Enalapril
Discount enalapril 5 mg otc
The presence In summary arrhythmia 25 years old quality enalapril 10 mg, ultrasound has become a reliable and important tool in of? Diagnostic perito neal lavage is superior to clinical evaluation in blunt abdominal 2. J Trauma With Sonography in Trauma) Accurate for Cardiac and Intraperito 1996;40:875?883. Emergency de partment right upper quadrant ultrasound is associated with a re 18. The use of duced time to diagnosis and treatment of ruptured ectopic pregnan echocardiography in the emergency management of nonpenetrating cies. Emergency center ultrasonography in the evaluation of hemoperitoneum: a prospective study. Clinical and Practice Management: Use ultrasound to quickly detect bleeding in the belly. Thoracic diagnostic accuracy of lung ultrasonography in the emergency de Trauma and Critical Care. Pneumothorax and introduction to ultrasound st sonography for detecting post-traumatic pneumothoraces: the Ex signs in the lung. Although comprehending image ori Trauma 4 entation and acquiring images can be somewhat challenging, clini cian performed bedside echocardiography has a major impact on Scope of Basic Cardiac Bedside Ultrasound: our ability to detect cardiac abnormalities and on patient care, and 5-6 Global Left Ventricular Function can be life-saving. Bedside echocardiography provides clinicians Pericardial Effusions with time-sensitive anatomic and physiologic information in a variety Right Heart Failure of cardiac-related scenarios, including cardiac arrest, unexplained 6-11 hypotension, syncope, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Bedside echocardiography can help clinicians risk tation (chamber sizes) are within the scope of clinicians and can help 12-13 8 stratify patients and further guide resuscitative efforts. The probe is then gently dragged over the nd th chest wall from the 2 to 5 intercostal spaces, searching for the best acoustic window (Movie 2. The api 29 cal 4-chamber (A4C) view is obtained by placing the probe inferior as in other views, allows for the requisite angling of the probe where and lateral to the left nipple in men or under the left breast in it is almost? The subxiphoid view uses the left lobe of the liver as an acoustic window and involves angling the face of the probe up from the abdomen and into the left chest. With appropriate education and training, clinicians can differentiate between normal and severely depressed left ventricular 15 systolic function similar to cardiologists. Moore et al demonstrated that, with focused training, emergency physicians can accurately de 15 termine left ventricular function in hypotensive patients. Pericardial effusions Tamponade is a clinical diagnosis that depends more on pres are caused by a variety of disorders (infection, malignancy, connec sure and physiology than size of effusion tive tissue disease, renal failure, trauma) and may also develop after Pericardial and pleural effusions can frequently be differenti cardiac surgery or invasive cardiac procedures (pacemaker place ated based on location of? Pericardial effusions are not an uncommon diagnosis in 11,19 patients presenting with dyspnea or hypotension. Although car diac tamponade is largely a clinical diagnosis, bedside echocardi ography may demonstrate? When com pared with expert over-read of images, emergency physician?per formed emergency echocardiography for effusion has a sensitivity of 96% to 100%, a speci? It is important not to confuse ventricular or atrial systole with diastolic collapse. While large pleural effusions may be misinterpreted as peri cardial effusions, the descending thoracic aorta can be used to differ entiate the two diagnoses. Pleural effusions run posterior or lateral to the descending thoracic aorta, while pericardial effusions track an teriorly or medially (Movies 2. Patients with pulmonary embolism and evidence of right-heart dysfunction, however, have in creased morbidity and mortality, and bedside echocardiography can 30, 33 be used to risk-stratify and to better manage these patients. The ability to as Conclusion sess patients for pericardial effusions, global left ventricular function, and right heart dilatation can provide answers to critical questions, risk-stratify patients, and further guide resuscitative efforts. Focused Cardiac Ultra sound in the Emergent Setting: A Consensus Statement of the Ameri can Society of Echocardiography and American College of Emer gency Physicians. Echocardiography per trial of immediate versus delayed goal-directed ultrasound to identify formed by emergency physicians: impact on diagnosis and therapy. Incidence of pericardial effusion in patients presenting Cardiac Ultrasound Probe and Image Conventions. Bedside echocardi diac ultrasonographic examination in patients with suspected cardiac ography by emergency physicians. Outcome in cardiac arrest patients found to temporary medical patients: detection before hemodynamic embar have cardiac standstill on the bedside emergency department echo rassment. Phila gency physician assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction and delphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2004. Emergency echocardiography to detect peri echocardiography improves outcome in penetrating cardiac injury. Implications of echocar sion of the right atrium: a new echocardiographic sign of cardiac diographically assisted diagnosis of pericardial tamponade in con tamponade. Use of transthoracic echo cardiography combined with clinical and electrocardiographic data to predict acute pulmonary embolism. Systematic review and meta-analysis of strategies for the diagnosis of suspected pulmonary embolism. Echocardiogra phy Doppler in pulmonary embolism: right ventricular dysfunction as a predictor of mortality rate. Up to Introduction 62% of patients with ruptured aneurysms die before reaching the hospital, and the overall mortality rate after rupture may exceed 2 90%. Indications/Anatomy Indications may include abdominal pain, back pain, chest pain, a pul satile abdominal mass, renal colic, syncope, hypotension, weak ness, or neurologic changes in the extremities. One high-risk group, in particular, includes older males with hypertension and a history of tobacco abuse. You will need to scan from this mid-epigastric location caudally to the bifurcation of the aorta, visualizing the transverse high, mid, and low aorta. Again, you will scan As you scan cephalad to caudad (head to toe), identify the follow from the mid-epigastrium to the bifurcation at the umbilicus. The vertebral body is horseshoe-shaped with an intense echogenic anterior surface and posterior shadowing. Scan caudally to the aortic bifurcation with Transverse aorta with celiac trunk (seagull sign); Hep A = methodical real-time hepatic art, Spl A = splenic art, * = aorta) visualization, without skipping any section of the aorta. Imaging impediments due to bowel gas usu dinal view of ally originate from the transverse colon, which sits in the epigastrium. To avoid this error, Pearls and Pitfalls adjust the gain so that aortic lumen is black. If possible, decrease the dynamic range to improve the contrast between vessel wall and lumen. Systematic, continuous scanning in both longitudinal and transverse planes is essential to prevent a false negative diagnosis. Emergency department ultra sound scanning for abdominal aortic aneurysm: accessible, accurate and advantageous. For the last several decades the main stay for initial diagnostic imaging has been the chest radiograph. The biggest challenges for thoracic ultrasound are to get the Lung Ultrasound is a paradigm shift physician to think in a radically different way about how to visualize pathology and to empower the clinician to feel that the thoracic ultra sound images are an equal, if not a more valid, indication of pathol "The voyage of discovery is not in seeking new landscapes but ogy and disease. Rib shadows help to orient the sonographer by serving as a landmark for pleural line identi? As the ribs approach the sternum, they become carti laginous, and so sound can penetrate through the rib at this point. Image of normal pleura the pleural line Effusion separating visceral from parie must be deep to the rib shadow. If you see this anteriorly, a large effusion or one that is located anteriorly is suspected. It is important to remember that a normal lung has well-aerated alveoli and very thin intersti tial tissue holding the alveoli together. It is also important to remember that air does not transfer sound well, but instead scatters it so that the sound does not return to the probe in an organized fashion (Figure 4. Drawing demonstrating the disorgan ized scatter from air low density air molecules reflect sound in a non uniform pattern. Instead, the bouncing back and forth between the skin surface and the pleural line creates a horizontal reverbera tion artifact that is called an A-line (Movie 4. These vertical lines are called B-lines and are a marker of interstitial thickening (from? There are a few features of B-lines that should be highlighted to ensure that what is seen is truly a marker of interstitial?
Diseases
- Fanconi syndrome, renal, with nephrocalcinosis and renal stones
- Deafness craniofacial syndrome
- Cystic hamartoma of lung and kidney
- Sclerotylosis
- Pulmonary blastoma
- Cancer
- Gigantism advanced bone age hoarse cry
- Trichomegaly cataract hereditary spherocytosis
- Ethylmalonic adipic aciduria
- Spondylohypoplasia arthrogryposis popliteal pteryg
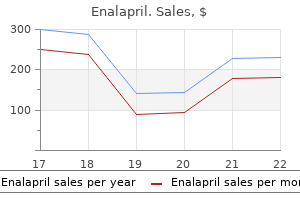
Purchase enalapril cheap online
Chronic hepatitis is defined as continuing or relapsing i) Inflammatory cell infiltration by lymphocytes heart attack age order enalapril australia, plasma hepatic disease for more than 6 months with symptoms along cells and macrophages (triaditis). Majority of cases of chronic iii) Additionally, chronic hepatitis C may show lymphoid hepatitis are the result of infection with hepatotropic aggregates or follicles with reactive germinal centre and viruses?hepatitis B, hepatitis C and combined hepatitis B 612 Figure 21. Diagrammatic representation of pathologic changes in chronic hepatitis (B) contrasted with normal morphology (A). Photomicrograph on right (C) shows stellate-shaped portal triad, with extension of fibrous spurs into lobules. The portal tract is expanded due to increased lymphomononuclear inflammatory cells which are seen to breach the limiting plate. Necroinflammatory activity: vii) Cases of chronic hepatitis B show scattered ground Periportal necrosis i. The onset of fibrosis in chronic Intralobular necrosis, focal or confluent (ranging from score hepatitis from the area of interface hepatitis and bridging 0 as none to score 4 for >10 foci for focal necrosis, and necrosis is a feature of irreversible damage. Extent and depth of portal inflammation (ranging from grade necrosis in which the liver failure is rapid and fulminant 613 0 as no inflammation to grade 4 having marked portal occurring in 2-3 weeks. Fulminant hepatitis of either of the two varieties can occur from viral and non-viral etiologies: B. In addition, hepatitis are quite variable ranging from mild disease to full herpesvirus can also cause serious viral hepatitis. Non-viral causes include acute hepatitis due to drug i) Mild chronic hepatitis shows only slight but persistent toxicity. The patients present with features of hepatic failure with hepatic encephalopathy (page 602). The mortality rate is high iii) Laboratory findings may reveal prolonged prothrombin if hepatic transplantation is not undertaken. Grossly, the liver is small iv) Systemic features of circulating immune complexes due and shrunken, often weighing 500-700 gm. The sectioned surface shows diffuse complex vasculitis, glomerulonephritis and cryoglobuli or random involvement of hepatic lobes. Fulminant Hepatitis Regeneration in submassive necrosis is more orderly and (Submassive to Massive Necrosis) may result in restoration of normal architecture. Fulminant hepatitis is the most severe form of acute hepatitis ii) In massive necrosis, the entire liver lobules are in which there is rapidly progressive hepatocellular failure. As a result of loss of hepatic parenchyma, all that Two patterns are recognised?submassive necrosis having a is left is the collapsed and condensed reticulin framework less rapid course extending up to 3 months; and massive and portal tracts with proliferated bile ductules plugged Figure 21. There is wiping out of liver lobules with only collapsed reticulin framework left out in their place, highlighted by reticulin stain (right photomicrograph). Regeneration, Cholangitis is the term used to describe inflammation of the if it takes place, is disorderly forming irregular masses of extrahepatic or intrahepatic bile ducts, or both. Fibrosis is generally not a feature of main types of cholangitis?pyogenic and primary sclerosing. While primary sclerosing cholangitis is discussed later with biliary cirrhosis (page 625), pyogenic cholangitis is described the clinicopathologic course in two major forms of below. Most prevention of its spread to the contacts after detection and commonly, the obstruction is from impacted gallstone; other identification of route by which infection is acquired such as causes are carcinoma arising in the extrahepatic ducts, from food or water contamination, sexual spread or carcinoma head of pancreas, acute pancreatitis and parenteral spread. Bacteria gain entry a few hepatitis vaccines have been developed and some more to the obstructed duct and proliferate in the bile. The principle underlying either of spreads along the branches of obstructed duct and reaches these two forms of prophylaxis is that the persons who the liver, termed ascending cholangitis. The common infecting develop good antibody response to the antigen of the bacteria are enteric organisms such as E. Immunoprophylaxis and hepatitis vaccination are small beaded abscesses accompanied by bile stasis along unnecessary if the pre-testing for antibodies is positive. Passive immunisation with immune in time are replaced by chronic inflammatory cells and globulin as well as active immunisation with a killed vaccine enclosed by fibrous capsule. Current Most liver abscesses are of bacterial (pyogenic) origin; less recommendations include pre-exposure and post-exposure often they are amoebic, hydatid and rarely actinomycotic. Ascending cholangitis through ascending infection in the with combination of hepatitis B immune globulin and biliary tract due to obstruction. Amoebae multiply and block small intrahepatic portal radicles resulting in infarction necrosis of the adjacent liver parenchyma. The patients, generally from tropical and subtropical countries, may give history of amoebic dysentery in the past. Intermittent low-grade fever, pain and tenderness in the liver area are common presenting features. A positive haemagglutination test is quite sensitive and useful for diagnosis of amoebic liver abscess. Grossly, amoebic liver abscesses are usually solitary and more often located in 2. Portal pyaemia by means of spread of pelvic or gastro the right lobe in the posterosuperior portion. Amoebic intestinal infection resulting in portal pylephlebitis or septic liver abscess may vary greatly in size but is generally of emboli. The centre of the abscess contains diverticulitis, regional enteritis, pancreatitis, infected large necrotic area having reddish-brown, thick pus haemorrhoids and neonatal umbilical vein sepsis. Iatrogenic causes include liver biopsy, percutaneous biliary found in the liver tissue at the margin of abscess. The diagnosis is possible by liver right upper quadrant, fever, tender hepatomegaly and biopsy. There may be leucocytosis, elevated serum alkaline phosphatase, elevated serum alkaline phosphatase levels and hypoalbuminaemia and a positive blood culture. The basic lesion is the the cause for pyogenic liver abscess, they occur as single epithelioid cell granuloma characterised by central or multiple yellow abscesses, 1 cm or more in diameter, in an enlarged liver. There are multiple small neutrophilic abscesses with areas of extensive necrosis of the affected liver parenchyma. The adjacent viable area shows pus and blood clots in the portal vein, inflammation, congestion and proliferating fibroblasts. Direct extension from the liver may lead to subphrenic or pleuro-pulmonary suppuration or peritonitis. There may be small pyaemic abscesses elsewhere such as in the lungs, kidneys, brain and spleen. The dog is the common definite host, while man, sheep and cattle are the intermediate hosts. The infected faeces of the dog contaminate grass and farmland from where the ova are ingested by sheep, pigs and man. Thus, man can acquire infection by handling dogs as well as by eating conta minated vegetables. The ova ingested by man are liberated from the chitinous wall by gastric juice and pass through the intestinal mucosa from where they are carried to the liver by portal venous system. These are trapped in the hepatic sinusoids where they eventually develop into hydatid cyst. About 70% of hydatid cysts develop in the liver which acts as the first filter for ova. However, ova which pass through the liver enter the right side of the heart and are caught in the pulmonary capillary bed and form pulmonary hydatid Figure 21. Some ova which enter the systemic circulation give shows epithelioid granulomas with small areas of central necrosis and rise to hydatid cysts in the brain, spleen, bone and muscles. The disease is common in sheep-raising countries such as Australia, New Zealand and South America. The uncomplicated hydatid cyst of the liver may be silent or may caseation necrosis with destruction of the reticulin produce dull ache in the liver area and some abdominal framework and peripheral cuff of lymphocytes distension. Rare the peritoneal cavity, bile ducts and lungs), secondary lesions consist of tuberculous cholangitis and tuberculous infection and hydatid allergy due to sensitisation of the host pylephlebitis. The diagnosis is made by peripheral blood eosinophilia, radiologic examination and serologic tests such as indirect haemagglutination test and Casoni skin test. The cyst wall is composed of whitish membrane resembling the membrane of a hard boiled egg.
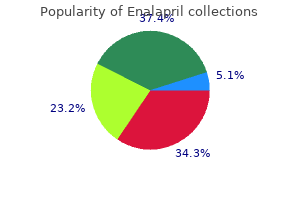
Order enalapril online
Carcinoma of the oeso Carcinoma of the oesophagus is diagnosed late heart attack the song buy enalapril 5 mg amex, after phagus is mainly of 2 types?squamous cell (epidermoid) symptomatic oesophageal obstruction (dysphagia) has and adenocarcinoma. The sites of predilection for each of developed and the tumour has transgressed the anatomical these 2 forms is shown in Fig. The tubular structure has thick muscle in its wall and has longitudinal mucosal folds. There is a concentric circumferential thickening in the middle (arrow) causing narrowing of the lumen (arrow). B, Photomicrograph shows whorls of anaplastic squamous cells invading the underlying soft tissues. It is exceeded in incidence oesophagus in which there are foci of gastric or intestinal by carcinoma colon, rectum and stomach amongst all the type of epithelium. The disease occurs in 6th to 7th Grossly, oesophageal adenocarcinoma appears as decades of life and is more common in men than women. The sites of predilection are the three areas of oesophageal Microscopically, adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus can constrictions. Half of the squamous cell carcinomas of have 3 patterns: oesophagus occur in the middle third, followed by lower i) Intestinal type?is the adenocarcinoma with a pattern third, and the upper third of oesophagus in that order of similar to that seen in adenocarcinoma of intestine or frequency. It an irregular admixture of adenocarcinoma and squamous appears as a cauliflower-like friable mass protruding into cell carcinoma. Besides the two main Microscopically, majority of the squamous cell carcinomas histological types of oesophageal cancer, a few other of the oesophagus are well-differentiated or moderately varieties are occasionally encountered. Prickle cells, keratin forma i) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is a tumour having tion and epithelial pearls are commonly seen. However, characteristics of squamous cell as well as mucus-secreting non-keratinising and anaplastic growth patterns can also carcinomas. An exophytic, slow-growing, extremely well ii) Malignant melanoma is derived from melanoblasts in differentiated variant, verrucous squamous cell carcinoma, the epithelium of the oesophagus. It occurs predominantly in men in which cannot be classified into any recognisable type of their 4th to 5th decades. Body is the middle portion of the stomach between the and is of great importance for surgical treatment. Pylorus is the junction of distal end of the stomach with above into the hypopharynx, into the trachea resulting in the duodenum. The tumour may invade the muscular wall of fundus are loose (rugae), while the antral mucosa is the oesophagus and involve the mediastinum, lungs, bronchi, somewhat flattened. Submucosal lymphatic permeation curvature; it is the site for numerous pathological changes may lead to multiple satellite nodules away from the main such as gastritis, peptic ulcer and gastric carcinoma. Besides, the lymphatic spread may result in the stomach receives its blood supply from the left gastric metastases to the cervical, para-oesophageal, tracheo artery and the branches of the hepatic and splenic arteries bronchial and subdiaphragmatic lymph nodes. Blood-borne metastases from which communicate freely with each other are also present. Nerve plexuses and ganglion cells are present the stomach is gland with cavity, extending from its between the longitudinal and circular layers of muscle. The junction with lower end of the oesophagus (cardia) to its pyloric sphincter is the thickened circular muscle layer at junction with the duodenum (pylorus). Submucosa is a layer of loose fibroconnective tissue Hydrochloric acid is produced by the parietal (oxyntic) cells binding the mucosa to the muscularis loosely and contains by the interaction of Cl ions of the arterial blood with water branches of blood vessels, lymphatics and nerve plexuses and carbon dioxide in the presence of the enzyme, carbonic and ganglion cells. Injection of histamine can Between the two layers is the lamina propria composed of stimulate the production of acid component of the gastric network of fibrocollagenic tissue with a few lymphocytes, juice, while the pepsin-secreting chief cells do not respond plasma cells, macrophages and eosinophils. Physiologically, the gastric secretions are externally bounded by muscularis mucosae: stimulated by the food itself. It consists of a single layer of surface the control of gastric secretions chiefly occurs in one of the epithelium composed of regular, mucin-secreting, tall following 3 ways: columnar cells with basal nuclei. Gastric phase?is triggered by the mechanical and fundus and body with which it gradually merges. Depending upon the structure, these ii) Chemical stimulation is by digested proteins, amino acids, glands are of 3 types: bile salts and alcohol which act on gastrin-producing G cells. Gastrin then passes into the blood stream and on return to a) Glands of the cardia are simple tubular or compound the stomach promotes the release of gastric juice. An intestinal hormone capable b) Glands of the body-fundus are long, tubular and tightly of stimulating gastric secretion is probably released into the packed which may be coiled or dilated. Parietal cells In various diseases of the stomach, the laboratory tests to are triangular in shape, have dark-staining nuclei and measure gastric secretions (consisting of gastric acid, pepsin, eosinophilic cytoplasm. These cells are responsible for mucus and intrinsic factor) and serum gastrin are of production of hydrochloric acid of the gastric juice and particular significance (Table 20. Their basal nuclei are large with prominent nucleoli and the cytoplasm is coarsely 1. Tests for gastric acid secretions Endocrine (Kulchitsky or Enterochromaffin) cells?are i) Histamine stimulation widely distributed in the mucosa of all parts of the ii) Histalog stimulation alimentary tract and are described later (page 561). Tests for pepsin Pepsin inhibitors secreting cells resembling neck cells and occasional parietal 3. Gastrin-producing G-cells are present Protein content of mucus predominantly in the region of antropyloric mucosa, with a 4. Gastrin provocation tests gastric juice and the intrinsic factor, required for absorption of i) Secretin test vitamin B12. In its absence, the absorption of vitamin stomach is stimulated to secrete maximal acid which is B12 is impaired as occurs in chronic atrophic gastritis and similarly collected for one hour and the acid content called gastric atrophy. Pentagastrin is currently the most preferred agent administered in the dose atrophic gastritis (with low gastric acid secretion); of 6? This test is based on the fact that in a state of hypoglycaemia, direct vagal following surgery on the stomach. No increase in acid gastrinaemia and gastric acid hypersecretion as follows: production should occur if the vagal resection is complete. The release of dye by the action of gastric rise by more than 50% of basal value in 5-15 minutes, it is acid and its appearance in the urine indicates the presence diagnostic of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (gastrinoma). The test can be repeated after giving stimulant rise does not occur in other conditions. Symptomatic Low value or achlorhydria are observed in: cases may present in newborn or later in life. Microscopically, both normal mature pancreatic acinar and Pepsin inhibitors are used for analysis of pepsin derived from ductal tissue are seen. The term gastritis is commonly employed for any clinical condition with upper abdominal discomfort like indigestion Pyloric Stenosis or dyspepsia in which the specific clinical signs and radiological abnormalities are absent. The condition is of Hypertrophy and narrowing of the pyloric lumen occurs great importance due to its relationship with peptic ulcer predominantly in male children as a congenital defect and gastric cancer. Chronic gastritis can further be of as a result of late manifestation of mild congenital anomaly various types. The exact cause of congenital (infantile) pyloric stenosis is not known but it appears to have familial Acute Gastritis clustering and recessive genetic origin. The acquired (adult) Acute gastritis is a transient acute inflammatory involvement pyloric stenosis is related to antral gastritis, and tumours in of the stomach, mainly mucosa. A variety of etiologic agents have been implicated in the causation of acute gastritis. Grossly and micros as follows: copically, there is hypertrophy as well as hyperplasia of 1. Diet and personal habits: the circular layer of muscularis in the pyloric sphincter Highly spiced food accompanied by mild degree of fibrosis (Fig. The patient, usually a first born Malnutrition male infant 3 to 6 weeks old, presents with the following Heavy smoking. Visible peristalsis, usually noticed from left to right side of the upper abdomen. Acute non-infective gastritis Bezoars are foreign bodies in the stomach, usually in patients B. Chemical (reflux) gastritis : Antral-body predominant Trichophytobezoars combining both hair and vegetable 5. Chemical and physical agents: etiologic agents is by cytotoxic effect of the injurious agent Intake of corrosive chemicals such as caustic soda, phenol, on the gastric mucosal epithelium, thus breaking the barrier lysol and then inciting the inflammatory response.
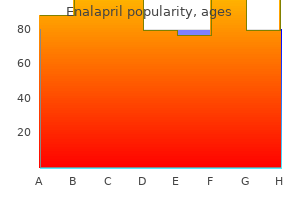
Buy enalapril 5mg with mastercard
As maturation proceeds blood pressure 6240 order enalapril 5mg with amex, more vi) Drug response of granulation tissue is similar to that of and more of collagen is formed while the number of active smooth muscle. The wound starts contracting after 2-3 days and the process Wound healing can be accomplished in one of the following is completed by the 14th day. During this period, the wound two ways: is reduced by approximately 80% of its original size. Contracted wound results in rapid healing since lesser Healing by first intention (primary union) surface area of the injured tissue has to be replaced. A, the incised wound as well as suture track on either side are filled with blood clot and there is inflammatory response from the margins. B, Spurs of epidermal cells migrate along the incised margin on either side as well as around the suture track. C, Removal of suture at around 7th day results in scar tissue at the sites of incision and suture track. When sutures are removed i) clean and uninfected; around 7th day, much of epithelialised suture track is avulsed ii) surgically incised; and the remaining epithelial tissue in the track is absorbed. Immediately after injury, the space close apposition of the margins of wound; the use of adhesive between the approximated surfaces of incised wound is filled tapes avoids removal of stitches and its complications. This occurs within 24 this is defined as healing of a wound having the following hours with appearance of polymorphs from the margins of characteristics: incision. By 3rd day, polymorphs are replaced by i) open with a large tissue defect, at times infected; macrophages. A well primary union but differ in having a larger tissue defect approximated wound is covered by a layer of epithelium in which has to be bridged. The migrated epidermal cells separate the base upwards as well as from the margins inwards. The underlying viable dermis from the overlying necrotic healing by second intention is slow and results in a large, at material and clot, forming scab which is cast off. The basal times ugly, scar as compared to rapid healing and neat scar cells from the margins continue to divide. By 5th day, new collagen fibrils start forming space is filled with blood and fibrin clot which dries. There is an initial acute inflam scar tissue with scanty cellular and vascular elements, a few matory response followed by appearance of macrophages inflammatory cells and epithelialised surface is formed. As in primary healing, the epidermal incites the same phenomena as in healing of the primary cells from both the margins of wound proliferate and migrate 169 Figure 6. A, the open wound is filled with blood clot and there is inflammatory response at the junction of viable tissue. B, Epithelial spurs from the margins of wound meet in the middle to cover the gap and separate the underlying viable tissue from necrotic tissue at the surface forming scab. C, After contraction of the wound, a scar smaller than the original wound is left. Bacterial contamination of an open in the middle and re-epithelialise the gap completely. In this way, pre-existing viable debridement, helps in preventing the bacterial infection of open connective tissue is separated from necrotic material and clot wounds. In time, the Differences between primary and secondary union of regenerated epidermis becomes stratified and keratinised. Granulation tissue is formed by proliferation Complications of Wound Healing of fibroblasts and neovascularisation from the adjoining During the course of healing, following complications may viable elements. The newly-formed granulation tissue is deep occur: red, granular and very fragile. Infection of wound due to entry of bacteria delays the maturation becomes pale and white due to increase in healing. Specialised structures of the skin like hair follicles and sweat glands are not replaced 2. Implantation (epidermal) cyst formation may occur due to unless their viable residues remain which may regenerate. Some coloured important feature of secondary healing, not seen in primary particulate material left in the wound may persist and impart healing. Healing Scanty granulation tissue at the incised Exuberant granulation tissue gap and along suture tracks to fill the gap 6. Complications Infrequent, epidermal inclusion cyst formation Suppuration, may require debridement 170 5. At times the scar Plasma fibronectin is synthesised by the liver cells and is formed is excessive, ugly and painful. Excessive formation trapped in basement membrane such as in filtration through of collagen in healing may result in keloid (claw-like) the renal glomerulus. Hypertrophied Tissue fibronectin is formed by fibroblasts, endothelial scars differ from keloid in that they are confined to the cells and other mesenchymal cells. It is responsible for the borders of the initial wound while keloids have tumour-like primitive matrix such as in the foetus, and in wound healing. An exaggeration of wound fibroblasts and appears in wound about 48 hours after injury. Elastases degrade the glycoproteins, basement membrane, elastic fibres, and elastic tissue. The collagens are a family of proteins having 2 components?an essential carbohydrate polymer which provide structural support to the multicellular (called polysaccharide or glycosaminoglycan), and a protein organism. It is the main component of tissues such as fibrous bound to it, and hence the name proteo-glycan. Various tissue, bone, cartilage, valves of heart, cornea, basement proteoglycans are distributed in different tissues as under: membrane etc. The collagen synthesis iii) Dermatan sulphate?in dermis is stimulated by various growth factors and is degraded by iv) Keratan sulphate?in cartilage collagenase. On the other hand, defective regulation of collagen the strength of wound also depends upon factors like synthesis leads to hypertrophied scar, fibrosis, and organ the site of injury, depth of incision and area of wound. Type I collagen the matrix proteins comprising it undergo marked is normally present in the skin, bone and tendons and remodeling during foetal life which slows down in adult accounts for 90% of collagen in the body: tissues. Other types of collagen are non-fibrillar and amorphous material seen as component of the basement membranes. Factors Influencing Healing Morphologically, the smallest units of collagen are Two types of factors influence the wound healing: those collagen fibrils, which align together in parallel bundles to acting locally, and those acting in general. Infection is the most important factor acting locally which of fibronectin, tenascin (cytotactin) and thrombospondin. Foreign bodies including sutures interfere with healing and previously diseased bone); cause intense inflammatory reaction and infection. Exposure to ionising radiation delays granulation tissue However, basic events in healing of any type of fracture formation. Type, size and location of injury determines whether Primary union of fractures occurs in a few special healing takes place by resolution or organisation. Wound healing is rapid in young and somewhat bony union takes place with formation of medullary callus slow in aged and debilitated people due to poor blood supply without periosteal callus formation. The patient can be made ambulatory early but there is more extensive bone necrosis to the injured area in the latter. Deficiency of constituents like protein, vitamin Secondary union is the more common process of fracture C (scurvy) and zinc delays the wound healing. Administration of glucocorticoids has anti-inflammatory i) Procallus formation effect. Uncontrolled diabetics are more prone to develop infections iii) Remodelling and hence delay in healing. Haematologic abnormalities like defect of neutrophil func below: tions (chemotaxis and phagocytosis), and neutropenia and I. Loose Healing of the skin wound provides an example of general meshwork is formed by blood and fibrin clot which acts as process of healing by regeneration and repair. C, Formation of procallus composed of woven bone and cartilage with its characteristic fusiform appearance and having 3 arbitrary components?external, intermediate and internal callus.
Sulforaphane Glucosinolate (Sulforaphane). Enalapril.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Sulforaphane.
- How does Sulforaphane work?
- What is Sulforaphane?
- Preventing cancer.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97016
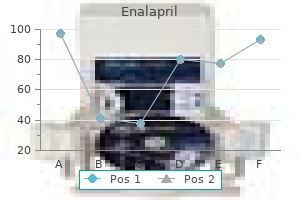
Buy 10mg enalapril with mastercard
It is for this reason that mothers and babies should be accommodated in the same room arrhythmia event monitor order on line enalapril. The mother can then breastfeed for however long and at whatever frequency the baby demands. It is a fact that adequate milk production is dependent upon regular breastfeeding. Putting babies to the breast at frequent intervals is the most important factor in achieving breastfeeding success. The mother should take the baby in her arm s and breastfeed whenever the baby cries (Buswell & Spatz, 2006; Jansen et al. The close contact of mother and baby after the birth and frequent breastfeeding is the best method of speeding up milk production. The mother should pick the baby up in her arms and breastfeed whenever she wants or whenever the baby cries. Rooming in provides healthy babies with the opportunity to suckle at frequent intervals. Because problems such as crying and feeling hungry are solved on the spot, the baby can rest more peacefully. It has been observed that mothers in rooming-in situations are more successful at breastfeeding (Neyzi & Ertugrul, 2002). In a study in which the relationship between breastfeeding and where the baby was kept was explored, C? Other studies as well have shown that babies sleeping in the same room with their mothers are breastfed during the night three times more frequently than babies in separate rooms and that overall, this is twice the frequency experienced by babies in separate rooms (Blair & Ball, 2004). Breastfeeding as early as possible after the birth starts mother and baby off on their bond together. When they are accommodated in the same room, mothers tend to more quickly adapt to their own roles and develop increasing interaction with their babies (Gorak, 2002; Hofer, 2005). For this reason, in the first days after birth, together with the start of breastfeeding, nurses need to promote an adequate, successful, and sustained interaction between the mother and her baby (Soysal et al. The method is also known to help to develop mothers caregiving skills and also regulate babies periods of sleep. It is also regarded as a safe and non-pharmacological model of baby care (Derebent & Yigit, 2006). In various studies, it has been found that skin-to-skin contact between mother and child in the first 15-60 minutes after birth has a positive effect on the behavior of both mother and baby throughout the feeding period. Studies conducted since 1980 have found that babies exposed to skin-to-skin contact with their mothers after birth successfully seek the breast, grasping it and suckling without any help from mother (Bystrova et al. The skin contact between mother and child not only helps in breastfeeding but also offers benefits for the process of bonding as well. Early skin contact between the baby and mother has been shown to increase the time and the quality of time at the breast, strengthening the bond between the mother and child and encouraging the mother to be more caring for her baby. It has been observed that mothers who spend more time with their babies, who have more skin contact and practice massaging the baby are more successful at breastfeeding and are able to breastfeed for longer periods of time. In a study by Glover et al (2002), it was noted that mothers in postnatal depression who attended a massage course experienced an increase in the secretion of the hormone oxytocin. In short, it can be suggested that parents of newborns be informed about kangaroo care and the advantages it provides so that the method can be practiced with more awareness and consequently with more benefits. Mothers who deliver by cesarean section can breastfeed their babies just like women who have had normal childbirth. Cesarean mothers may however encounter problems, some of them having to do with the mother, and some related to the baby. It is inevitable that nurses at hospitals and health clinics have major responsibilities in this context, as they are the health professionals that spend the most time with mothers giving childbirth. Since nurses/midwives are key figures in helping mothers to decide on and continue with breastfeeding, their duties and responsibilities in supporting breastfeeding starts from before the birth and should continue until the time the baby is weaned from the breast. Besides making sure that the baby is provided with good care and nutrition, the nurse should also have knowledge about breastfeeding mechanisms and methods and also the skills to assist mothers in coping with and solving the problems that they may encounter in breastfeeding. For this reason, breastfeeding methods should be observed and improvements suggested so that the mother can be in an optimum position to nurse her baby and to ensure that she will later be able to correctly breastfeed the infant on her own. Health professionals should realize that breastfeeding and mother-baby bonding following a cesarean birth are multi-faceted processes. Their efforts should also go into increasing the parents self-confidence about baby care and helping mothers and fathers to develop their respective parental roles. Merih experienced her first delivery via elective cesarean section under general anasthesia. She said that about her experiences and feelings after the caesarean section: When I met with my daughter, my consciousness was not totally open. The first thing I could remember, breastfeeding was tried to be done with my breasts by nurses instead of me. Things that I most wanted after delivery were sitting comfortable, hugging my baby easily, breastfeed her troubleless and comfortable and dressing her up. Because of these reasons I said I wish, I had a normal delivery and I felt guilty for being elective cesarean. What kind of experiences this mother has about breastfeeding and which problems might be later on? When Mrs Karabacak was 41 weeks pregnant, she was admitted to the hospital for Cesarean section. Mrs Karabacak 150 Cesarean Delivery was transferred to the postpartum unit, and the baby girl Karabacak was transferred to the nursery. Because Mrs Karabacak stated that she was tired and that she was not able to look after the baby at the time. During a conversation with the nurse, Mrs Karabacak said that if the baby had been a boy, her husband would have been very happy. There is Rh incompatibility with her husband and as a result, Baby Ege has developed jaundice. Each time they saw the baby cry, Esra and her husband couldn?t help themselves and cried along with him. After two days of treatment, the reading came down to 11 and they were discharged. Ultimately, inadequate liver enzymes were suspected and the baby was started on oral treatment. At the time they came in for a check-up after the dose of medicine was completed, the jaundice reading had fallen to 5. Ayse had always wanted to have a baby but because her husband was in a different city due to his job, the husband felt that Ayse would have trouble with a baby on her own so the couple decided to postpone pregnancy. The pregnancy gave Ayse a craving for certain foods but no one paid her any attention. She was very upset by all of this and she would cry herself to sleep almost every night. Acknowledgment We wish to acknowledge our families for their patience and support throughout the writing process especially summer time. Kangaroo Mother Care as Compared to Conventional Care for Low Birth Weight Babies. Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in the Newborn Infant 35 or More Weeks of Gestation, In: Pediatrics,Vol. Effect of labor epidural anesthesia on breast-feeding of healthy full-term newborns delivered vaginally. Pregnancy in Postpartum Period and Psychosocial Adaptation of the Family, In: Perinatal Nursing, 1. An approach to failure to thrive, In: Reprinted from Australian Family Physician, Vol. Early Contact Versus Separation: Effects on Mother-Infant Interaction One Year Later. Risk factors for excess weight loss and hypernatremia in exclusively breast-fed infants.
Best buy for enalapril
In the United States arteria3d review buy 5 mg enalapril, preterm birth rates and low birth weight rates in homeless women exceed national averages. It is important for physicians to identify patients within the practice who are (or are at risk of becoming) homeless by asking questions about living condi tions, nutrition, substance abuse, and intimate partner violence; provide health care, including preventive care, for homeless women without bias; and not with hold treatment based on concerns about lack of adherence. Health care profes sionals are advised to simplify medical regimens and address barriers, including transportation needs for follow-up health care visits. In addition, physicians should become familiar with and inform patients who are (or at risk of becom ing) homeless about appropriate community resources, including local substance abuse programs, intimate partner violence services, and social service agencies. With all disabilities, consideration of the history of the disability, the number and severity of limitations, and its expected progression is critical in meeting the health care needs and concerns of women. This information may be accessible through various means, such as consultation with rehabilitation physicians or other disability health care providers, further investigation of medical literature, disability organizations, and through discussion with the woman and her family. Many women are well informed about their disabilities and the resources available to them. Language and educational differences between women and their health care providers are barriers to effective care. Women with disabilities also may need extra time allotted for their appoint ment. When scheduling appointments, asking patients about the need for extra time or services in a nonjudgmental and nonstigmatizing fashion may be one way of accommodating such needs. Creativity and flexibility on the part of each staff member can go a long way in ameliorating these challenges and establish ing mutually rewarding and respectful services. Pregnancy and parenting for women with physical disabil ities may pose unique medical and social challenges but rarely are precluded by the disability itself. Health care professionals have the responsibility to provide appropriate reproductive health services to these women or arrange adequate consultation or referral. Nonbiased preconception counseling for couples in which one partner has a physical disability may decrease subsequent psychosocial and medical complications of pregnancy. Screening and provision of disability specific information, such as condition-appropriate genetic counseling and folate supplementation for women who have spina bifida, is highly desirable (see also Preconception Nutritional Counseling earlier in this chapter). Detailed pregnancy care plans should be developed in negotiation with managed care plans and other insurers to increase access to and use of pre Preconception and Antepartum Care 155 natal care services, ensure appropriate postpartum hospital length of stay, and arrange postpartum home care services, if necessary. Assessment of the need for additional assistance during pregnancy to ambulate, perform safe transfers, and maintain hygiene and household activities is recommended. Regular consulta tion or referral may be required to achieve the optimum outcome. In caring for pregnant women with intellectual and developmental disabilities, it is important to consider the following psychosocial factors: whether the individual lives at home or in a domiciliary care setting; whether there is a reliable caregiver present; previous history of sexual abuse; and cognitive factors, including her ability to relay a personal or family history of disease and symptoms. Genetic screening is par ticularly important for pregnant women with Down syndrome. First-trimester alpha-fetoprotein testing and ultrasound examinations focused on nuchal translucency, cardiac malformations, and other fetal indications of Down syndrome should be offered (see also Antepartum Genetic Screening and Diagnosis earlier in this chapter). Before examination, it should be determined who will give consent for the examination and any consequential treatment. It also is important at this time to ascertain if the patient is competent to understand findings and health rec ommendations or whether this information needs to be transmitted to an iden tified guardian or caregiver. For women with intellectual and developmental disabilities, making materials available in pictorial formats or in simple, straight forward language can facilitate communication greatly. This will help emergency room personnel, new health care providers, or consulting physicians when records are not available. Consent and Power of Attorney Obtaining informed consent for medical treatment is an ethical requirement that is partially reflected in legal doctrines and requirements. Communication is necessary if informed consent is to be realized, and physicians can and should help to find ways to facilitate communication not only in individual relations with patients but also in the structured context of medical care institutions. In emergency situations, medical professionals may have to act according to their perceptions of the best interests of the patient; in rare instances, they may have to forgo obtaining consent because of some other over riding ethical obligation, such as protecting the public health. An advance directive is the formal mechanism by which a patient may express her values regarding her future health status. Proxy directives, such as the durable power of attorney for health care, designate a surrogate to make medical decisions on behalf of the patient who is no longer competent to express her choices. Instructional directives, such as living wills, focus on the types of life-sustaining treatment that a patient would or would not choose in various clinical circumstances. Although courts at times have intervened to impose treatment on a pregnant woman, currently there is general agreement that a pregnant woman who has decision-making capacity has the same right to refuse treatment as a nonpreg nant woman. When a pregnant woman does not have decision-making capacity, however, legislation frequently limits her ability to refuse treatment through an advance directive. Statutes that prohibit pregnant women from exercising their right to determine or refuse current or future medical treatment are unethical. Second-Trimester and Third-Trimester Patient Education ^ Important topics to discuss with women before delivery include working, child birth education classes, choosing a newborn care provider, anticipating labor, preterm labor, breech presentation at term, trial of labor after cesarean delivery, elective delivery, cesarean delivery on maternal request, umbilical cord blood banking, breastfeeding, preparation for discharge, and neonatal interventions. Working A woman with an uncomplicated pregnancy usually can continue to work until the onset of labor. Women with medical or obstetric complications of pregnancy may need to make adjustments based on the nature of their activities, occupa Preconception and Antepartum Care 157 tions, and specific complications. It also has been reported that pregnant women whose occupations require standing or repetitive, strenuous, physical lifting have a tendency to give birth earlier and have small for gestational age infants. It also is important for the development of children and the family unit that adequate family leave be available for parents to be able to participate in early childrearing. The federal Family and Medical Leave Act and state laws should be consulted to determine the family and medical leave that is available. Childbirth Education Classes and Choosing a Newborn Care Provider Pregnant women should be referred to appropriate educational literature and urged to attend childbirth education classes. Studies have shown that childbirth education programs can have a beneficial effect on patient experience in labor and delivery. The prenatal period should be used to expose the prospective parents to information about labor and delivery, pain relief, obstetric compli cations and procedures, breastfeeding, normal newborn care, and postpartum adjustment. Other family members also should be encouraged to participate in childbirth education programs. Adequate preparation of family members may benefit the mother, the neonate, and, ultimately, the family unit. Many hospi tals, community agencies, and other groups offer such educational programs. The participation of physicians, certified nurse?midwives, and hospital obstet ric nurses in educational programs is desirable to ensure continuity of care and consistency of instruction. Integration of parenting education in prenatal education is beneficial in facilitating transition to parenthood. Sometime in the third trimester, it should be determined if the patient has a newborn care provider. If she does not have one, she should be referred to the appropriate resources to identify her newborn care provider before delivery, if possible. As pregnancy progresses, patients should be advised when and how to contact the health care provider should symptoms of labor or membrane rupture occur. If a patient has a birth plan, she should be encouraged to review it with her health care provider before labor. A detailed 158 Guidelines for Perinatal Care discussion should take place during the third trimester regarding analgesic and anesthetic options available for labor and delivery. The oral intake of modest amounts of clear liquids may be allowed for patients with uncom plicated labor. The patient without complications undergoing elective cesarean delivery may have modest amounts of clear liquids up to 2 hours before induc tion of anesthesia. Patients with risk factors for aspiration (eg, morbid obesity, diabetes, and difficult airway), or patients at increased risk of operative delivery may require further restrictions of oral intake, determined on a case-by-case basis. Pregnant women are at highest risk of aspiration pneumonitis when stomach contents are greater than 25 mL and when the pH of those contents is less than 2. The type of aspiration pneumonitis that produces the most severe physiologic and histologic alteration is partially digested food. Preterm Labor Preterm labor generally can be defined as regular contractions that occur before 37 weeks of gestation and are associated with changes in the cervix. Toward the end of the second trimester, signs and symptoms of preterm birth, rup tured membranes, and vaginal bleeding should be reviewed with the patient and she should be encouraged to contact the health care provider should these symptoms occur. Patients should be given a telephone number to call where assistance is available 24 hours per day. Short-term interventions to allow for steroid administration and transfer of the pregnant woman to an appropriate level of hospital for her situation are possible if a woman is seen early enough after onset of symptoms (see also Preterm Birth in Chapter 7).
Cheap enalapril amex
The adverse effects with iron dextran raised in iron overload and is normal in anaemia of chronic include hypersensitivity or anaphylactoid reactions heart attack zippy demi enalapril 5 mg overnight delivery, disorders. These granules stain positively with Prussian preventive measures are instituted to correct the cause of blue reaction as well as stain with Romanowsky dyes when blood loss. This is iron is corrected with iron therapy as under: because the reticulocytes on release from the marrow are i) Oral therapy. Iron deficiency responds very effectively finally sequestered in the spleen to become mature red cells. These are nucleated red cells (normo absorption is obtained by giving iron fasting, but if side blasts) containing siderotic granules which stain positively effects occur. Oral iron therapy is continued long enough, both to correct the anaemia and to replenish the body iron stores. The response to oral iron therapy is observed by reticulocytosis which begins to appear in 3-4 days with a peak in about 10 days. Poor response to iron replacement may occur from various causes such as: incorrect diagnosis, non-compliance, continuing blood loss, bone marrow suppression by tumour or chronic inflammation, and malabsorption. The bone marrow cells commonly show chromosomal abnormalities, neutro penia and thrombocytopenia with associated bleeding diathesis. The spleen and liver may be either normal or mildly enlarged, while the lymph nodes are not enlarged. About 10% of individuals with refractory acquired sideroblastic anaemia develop acute myelogenous leukaemia. Drugs, chemicals and toxins: Isoniazid, an anti-tuberculous size and distribution of siderotic granules, sideroblasts may drug and a pyridoxine antagonist, is most commonly be normal or abnormal (Fig. Other granules representing iron which has not been utilised for drugs occasionally causing acquired sideroblastic anaemia haemoglobin synthesis. These cells comprise 30-50% of are: cycloserine, chloramphenicol and alkylating agents. All these agents cause reversible sideroblastic anaemia which usually resolves following Abnormal sideroblasts are further of 2 types: removal of the offending agent. Haematological disorders: these include myelofibrosis, scattered, coarse cytoplasmic granules and are seen in polycythaemia vera, acute leukaemia, myeloma, lymphoma conditions such as dyserythropoiesis and haemolysis. Miscellaneous: Occasionally, secondary sideroblastic the other type is ringed sideroblast in which haem anaemia may occur in association with a variety of inflam synthesis is disturbed as occurs in sideroblastic anaemias. The ringed arrangement of these granules is due to the presence Laboratory Findings of iron-laden mitochondria around the nucleus. Sideroblastic anaemias usually show the following haematological features: Types of Sideroblastic Anaemias 1. The acquired type is further may be microcytic, or there may be some normocytic red divided into primary and secondary forms: cells as well (dimorphic). The affected males have moderate to marked anaemia while the females are carriers of the disorder and 4. Hb electrophoresis Normal Normal Abnormal Normal Treatment tions, the anaemia is complicated by other causes such as iron, B12 and folate deficiency, hypersplenism, renal failure the treatment of secondary sideroblastic anaemia is with consequent reduced erythropoietic activity, endocrine primarily focussed on removal of the offending agent. However, in general, 2 factors appear to definite treatment is available for hereditary and idiopathic play significant role in the pathogenesis of anaemia in chronic types of sideroblastic anaemias. These are: defective red cell production and reduced administered routinely to all cases of sideroblastic anaemia red cell lifespan. Though there is abun Differential diagnosis of various types of hypochromic dance of storage iron in these conditions but the amount of anaemias by laboratory tests is summarised in Table 12. A defect in One of the commonly encountered anaemia is in patients of the transfer of iron from macrophages to the developing a variety of chronic systemic diseases in which anaemia erythroid cells in the marrow leads to reduced availability develops secondary to a disease process but there is no actual of iron for haem synthesis despite adequate iron stores, invasion of the bone marrow. In general, anaemia in chronic of erythropoieitn by inflammatory cytokines at some stage disorders is usually normocytic normochromic but can have in erythropoiesis, and hepcidin which is the key iron mild degree of microcytosis and hypochromia unrelated to regulatory hormone. Decreased survival of circulating red cells in chronic renal disease is attributed to A number of factors may contribute to the development of hyperplastic mononuclear phagocyte system. Since cell division is slow but cytoplasmic development progresses normally, the nucleated red cell precursors tend to be larger which Ehrlich in 1880 termed megaloblasts. Megaloblasts are both morphologically and functionally abnormal with the result that the mature red cells formed from them and released into the peripheral blood are also abnormal in shape and size, the most prominent abnormality being macrocytosis. Measurement of erythrocyte survival anaemia, an outline of vitamin B and folic acid metabolism 12 generally reveals mild to moderate shortening of their is given for a better understanding of the subject. Examination of the marrow generally of vitamin B12 and folic acid are summarised in Table12. Cases of chronic infection often organometallic compound having a cobalt atom situated have myeloid hyperplasia and increase in plasma cells. The only dietary sources of vitamin B12 are foods between true iron-deficiency anaemia and iron-deficient of animal protein origin such as kidney, liver, heart, muscle erythropoieisis in anemia of chronic diseases. In addition, certain other and vegetables contain practically no vitamin B unless 12 plasma proteins called phase reactants are raised in contaminated with bacteria. Cooking has little effect on its patients with chronic inflammation, probably under the activity. Body stores 2-3 mg (enough for 2-4 yrs) 10-12 mg (enough for 4 months) 304 thus, the humans are entirely dependent upon dietary sources. After ingestion, vitamin B12 in food is released and forms a stable complex with gastric R-binder. Vitamin B12 plays an important role in general action as co-enzyme, polyglutamates must be reduced to cell metabolism, particulary essential for normal dihydro and tetrahydrofolate forms. Folate exists in different plants, bacteria and 12 biochemical reactions in the body: animal tissues. Its main dietary sources are fresh green leafy vegetables, fruits, liver, kidney, and to a lesser extent, muscle Firstly, as methyl cobalamin (methyl B12) in the methylation meats, cereals and milk. Folate is labile and is largely of homocysteine to methionine by methyl tetrahydrofolate destroyed by cooking and canning. The homocysteine-methionine reaction is closely synthesised by bacteria in the human large bowel is not linked to folate metabolism (Fig. However, Secondly, as adenosyl cobalamin (adenosyl B12) in propionate absorption depends upon the form of folate in the diet. Synthetic folic Adenosyl B12 acid preparations in polyglutamate form are also absorbed Propionyl CoA > Methyl malonyl CoA > Succinyl CoA as rapidly as mono and diglutamate form because of the absence of natural inhibitors. An alternative hypothesis of inter-relationship a carrier protein, it is reconverted to polyglutamate (see of B12 and folate is the formate-saturation hypothesis. Normally, folate is lost from the sweat, Etiology and Classification of Megaloblastic Anaemia saliva, urine and faeces. It acts as a co-enzyme for 2 important bio anaemia is classified into 3 broad groups: vitamin B12 chemical reactions involving transfer of 1-carbon units (viz. This reaction is Indian Hindus and breast-fed infants have dietary lack of linked to vitamin B metabolism (Fig. Gastrectomy by lack of intrinsic factor, and small 12 these biochemical reactions are considered in detail intestinal lesions involving distal ileum where absorption of below together with biochemical basis of the megaloblastic vitamin B12 occurs, may cause deficiency of the vitamin. Deficiency of vitamin B12 takes at least 2 years to develop when the body stores are totally depleted. Folate deficiency is more often the basic biochemical abnormality common to both vitamin due to poor dietary intake. This reaction requires the presence such as methotrexate and pyrimethamine; alcohol, congenital enzyme deficiencies. In addition to the cardinal features mentioned and in various disease states, chronic alcoholism, and excess above, patients may have various other symptoms. Combined deficiency of vitamin B Laboratory Findings 12 12 and folate may occur from severe deficiency of vitamin B12 the investigations of a suspected case of megaloblastic because of the biochemical interrelationship with folate anaemia are aimed at 2 aspects: metabolism. In addition to deficiency of vitamin blood picture, red cell indices, bone marrow findings, and B and folate, megaloblastic anaemias may occasionally be biochemical tests. Based on these principles, the following scheme of investigations is followed: Clinical Features A. General Laboratory Findings Deficiency of vitamin B12 and folate may cause following clinical manifestations which may be present singly or in 1. Esti combination and in varying severity: mation of haemoglobin, examination of a blood film and evaluation of absolute values are essential preliminary 1. Typically, the patient has a smooth, beefy, red concentration may be of a variable degree.
Order genuine enalapril line
While searching PubMed Database I have found the food restricton and subsequent risk of micronutrient and only one systematc review [16] blood pressure chart with age purchase enalapril with amex. In Most of the publicatons protein defciencies in the frst year post bariatric surgery [34]. Although the benefts of bariatric surgery are well established, Treatment and prophylactc the potental for adverse efects on skeletal integrity remains an important concern. If you search for ostemalacia and bariatric surgery, References you can fnd over 25 papers. If the patent has no appropriate monitoring and treatment secondary hyperparathyroidism, 1. Clinical Practce Guidelines recommend calcium and vitamin D supplementaton postoperatvely afer malabsorbtve obesity 2. To work out the optmal supplementaton regimen is a outcome afer silastc ring Roux-en-Y gastric by-pass: 8 years of great need! Brolin R, Leung M (1999) Survey of vitamin and mineral supplementaton afer gastric bypass and biliopancreatc diversion for morbid obesity. J gastric bypass and afer biliopancreatc diversion with Roux-en-Y Clin Endocrin Metab 95(8): 3973-3981. Internatonal Journal of Nutritonal, Metabolic, and Nonsurgical Support of the Bariatric Surgery 12: 976-982. Associaton of Clinical Endocrinologists, the Obesity Society, and (2008) the Decline in Hip Bone Density afer Gastric Bypass American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery. Hypponen E, Power C (2006) Vitamin D status and glucose homeostasis in the 1958 Britsh Birth Cohort. McGill A, Stewart J, Lithander F, Strick C, Poppit S (2008) Surg Obes Relat Dis 10(2): 262-268. Relatonships of low serum vitamin D3 with anthropometry and markers of metabolic syndrome and diabetes in overweight and 37. Vitamin B Complex (with 50 mg thiamin): 1 serving daily** Serving Average Brand Name Thiamin (mg) size cost/month Bariatric Vitamin B-50 Complex 2 capsules 50 7* Advantage Celebrate Vitamin B-50 Complex 1 capsule 50 4 Kirkland Super B-Complex with Electrolytes 1 tablet 100 2 Now Vitamin B-100 1 capsule 100 4 Source Vitamin B-50 Complex 1 tablet 50 4 Naturals Stress B-Complex Capsules with Twin Lab 2 capsules 50 5 Vitamin C *with the Bariatric Advantage discount (promo code Kaiser) **Note: your lab values will be high when taking this amount of B vitamins. Jensen, as well as some insurers and government officials, who fear that inexperienced surgeons and inadequate screening and follow-up may harm patients. Multiple studies have demonstrated that poor compliance with prescribed dietary intakes and vitamin and mineral supplements is common. Preoperative eating behavior, postoperative dietary adherence, and weight loss after gastric bypass surgery. Nutritional deficiencies after gastric bypass for morbid obesity often cannot be prevented by standard multivitamin supplementation? Am J Clin Nutr 2008;87:1128-1133 Copyright 2008 the American Society for Nutrition Conclusions? Best practice guidelines are needed for screening, evaluation, and follow up care. Starting Now: Higher Protein Healthy Meal Plan?1200 calories (usually for women); 1500 calories (usually for men): 3 meals; one snack. Make egg salad with one hard-boiled egg and the whites from 3 other hard-boiled eggs. Or if you scramble your eggs, use one whole egg and the rest egg whites (1/2 cup egg whites or egg substitutes) Vegetarian Protein Choices: Tofu and Veggie Burgers (see page 3) Low-fat Dairy Protein (2 3 servings per day) Beverages: 1 cup skim or 1% milk (can be lactose-reduced), skim milk plus or unsweetened soy milk; almond milk (acceptable but is lower in protein?add protein powder); Yogurt choices (140 calories or less): 5-6 oz. Dash, vinegar, lemon coffee or tea, Diet decaf iced tea juice, non-stick Pam cooking spray, herbs, Can have artificial sweeteners: Equal spices, mustard, Worcestershire sauce, (NutraSweet/Aspartame); Splenda (sucralose); Tabasco sauce, low-sodium and fat-free broth Stevia. No sugar alcohols (sorbitol, xylitol; erythritol, mannitol others) Low Fat Cheese Choices. Cabot 50% Reduced Fat Light Cheddar (50 calories/slice) (70 calories/1-inch cube). Cabot 75% Reduced Fat Light Cheddar (35 calories/wedge) (50 calories/1-inch cube). Mozzarella Reduced Fat Shredded (various brands, see label) Low-calorie Salad Dressings?less than 35 calories/2 Tbsp. Better n Peanut Butter Peanut Butter (1/2 the calories of regular peanut butter). Some may be found in the Vitamin Shoppe or other local health food stores but all can be found online and website links are included. Products without artificial sweeteners: Optimum Nutrition-Naturally Flavored Gold Standard 100% Whey; no artificial flavors or sweeteners, flavored with a small amount of natural sugar. Breakfast French Toast Eggs Your Way 2 slices light bread 1/2 cup egg whites or egg substitutes 1/2 cup non-fat, 1% or soy milk (can use egg whites) 1/4 cup egg whites or egg substitutes, 1 slices whole grain toast or 2 slices Mix milk and egg whites and dip bread. Brown using non-stick pan using small (can scramble with or add veggies amount oil. Hamburger (lean) patty or peppers, tomatoes, cucumbers) veggie burger 1/2 tuna canned in water, or sliced 100 calorie flat sandwich bun turkey (3 oz. Add stir fried veggies (can be fresh or frozen) and serve over 1/2 cup cooked Low-fat salad dressing quinoa or brown rice (Vegetarian option: use cubed firm tofu) Pasta Dinner Salmon or Chicken Dinner 3 4 beef or turkey or vegetarian 4 oz. Grilled salmon or chicken or use meatballs (Gardein) sliced grilled tofu 1/2 cup cooked whole wheat pasta 1/2 Small-medium baked sweet or white 1/2 cup spaghetti sauce potato 1 cup steamed broccoli or other 1 cup cooked vegetables. Easy to use app Cookbooks by Dietitians Weight Loss Surgery Cookbook for Dummies by Brian K. Davidson and Sarah Krieger Fresh Start Bariatric Cookbook: Healthy Recipes by Sarah Kent Everyday Dinners Best Fork Forward: after Weight Loss Surgery, by Steph Wagner * Calories are approximate (Read labels) Nov 2017 12. Diabetes remission was definedasnoglucose-loweringdrugusewithHbA1c <48 mmol/mol (<6. Data on complications were ascertained from medical registries with complete follow-up. Predictors of non-remission were age >50 years, diabetes duration >5 years, use of glucose-lowering drugs other than metformin, and baseline HbA1c >53 mmol/mol (>7. On the other hand, emerging long-term follow-up data reveal a con Methods siderable risk of type 2 diabetes relapse after initial remission [12, 13]. Whether chances of remission, relapse and predictors Setting We conducted a population-based observational co of remission apply to large real-world population-based co hort study in individuals with type 2 diabetes living in horts with complete follow-up is unknown [14, 15]. Since no patient contact was involved, no separate permission from the Danish Scientific Ethical Committee was Diabetes remission, non-remission and relapse For each required according to Danish Legislation. Loss to follow-up was not a thrombotic drugs (within 100 days before the index date). Finally, we retrieved data on annual prevalence of diabetes relapse from day 366 and on diagnosis or treatment of selected conditions not included in the wards, with our main endpoint being prevalence of relapse at Diabetologia year 5. The adjusted hazard of macrovascular events was an individual with HbA1c <42 mmol/mol (<6. This more liberal definition explains the higher remission rates seen in our comparison cohort compared with those reported in previous studies (13?20% vs 0?16%) [12, 13, Discussion 16]. Still, our real-world data diabetes duration and greater severity of diabetes at index date. It seems these remission predictors 1 year was a clear predictor of fewer microvascular complications. Our 5 year prevalent statistical analysis, whether or not attrition rates are taken into remission rate of 70% concurs with previous findings [5, 34]. Of account and whether the setting is population or clinic based, note, there is evidence that operated individuals not reaching the hampering generalisability of previous results [15]. Furthermore, we present real-world clinical data in a in a study of 343 bariatric-operated and 260 non-operated indi population-based setting, representing 30% of the Danish popu viduals with type 2 diabetes with a median follow-up of 17. This setting may reduce the selection bias aris study based on insurance claims [17]. O?Brienetal[18] et al presented an even longer follow-up, although that study found lower risks of diabetic kidney disease, diabetic retinopathy was based on 88 participants with type 2 diabetes only [34]. Finally, due to a limited our ability to adjust for diabetes duration and severity might number of the individual micro and macrovascular complica partly explain the differences in estimates. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2(1): Research Fund of Central Denmark, the Novo Nordisk Foundation and 38?45. Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A et al (2015) Bariatric associated with this manuscript.
Purchase enalapril 10mg visa
If low-intensity exercise is prolonged to the point that glycogen is depleted blood pressure medication without food generic 5 mg enalapril with mastercard, the fast-twitch motor units are recruited. These motor units have more muscle fibers and result in less control of movements. Type 1 fibers cannot be converted to type 2 fibers, but type 1 fibers can improve their ability to use anaerobic metabolism, and type 2 fibers can improve their ability to use aerobic metabolism. Type 2b fibers can be converted to type 2a fibers with endurance training or strength training. This is caused by an increase in capillary and mitochondria content and aerobic oxidative enzyme activity. The cross-sectional area of the muscle decreases, resulting in shorter diffusion distances for oxygen and carbon dioxide. Resistance training causes synthesis of proteins in thick and thin filaments, resulting in an increase in the cross-sectional area. The aerobic capacity of the muscle decreases, which hinders performance in endurance activities. It takes about 6 to 8 weeks for the addition of protein filaments, but conversion of type 2b to type 2a fibers begins after about 2 weeks. These hormones inhibit the release of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, which results in decreased levels of estradiol. Studies have shown that physical and emotional stress, diet, and the presence of menstrual irregularity before training also contribute. There is some evidence to suggest this, but there is also evidence stating otherwise. Summarize some physiologic changes that occur during pregnancy that affect exercise. After the first trimester, the supine position results in relative obstruction of venous return by the enlarging uterus and a significant decrease in cardiac output. Stroke volume and cardiac output during steady-state exercise are increased significantly. Exercise during pregnancy induces a greater degree of hemoconcentration than does exercise in the nonpregnant state. For vigorous intensity physical activity, 20 minutes for 3 days per week is recommended. Such a program decreases weight, decreases fat mass, and maintains or increases fat-free mass. Exercise should be performed at least 3 days per week at an intensity and duration to expend 250 to 300 kilocalories per exercise session for a 75-kg person. This usually requires a duration of at least 30 to 45 minutes for a person in average physical condition. Type of exercise should include weight-bearing endurance activities such as tennis, stair climbing, and jogging intermittently during walking; jumping activities such as volleyball and basketball; and resistance exercises that involve all major muscle groups, such as weight lifting. How do exercise and training affect the endocrine system and the resting levels of hormones? Most hormone levels increase during submaximal, short-term exercise with the exception of insulin, which decreases, and thyroid hormones, which do not change. Discuss prolonged, moderate-intensity exercise training and blood glucose levels in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Blood glucose levels do not seem to change with a prolonged exercise program in individuals with type 1 diabetes, but they decrease in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Exercise causes the cells of type 2 diabetic patients to be less resistant to insulin. Exercise may help to reduce body fat percentage, which results in an increase in the number of insulin receptors, an increase in their sensitivity, or both. This, along with the accompanying weight loss, decreases the cardiovascular risk factors of these individuals, which is the most significant benefit of performing exercise. Although exercise has not been shown to improve blood glucose levels in individuals with type 1 diabetes, it is still recommended for the same reasons that exercise is recommended for individuals without diabetes. Some studies have shown improvements in endurance, whereas others have found no change. How does the heart rate response to exercise differ between normal individuals and individuals who have had heart transplants? In normal individuals, heart rate increases rapidly with moderate exercise as a result of a decrease in parasympathetic nerve activity and an increase in sympathetic nerve activity. Any change in heart rate must be caused by changes in circulating levels of catecholamines, which takes more time than altering nerve activity. It takes longer for the heart rate to increase when exercise is initiated, and it takes longer for it to return to resting levels after exercise. How does resting heart rate differ between normal individuals and individuals who have had heart transplants? Resting heart rate is higherin individuals who have had a heart transplant becausethey no longer have the normal parasympathetic tone to slow the intrinsic rate of depolarization of the sinoatrial node. Why are individuals with thoracic-level spinal cord injuries at risk for fainting after exercising in the upright position with the upper extremities? There is no sympathetic innervation to the lower limb vasculature, and there may not be any innervation to the adrenal glands (depending on how high the injury is). Compared with a thermoneutral environment, exercising in the cold results in less lipid metabolism and free fatty acid use but greater lactate production and higher ventilation, oxygen consumption, respiratory heat loss, and peripheral heat loss. List possible causes for decreased maximal muscle strength and power with hypothermia. What are the two most common problems associated with exercising in hot environments? These problems cannot be avoided completely, but they can be limited by ingesting fluid while exercising. There appears to be a similar benefit between ingestion of pure water compared with carbohydrate and electrolyte drinks as far as controlling core temperature and cardiovascular changes. The principal physiologic responses of exercise in the heat include skin and muscle vasodilation, nonactive tissue vasoconstriction, maintenance of blood pressure, and sweating. Hematocrit levels increase after about 25 days of exposure to high altitude, which should increase performance. Some studies indicate that pulmonary function, cardiac output, muscle enzyme capacity, and lean body mass decrease at high altitudes. World-class athletes performing endurance exercises consistently seem to perform better if they train at a moderate altitude. Position stand: the recommended quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, and flexibility in healthy adults. Acute and chronic effects of aerobic and resistance exercise on ambulatory blood pressure. Dose response association between physical activity and biological, demographic, and perceptions of health variables. Physicalactivityand the brain: A review of thisdynamic, bi-directionalrelationship. The Fit but Fat paradigm addressed using accelerometer-determined physical activity data. Thermoregulation during exercise in the heat strategies for maintaining health and performance. Which of the following muscle fiber types is activated primarily during prolonged, low-intensity exercise? List uses and potential side effects of medications commonly used to treat types of arthritis. It may begin at any age, but there is a peak of onset in women of childbearing years and a second peak in elderly men and women. Genetic influences are important, with concordant rates of arthritis at 15% in monozygotic twins. It has been clearly shown that outcomes are much improved in terms of joint preservation and function with early initiation of treatment. Chronic changes include thickening and edema of the synovial lining of the affected joints.

