Nizagara
Order nizagara pills in toronto
He devised a device for measuring the size of a red blood cell impotence herbal medicine purchase nizagara 100mg amex, with his measurements showing a size of 7. He also studied uid ow in pipes and bends, and the propagation of impulses in elastic vessels, and then applied this to analysis of blood ow in the arteries. He correctly deduced that peristaltic motion of the artery wall did not contribute to the circulation of blood, and instead that the motive power must come from the heart [31]. Of the two, Wolff is better known to biomedical engineers because 10 Introduction Figure 1. Both were German physicians who were interested in how mechanical forces could influence the structure and development of bone. Legend has it [32] that the structural engineer Karl Culmann saw a presentation by the anatomist Hermann von Meyer, in which von Meyer described the internal architecture of the bone in the head of the femur. Culmann was struck by the similarity between the pattern of solid elements in the cancellous (spongy) bone of the femur and the stress trajectories5 in a similarly shaped crane that he was designing. He then went on to formulate his law of bone 5 A stress trajectory is an imaginary line drawn on a surface that is everywhere tangent to the principal stress directions on the surface. Stress trajectories help to visualize how the stress is carried by an object, and they can be used as the basis of a graphical procedure for determining stress distributions in bodies. This graphical solution method is now obsolete, having been replaced by computational methods. The smaller drawings provide details of the mechanics of the crane and the stress distributions in various structures. This picture originally appeared in the article by von Meyer [33], as reproduced in [32]. Wolff went on to claim a rigorous similarity between cancellous bone architecture and stress trajectories. Cowin has shown that this is based on a false comparison of apples and oranges. Roux was very interested in developmen tal biology and physiology, carrying out his doctoral work on the factors governing the bifurcation of blood vessels [36]. He was convinced that mechanical and phys ical principles played important roles in development. In 1894, he also founded a journal enti tled Archiv fur Entwicklungsmechanik(Archives of Developmental Mechanics) and served as its editor for many years, stirring up his fair share of controversy along the way [38]. In the years since Wolff and Roux, there have been many advances in biome chanics. This is not the place to try to provide a complete history of biomechanics, and we will not list all of the outstanding investigators who have worked (or are working) in this fast-growing eld. An important event in the maturation of the eld of biomechanics was the publication, in 1981, of the book Biomechanics: Mechanical Properties of Living Tissues, by Yuan-Cheng Fung. Fung was born in 1919 and was trained as an aeronautical engineer, a eld in which he made many techni cal contributions in the early years of his career. However, in the late 1950s, he became interested in biomechanics and consequently changed his research focus away from aeronautics. In addition to his 1981 book, Fung has also written sev eral other books in biomechanics [40,41]. Membership in all three of these learned societies is surely a testament to the abilities of Dr. Fung, but it is also a re ection of the highly interdisciplinary nature of biomechanics, which (when done properly) should tightly integrate engineering, medicine, and biology. We will follow this approach in this book because we believe that this is the best way for the student to be introduced to a topic. The basic unit of life is the cell, and an understanding of cellular behavior is a cornerstone of modern bioengineering. In Chapter 2, we describe the basic components of the cell, with special emphasis on molecules that play a role in the biomechanical behavior of the cell. We then attempt to synthesize our understanding of these molecular components to answer basic questions about 13 1. Fung, who has played an important role in the establishment of biomechanics as a modern, rigorous discipline, primarily through the publication of an influential series of books on biomechanics. How does the cell respond to external forces, and what implications does this have for tissue organization At a higher level, physiologists subdivide the body into organs, which are tissues specialized for a speci c purpose, and systems, which are collections of organs working in concert. There are many such systems; here is a partial list and description of their functions, with emphasis on the biomechanical aspects. This system delivers nutrients and picks up waste products from the cells, as well as delivering signaling molecules, such as hormones, between different organs. Excess uid is passively collected from tissues and returned to the heart via a network of ducts and channels that make up the lymphatic system. We will not examine the lymphatic system in detail, although it is brie y touched upon in Ch. The nervous system consists of the nerves and brain and is responsible for signaling and control within the body. The sensory organs provide input to the nervous system; we will brie y consider ocular biomechanics in Ch. This is accomplished by exposing the blood to the air through a very thin membrane of enormous surface area. This membrane is convoluted and folded to form a large number of small sacs within the lung. The respiratory system consists of the lungs, plus structures that assist air passage in and out of the lungs. The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys are responsible for removing waste products from blood and for the production of urine, which is then stored in the bladder and excreted through the urethra. Unfortunately, consideration of the urinary system is beyond the scope of this book. Muscular action is required for locomotion (movement of the body), motion of individual body parts, and bulk transport of materials within the body. This framework of bones and soft connective tissues (cartilage, ligaments, and tendons) provides a rigid, supportive, and protective structure for the body. The bony skeleton also provides attachments for muscles, serves as a system of levers for movement and locomotion, and has important metabolic functions. Bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons will be discussed in greater detail in Ch. The digestive system comprises the gastrointestinal tract (mouth to anus) plus the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas. The digestive system is responsible for ingestion and breakdown of food, delivery of foodstuffs to the blood, and waste excretion. This system consists of specialized cells and molecules dis tributed throughout the body (in organs such as the spleen and as cells in the blood stream and interstitial uid). It is responsible for identi cation and destruction of 15 References foreign entities, including viruses and bacteria. The goal here is to integrate information at the genomic, protein, and higher levels to understand how biological systems work as functional units. A wonderful example of a systems biology approach is the work of Davidson and coworkers [46], who are mapping the genetic regulatory network in the sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) embryo.
Generic nizagara 100 mg on line
Red blood cell and plasma manganese levels were increased only in rats exposed to the highest dose for the 10-day exposure period statistics for erectile dysfunction order generic nizagara pills. These data indicate that even at lower doses manganese can accumulate in the olfactory bulb and that the neuronal pathway to the brain is significant for inhaled manganese in rodents. Mainstream manganese entry into the brain from blood occurs through capillary endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier and through the cerebral spinal fluid via the choroid plexuses (Bock et al. A number of transport mechanisms (including facilitated diffusion, active transport, transferrin-mediated transport, divalent metal transporter-1 mediation, store-operated calcium channels) have been proposed to transport manganese across the blood barrier, but current understanding is inadequate to determine the predominant mechanism of transport (Aschner et al. A concern that inhaled manganese, compared with ingested manganese, may more readily result in manganese accumulation in the brain, a principal toxicity target of manganese, has led to recent detailed investigations of manganese concentrations in various brain regions and in other tissues following inhalation exposure of animals to environmentally relevant forms of manganese. The results from these animal studies indicate that tissue manganese concentrations in the brain depended on aerosol concentration, exposure duration, and brain region. Tissue manganese concentrations generally increased with increasing air concentrations and durations of exposure. Comparison of manganese concentrations across tissues shows the following order in exposed maternal rats: liver > pancreas > olfactory bulb > lung > striatum femur > milk > cerebellum >> whole blood (Table 3-9). In young Rhesus monkeys after 65 days of exposure, the order was: bile > olfactory epithelium > pituitary > liver > pancreas globus pallidus > olfactory bulb > kidney > putamen > caudate > cerebellum > heart >skeletal muscle > frontal cortex > lung > parietal bone femur >> blood (Table 3-10). Brain tissues from the monkeys were dissected into more regions than the rat brains and, immediately following 65 days of exposure to the highest exposure concentration, showed the following order of elevated manganese concentrations: pituitary>globus pallidus>olfactory bulb>putamen>caudate> cerebellum>frontal cortex>trigeminal nerve (see Table 3-10). These results are consistent with the evidence that the human striatum, globus pallidus, and substantia nigra are the primary neurotoxicity target for manganese (Aschner et al. Three to 5-fold increases (over air control values) in mean manganese tissue concentrations were found in the globus pallidus, putamen, and caudate 3 in monkeys exposed to 1. Comparison with the rat results in Table 3-9 suggests that rodents do not accumulate manganese in the basal ganglia. Recent corroborative findings showed that marmosets, a nonhuman primate, accumulated more manganese in the brain (especially in the basal ganglia and the visual cortex) than rats following intravenous injection of equivalent mg/kg body weight doses of manganese chloride (Bock et al. The mechanisms by which manganese accumulates in the basal ganglia of primates are poorly understood (Aschner et al. In pregnant rats repeatedly exposed to inhaled manganese, the placenta appears to partially limit the transport of manganese to the developing fetus (Dorman et al. In contrast, statistically significant elevations of manganese concentrations in sampled fetal tissues were observed only in the liver at 0. The results from this study suggest that the brain in developing fetuses and neonates is partially protected from excess manganese by the placenta, and that the neonatal period, compared with adulthood, is relatively more susceptible to increased manganese concentration in brain tissues with inhalation 3 exposure to manganese sulfate aerosol concentrations between 0. Bar graphs were digitized to obtain numerical estimates of means for male and female offspring combined. No age-related effects were observed on the order of manganese concentrations in the various tissue. These results are consistent with results from 14-day inhalation studies (Dorman et al. These studies show that manganese preferentially accumulates in the basal ganglia, especially the globus pallidus, and the substantia nigra. Rats given a single oral dose of 416 mg manganese/kg body weight (as manganese chloride tetrahydrate) exhibited little tissue accumulation of manganese 14 days later (Holbrook et al. Studies in animals indicate that prolonged oral exposure to manganese compounds results in increased manganese levels in all tissues, but that the magnitude of the increase diminishes over time (Kristensson et al. Table 3-12 provides illustrative data based on rats exposed to 214 mg manganese/kg(body weight)/day (as manganese tetroxide) for up to 224 days. As the data reveal, large increases in tissue levels of manganese compared with the controls occurred in all tissues over the first 24 days, but levels tended to decrease toward the control levels as exposure was continued. This pattern is thought to be due to a homeostatic mechanism that leads to decreased absorption and/or increased excretion of manganese when manganese intake levels are high (Abrams et al. Although the percentage of manganese absorbed decreased, the total amount of manganese absorbed increased when higher levels of manganese were fed. Manganese Levels in Rat Tissue After Oral Exposure a Tissue concentrations (percent of control) Tissue 24 Days 60 Days 224 Days Liver 810 137 138 Kidney 430 102 128 Brain 540 175 125 Testes 260 125 100 a Values presented are the ratio (expressed as a percentage) of tissue levels of manganese in animals receiving 3,550 ppm manganese in the diet (as manganese tetroxide) compared to animals receiving a normal diet (50 ppm). A study measuring the retention of a single oral dose of radiolabeled manganese in adult and neonatal rats indicated that retention of the label 6 days after exposure was much greater in pups (67%) than in adults (0. The distributional differences in rats exposed to either manganese chloride or manganese dioxide by gavage were investigated by Roels et al. Manganese concentrations were significantly elevated in the blood (approximately 83% increase over controls) and the cortex of the brain (approximately 39% increase over controls). Gavage administration of manganese dioxide, by contrast, did not significantly increase the amount of manganese in blood or any section of the brain. In addition, administration of manganese as manganese chloride by gavage caused roughly the same amount of increased manganese in the blood as intratracheal administration of manganese in the same form; it did not cause as significant an increase of manganese in the cortex (Roels et al. These data indicate that inhalation exposure to manganese in the form of manganese chloride or manganese dioxide causes accumulation of manganese in the brain more readily than oral exposure. Acute manganese exposure in drinking water was found to alter brain regional manganese levels in neonatal rats; after 5 days of exposure, the highest level was in the striatum (12. After 10 days, the highest concentrations were in the pons and medulla and the lowest were in the hypothalamus. No studies were located regarding tissue distribution of manganese in humans or animals after dermal exposure to organic manganese. A number of studies have been conducted that investigated various facets of the distribution of inorganic manganese in animal models. The studies utilized a number of routes of administration, and the results suggested that route may play an important role in distribution. In an intraperitoneal study performed in monkeys, manganese was reported in all tissues studied. The highest levels were found in the pancreas, liver, and kidney, and the lowest levels were found in the blood; levels in the central nervous system were found to decrease more slowly than those in other tissues (Dastur et al. Calves injected 54 intravenously with Mn were found to have 3-fold higher liver manganese concentrations and 13-fold higher pancreatic manganese concentrations than calves fed manganese (Carter et al. Identical dosing of rats with manganese dioxide resulted in significant increases in manganese levels in blood (79%), cerebellum (40%), striatum (124%), and cortex (67%) over those in controls. These data indicate that administration of manganese dioxide by this route resulted in greater accumulation of manganese in the brain than did manganese chloride. The distribution of manganese in the brain was investigated using Cebus (Newland and Weiss 1992; Newland et al. Magnetic resonance images indicated hyper-intensity of the globus pallidus and substantia nigra consistent with an accumulation of manganese in these areas (Newland and Weiss 1992; Newland et al. Substantial accumulation of manganese was also noted in the pituitary at low cumulative doses (Newland et al. Concentrations of manganese in these four tissues was still elevated (~1 mg/kg) at 96 hours post-dosing. The experiment was divided into an acute study (one dose) or a chronic study (ten doses). The brain manganese level in the mice administered 10 doses of 11 mg/kg each was 1. The manganese level in brain after manganese chloride exposure followed the same increasing trend over the 24 hour analysis period, but was higher at each time point, with a maximum value of >2. Clinical studies involving cancer patients or healthy volunteers have analyzed the usefulness of mangafodipir as a contrast agent for the identification of certain abdominal tumors. Although these studies do not necessarily quantify the amount of manganese, or mangafodipir, in particular tissues, they are useful tools in identifying the location of the metal; also relative proportions of manganese among two or more tissues that contain the metal can be observed by differences in signal from these imaging studies. Several studies have shown the qualitative presence of manganese in the liver due to increased signal in that organ following mangafodipir administration of 0. The renal cortex was the only other tissue to reach a 100% increase over baseline signal at 0. The signal from the renal cortex at the lower dose had a maximum of 80% over baseline, whereas the signal in the liver at this dose was ~75% of the baseline value (Wang et al.
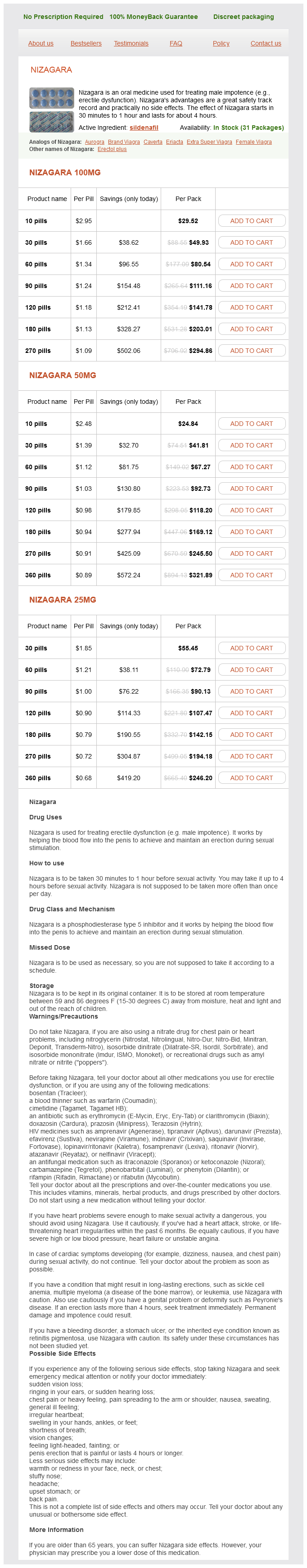
| Comparative prices of Nizagara | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | The Home Depot | 389 |
| 2 | Sherwin-Williams | 516 |
| 3 | McDonald's | 368 |
| 4 | Target | 931 |
| 5 | HSN | 591 |
| 6 | Gap | 189 |
| 7 | Abercrombie & Fitch | 176 |
Buy discount nizagara 50mg line
The child with chronic pulmonary aspiration typically has a history of recurrent pneumonia or pneumonitis that is variable in location erectile dysfunction blood pressure medications side effects order nizagara 25 mg. In between episodes of aspiration, clinical and radiographic resolution is expected. The child with a chronically retained foreign body in the tracheobronchial tree may present late with pneumonia, abscess formation, or bronchiectasis. The child with primary ciliary dyskinesia may have recurrent bronchitis and/or pneumonia, but would also have chronic cough, chronic purulent rhinitis, and recurrent ear and sinus infections. A child with severe immunodeficiency who has pneumonia would not be be asymptomatic or expected to have a lobar preference. In utero and/or in the setting of infection, the cysts may be filled with fluid and the radiographic appearance may be confused with sequestration. Pulmonary sequestrations may become infected repeatedly, which may be an indication for surgical removal. Removal of large lesions may be necessary because of compression of surrounding vital structures. She is a competitive soccer player, and last week, she and another player collided, their heads hit together, and the adolescent sustained a concussion. She reports that not being able to play soccer is making her depressed and irritable. You recommend graded return to academic and physical activity, and mandate complete recovery before returning to play. If she does not get a second concussion during recovery, it is most likely that she will have no detectable neurocognitive sequelae from this concussion. Personal characteristics such as apolipoprotein E4 genotype and history of learning disability or migraines (but not multiple sclerosis) may increase susceptibility for chronic deficits after a concussion. Heading the ball in soccer, however, has not been shown to increase the risk of deficits. This is a neurodegenerative disorder that progresses after the person has stopped sustaining concussions. Clinicians should keep themselves updated on the newest return-to-play guidelines. Summary of evidence-based guideline update: evaluation and management of concussion in sports. He is currently awake and alert, but is complaining of difficulty breathing and has severe pain on the lower anterior aspect of his right chest. In addition, he has paradoxical chest wall movement in which the affected segment moves inward during inspiration and outward during exhalation. This clinical condition is known as flail chest, and the mainstay of treatment is pain control with morphine sulfate. Evaluation and management of flail chest begins with a standard trauma assessment of airway, breathing, and circulation. If flail chest is determined to be the primary lesion, management depends on the severity of impairment of oxygenation and ventilation. Intubation and mechanical ventilation can allow the flail segment to move along with the rest of the unaffected rib cage, but it is not necessary because this child is maintaining adequate oxygenation and ventilation. Internal fixation of the anterior ribs is indicated for patients with more extensive flail chest who require thoracic surgery for other injuries, those who cannot be weaned from mechanical ventilation, and more severe chest wall instability. Lastly, a chest tube would be indicated if the patient had a concomitant hemothorax or pneumothorax. If oxygenation and ventilation are severely impaired, positive pressure ventilation (and in some cases, surgical fixation) may be indicated. He has no evidence by history or physical examination of an underlying growth disorder or systemic disease, and he is in early puberty, making permanent hypogonadism unlikely. If height is plotted for bone age, it falls within the target height range percentiles, as noted for the boy in this vignette. Any laboratory work done to screen for underlying systemic disease, such as complete blood cell count, serum chemistries, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, celiac screen, urinalysis, and thyroid function is normal. His body mass index is normal, making caloric deficiency and gastrointestinal or other systemic disease unlikely. Predicted adult height in this boy based on current height and bone age is 174 cm (68. Management of constitutional delay consists of reassurance regarding future pubertal development and height, in addition to clinical observation. Referral for gastrointestinal evaluation is not preferred due to lack of evidence of an underlying disorder. Although follow-up is indicated, 2 to 3 months will likely be too short of a time frame and providing reassurance is the better answer. There is a significant risk for overdosage and toxicity if young children ingest large quantities of vitamins acutely or have long-term overuse. Symptoms of acute vitamin D intoxication are the result of hypercalcemia, which may lead to emesis, anorexia, pancreatitis, hypertension, arrhythmias, nephrolithiasis, renal failure, and central nervous system effects. Long-term intake of excess vitamin E supplementation has been associated with an increased risk for sepsis in premature infants and increased risk for hemorrhage and mortality in others. You seek a study design that will best evaluate the risks and benefits of treatment. In this type of registry, the study population will be routinely contacted over time for updates on outcomes, causes of death, or other complications. A case control study is a retrospective study that uses subjects who are similar and divides them into groups based on the absence or presence of the outcome of interest. Cause and effect may be suggested in this type of study, but not definitively determined. This type of study is relatively weak because of the presence of many uncontrollable factors that could likewise affect outcome. A cross-sectional study is a good method to ascertain the efficacy of a diagnostic test. It compares the results of a new diagnostic or screening test with a known gold standard in the same population group. At the conclusion of the study, the frequency of the outcome(s) is calculated and compared across the groups. This type of study can have many confounders, is expensive to perform, and takes a long time to achieve results. You obtain a vaginal swab of the discharge, and examine a wet mount of the sample (Item Q98A, Item Q98B). Risk factors for T vaginalis infection include having multiple sexual partners, a greater number of lifetime sexual partners, and other sexually transmitted diseases. Symptoms of T vaginalis infection in girls include purulent vaginal discharge, vulvovaginal pruritus and irritation, abdominal pain, dysuria, and dyspareunia. Culture is considered the gold standard for diagnosis of trichomoniasis because its specificity approaches 100%, but this test is not widely available and its sensitivity can be as low as 75%. Alcohol should be avoided for an additional 24 hours after completion of metronidazole and 72 hours after completion of tinidazole. Due to compliance concerns, a single dose of metronidazole is recommended as opposed to twice daily dosing for seven days. Concurrent treatment for all sexual partners is recommended for microbiologic cure and prevention of transmission and reinfections. Her worries increased when the start of kindergarten coincided with her separation from his father.
Order 50 mg nizagara amex
Perseveration is a pragmatic problem at least well as the use of different psychological processes to in the sense that it results in a failure to adhere to access and use that knowledge diabetic erectile dysfunction pump generic nizagara 100 mg overnight delivery. There is also evidence that there is variability in Perseveration also interferes with normal linguistic the degree of impairment across different syntactic fea interaction [121]. In fact, pragmatic ability is more impaired the volume of the cerebellar vermis and temporal lobe on average than is the ability to master syntax. Broad-based measures ings re ect differences among groups of participants, of adaptive behavior that include an assessment of with the small sample sizes of most studies mak pragmatic skills. For example, animal studies have experimental or laboratory-based measures, have also shown that the cerebellum and hippocampus are espe uncovered substantial impairments. The volume of the cerebellar vermis ably pro cient at judging the emotionality of the faces has been found to be negatively correlated with sever correctly. The cerebellar vermis may also contribute to photographed faces than did the typically developing problems in attention, language, tactile defensiveness, controls. There is also evidence of individuals with idiopathic autism have problems in lower levels of psychological well-being. Whatever human faces, particularly those clearly depicting emo the source, however, lower levels of maternal well tions such as happiness and fear [173]. In fact, acterized by intention tremor and ataxia, problems in the premutation is associated with a complex pattern of memory and executive function, and increased anxiety alterations in several biochemical processes important and disinhibition [194, 195]. Individuals who the premutation, on average, have problems (relative have the full mutation have especially severe prob to typically developing age-matched peers) in several lems in the inhibitory and sustained aspects of atten cognitive domains, including executive function, atten tion, auditory memory, and sequential processing. They are social aspects of language and verbal perseveration also at elevated risk for various forms of psychopathol are also areas of special challenge. All of these the syndrome is characterized by considerable vari problems, however, occur less often and in a less ation in the phenotype, however, with more severe severe form, on average, in males with the premuta symptoms in males than females and in those with tion than in males with the full mutation. Recently, Mervis and colleagues organization, but the interdependence of language with reported scores obtained in response to administra patterns of strengths and weaknesses in other cognitive tion of the second edition of the Differential Abilities domains. Loss of the elastin gene is the demonstrating overfriendliness and a strong drive for single most important contributor to the cardiovascu social contact [218]. In this task, which is administered in Linguistic Dimensions of the Behavioral the context of a snack, the examiner uses nonverbal Phenotype affective cues to indicate a strong preference or dislike for a certain food. Given the contribution of facial affect and vocalizations than children in the verbal short-term memory to the development of lan comparison group [220]. Nevertheless, weaknesses in experimenter the liked food as the disliked food (39 language relative to other domains of functioning have vs. Nine of these 10 of children with hypersensitivity to sound also had children began to produce words several months before other speci c phobias. In addition, Mervis and colleagues have ory, to overcome challenges to language learning that identi ed decreased gray matter and sulcal depth in result from relative weaknesses in nonverbal cognitive the area of the inferior parietal cortex and have sug ability [199]. Thus, the skillful clinician, who the process of language acquisition than do typically is likely to have but a limited amount of time and developing language learners. Issues in the Neuropsychological It is apparent from the review of the behavioral phe Assessment of Individuals with notypes of the three syndromes on which we have Intellectual Disabilities of Genetic Origin focused that the differences between them are seldom adequately captured by the types of gross summary measures generated by many standardized tests avail the research on the behavioral phenotypes of Down, able today. In short, gross measures that subsequent trials despite the fact that the former was collapse a wide swath of psychological and behavioral successfully understood by the listener. Such incon functioning are likely to obscure the pro le of rela sistency increased the processing demands on the lis tive strengths and weaknesses that distinguishes one tener. In this task, the par coherence according to developmental theory, or their ticipant was the speaker and a researcher served as bases in brain mechanisms thought to be affected in the listener. The speaker and listener were teristics that fall outside of the construct of interest. If the individual often extended the same description to multiple shapes being tested is plagued by social anxiety, as is true. The latter descriptions are technically tion of this challenge than of the construct the test ambiguous and thus uninformative to the listener. Moreover, the variable pro les that con across these language sampling contexts, such that stitute the behavioral phenotypes of the syndromes some types of perseverative language are more com described in this chapter complicate test interpreta mon in conversation and other types are more common tion even further because different extraneous fac in narration [252]. Consequently, differences in ability tors will be important for individuals with different among diagnostic groups are more likely to be detected syndromes. Moreover, the extent to which they Virtually all of the measures available for assessing the successfully signaled noncomprehension was signi psychological and behavioral functioning of individu cantly correlated with their scores on a measure of als with intellectual disabilities, whether standardized receptive vocabulary and a measure of theory of mind tests or laboratory-based experimental measures, are. The implication cating in large measure how much of the typical for clinical practice is that the assessment of individu developmental path has been traversed to that point. However, it is precisely A different approach to dealing with the multifac the processes underlying learning and problem solv torial nature of any measure of a psychological or ing about which we want to know, because it is these behavioral construct is to employ multiple measures of processes we hope to change through intervention. In the construct of interest, each with somewhat differ targeting vocabulary, for example, it would be betterent performance demands. The value of this approach to improve the way in which an individual approaches is demonstrated by several studies in which expres learning when he or she encounters a new word rather sive language samples have been obtained from the than simply teaching a predetermined (and limited) same participants in conversation and narration or sto set of new words within the context of an interven rytelling. Careful analysis of the pro le of errors that a more complex syntactic forms from participants with client makes in response to items on a standardized intellectual disabilities as well as from young typically tests can occasionally provide some insights into the developing children, whereas conversational contexts more dynamic processes of interest; however, these tend to elicit more varied vocabulary forms [250, 251]. McDuffie compatible with multiple interpretations of underly It is important to note two additional limitations ing processes and thus, ultimately, of limited clinical of the measures available for assessing the function utility. First, ioral phenotypes associated with the genetic syn many of the standardized tests available to measure dromes of interest has largely ignored the dynamic cognition and language offer limited discrimination processes underlying learning and problem solving. A for individuals functioning in the range of intellectual notable exception is in the area of vocabulary learning disabilities. The premise underlying this normed in such as a way as to ensure that virtually paradigm is that young children encountering a novel any individual with intellectual disability will receive word do not wait to be explicitly taught or somehow the lowest standard score possible. This has led us to learn its full meaning; instead, they appear to cre use the psychometrically less desirable raw scores or ate at least a tentative mapping of the word and its age-equivalent, neither of which is satisfactory from intended referent. These initial mappings are not ran the perspective of a clinical assessment of an individ dom or idiosyncratic, but highly constrained by general ual client. Second, there are few tests that are normed principles and strategies that ensure a reasonable rst in such a way as to be applicable across a wide age approximation to the adult meanings of words. From a research perspective, this leads us to for example, demonstrated that when typically devel use different tests of (presumably) the same construct oping preschoolers heard the novel word chromium at different points in the life course, with all of the uttered along with a vague gesture toward two objects, associated interpretive problems. From a clinical per one an odd greenish color and the other a more stan spective, this is especially problematic if interest is dard color. Moreover, Families and the Neuropsychological the usefulness of this paradigm for understanding word Assessment of Individuals with learning in atypical populations has also been demon Intellectual Disabilities of Genetic Origin strated. Knowledge of these fast mapping pro gleaned only through the reports of parents because cesses could be the basis of interventions designed to they have the opportunity to observe their sons and encourage the use of more adaptive learning strategies; daughters on a daily basis and in a variety of contexts. Etiology-related differences among fathers and recommendations for further testing and intervention siblings have also been documented [257]. If parents are unreliable in the ability of family members to participate success in their input or fail to follow through on recommen fully in the assessment process. Unfortunately, and Abbeduto have argued for a systems approach to parents often may be grappling with many issues that assessment [257]. In Without such a systems approach, there is the risk that the case of individuals with developmental disabili the neuropsychological assessment may be based in ties, many parents report experiencing higher levels part on faulty data or, worse yet, never be implemented. References At the same time, there are etiology-related dif ferences among parents in terms of their experience 1. These moth population-based study on the causes of mild and severe ers report higher levels of parenting stress and lower mental retardation.
Generic nizagara 25 mg with mastercard
While there are many approaches to temper tantrums erectile dysfunction homeopathic treatment cheap nizagara 25mg, letting the child ride out the tantrum in a safe place away from others acknowledges his developmentally appropriate frustration, while minimizing exposure of unsettling noise and activity to other patients, parents, and staff. Letting a child continue the tantrum while gently acknowledging his disappointment and distracting the child with songs, funny, familiar stories, or conversation builds emotional health and resilience. Moreover, a time-out would fail to acknowledge that a tantrum is a developmentally appropriate response to having to stop an enjoyable activity before the child was ready. Rescheduling the vaccine is not clinically indicated and would delay protection from influenza and may be inconvenient for the family. While the child will likely get upset after receiving the vaccine, giving the vaccine will be easier for the child and staff if done when the child is calm. The laboratory findings and chest radiograph also point towards a viral respiratory infection. Also, pertussis presents with marked lymphocytosis that may be seen on the complete blood cell count and a history of the infant being unvaccinated or undervaccinated. The chest radiograph could be that of a patient with Mycoplasma pneumonia, as could the wheezing and otitis media, but Mycoplasma infections are very uncommon in children younger than 5 years of age. He is afebrile with a heart rate of 123 beats/min, blood pressure of 117/80 mm Hg (crying), respiratory rate of 37 breaths/min, and oxygen saturation of 97% on room air. Identification and urgent correction of the cause of urinary obstruction is important to decrease renal injury and the risk of chronic kidney disease. In the presence of unilateral obstruction with 2 previously normal kidneys, the compensatory increase in glomerular filtration in the contralateral kidney prevents the development of electrolyte abnormalities associated with acute renal failure. Bladder obstruction in children is most often observed in patients with abdominal soft tissue sarcomas or posterior urethral valves. Ultrasonography is safe, noninvasive, and the preferred initial imaging method for patients with acute renal failure. Hydronephrosis, unilateral or bilateral, is also seen in patients with vesicoureteral reflux; however, such patients usually present with urinary tract infections. Hypertonic 3% saline is indicated for the management of hyponatremia in patients with a serum sodium concentration less than 120 mEq/L (120 mmol/L) or patients with associated neurologic manifestations such as headaches, seizures, behavioral changes, obtundation, coma, and respiratory arrest. Intravenous furosemide is indicated for treating volume overload and hyperkalemia in patients with acute renal failure. Renal replacement therapy (eg, intermittent hemodialysis, continuous hemofiltration, and peritoneal dialysis) is considered for patients with renal failure and complications of volume overload, hyperkalemia, uremia (blood urea nitrogen > 100 mg/dL [> 35. Falsely-elevated serum potassium in such cases is not clinically significant, although a repeated serum chemistry from a nonhemolyzed venous sample would not be the best next step in management for the boy in the vignette. Initial evaluation should ensure there is no constriction of blood vessels or nerves in the affected limb. For isolated defects without constriction of blood vessels or nerves, infants should be referred to a plastic surgeon for repair and to maximize limb function. Amniotic band syndrome is not due to a germ cell mutation which would involve inheritable genetic defects. For example, infants with thanatophoric dysplasia have dramatic shortening of long bones. She notes that he has recently started to speak in 2-word phrases and that he uses approximately 200 spontaneous words. He seems to understand everything that his family members say to him and will follow a 2-step command. Head and Neck Surgery, American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Otitis Media With Effusion. The girl states that within 3 to 5 minutes of maximal exertion, she feels a shortness of breath with a choking sensation. Paradoxical vocal fold dysfunction and vocal cord dysfunction are terms often used interchangeably, but the term vocal cord dysfunction is less specific because it includes other vocal cord abnormalities. Paradoxical vocal fold dysfunction may be present with exertional or nonexertional dyspnea in isolation. Paradoxical vocal fold dysfunction is defined by adduction of the vocal cords during inspiration, or during inspiration and expiration, with preservation of a posterior region of glottic opening known as a posterior glottic chink. However, 50% of affected patients have identifiable and nonpsychiatric comorbidities, which may trigger vocal cord dysfunction and make it more difficult to treat. Tobacco abuse, laryngopharyngeal reflux, sleep apnea, allergic rhinitis, and rhinosinusitis are all recognized comorbidities, and their presence should be considered and treated. This treatment, demonstrated to be effective in 95% of patients, focuses on diaphragmatic breathing and laryngeal relaxation techniques. Although dyspnea is the most common presenting symptom of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children, occurring in as many as 90% of symptomatic patients, the absence of a cardiac murmur, syncope, palpitations or angina-type chest pain makes this diagnosis unlikely. In this patient, the lack of a weakened voice or chronic stridor makes a paralyzed vocal cord unlikely. Bilateral vocal cord paralysis is associated with harsh stridor that is persistent and is associated with significant respiratory distress; in these cases, a tracheostomy will be required to maintain airway patency. Multidisciplinary collaboration involving otolaryngology, pulmonary, speech and language pathology, and general medicine is advocated. He has had occasional seizures since he was 1 year of age, and takes levetiracetam. His neurological examination shows decreased spontaneous movement of his left arm and left leg, with normal tone. Cervical spine injury can cause hemiparesis, but there is no history of injury in this case. Nerve and muscle disorders are very unlikely to cause hemiparesis, so electromyography and nerve conduction study are not the best tests. Once embolic ischemic stroke is confirmed, there should be prompt investigation for a source. Chronic hemiparesis in a former premature infant may be due to periventricular leukomalacia or neonatal stroke. Clinicians should know that acute spinal cord lesions do not always present with hyperreflexia, especially in the acute phase. Electromyography/nerve conductions study is also often normal early in the course of Guillain Barre syndrome and other acute neuromuscular disorders. Management of stroke in infants and children: a scientific statement from a Special Writing Group of the American Heart Association Stroke Council and the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. This results in dizziness, air hunger, and syncope with positional changes and exertion. Lymphoid malignancies causing anterior mediastinal masses include non-Hodgkin lymphoma, acute lymphocytic leukemia, and Hodgkin disease. A characteristic widened mediastinum is suggestive of an anterior mediastinal mass (Item C11). However, the child in this vignette does not have signs of increased lower body venous pressure such as hepatosplenomegaly or lower extremity swelling, nor is there any sign of pulmonary edema. Superior vena cava syndrome can cause facial and upper extremity swelling, jugular venous distention, and inability to increase cardiac output on demand. In previously healthy children, these symptoms should raise suspicion for a malignant anterior mediastinal mass, which can be associated with life-threatening airway obstruction. Extreme caution should be exercised before providing anesthesia, sedation, or positive-pressure ventilation. Her mother has type 2 diabetes diagnosed at 35 years of age, and she is worried that her daughter has diabetes. Transition to oral metformin may be possible after achievement of initial blood sugar control, but would not be appropriate as the primary initial therapy in this case. As there is no evidence of hemodynamic instability, a bolus of intravenous fluids is not indicated.
Syndromes
- Loss of urine without meaning to urinate
- Abdominal growth
- Reassure the person. Try to keep him or her calm.
- Start CPR, if necessary.
- Loss of sensation
- Vardenafil (Levitra)
- Prolonged prothrombin time
- Through sexual contact -- including oral, vaginal, and anal sex
Buy nizagara with paypal
Summarize how the fossil record for ancestors and relatives of the horse supports the relationship between evolution and changing environments erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation purchase 100mg nizagara with mastercard. Compare and contrast homologous and analogous structures as evidence for evolution. Use an example to show how vestigial structures support evolution by natural selection. List the molecular similarities found in all species of organisms, which support common ancestry. Relate the distribution of plants and animals to changes in geography and climate, using at least one speci c example. Use a speci c example to illustrate the explanation given by both Darwin and Wallace for the distribution of few, closely related species across island chains. A large number of similarities between two species may be an indication that the two species A. Whales have a pelvis and the beginning of a thigh bone indicating that they once had hindlimbs. Relative dating is a method used by paleontologists to analyze fossils by looking at A. In mammals, the gill slits found during early embryonic development later function in A. Geologists are scientists who study the preserved remains and traces of animals, plants, and even microorganisms to reconstruct the history of life on Earth. Structures that evolved independently in two di erent species are referred to as homologous. A scienti c theory is an explanation that ties together or uni es a large group of observations. Cladograms are tree-like diagrams that show representations of the evolu tionary relationships among organisms. The study of the distribution of plants and animals and the processes that in uence their distribution is called Biogeography. The study of the similarities and di erences in organismsstructures is called. The process where a single ancestor rapidly evolves into a large number of di erent species is known as. The supercontinent that existed when all of the continents were united is called. A is an explanation which ties together or uni es a large group of observations. A is a proposed, testable answer to a question or explanation of an observation. The mineralized remains of an animal, plant, or other organism is called a(an). Key Concepts Humans continue to try and control and manipulate nature using arti cial selection and methods of genetic engineering. Be sure to correct any misconceptions students already have about these epi demics before discussing their relevance to this lesson. Activity Have the students complete one of the rst three tutorials (Relevance of Evolution: Agricul ture, Conservation, or Medicine) found at this website: evolution. Di erentiated Instruction: Word Wall Post lesson vocabulary words and their de nitions, examples, etc. The pamphlet could include a de nition of antibiotic resistance, reasons why people should be aware of the problem, and actions the average person can take. Science Inquiry Analyzing Data Show students the graph at the following website. Ask students to write a paragraph explaining what is occurring in the graph and also ask students to provide a hypothesis as to why it is occurring. Lesson Worksheets Copy and distribute the four lesson worksheets in the Supplemental Workbook. Interbreeding two separate species such as dogs and wolves is referred to as what Only take antibiotics for bacterial infection, not for infections such as the u which is caused by a virus. Never take antibiotics which are left over from an earlier illness or prescribed for someone else. Consider purchasing meats and other animal products from animals not treated with antibiotics. The nches with smaller beaks who were able to eat the smaller, softer seeds that remained. The nches with larger beaks who were able to crack the tough seeds that remained. The experiments were the rst to show natural selection and evolution at work in an observable period of time. What is the nickname given to bacteria, viruses, parasites, and other organisms that have developed a strong resistance to human medicines What type of animal genes have been inserted into Zebra Fish to make the sh glow in the dark The event where hybrids interbreed with natural varieties is called. Epidemics that become wide-spread and impact large numbers of people world-wide are referred to as. Dolly the sheep was produced using the genetic engineering method of. Michael Pollan believes that humans have with domesticated crops, animals, and pets. Viral epidemics occur when chance viral adapt the virus to new hosts. Bacteria were genetically engineered to produce for the use in treatment of diabetes. A pest population that no longer is killed by a certain type of pesticide is consid ered to that pesticide. Explain why an individual bacterium cannot on its own change from sensitive to resistant to antibiotics. At rst, most of the pests die, but over time the gardener begins to notice the pest population returns to the same number of pests as there were before the pesticide was used. A change in allele frequency (evolution) can be caused by gene ow, genetic drift, mutation, or natural selection. If a population is not experiencing any changes in allele frequencies, it is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. There are two models, gradualism and punctuated equilibrium, that attempt to explain the rate at which evolution occurs. Evolution is Still Being Debated Students sometimes view the debate over the rate of evolution (gradualism vs. Stress to students that evolutionary theory has an incredible amount of evidence supporting it (see the Evolutionary Theory chapter), and that arguments over the rate at which it occurs do not weaken the overall theory of evolution. Making the FlexBook Flexible An important advantage of the FlexBook is the ability it gives you, the teacher, to choose the chapters and lessons that you think are most important for your own classes.
Purchase nizagara canada
As is emphasized throughout this book circumcision causes erectile dysfunction nizagara 25mg on line, you should do scans and blood tests as you go through the 21 Day Program. Only the vitamin sources listed here were found to be pollution-free, and only the herb sources listed here were found to be potent, al though there may be other good sources that have not been tested. Other than that, she has no financial interest in, influence on, or other connection with any company listed. In my experience, an uninformed manufacturer most likely has a pol luted product! This chapter will be updated as I be come aware of acceptable sources outside the United States. Cascara sagrada Natures Way, health food store Chemical Supply Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. Citric acid Now Foods or health food store Cloves San Francisco Herb & Natural Food Co. Dental help in Europe Naturheilverein Digestive enzyme Self Health Resource Center mixture Electromagnetic field Alphalab, Inc. Germanium, organic Herbs such as garlic, hydrangea, or aloe Ginger capsules Self Health Resource Center. Hydrogen peroxide 35% New Horizons Trust (food grade) Iodine, pure Spectrum Chemical Co. Non-alcoholic Green See Green Black Walnut Hull freeze Black Walnut Hull dried capsules capsules Olive leaves for tea San Francisco Herb & Natural Food Co. Peppermint oil Star West Botanicals Peroxy See Hydrogen peroxide Plastic coated water See epoxy coating pipes Potassium chloride Now Foods Potassium gluconate Spectrum Chemical Co. Thyroid, dessicated Your doctor Tooth Truth New Century Press Uva Ursi Natures Way or health food store Vitamin B1 Spectrum Chemical Co. Vitamin C (ascorbic Hoffman-LaRoche (all other sources I acid) tested had either toxic selenium, yttrium, or thulium pollution! Wormwood capsules Self Health Resource Center, Kroeger Herb Products, New Action Products Yunnan paiyao China Healthways Institute Abbott Laboratories Aqua Tech Environmental 100 Abbott Park Road Laboratories, Inc. Koch, 157 151, 152, 158, 185, 186, 189, 190, wintergreen oil, 138, 161, 184, 192, 191, 193, 194, 199, 237, 338, 370, 193, 195, 199, 200, 201, 540, 572, 380, 398, 418, 431, 593 573 vitamin B12, 14, 110, 137, 151, 152, wormwood, 49, 50, 65, 180, 181, 184, 185, 186, 189, 190, 191, 193, 194, 186, 189, 190, 191, 193, 194, 198, 199, 237, 338, 370, 380, 398, 418, 199, 200, 270, 291, 299, 440, 471, 431, 593 474, 479, 481, 491, 492, 593 vitamin B2, 158, 198, 200, 514, 593 vitamin B6, 137, 158, 190, 191, 193, 194, 199, 226, 560, 561, 593 X vitamin C, 1, 18, 156, 157, 173, 185, 198, 200, 239, 418, 593 xanthine, 142, 145, 223, 224, 431, vitamin D, 148, 171, 198, 418, 541, 445, 483, 492, 583 593 xanthine oxidase, 142, 145, 223, 224, vitamin E, 53, 66, 160, 188, 189, 190, 431, 445 191, 193, 194, 199, 200, 216, 350, 593 Y vitamin K, 175 yeast, 100 ytterbium, 22, 169, 508 W yttrium, 22, 508, 593 warts, 27, 188 Yunnan paiyao, 139, 140, 176, 324, water accumulation, 112, 339, 372, 334, 371, 422, 443, 593 459 water pick, 84, 86, 87, 88, 203, 497, Z 498 water pipe, plastic, 132 zapping, 51 weight gain, 132, 204, 343 zearalenone, 30, 124, 125, 129, 194, white blood cells, 14, 16, 21, 31, 33, 196, 359, 475, 502, 503, 507, 522, 51, 60, 62, 63, 91, 122, 166, 167, 533 168, 169, 171, 181, 185, 197, 198, zinc, 78, 89, 90, 103, 168, 194, 195, 208, 211, 212, 238, 285, 315, 495, 199, 270, 274, 308, 315, 330, 365, 505, 506, 507, 508, 509, 570, 579, 447, 455, 498 585, 587 zinc oxide, 78, 89, 447, 455 white iodine, 81, 82, 315, 381, 404, zinc phosphate, 89, 90 454, 456, 464, 540 610 Cancer Can Now Be Cured, not only the early stages, but also advanced cancer, stages four and five, including imminent death. The Cause of the Malignancy is explained in the earlier book, the Cure For All Cancers. But removing the malignancy left behind the tumors as they were, prior to the malignant develop ment. So, eliminating tumors became the focus of additional research, and is the subject to this book. It is a total approach that not only shrinks tumors, but also normalizes your blood chemistry, lowers your cancer markers, and returns your health. The small failure rate (5%) is due to clinical emergencies that beset the advanced cancer sufferer. However, if you combine the advice in this book with access to hospital care, even hopeless patients can gain the time necessary to become well again. Clark has a Bachelor of Arts, Magna Cum Laude, and the Master of Arts with High Honors from the University of Saskatchewan, Canada. Then she studied for two years at McGill University before attending the University of Minnesota and obtaining her Doctorate degree in physi ology in 1958. After doing government sponsored re search for almost ten years at Indiana University, she began private consulting in nutrition in 1979. She con tinued her studies to earn a Naturopathy Degree and an amateur radio license. The freedom to follow her most promising observations led to the breakthrough discov eries described in this book. Sterilize everything 185 31 with shark cartilage, two with shark cartilage, two 188 last See instructions, page 558. She 448 4 11/ 13 11/ 18 11/ 25 11/13 11/18 11/25 468 31-33 this showed that. An Electronic Silent Spring describes how wildlife and peopleshealth are affected. Signals emitted by metal detectors, smart utility meters, hybrid cars, and other common electronics can shut off a medical implant. The American Academy of Pediatrics warns pregnant women and children not to use cell phones. Federal regulations protect the engineering needs of electronic devices and telecom companies. Federal law prohibits local offcials from refusing installation of a cell tower based on health or environmental concerns. Best advise companies not to insure against damages to health caused by wireless devices. An Electronic Silent Spring Facing the Dangers and Creating Safe Limits Katie Singer Portal Books 2014 2014 Portal Books Distributed by SteinerBooks 610 Main St. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or trans mitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photo copying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher. Cover image and design by Kendra Arnold Author photo by Jeremy Green Publication of this work was made possible in part by grants from the F&S Fund, Santa Fe Community Foundation; New Hampshire Charitable Foundation; and the Bloom-Frankel Family Fund, a donor advised fund of Combined Jewish Philanthropies of Greater Boston, Inc. The author and publisher are not engaged in providing electrical or medical advice or services. The author and publisher provide this information and the reader accepts it with the understanding that everything done or tried as a result of reading this book is at his or her own risk. The author and publisher shall have neither liability nor responsibility to any person or entity with respect to any loss, damage, or injury caused or alleged to be caused directly or indirectly by the information contained in this book. Throughout this book, I refer to digital, wireless, transmitting utility meters as smart meters. When reprinting letters by others who have written about these meters, I have kept the spelling true to their original letters. Gary Olhoeft: Revising Electrical Code 56 Part Two: Radio-frequency Fields 57 How Charge Moves 57 the Electromagnetic Frequency Spectrum 58 the Ionizing and Non-ionizing Spectrum 58 the Frequencies of Some Electronic Devices 60 Transmitting the Voice and Pictures on Phones 61 Analog and Digital Signals 62 Pulse and Modulation: Signals Not Found in Nature 63 the Function of an Antenna in Wireless Communications 64 Smart Meters: Transmitting, Digital Utility Meters 64 Cindy Sage and James Biergiel: Harmonics 66 Broadband Over Powerlines 66 Fiber Optics 67 Our New Electromagnetic Environment 67 6. Gary Olhoeft: Living with a Medical Implant 111 Medical Equipment 112 Katharine J. Lee: Living with a Power Chair 113 Emma Gunn: Wireless Devices in Hospitals 113 Fertility 115 Dr. Other Dangers from Wireless Devices 128 Energy and Natural Resources 128 Worker Safety and Violation of Radiation Limits 129 Fires Caused by Telecom Equipment and Smart Meters 130 Hacking and Privacy 130 the Loss of Libraries and History 131 Psychological Issues 132 Distracted Drivers and Walkers 132 Flight Safety 133 Worker Safety 134 Liability 135 Continuing Developments 135 8. Gary Olhoeft: Medical Implants 148 Sandra Chianfoni: Pure Tones on the Smart Grid 149 Josh Hart: stopsmartmeters. Educate Others and Take Political Action 200 Petition Congressional Representatives to Sponsor Legislation 203 Petition Your School Board and School Administrators 203 Report Problems 204 12. Yet our global economic, medi cal, educational, utility, military and other systems now depend on digital electronics. Electricity, electronics, and wireless devices have created profound benefts for humanity.

Order 100mg nizagara fast delivery
This increased response time is thought to result from inhibitory processes acting upon the distract References ing stimulus during the prime trial impotence legal definition purchase 25 mg nizagara with amex, to prevent further processing. On the true philosopher and the true phi cessing time as compared to younger adults. London: Swedenborg can infer that inhibitory de cits are not always present Society; 2005. Early studies on cerebral localization and the does not posit an environmental support mechanism. Regional That interaction, along with the changes in other cog brain changes in aging healthy adults: general trends, nitive domains and increases in cognitive variability individual differences and modi ers. Adult age differ broadly focus on the interaction between changes in ences in attention: ltering or selection We gerontologists cognition relations in adulthood: estimates of linear and now are beginning to understand the important rela nonlinear age effects and structural models. Memory changes normal aging and the resulting behavioral manifes in healthy older adults. An application of prefrontal cortex func vation of inferior prefrontal cortex during cognitive set tion theory to cognitive aging. Age and hemisphere effects on prefrontal cortex during the Wisconsin Card Sorting test dendritic structure. Age Neuroanatomical correlates of cognitive aging: evi related slowing of digit symbol substitution revisited: dence from structural magnetic resonance imaging. Age and the availability of infer factors in age-related differences in simple reasoning. The role of pre Human memory development and its dysfunction after frontal regions in the Stroop task. Dissociations in hip formance in focal lesion patients: dissociation of pro pocampal and frontal contributions to episodic memory cesses and frontal lobe lesion location. Age effects ory for auditory-spatial associations following unilat on executive ability. Double dissocia ited to the hippocampal region produces long-lasting tion between item and source memory. Effects of nitive impairment can be distinguished from Alzheimer age, gender and education on selected neuropsychological disease and normal aging for clinical trials. Individual differences in 16-year impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. The socio-cultural con and training modulate spatial memory in the Rhesus text in understanding older adults: contextual adult lifes Monkey (Macaca mulatta). A cognitive training program determinants of neuropsychological functioning in late based on principles of brain plasticity: results from the life depression. Impact association of age and depression among the elderly: of working memory training on memory performance in an epidemiologic exploration. Physical exercise at midlife and risk of cognitive performance in later life: relationships to self dementia three decades later: a population-based study reported health and activity life style. The memory bible: an innovative strategy for performance of very old men and women: contributions keeping your brain young. Age-related equivalence of iden Leisure activities and the risk of dementia in the elderly. Chapter 17 Neuropsychology of Movement Disorders and Motor Neuron Disease Alexander I. These disorders are grouped into upper and lower increases until the ninth decade [3]. The various loci have all been mapped normal accuracy (number of moves) but a slowness to chromosomes 1, 2, 4, 6, or 12. Set cell loss from the substantia nigra, and dopamine shifting ability, in particular, appears to be a critical depletion in the striatum is greater in the putamen determinant of whether patients demonstrate difficulty than the caudate. The neural basis of executive de cits is being elu cidated with functional neuroimaging. Impairments resulting from dopaminergic replacement therapy in are also observable on many tasks. Executive de cits have also been tive attention, and both limited attentional resources linked to cholinergic de cits observed on functional and attentional set shifting may underlie poor neuroimaging [39]. Early in 17 Movement Disorders 317 the disease, processing speed may be ameliorated by and recognition are compromised [65]. In contrast to semantic encoding, serial encoding appears to be preserved [66, Language 68], as are serial position effect [69]. A possible expla nation for these ndings is that serial encoding re ects Motor speech abnormalities. Lexical and semantic verbal uency is often imental memory tasks putatively sensitive to frontal intact in patients without dementia [45]. The most recent studies provide evidence de cits [51] or to a de cit in an underlying process of abnormal semantic priming [84] and the possibility such as switching but not semantic clustering. At the present time at antidepressant dosages within the highest recom there are no effective pharmacological or neurosurgical mended ranges [93]. Neuronal loss and [101], though one recent study reported current and atrophy of the frontal cortex, including both prefrontal lifetime prevalence rates above 40% [102]. An early onset of cognitive syndrome [106, 107], progressive supranuclear palsy de cits may be a harbinger of more rapid disease 17 Movement Disorders 319 progression and mortality [114]. Remote memory is largely unaf range of dysexecutive signs may be present, includ fected [28], but tests of recent episodic memory reveal ing de cits in planning, problem solving [119], and a mixed encoding/retrieval pro le whereby free recall cognitive exibility [120]. De cits in problem solv is impaired, but recognition discrimination is generally ing and cognitive exibility may be more vulnerable within normal limits [131]. Other Motor Skills and Information Processing Speed neuro-opthalmological abnormalities may include ble pharospasm and reduced blinking frequency, all of Bradykinesia and bradyphrenia are among the most which may interfere with higher level spatial cogni prevalent and severe neurocognitive de cits associ tion. Impairment is observed on simple tests of with greater severity of oculomotor de cits [132]. Although apathy is some heterogeneity in the neuropathophysiology of the dis times misdiagnosed as depression, the latter does not order [139]. Whether these alterations translate also exhibit elevated behavioral signs of disinhibition into neurodegenerative changes that are viewable with [135]. The tremor is typically bilateral (although often asym metrical), slowly progressive, and of long duration Prevalence estimates of cognitive impairment rates. As noted above, some patients may present with a vocal tremor or dysarthria, with the latter being Several studies have shown mild impairment on mea more common in patients who have undergone thala sures of complex auditory attention and working mem mic deep brain stimulation [157]. Formal neuropsy tion are also evident, including on measures of letter chological evaluation will commonly reveal impair cancellation [153] and continuous performance tasks ment in verbal uency, including both letter [154] and [153]. Qualitative analysis may show Trailmaking Test, Part B), prepotent response inhi an increased rate of perseverative responses on letter bition. Findings regarding higher level executive information processing, a degradation of semantic functions, such as abstraction, verbal and nonverbal stores, and/or inefficient a lexicosemantic switch concept formation, and planning, are mixed across the ing/retrieval is not yet known. When present, de cits in attention and executive functions may be Consistent with other movement disorders. Impairment De cits in facial recognition [159] and judgment of is observed on measures of psychomotor processing line orientation [155] may be evident. De cits are also cognition are not commonly associated with cerebellar apparent on nonmotor measures of information pro dysfunction, there is more recent evidence to that effect cessing, including the Color trial of the Stroop Test [160, 161] and they are documented in other movement [152, 155]. Woods Neuropsychiatric Factors but multiple aspects of the basal ganglia and fron tostriatal loops are affected, including the putamen, Although research in this area is still sparse, it appears substantia nigra, and globus pallidus [133]. Diagnosis is typically made in mid-life (late thirties and early forties), but persons Both basic. With regard to the latter, de cits are appar been described, whereby some individuals evidenceent in a wide range of functions, including work subtle neural changes, cognitive impairment, and psy ing memory and the divided, sustained, and selective chiatric features prior to receiving a formal diagnosis.

Effective nizagara 100mg
In the biomedical area erectile dysfunction medications causes symptoms 25 mg nizagara sale, he established, with von Helmholtz, the theory of color, discovered and measured astigmatism in the 9 1. Poiseuille portrait reproduced with permission from [24] as modified by Sutera [25]; Young portrait by Sir Thomas Lawrence, engraved by G. By using a variety of techniques, including perturbing the function of regulatory genes and observing their effects on embryo development, they have produced maps of genetic regulatory networks that convey a taste of the complexity of life. Readers will note that there are no biomechanical stimuli listed in this diagram; these have yet to be elucidated. Long-term intermittent shear deformation improves the quality of cartilaginous tissue formed in vitro. Cardiovascular physiology in the twentieth century: great strides and missed opportunities. Recherches exp erimentales sur le mouvement des liquides dans les tubes de tr`es-petits diam`etres. We will begin by brie y reviewing some of the key components of a eukaryotic cell. These barriers are primarily made up of lipids in a bilayer arrangement, augmented by specialized proteins. They serve to enclose the cell, the nucleus, and individual organelles (with the exception of the cytoskeleton, which is distributed throughout the cell). The function of membranes is to create compartments whose internal materials can be segregated from their surroundings. The importance of the cell membrane is shown by the fact that cell death almost invariably ensues if the cell membrane is ruptured to allow extracellular materials into the cell. This organelle consists of long rod-shaped molecules attached to one another and to other organelles by connecting molecules. A living system must satisfy the following ve characteristics: r it must show complex organization (specialization) r it must be able to metabolize (assimilate food, transform it, and excrete it) r it must show responsiveness, including the ability to adapt to differing conditions r it must be able to reproduce r it must have evolutionary capability. These organelles produce most of the basic energy containing molecules from certain substrates such as glucose. Then these energy containing molecules are used by other subsystems within the cell. This very important task is handled by the Golgi apparatus, which takes the protein output of the endoplasmic reticulum and trims, modi es, and packages it in membrane-delimeted structures (the vesicles) that are sent to var ious locations within or outside the cell. Misfolded and otherwise defective pro teins must be disposed of immediately since they are potentially harmful to the cell. This system of vesicles contains enzymes (catalytic proteins) which act to break down metabolic by-products, misfolded proteins, ingested extracellular material, and other unwanted substances. It is also a miracle of miniaturization: all of the above systems t into a neat package having a typical mass of 2 10 8 g, and a typical diameter of order 15 m! Now that we have a basic overview of the components of a eukaryotic cell, let us look in more detail at cellular biomechanics and mechanobiology. Then we will delve into more detail about the cytoskeleton of the cell, focussing on its mechanical properties and how it helps to anchor the cell to its surroundings (Sections 2. The main focus here will be to give the reader enough biological background to understand Sections 2. This diagram is highly schematized but serves to indicate the major features of the cellular organelles. When engineers talk about the mechanics of conventional engineering materials, they can refer to handbooks that tabulate the properties of, for example, different types of stainless steel, and describe the internal structure of these steels. Not quite, but a body of data is slowly being accumulated about the mechanical properties of cells. A prominent nucleus delimited by the nuclear envelope (membrane) is present, as are several organelles in the cytoplasm: mitochondria, Golgi complex, and endoplasmic reticulum with associated ribosomes. One of the remarkable things about most cells is how good they are at sens ing relatively small levels of mechanical stimulation, while living in a constantly changing biomechanical environment. Many details of this process, known as mechanotransduction, are unknown, but in Section 2. Using these devices, the effects of mechanical stimulation on several cell types have been determined. At the cellular level, energy-consuming tasks include: r motion, including both cellular shape changes and locomotion of the cell on its substrate r synthesis of compounds r transport of ions and other molecules, both within the cell and between the cell and its surroundings How does the cell utilize food energy When we eat a meal, the constituent food stuffs are acted upon by the digestive enzymes and broken down into simpler compounds, transferred into the bloodstream across the intestinal walls, and then transported throughout the body. Individual cells are therefore presented with a complex mixture of compounds from which they must obtain energy. The cell solves this problem by having spe cialized energy plants (mitochondria), which are able to use compounds such as glucose and fatty acids to produce a common energy-containing molecule that all cellular organelles can use. Students are encouraged to consult the references if they wish to learn more about the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton is an elaborate network of brous proteins that can adopt a remarkable range of con gurations. Cells were extracted with a detergent solution, fixed in glutaraldehyde, post-fixed, and gold sputter coated before visualization. G-actin has a molecular weight of approximately 43 kDa, and consists of a single polypeptide chain. F-actin chains are dynamic structures that grow and break down according to their position within the cell and the activities of the cell at any given instant. Thus, individ ual actin monomers move along laments, tending to be added at the + end and 26 Cellular biomechanics Figure 2. Tight actin filaments are evident in the microvilli, the finger-like structures in the top half of the image. The actin extends from microvilli into the cytoplasm of the cell, where it connects with a network of actin, intermediate filaments, myosin, and other cytoskeletal proteins. The polymerization and breakdown of F-actin are regulated by several proteins, including actin depolymerizing factor/co lin, members of the gelsolin/villin pro tein family, and CapZ. Con uent cells tend to be relatively quiescent, exhibiting only modest amounts of cellular movement. In all cells, it is present in a thin layer adjacent to the cell membrane, in the so-called cortical actin layer.

Purchase cheap nizagara line
Creation of C-C/C=C/C-H bonds (for the purpose of building a structural framework) 2 impotence hernia nizagara 25mg free shipping. Creation of functional groups (to give functionality to the framework) Appendix 3. Detailed discussion and mechanisms for these reactions are not provided, but are available in many textbooks of basic or advanced organic chemistry. The synthesis of a complicated drug molecule from simple starting materials must be approached in a rigorous and sys tematic fashion. This approach is based upon the notion that it is easier to work backwards from the target molecule. In retrosynthetic analysis, a procedure known as disconnection is used to dissect a molecule into progressively smaller and smaller frag ments until readily available starting materials are obtained. Typically, a bond is broken and the electron pair is assigned to one of the fragments, resulting in a positively charged synthon and a negatively charged synthon. The next task is to find readily available starting materials that can actually be used as sources of these synthons. These available materials that are equivalent to a syn thon are referred to as synthetic equivalents, and are generally commercially available compounds that represent the nucleophile and the electrophile that must react. Cyclohexanol may be disconnected to a hydride ion and a hydroxycarbocation (the syn thons). Sodium borohydride and cyclohexanone are the synthetic equivalents of these two synthons. It is apparent that this system of disconnections can be applied to molecules of sig nificant complexity to deduce a synthetic route. At the research level, it is acceptable for a synthetic scheme to employ unusual catalysts or large amounts of organic solvents. If a drug costs $85 per milligram to synthesize and will be administered at 60 mg/day for many months, then it will not be a commercially viable drug. If a drug is to be successful it will have to be produced in large quantities in an industrial setting, necessitating the implementation of syntheses that are scalable, effi cient, and environmentally friendly. A synthetic scheme with fewer steps and employing water as a preferred solvent has distinct advantages over a technically complicated, low yield synthesis that uses large quantities of organic solvents that are difficult to dispose of. Thus, there are some differences between a classical synthetic organic chemist and a synthetic medicinal chemist. The classical synthetic organic chemist is proud of a com plex multistep synthesis which may, regrettably, have a low yield. The synthetic medi cinal chemist is pleased to design a molecule that can be synthesized in as few steps as possible, hopefully with a high yield and few by-products. A number of very important characteristics go into making a biological assay useful. Ideally, the assay should be rapid, cost-effective, efficient, and easy to implement. The alcohol functionality then undergoes a functional group interchange by conversion to a bromide. This is particularly true if one is pursuing lead compound discovery by high throughput screening of millions of compounds. More importantly, the biological model should accurately reflect the human disease for which it is being used as a drug-screening tool. Just because an animal model pro duces a similar disease as is found in humans, there is no guarantee that it will truly reflect the corresponding human disease. For example, occluding the middle cerebral artery in a gerbil will produce a gerbil stroke. A drug that successfully treats strokes in gerbils may not nec essarily treat strokes in humans. Alternatively, there may be diseases that are unique to humans or primates, thereby making it difficult to develop meaningful biological assays in species such as rodents. Biological assays for compound evaluation may be broadly categorized as follows: 1. Consequently, in silico methods are acceptable for preliminary screens, but are completely unacceptable for the advanced assessment of a candidate compound. Radiolabeled competitive binding studies can be used to ascertain whether a drug binds to a receptor. A second equivalent of the p-chloroaniline leads to a six-membered ring with two nitrogens. This is hydrolytically opened to expose a free amino group which reacts with an aminoester to yield a seven-member ring. Functional in vitro assays with a measurable biological outcome are required to tell whether a compound is functioning as an agonist or an antagonist. Regrettably but understandably, this assay is the most labor-intensive and costly. In vivo assays give the highest quality information about the efficacy of a lead compound. Ideally, a candidate drug molecule should not be advanced in the development process unless it demonstrates good to excellent efficacy in an appropriate in vivo model. Nevertheless, the optimization of a lead compound is a lengthy and expensive undertaking, fraught with a frighteningly high rate of failure. It means the application of previously recognized correlations of biological activity with physico chemical characteristics in the broadest sense, in the hope that the pharmacological suc cess of a not yet synthesized compound can be predicted. Although some practicing biologists and pharmacologists still regard efforts at drug design with some condescension and ill-concealed impatience, a slow but promising development gives renewed hope that progress in this area will not be less rapid than in the application of biology and physical chemistry to human and animal pathology. The explosive development of computer-aided drug design and bioinformatics (see chapter 1) promises to lead to the era of true rational drug design. The probabilities of finding a clinically useful drug were not good; it was estimated that anywhere from 3000 to 5000 compounds were synthesized in order to produce one optimized drug. The guiding principle was the paradigm that minor changes in a molecular structure lead to minor, quantitative alterations in its biological effects. Although this may be true in closely related series, it depends on the definition of minor changes. Extension of the side chain of diethazine by only one carbon atom led to the serendipitous discovery of chlorpromazine and the field of modern psychopharmacology. First, a merely structural change in an organic molecule is meaningless as long as its physicochemical consequences remain unexplored and the molecular basis of its action remains unknown. Structure, in the organic chemical sense, is only a repository, a carrier of numerous parameters of vital importance of drug activity, as is amply illustrated in the first chapter of this book. Although a beginning has been made, drug design is far from being either automatic or foolproof. Now, however, in the 21st century we can at least have some confidence (thanks in no small part to computer aided molecular design and bioinformatics) that the optimization of lead compounds and the corresponding discovery of new drugs will be able to keep pace with the progress of biomedical research. Optimizing the lead compound for the pharmacodynamic phase is likewise approached via a two-step strategy: 1. As emphasized earlier at several points, structural modifications expressed in organic chemical terms are really only symbols for modification of the physicochem ical properties of various structures. Nevertheless, the medicinal chemist usually thinks in terms of structure, since that is the language of organic synthesis.