination with a global score of 30 15 th percentile or more. A performance below 30 percentile will require performance review by program director. Trainee must fulfill complete requirements for credentialing for year of training with consultation with fellowship program director. Trainee must carry out procedures with attending input and supervision as required before, during and after procedure. Trainee will play a major role in instruction and supervision of radiology residents as well as medical students. Trainee will interact with residents and attending physicians on other services on a co-equal footing in relation to procedures and diagnostic test results as part of integrated patient care team. Trainee must demonstrate competence to function independently without significant faculty supervision as a general diagnostic radiologist for coverage of services outside of their subspecialty field of study, according to radiology department needs. Trainee will be expected to be qualified to pass the corresponding examination for their field of subspecialty training conducive to Certificate of Added Qualifications of the American Boards of Radiology by the completion of their training or other relevant certification. Call Responsibilities: General Considerations Radiology Call is a combination of a Night Float rotation and short individual calls overlapping with the Night Float. We provide a secure Call Room within the Radiology Department, with private sleeping and shower facilities, phone and networked computer. The resident on short call starts his day at the 7:30 am conference and stays in the hospital until 9 pm, overlapping one hour with the Night Float resident to take care of case backlogs and allow a smooth transition to the Night Float. The night float schedule is established for the entire year according to the yearly rotation schedule. The chief resident prepares the call schedule distributing short calls among residents not on the night float rotation for the specific time period to be covered (See Appendix B). Radiology faculty call is provided 24 hours a day by attending radiologists for each section, and consultation on digital imaging examinations is provided in person or by teleradiology. Call Schedule the night float, short call, weekend and holiday call schedule is prepared by the chief Resident and approved by the Program Director. The schedule is created in conjuction with the rotation scheduled prepared by the Program Director. Once the weekly call schedule has been made and distributed, changes can be made only in the case of emergencies. Any changes in the call schedule must be approved by the Program Director and chief resident, and given to the Resident Coordinator prior to 3:00 pm. All residents will begin freshman supervised call with upper level residents beginning August of freshman year. This is an observational exposure only with no interpretation or dictation duties allowed. Freshmen resident ill gradually increase their number and length of Freshman Supervised Call as they progress through their R1 year. The communication of findings will also be monitored by the upper level or attending radiologist. Competency or Objective: Residency Review Committee and American Board of Radiology requirements, Medical Knowledge, Interpersonal and Communication Skills, Professionalism Documentation: Peer Evaluations, Faculty Evaluations, Technologists Evaluations. It is the responsibility of the original resident taking call to notify all appropriate personnel of any changes in the call schedule. Any resident who does not cover his/her scheduled call will be assigned double the call duty missed by the Chief Resident, unless there are extenuating circumstances.

Order female viagra 50mg free shipping
Ingredients are separated by dashes (for two ingredients only) or semi-colons (for three or more ingredients) menstrual flow is actually sloughed off buy female viagra 100mg line. This License Agreement (the "License") applies to the Multum Lexicon database (the "Database"). This License does not apply to any other products or services of Cerner Multum, Inc. A "work based on the Database" means either the Database or any derivative work under copyright law; i. A translation of the Database is included without limitation in the term "modification". Your use of the Database acknowledges acceptance of these restrictions, disclaimers, and limitations. You expressly acknowledge and agree that Multum is not responsible for the results of your decisions resulting from the use of the Database, including, but not limited to , your choosing to seek or not to seek professional medical care, or from choosing or not choosing specific treatment based on the Database. Every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided in the Database is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. Multum does not assume any responsibility for any aspect of healthcare administered or not administered with the aid of information the Database provides. You may copy and distribute verbatim copies of the Database as you receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuously and appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright notice and disclaimer of warranty; keep intact all the notices that refer to this License and to the absence of any warranty; and give any other recipients of the Database a copy of this License (the readme. You may modify your copy or copies of the Database or any portion of it to form a derivative work, and copy and distribute such modifications or work under the terms of Section 2. Students will most likely understand them much easier than the relatively impersonal original microphotographs of the same histopathologic lesions. Flow-charts are most efficiently used to explicate the pathogenesis of various lesions or the pathophysiology of disease processes. The tables are good for classifications and comparative listings of closely related diseases and their pathologic features. I always recommend to my students to buy a major textbook and a smaller review book containing a digest of the most important concepts; or a book of questions and answers, so that the student could test his/her knowledge of pathology and the understanding of the material in the main textbook. I was pleased to see that Professor Mohan shares my teaching philosophy and has taken upon himself to prepare for his students a shorter version of main text. At the same time, they have a unique opportunity to see, from the example set by their teacher, on how the same material can be approached from two points of view, and presented in two formats. The old adage, that you have never learned anything unless you have seen it at least from two sides, is clearly illustrated here. For the students of medicine the message is clear: if you understand the material presented in both the shorter and the longer version you can be assured that you know your Pathology inside out; and you are ready for the final examination and clinical training. This is the most common question my students ask me and I hope that you believe me when I say that you do not have to know it all. Second, few of us have photographic memory and infinite storage space in our brains and thus even theoretically, very few of us could learn this book by heart. I can assure you that the book was not written for those geniuses, but for the average persons like most of us. Third, your goal should not be to memorize all the facts listed in the textbook, but rather to understand the main concepts. The more details you know, the deeper your understanding of the basic concepts will be. Memorizing the details without the understanding of concepts that hold them together is not something that I would recommend. The beauty of it all is that you can decide for yourself how deep to dig in, when to stop, what to keep and memorize, and what to eliminate. And remember, deciding on what to eliminate is almost as important as choosing what to retain. As the educational gurus teach us, that is the gist of what they call active learning. I hope that you will be similarly excited and I hope that it will inspire in you enthusiasm for Pathology. Remember also the words of the great clinician William Osler, one of the founders of modern medicine in late 19th and early 20th Century, who said that our clinical practice will be only as good as our understanding of Pathology. I hope that I have answered most of the questions that you might have had while opening this book. If you have any additional questions that I did not anticipate, please feel free to send me an email at idamjano@kumc. In preparing 6th revised edition of my, I pursued this goal with profound enthusiasm and passionate zeal. I am, thus, pleased to present to users a wholly transformed appearance and updated contents in the revised edition. While full colour printing had been introduced in the last edition 5 years back maturing the book into an international edition, the present redesigned and revised edition has utlilised the contemporary technological advances in its full form in illustrations, lay-out and in printing. The revised edition has almost thrice the number of illustrations of large number of common diseases placed along with the text, and it is hoped that it will enhance understanding and learning of the subject readily, besides being a visual treat. In recent times, advances in genetics, immunology and molecular biology have heightened our understanding of the mechanisms of diseases. Surely, the students of current times need to be enlightened on these modern advances in diseases; these aspects have been dealt in the revised edition with a simple and lucid approach. Some of the of the Sixth Edition are as follows: Thorough Textual Revision and Updating: All the chapters and topics have undergone thorough revision and updating of various aspects, including contemporary diagnostic modalities. While most of the newer information has been inserted between the lines, a few topics have been rewritten. Past experience has shown that the readers find tables on contrasting features and listing of salient features as a very useful medium for quick learning; considering their utility 15 new tables have been added in different chapters in the revised edition. Profusely Illustrated: Majority of illustrations in the revised Edition are new additions while a few old ones have been done again. All the line-drawing and schematic cartoons have been updated and improved in content as well as their presentation by preparing them again on CorelDraw in soft colours, eliminating the shortcomings noticed in them in previous edition. All free-hand labelled sketches of gross specimens and line-drawings of microscopic features of an entity have been placed alongside the corresponding specimen photograph and the photomicrograph respectively, enhancing the understanding of the subject for the beginner students in pathology. In doing so, the number of figures has gone up by about three-folds in the present edition, some incorporated as an inset with focus on a close-up microscopic view. Truly User-friendly: Rational use of various levels of headings and subheadings in different colours, bold face and in italics has been done in the text in order to highlight key points. All the citations of figures and tables in the text have been shown in colour now to make the related text vividly visible and to help user locate the same quickly on a page. It is hoped that these features will enable the user with rapid revision at the end of a topic, making the book truly user-friendly. Much More Content but Unaltered Volume: While the new edition has a lot more updated textual material, more tables and a marked increase in the number of figures than the previous edition, a meticulous and rational page management has helped in retaining almost the same girth of the book as before. The students would find these useful for quick review and for self assessment in which an unlabelled image (gross specimen or a photomicrograph) appears, followed by the labelled image with diagnosis corresponding to the same figure and table in the textbook. Besides, ready availability of these downloadable images and tables would be useful to fellow teachers for possibly including the same in their lectures. This small book has been found profoundly useful by the students just before practical examination to face when they need to revise huge course content in a short time, or by those preparing to take postgraduate entrance examinations. In essence, the revised edition is a comprehensive text of pathology meant primarily for students of pathology; however, the practicing clinicians and students of other branches of medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, alternate system of medicine, and paramedical courses may also find it useful. All the photomicrographs included in the present edition have been exposed afresh which has been made possible by the most valuable and selfless assistance rendered by my colleagues, Drs Shailja, Tanvi and Ujjawal, Senior Residents in Pathology, all of whom worked tirelessly for endless hours for months, much to the sacrifice of their personal comfort and time of their families, for which I am indebted to them. Here, I also recall the help accorded by my former students and colleagues in preparation of earlier editions of the book and thank once again, even though much of that may have been replaced. Constant strategic support and encouragement extended by the Department of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh Administration, during the completion of work is gratefully acknowledged.