Lanoxin
Cheap 0.25 mg lanoxin otc
Quality of life in complete spinal cord injury patients with a Brindley bladder stimulator compared to a matched control group prehypertension headaches discount lanoxin 0.25 mg without a prescription. Sacral neuromodulation for neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: systematic review and meta-analysis. Enveloping the bladder with displacement of flap of the rectus abdominis muscle for the treatment of neurogenic bladder. Restoration of voluntary emptying of the bladder by transplantation of innervated free skeletal muscle. The latissimus dorsi detrusor myoplasty for functional treatment of bladder acontractility. Laparoscopic laser assisted auto-augmentation of the pediatric neurogenic bladder: early experience with urodynamic followup. Bladder auto-augmentation-an alternative for enterocystoplasty: preliminary results. Differences in urodynamic study variables in adult patients with neurogenic bladder and myelomeningocele before and after augmentation enterocystoplasty. Reconstruction of the urinary bladder by auto-augmentation, enterocystoplasty, and composite enterocystoplasty. Laparoscopic bladder auto-augmentation in an incomplete traumatic spinal cord injury. Sigmoidocolocystoplasty with ureteral reimplantation for treatment of neurogenic bladder. Bladder augmentation and urinary diversion in patients with neurogenic bladder: non-surgical considerations. Simultaneous Malone antegrade continent enema and Mitrofanoff principle using the divided appendix: report of a new technique for prevention of stoma complications. Improved quality of life and sexuality with continent urinary diversion in quadriplegic women with umbilical stoma. Comparison of long-term renal function after spinal cord injury using different urinary management methods. Urinary diversion and orthotopic bladder substitution in children and young adults with neurogenic bladder: a safe option for treatmentfi Intermittent self-catheterization by quadriplegic patients via a catheterizable Mitrofanoff channel. Transverse retubularized sigmoidovesicostomy continent urinary diversion to the umbilicus. Prospective study of the impact on quality of life of cystectomy with ileal conduit urinary diversion for neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Functional outcomes after management of end-stage neurological bladder dysfunction with ileal conduit in a multiple sclerosis population: a monocentric experience. Retubularization of the ileocystoplasty patch for conversion into an ileal conduit. Ileovesicostomy for the neurogenic bladder patient: outcome and cost comparison of open and robotic assisted techniques. Bladder augmentation versus urinary diversion in patients with spina bifida in the United States. Fate of 90 children with ileal conduit urinary diversion a decade later: analysis of complications, pyelography, renal function and bacteriology. Advantages and risks of ileovesicostomy for the management of neuropathic bladder. Incontinent ileo-vesicostomy urinary diversion in the treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction. Treatment of urinary tract infection in persons with spinal cord injury: guidelines, evidence, and clinical practice. Nitrite and leukocyte dipstick testing for urinary tract infection in individuals with spinal cord injury. Urinary tract infections in patients with spinal cord lesions: treatment and prevention. Urinary tract infections in spinal cord injury: prevention and treatment guidelines. Detrusor botulinum toxin A injection significantly decreased urinary tract infection in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury. Hydrophilic catheters versus noncoated catheters for reducing the incidence of urinary tract infections: a randomized controlled trial. Evaluation of 3 methods of bladder irrigation to treat bacteriuria in persons with neurogenic bladder. Oral immunotherapy in paraplegic patients with chronic urinary tract infections: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Multicenter randomized controlled trial of bacterial interference for prevention of urinary tract infection in patients with neurogenic bladder. Usefulness of classical homoeopathy for the prevention of urinary tract infections in patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction: a case series. Comparative effectiveness and safety of oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Treating erectile dysfunction and central neurological diseases with oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. Efficacy and safety of medium and long-term tadalafil use in spinal cord patients with erectile dysfunction. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in spinal cord-injured men. A double blind, randomised study of sildenafil citrate for erectile dysfunction in men with multiple sclerosis. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil for erectile dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic men: a randomized doubleblind and placebo-controlled study. Optimization of sexual function outcome after radical prostatectomy using phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. Prospective comparison of topical minoxidil to vacuum constriction device and intracorporeal papaverine injection in treatment of erectile dysfunction due to spinal cord injury. Vacuum erection device in spinal cord injured men: patient and partner satisfaction. The application of intracavernous injection of vasoactive medications for erection in men with spinal cord injury. Treating men with predominantly nonpsychogenic erectile dysfunction with intracavernosal vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and phentolamine mesylate in a novel auto-injector system: a multicentre double-blind placebo-controlled study. Use of intracavernous injection of prostaglandin E1 for neuropathic erectile dysfunction. Intracavernous pharmacotherapy for management of erectile dysfunction in multiple sclerosis patients. Intraurethral alprostadil for treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with spinal cord injury. Penile prostheses for the management of the neuropathic bladder and sexual dysfunction in spinal cord injury patients: long term follow up. Penile prosthetic surgery in neurologically impaired patients: long-term followup. Prostatic massage: a simple method of semen retrieval in men with spinal cord injury. Electroejaculation versus vibratory stimulation in spinal cord injured men: sperm quality and patient preference. A comprehensive approach to the management of male infertility following spinal cord injury. Application of 2 vibrators salvages ejaculatory failures to 1 vibrator during penile vibratory stimulation in men with spinal cord injuries.
Buy lanoxin online pills
Acquired hemoglobinopathies include modifications of the hemoOf the many methods available for hemoglobin analyglobin molecule by toxins hypertension 1 buy lanoxin with a visa. Comparison of results obtained in each system Hemoglobinopathies are especially common in usually allows unambiguous diagnosis, but some imporareas in which malaria is endemic. HbA2 is frequently elevated in fi-thalassemia trait and depressed in iron deficiency. In most laboratories, quantitation is performed Capillary venule occlusion Shortened red cell only if the test is specifically ordered. The boxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin, employing specrigid adherent cells also clog small capillaries and trophotometric techniques, can readily be obtained from venules, causing tissue ischemia, acute pain, and gradual most clinical laboratories on an urgent basis. This venoocclusive component usuComplete characterization, including amino acid ally dominates the clinical course. Prominent manifestasequencing or gene cloning and sequencing, is available tions include episodes of ischemic pain. The prototype disease, sickle cell by recognition of a characteristic history, physical findanemia, is the homozygous state for HbS (Table 8-2). However, natural history and drug the sickle cell syndromes are caused by a mutation in therapy trials suggest that an increase in the hematocrit the fi-globin gene that changes the sixth amino acid and feedback inhibition of reticulocytosis might be 6 Glu>Va1 beneficial, even at the expense of increased blood visfrom glutamic acid to valine. Sickled painful crises, infectious episodes, and other intercurrent cells lose the pliability needed to traverse small capillaries. They possess altered sticky membranes (especially reticVasoocclusion causes protean manifestations. Chronic lower leg manifested by acute pain and tenderness, fever, tachycarulcers probably arise from ischemia and superinfection dia, and anxiety. Their Acute chest syndrome is a distinctive manifestation charfrequency and severity vary greatly. Pain can develop acterized by chest pain, tachypnea, fever, cough, and almost anywhere in the body and may last from a few arterial oxygen desaturation. Repeated crises requiring hospitalizapulmonary emboli, bone marrow infarction and embolism, tion (more than three per year) correlate with reduced myocardial ischemia, or in situ lung infarction. Acute survival in adult life, suggesting that these episodes are chest syndrome is thought to refiect in situ sickling associated with accumulation of chronic end-organ within the lung producing pain and temporary puldamage. Often it is difficult or impossible to excessive exercise, anxiety, abrupt changes in temperadistinguish among other possibilities. Acutely, reduction in arterial oxyof life, causing susceptibility to infection, particularly by gen saturation is especially ominous because it promotes pneumococci. Chronic acute or subacute (splenic sequestration crisis), a rare occurrence in early pulmonary crises lead to pulmonary hypertension and childhood, may require emergency transfusion and/or cor pulmonale, an increasingly common cause of death splenectomy to prevent trapping of the entire arterial as patients survive longer. Occlusion of retinal Sickle cell syndromes are remarkable for their clinical vessels can produce hemorrhage, neovascularization, and heterogeneity. Renal papillary necrosis invariably matic into or even through adult life, whereas others produces isosthenuria. More widespread renal necrosis suffer repeated crises requiring hospitalization from early leads to renal failure in adults, a common late cause of childhood. The hand-foot syncell anemia, is frequently marked by lesser degrees of drome is caused by painful infarcts of the digits and hemolytic anemia and a greater propensity for the develdactylitis. Stroke is especially common in children; a opment of retinopathy and aseptic necrosis of bones. Stroke is most respects, however, the clinical manifestations resemless common in adults and is often hemorrhagic. Some rare hemoglobin variants ticularly painful complication in males is priapism, due to actually aggravate the sickling phenomenon. The clinical infarction of the penile venous outfiow tracts; permanent variability in different patients inheriting the same disease-causing mutation (sickle hemoglobin) has made 87 sickle cell disease the focus of efforts to identify modifying genetic polymorphisms in other genes that might account for the heterogeneity. To date, these genome screening efforts have not yielded modifying genes, other than those known to affect the hemoglobin profile directly. Nevertheless, a number of interesting patterns have emerged from these modifying gene analyses. The elongated and crescent-shaped red cytokine expression appear to be modifying candidates. Patients with a history of cerebrovascular accidents are at higher risk for Clinical Manifestations of Sickle Cell Trait repeated episodes and require especially close monitoring using Doppler carotid fiow measurements. Anemia and with severe or repeated episodes of acute chest synpainful crises are exceedingly rare. An uncommon but drome may need lifelong transfusion support, using parhighly distinctive symptom is painless hematuria often tial exchange transfusion, if possible. Familiarity with the pattern of sympDiagnosis toms provides the best safeguard against excessive use of the emergency department, hospitalization, and Sickle cell syndromes are suspected on the basis of habituation to addictive narcotics. Diagnosis is conmonitor development of retinopathy; antibiotic profirmed by hemoglobin electrophoresis and the sickling phylaxis appropriate for splenectomized patients durtests already discussed. Pneumococcal and Haemophilus usually established in childhood, but occasional patients, infiuenzae vaccines are less effective in splenectomized often with compound heterozygous states, do not individuals. Thus patients with sickle cell anemia should develop symptoms until the onset of puberty, pregnancy, be vaccinated early in life. Genotyping of family members and the management of acute painful crisis includes potential parental partners is critical for genetic counselvigorous hydration, thorough evaluation for underlying ing. Details of the childhood history establish prognosis causes (such as infection), and aggressive analgesia and need for aggressive or experimental therapies. Inhalation of nitrous oxide can provide shorta major role in the pathogenesis of sickle cell crisis, and term pain relief, but great care must be exercised to their suppression may be an important benefit of avoid hypoxia and respiratory depression. Hydroxyurea should be considered in patients expeIts use should be restricted to experts. Many crises can riencing repeated episodes of acute chest syndrome or be managed at home with oral hydration and oral analwith more than three crises per year requiring hospitalgesia. The usefulness of this agent for reducing the reserved for especially severe symptoms or circumincidence of other complications (priapism, retinopathy) stances in which other processes. Nasal oxygen should be employed Hydroxyurea offers broad benefits to most patients as appropriate to protect arterial saturation. HbF levels reserved for extreme cases: transfusions do not shorten increase in most patients within a few months. The antitumor drug 5-azacytidine was the first agent No tests are definitive to diagnose acute painful found to elevate HbF. Critical to good management is an approach that use because of concerns about acute toxicity and carrecognizes most patients reporting crisis symptoms do cinogenesis. However, low doses of the related agent indeed have a crisis or another significant medical prob5-deoxyazacytidine (decitabine) can elevate HbF with lem. In adults, the possibility of aseptic necrosis or cures but is known to be effective and safe only in chilsickle arthropathy must be considered, especially if pain dren. Prognostic features justifying bone marrow transand immobility become repeated or chronic at a single plant are the presence of repeated crises early in life, a site. Nonsteroidal anti-infiammatory agents are often high neutrophil count, or the development of hand-foot effective for sickle cell arthropathy. Children at risk for stroke can now be identiAcute chest syndrome is a medical emergency that fied through the use of Doppler ultrasound techniques. Prophylactic exchange transfusion appears to reduce Hydration should be monitored carefully to avoid the the risk of stroke substantially in this population.
Discount 0.25 mg lanoxin with mastercard
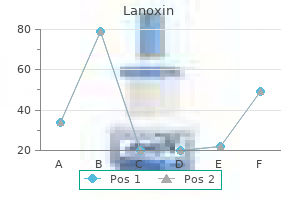
Girls were found to have a larger capacity than boys blood pressure chart pictures purchase lanoxin no prescription, but the rate of increase with age was not significantly different between them. Data obtained from the International Reflux Study indicate that there is not a linear relation between age and capacity and that there is a huge variability (Figure 3). Kaefer and co-workers demonstrated that a non-linear model was the most accurate for the relation between By age 12, the daily pattern of voiding includes 4-6 age and bladder capacity, and they determined two voids per day [17]. Grade of recommendation: B As in adults, flow rates are clearly dependent upon voided volume, and normal values can only be applied Many signs and symptoms related to voiding and to flow rates that have been registered when voiding wetting are new to the parents, and they should be at a bladder volume approximating the normal capacity specifically asked for, using the questionnaire as for age [18,21]. If possible the child should be addressed as the patient and questioned directly, as the symptoms prompting the parents to seek consultation may be different from those are problematic for the child. Checklists and frequency volume chart can be filled out at home, Even with clear definitions, the approach to historyand checked at the first visit to the clinics. Also, the general history-taking should include questions sociocultural aspects and psychomotor development relevant to familial disorders, neurological and will distort the presentation. Validated questionnaires congenital abnormalities, as well as information on are very helpful in structuring the history-taking; they previous urinary infections, relevant surgery and at least provide checklists [1]. Information should be obtained on monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis can be made medication with known or possible effects on the lower with confidence. This is important in view of the potential these conditions have to cause irreversible loss of kidney Level of evidence: 4. Asymmetry of buttocks, legs or feet, as well In order to be comprehensive, physical examination as other signs of occult neurospinal dysraphism in should include urinalysis to identify patients with the lumbosacral area (subcutaneous lipoma, skin urinary tract infection, diabetes mellitus, diabetes discoloration, hair growth and abnormal gait) should insipidus and hypercalciuria if indicated [9]. In pelvic floor relaxation and obstructing the free flow of order to obtain a complete picture, defecation urine [8] (Figure 4). Grade of recommendation: D Then, this becomes termed as bladder-bowel diary due to its complexity. Whenever possible, filling out the chart is the responsibility of the child: the parents provide assistance and support. Ideally the chart should cover 3 complete days, but in reality completion over a weekend restricts the record to 2 days. The frequency volume chart is a reliable non-invasive measure of maximum bladder storage capacity and can be used as an outcome measure in children with bladder dysfunction if care is taken to minimise confounding factors and sources of error during chart completion [10]. Children with bladder symptoms void smaller volumes of urine than may be expected from traditional estimates [10]. Figure 4: Improper position for voiding: the feet are this is unrelated to either gender, type of presenting not supported (unbalanced position) and the body is bent forward. Support of the feet will correct this incontinence or a positive family history of bladder and will allow the pelvic floor muscles to relax dysfunction. Data in normal children and children without constipation the mean diameter was in children with different categories of incontinence are 2,4 and 2,1 cm in two different studies respectively [23available for comparison [10-12]. In children with constipation the rectal diameter was on average 3,4 cm in one and 4,9 in the second In order to obtain a complete picture it is better to ask study. Both studies do not mention specificity nor for a bladder diary: fluid intake as well as voiding sensitivity. Finding a dilated and filled rectum on frequency, voided volumes, incontinence episodes ultrasound while the child feels no need to defecate and defecation frequency and/or soiling are recorded. Test/retest evaluation is not available; trend analyses Overt constipation should be dealt with before of frequency/volume charts can be extracted from embarking on treatment of incontinence or detrusor currently available data. For objective children with the exception of monosymptomatic grading, 12-hour pad test and frequency/volume charts bedwetting where voiding, as far as we know, is are validated instruments [12-14]. In children, the 12-hour pad test should also give Graphic registration of the urinary flow rate during information about fluid intake. Flow patterns complementary to the bladder diary, which denotes and rates should be repeated to allow for evaluation, more the frequency of incontinence and the distribution and several recordings are needed to obtain of wetting episodes than the quantities of urine lost. The amount of urine lost during sleep can be deterApproximately 1% of school children have a voiding mined by weighing diapers or absorbent pads, before that can be labelled abnormal with flattened or and after sleep. The remaining 99% have a nocturnal urine output, the volume of the early-morning bell-shaped flow curve [27]. It should be noted that a voiding should be added to the amount lost during normal flow does not exclude a voiding disturbance, sleep. Specific scores correlated with lower urinary tract dysfunction with a Flow recordings with a voided volume of less than specificity and sensitivity of about 90% [15,16]. If the bladder is still nearly empty the child should be asked to drink some water until the bladder Level of evidence: 3. An intermittent flow pattern [17-19] Reproducibility seems to be best using the shows a interrupted flow, whereas in fluctuating voiding method described by Leech [20-22]. A better way to match clues from the medical history with signs and symptoms is the measurement of Measurement of urinary flow is performed as a solitary colonic transit time. In measuring flow time, the time intervals In most clinical settings, ultrasound-imaging techniques between flow episodes are disregarded. Grade of recommendation: B can be readily detected, but detection of the more subtle expressions of these abnormalities require urological expertise on the part of the ultrasound operator [33]. Lower urinary tract abnormalities are even more difficult to assess for the inexperienced, aside from bladder wall thickness: a bladder wall cross-section of more than 3-4 millimetres, measured at 50% of expected bladder capacity, is suspicious of detrusor overactivity [34,35]. Because only a few studies have been conducted to compare bladder wall thickness in normal children without complaints and in children with lower urinary tract dysfunction, more studies need to be performed to validate these non-invasive techniques [36, 37]. Another possibility is to assess bladder volume and bladder wall thickness to calculate the Bladder Volume / Bladder Wall Thickness index. In children with nocturnal enuresis this index correlated well with response to treatment [38]. The identification or exclusion of post-void residual is therefore an integral part of the study of micturition. However, an uneasy child voiding in unfamiliar Figure 6: flow curve of 2 children with a static, Figure 7: intermittent flow curve in a child with anatomic obstruction; the curve is continuous but disco-ordination between detrusor contraction the flow is lower than normal and extended in time. Urinary flow may voiding on command with a partially filled or registration will detect the plateau-shaped flow curve overfilled bladder. This is of particular importance if the patient A clinically significant post-void residual on repeated is in a diuretic phase. In patients with gross occasions clearly points to incomplete bladder vesicoureteral reflux, urine from the ureters may enter emptying. The pad test will detect the cases with the bladder immediately after micturition and may obvious stress and urgency incontinence, or falsely be interpreted as residual urine. Ultrasound imaging will raise of residual urine is an observation of clinical value, but suspicion of an ectopic ureter. An In short, invasive diagnostics are indicated when the isolated finding of residual urine requires confirmation non-invasive testing raises suspicion of neurogenic before being considered significant, especially in detrusor-sphincter dysfunction (occult spinal infants and young children. With ultrasound, bladder filling is assessed and when the To diagnose the complex of non-neurogenic bladder capacity is equal to the functional or expected detrusor-sphincter dysfunction, recurrent urinary bladder capacity for age, the child is asked to void into tract infections and vesicoureteral reflux, urodythe flowmeter.
| Comparative prices of Lanoxin | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Best Buy | 964 |
| 2 | Barnes & Noble | 655 |
| 3 | The Home Depot | 512 |
| 4 | Target | 858 |
| 5 | Dollar Tree | 868 |
| 6 | Army Air Force Exchange | 104 |
| 7 | Alimentation Couche-Tard | 833 |
| 8 | Macy's | 859 |
| 9 | CVS Caremark | 467 |
| 10 | Limited Brands | 137 |
Order genuine lanoxin line
Hb synthesis and there are a number of other condiCut off tions and diseases which influence the Hb concenChildren tration hypertension signs and symptoms treatment purchase discount lanoxin. If this is not possible, an Children <120 g/L alternative can be to compare the Hb distribution aged 12-13 years curve from young children, women in childbearing Men <130 g/L age and men. If the shift between men and the other Non-pregnant women <120 g/L groups is bigger than in a standard reference group it indicates that the iron supply is not enough for Pregnant women <110 g/L young children and women, who have a relative higher requirement than men (2). Another solution is Currently the most important indicator for the to measure an indicator like sTfR, which is less iron status is the measurement of ferritin. Until now there are no plasma content correlates well with the iron clear cut off values for ferritin but they usually stores, and in the first stage of iron deficiency the range between 10 and 30 mg/L. A ferritin value concentration of ferritin already decreases, which below 10 mg/L certainly shows iron deficiency. Low ferBecause of its common use the cost for ferritin ritin always indicates storage iron depletion. The cost of the chemicals for immunovalue is not inevitably a sign of a good iron status. By including a standard parameters for acute and chronic infection, to disclinical chemistry control, which usually has valcover subjects in which the ferritin concentration ues for ferritin in different concentrations, it is might be increased by infection. Effect Race African descent 5-10 g/L lower Smoking 3-7 g/L higher Living in altitude 1000 m 1 g/L higher 1500 m 4 g/L higher 2000 m 7 g/L higher 2500 m 12 g/L higher 3000 m 18 g/L higher 40 H. The lowest ferritin concenthe hematocrit usually correlates well with Hb, tration in the clinical controls is also mostly relabut is even less sensitive for iron deficiency than tively high (around five times more than the cut Hb. Therefore it is not a very helpful indicator in off value) which can make the calculation of the diagnosis of nutritional anemia. The sTfR is released from the cells into the and a reduced size of the erythrocytes indicate iron blood stream depending on the iron requirements. A large number of clinical disorders affect of iron deficiency, after the iron stores are exthe transferrin saturation (1) and plasma iron has a hausted and the Hb concentration is still above the marked diurnal variation. Therefore ferritin/sTfR are usually the correlate very well it is relatively easy to get the more useful indicators under these circumstances. It is a very simthe calculation of the iron stores in mg/kg body ple and robust measurement and can be useful in weight similar to the results of bone marrow screening for iron deficiency (5). If this is not corrected it can have significant influence on the detection of anemia prevalence (8), especially when a large number of subjects Dried blood spots have Hb values around the cut off value. The best solution would is to centrifuge the sample and to measure ferritin be to have a robust method in the field to measure in dried plasma spots (9, 10). Therefore strict ples on filter paper can be an alternative rules have to be followed (good drying overnight (Figures 4. Assessment and C-reactive protein by an inexpensive, sensitive, of the prevalence and the nature of iron deficiency and simple sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorfor populations: the utility of comparing hemoglobin bent assay technique. Erythrocyte protoporphyrin spots from capillary and venous blood in children in or hemoglobin: which is a better screening test for Sri Lanka: a validation study. Nevin has over 650 publications to his name and has authored or edited more than 20 books. In countries feeding and common complementary feeding where meat consumption is low, such as India and practices alone. This sumpopulation age and sex groups are shown in Figmary of the functional consequences of iron defiure 5. The first stage, depletion of iron ciency begins with a brief outline of the iron stastores, has no functional changes. Where iron tus in humans in general, and the variations that stores are exhausted, and tissues begin to have are normal at different life stages for males and insufficient iron, the resulting condition is iron females. Negative effects, which have been from iron excess to degrees of iron deficiency found among those who are iron deficient but not anemia. Although iron needs vary for different outright anemic, include cognitive impairment, groups based on such factors as rapid growth (late decreased physical capacity, and reduced immuinfancy, adolescence, pregnancy) and differences nity, and are more serious with iron deficiency in normal iron losses (menstruation, childbirth), a anemia (7). Women tend to have substantially lower iron stores than men (one eighth of total body iron in A normal male body has in total approxiwomen compared to one third in men), making mately 4. Women iron is in hemoglobin in circulating red cells and of reproductive age lose iron during menses and in the muscle protein myoglobin. Negative iron stores indicate the amount of iron that must be replaced in circulating red cells before iron reserves can re-accumulate. Age or sex group Hemoglobin below g/dL Hematocrit below (%) Children 6 months to 5 years 11. Iron is also found in many essential increase cardiac output and redirect blood flow to iron dependent enzymes and other biochemically the heart muscles and brain (8). During the second half of pregnancy the iron with the pallor that reflects anemia, and current scirequired cannot be easily met by diet (9). Even ence points to adverse functional consequences most healthy women do not have sufficient body from iron deficiency even before anemia is present. Even Considerable emphasis is placed on reducing the though pregnant women have been shown to prevalence of iron deficiency in infancy and early absorb more iron from foods, a high prevalence of childhood, because a large body of evidence indianemia during the third trimester of pregnancy cates that poor iron status negatively affects coghas been consistently shown. In the United States nitive, motor and social development during this approximately 30% of pregnant women from period of rapid growth and development (14) Iron lower income groups are found to be anemic (11). Increased risk of maternal at which anemia occurs and its severity, some death may be related to several factors, including developmental deficits can be improved or even cardiac failure during labor with severe anemia to corrected with iron treatment, but with iron defilower tolerance of hemorrhagic blood loss during ciency in infancy some cognitive and social difchildbirth. All of these facthe risk of iron deficiency is high during tors require further research. Where well fortified infant cereals are Her infant is at greater risk of death, and is more available and affordable, they provide the relikely to be below normal birth weight and to be quired iron, as does iron fortified infant formula. Such an infant is more likely to become iron deficient and anemic the high risk of iron deficiency anemia in before six months of age. Scrimshaw 18 16 Anemia 14 Means +/2 Standard deviations 12 10 8 5 One month age cohorts Figure 5. Studies have also found the infants of mothers suffering from anemia durIron deficient schoolchildren in Indonesia and ing pregnancy have lower iron stores at birth. India have been found to have poorer perforCutting the pulsing umbilical cord before iron mance than those with normal iron status, and rich cord blood is transferred to the newborn also lower performance could be substantially imresults in lower iron in the infant at birth. Low proved after 12 weeks of iron supplementation birth weights account for up to 20% of infants in (19, 20). The area weeded by Thai language mathematics and other subjects formerly anemic workers increased with the iron than iron replete children. Among women there was no significant improvement following in Indonesia and men in Sri Lanka (26) working 14 weeks of daily iron supplementation that on tea plantations the productivity of iron defirestored hemoglobin levels to normal. It was sugcient individuals was significantly less than those gested that their iron deficiency as schoolchildren with normal hemoglobin concentrations. After reflected the iron deficiency that they had sufsupplementation with iron, the iron deficient subfered in infancy. Iron deficiency is disadvantageous to achievement of schoolchildren in various environments Once work capacity has been reduced by iron and across cultural groups, with serious implicadeficiency anemia, blood transfusion that restores tion for the effectiveness of education in many blood hemoglobin levels does not improve perdeveloping countries. Iron deficultural workers was found linearly related to ciency was reported to be associated with intheir hemoglobin status (Figure 5. It returned creased diarrheal and respiratory diseases in a to normal with iron supplementation (24). Morbidity from infections bin status was shown to affect work output and among anemic rubber tappers decreased after iron productivity-linked take home pay. When rubber supplementation in an Indonesia study (9, 32), tappers were given iron supplementation for and decreases in diarrheal and respiratory infec60 days, their pay increased by more than 30% tions were observed in family members receiving (25).
Discount lanoxin online
Treatment of post-prostatectomy incontinence with male slings in patients with impaired detrusor contractility on urodynamics and/or who perform Valsalva voiding fetal arrhythmia 34 weeks buy lanoxin master card. Successful outcome of artificial urinary sphincters in men with post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence despite adverse implantation features. Do clinical or urodynamic parameters predict artificial urinary sphincter outcome in post-radical prostatectomy incontinencefi Urodynamic parameters evolution after artificial urinary sphincter implantation for postradical prostatectomy incontinence with concomitant bladder dysfunction. Association between detrusor overactivity and postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing male bone anchored perineal sling. Male stress urinary incontinence: A review of surgical treatment options and outcomes. Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men: Etiology, Patient Assessment, and Predicting Outcome from Therapy 131 342. Prognostic role of prostate-specific antigen and prostate volume for the risk of invasive therapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia initially managed with alpha1-blockers and watchful waiting. Alfuzosin 10 mg once daily prevents overall clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia but not acute urinary retention: Results of a 2-year placebo-controlled study. Response to daily 10 mg alfuzosin predicts acute urinary retention and benign prostatic hyperplasia related surgery in men with lower urinary tract symptoms. Efficacy of alpha blocker treatment according to the degree of intravesical prostatic protrusion detected by transrectal ultrasonography in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Development of nomogram to predict acute urinary retention or surgical intervention, with or without dutasteride therapy, in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Sustained-release alfuzosin and trial without catheter after acute urinary retention: A prospective, placebo-controlled trial. Alfuzosin once daily facilitates return to voiding in patients in acute urinary retention. Alfuzosin 10 mg once daily in the management of acute urinary retention: Results of a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Tamsulosin in the management of patients in acute urinary retention from benign prostatic hyperplasia. Management of acute urinary retention: A worldwide survey of 6074 men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Intravesical prostatic protrusion is better than prostate volume in predicting the outcome of trial without catheter in white men presenting with acute urinary retention: A prospective clinical study. The 12-year symptomatic outcome of transurethral resection of the prostate for patients with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction compared to the urodynamic findings before surgery. Grading of benign prostatic obstruction can predict the outcome of transurethral prostatectomy. Urodynamic pressureflow studies can predict the clinical outcome after transurethral prostatic resection. Diagnostic and predictive value of voiding diary data versus prostate volume, maximal free urinary flow rate, and Abrams-Griffiths number in men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Analysis of the prognostic factors for overactive bladder symptoms following surgical treatment in patients with benign prostatic obstruction. Effect of the ratio of resected tissue in comparison with the prostate transitional zone volume on voiding function improvement after transurethral resection of prostate. Influence of prostate size on the outcome of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. Holmium laser prostatic resection for patients presenting with acute urinary retention. GreenLight laser vaporization of the prostate: Single-center experience and long-term results after 500 procedures. Vaporization of prostates of > or =80 mL using a potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser: Midterm results and comparison with prostates of <80 mL. Impact of prostate volume on the efficacy of high-power potassium-titanyl-phosphate photoselective vaporization of the prostate: A retrospective, short-term follow-up study on evaluating feasibility and safety. Photoselective vaporization of the prostate: Pursuing good indications based on the results of 400 Japanese patients. Photoselective vaporization of the prostate: Subgroup analysis of men with refractory urinary retention. Urodynamic predictors of outcomes with photoselective laser vaporization prostatectomy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and preoperative retention. Blanker, the Netherlands Hashim Hashim, United Kingdom Varant Kupelian, United States Stephen Marshall, United States Kari A. It is characterized by idiosyncratic response, with nocturia of equivalent severity producing very different effects on quality of life for different people. Speed of progression of nocturia is likely to influence propensity to present for medical consultation; implicitly, slower progression will enable coping adaptations that ameliorate bother, the latter being the ultimate arbiter of whether medical opinion is sought. Speed of progression is difficult to capture, as are other crucial influences, such as contextual environmental influence, personality trait, and coping strategies, and thus the complex interplay between severity and bother remains unclear. Day-by-day variation, habitual differences between work and non-work days, and temporal fluctuation over extended time periods hamper the reliable capture of a severity score. The terminology needs to not only be straightforward and manageable, but also deal with varied circumstances, such as shift workers (for whom nocturia may be a daytime event). Furthermore, the medical priority accorded to nocturia does not reflect the potential seriousness of possible underlying conditions. Many physicians disregard nocturia occurring on average once per night, stating that it does not bother the patient or represent a health risk. This is probably a mistake, as it is a state that has progressed from no nocturia, and may continue to progress to bother the patient subsequently. Thus, nocturia once per night might represent an opportunity for screening and instigation of measures to prevent progression to bothersome nocturia. There is merit to ascertaining severity thresholds above which nocturia becomes clinically significant or below Nocturia 139 which adequate therapeutic benefit can be claimed. However, it is essential that these are defined for specific populations and not extrapolated to all patients. For example, a threshold value for a healthy working person is likely to differ from that of a healthy older person or someone with neurological disease where multiple causes of sleep disturbance may be present. Even with the greater strength of proper assessment, inability to capture the issues alluded to above mandates caution in interpreting results. The extensive evidence base concerning nocturia is reflected in this chapter, but much of it fails to meet contemporary standards for high-quality evidence. When some of the interventions are potentially morbid, a strong case for their use is needed; without scientifically rigorous evaluation, such interventions should be avoided. The symptom of nocturia is the complaint that the individual has to wake at night one or more times to void. This definition does not include any reference to bother; many physicians regard nocturia once per night as not being clinically significant. However, some people can be substantially bothered by nocturia once per night, and the potential for symptom progression or a serious underlying medical condition means that a single episode of nocturia per night may have more importance than it is often given credit for. Nocturnal enuresis signifies voiding while remaining asleep and, technically, should be considered part of the nocturnal voided volume, though difficult to quantify in practice. The terminology in current use necessarily involves some compromise (8,9), and the area is one in which debate and consensus is ongoing. In general, the definition of a condition is a crucial factor in the evaluation of its epidemiology; nocturia is no exception (13). However, it has been suggested that if the definition needs to address the issue of sleep following the void, it may be the intention of going back to sleep after voiding which might be more clinically relevant (16).
Generic lanoxin 0.25mg otc
At necropsy arteria y vena poplitea purchase genuine lanoxin online, this was administration of steroids, which makes it a highly reflected in tubulorrhectic nephrosis with haespecific and sensitive marker (Xenolius et al. The latter has been described tem study of the case described here confirmed in chronic inflammatory conditions, resulting from chronic hepatobiliary damage due to mild periimmune system disorders (Brockus and Andreasen portal liver fibrosis with hepatic cord dissociation. Another known complication of acute pancreaWhen the complications in this animal suffering titis in humans is the development of acute renal the effects of acute pancreatitis are listed, i. The occurrence of this renal failure, haemolytic anaemia and thrombocycomplication is influenced by factors such as hytopaenia, it may be possible that it was developing povolaemia and renal endothelial damage caused one of the complications that occur in humans with by a severe systemic inflammatory response. Rare cases have been velopment of hypovolaemia, primarily by vomitreported in horses, dogs and cattle, but of gastroing that leads to a significant loss of chloride and enteric origin (Chantrey et al. One possible mechanism is that ischaemia leads to acute kidney injury and metaendothelial damage itself triggers it. The inflambolic acidosis is triggered by the accumulation of matory response to acute pancreatitis can trigger phosphate and sulphate. It is rare Moreover, special attention should be paid to the during acute pancreatitis, although if it occurs, it time of blood sampling for laboratory analysis and has a sudden onset and clinical manifestations may serum amylase activities must be correlated with be heterogeneous, even leading to death without the date of the pancreatic attack. Klimes J, Vlasin M, Svobodova V (2000): Diseases of In this case, it is difficult to determine what the gastrointestinal system and peritoneum. Sinha A, Rai R (2005): Haemolytic uraemic syndrome In conclusion, for the diagnosis of acute pancreafollowing acute pancreatitis. Executive summary of recommendations Prepregnancy counselling Women with red cell antibodies, particularly if there is a risk of fetal anaemia or if compatible donor red cells for transfusion may be difficult to obtain, should attend for prepregnancy counselling with a P clinician with knowledge and expertise of this condition. Red cell antibodies in pregnancy What red cell antibodies are clinically significant (maternal and fetal) during pregnancyfi All women should have their blood group and antibody status determined at booking and at 28 weeks D of gestation (Appendix 2). Clinicians should be aware that severe fetal anaemia can result in hydrops which significantly worsens D the perinatal outcome. Non-invasive fetal genotyping using maternal blood is now possible for D, C, c, E, e and K antigens. This C should be performed in the first instance for the relevant antigen when maternal red cell antibodies are present. P Anti-D prophylaxis should be given to cover invasive testing if the mother is rhesus D (RhD) negative D and is not sensitised. If the fetus is at risk of anaemia, when should referral to a fetal medicine specialist take placefi What thresholds should be used for the various antibodies that could cause fetal anaemia to trigger referral for further investigation or monitoringfi Referral for a fetal medicine opinion should therefore be made once anti-D levels are > 4 iu/ml. Referral for a fetal medicine opinion should therefore be made once anti-c levels are > 7. For anti-K antibodies, referral should take place once detected, as severe fetal anaemia can occur even with low titres. Anti-D and anti-c levels should be measured every 4 weeks up to 28 weeks of gestation and then every D 2 weeks until delivery. Although anti-K titres do not correlate well with either the development or severity of fetal anaemia, D titres should nevertheless be measured every 4 weeks up to 28 weeks of gestation, then every 2 weeks until delivery. For antibodies that could potentially cause problems with cross-matching or issues with the availability of appropriate blood, discussion with the blood transfusion service is required regarding the frequency P of antenatal testing. This may depend on the type of antibody as well as the likelihood of requiring blood at short notice. P If the fetus carries the corresponding antigen for a maternal antibody which is capable of causing fetal B anaemia and if the antibody levels/titres rise beyond the levels detailed in section 6. For antibodies other than anti-D, anti-c, anti-C, anti-E or anti-K, maternity staff should liaise with their local transfusion laboratory to assess and plan for any possible transfusion requirements, as obtaining P the relevant blood may take longer. How often should pregnant women with red cell antibodies who are at high risk of requiring a transfusion (placenta praevia, sickle cell disease etc. Pregnant women with red cell antibodies, who are assessed as being at high risk of requiring a blood transfusion, should have a cross-match sample taken at least every week. P If maternal transfusion is required, what type of donor blood or blood components should be usedfi Should RhD-negative women who have anti-D or non-anti-D antibodies receive routine antenatal or postnatal prophylaxisfi Anti-D immunoglobulin should be given to RhD-negative women with non-anti-D antibodies for routine B antenatal prophylaxis, for potential antenatal sensitising events and postnatal prophylaxis. D Discussion and liaison with the transfusion laboratory are essential in determining whether anti-D D antibodies are immune or passive in women who have previously received anti-D prophylaxis. Requirements for blood What are the logistics of obtaining blood or blood components for the woman, fetus or neonatefi Close collaboration between the maternity, neonatology and haematology staff is essential. P When blood is required for women with multiple antibodies or antibodies against high prevalence antigens, planning is required as rare blood donors may need to be called up to donate, or frozen blood P may need to be obtained from the National Frozen Blood Bank in Liverpool. What blood or blood components can be administered in the emergency situation to a woman known to have red cell antibodiesfi Timing of delivery for women with red cell antibodies that can cause fetal anaemia will depend on the antibody levels/titres, rate of rise as well as if any fetal therapy has been required. The mode, timing P and place of delivery are otherwise dependent on standard obstetric grounds. This depends on the risk of haemolysis or anaemia conferred by the relevant red cell antibody. The C neonate should have regular clinical assessment of its neurobehavioural state and be observed for the development of jaundice and/or anaemia. P the mother should be encouraged to feed the baby regularly to guard against dehydration, since dehydration can increase the severity of jaundice. P Clinicians should be aware that if bilirubin levels rise rapidly or above the interventional threshold, C phototherapy and/or exchange transfusion may be required. Pregnancies complicated by red cell alloimmunisation with a minimal or no risk of fetal or neonatal anaemia require no specific treatment. P Long-term consequences of red cell antibodies to women and their offspring What are the long-term health consequences for the womanfi P What are the long-term health concerns for the children of women with red cell antibodies during pregnancyfi Purpose and scope the purpose of this guideline is to provide guidance on the management of pregnant women with red cell antibodies predating the pregnancy or those developing antibodies during pregnancy. The guideline also includes the management of fetal anaemia caused by red cell antibodies, as well as the early management of the neonate at risk of anaemia and/or hyperbilirubinaemia. It does not address the management of the pregnant woman with anti-platelet antibodies or other autoimmune or alloimmune antibodies. Introduction and background epidemiology the presence of maternal red cell antibodies during pregnancy is a relatively common finding and requires close collaboration between the blood transfusion laboratory, obstetric and neonatal care providers. A population study from the Netherlands found that red cell antibodies were detected in 1. Some antibodies (including anti-D, anti-K (-Kell) and anti-c) confer significant fetal and neonatal risks such as anaemia requiring intrauterine or neonatal transfusion, jaundice or perinatal loss. There are many antibodies that are unlikely to significantly affect the fetus but can cause neonatal anaemia and hyperbilirubinaemia, while others may cause problems for the screening and provision of appropriate blood or blood components to the mother or fetus/neonate when required (Appendix 1).
Discount lanoxin online american express
High-dose cytarabine Heavy metals Arsenic trioxide arrhythmia band discount lanoxin 0.25mg otc, antimony is more effective than standard-dose cytarabine. Its with normal karyotypes who have other poor risk factors effectiveness in early relapsing (<6 months) or refractory. Pretreatdonor does not exist, novel therapeutic approaches are ment with glucocorticoids can diminish many of the infuconsidered. Other novel transplant strategies, including sion reactions associated with gemtuzumab ozogamicin. Bcr/Abl fusion proteins can transform Symptoms hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro. Furthermore, the clinical onset of the chronic phase is generally insidreconstituting lethally irradiated mice with bone marrow ious. Less inhibit the growth of t(9;22)-positive leukemic cells withcommon are features related to granulocyte or platelet out affecting normal colony formation. The events associated with transition to the acute phase, a common occurrence in the pre-imatinib era, were extensively studied. Persistent splenomegaly despite continued therapy is and/or molecular abnormalities is critical to the phenoa sign of disease acceleration. Large deletions adjacent to the myeloid sarcomas are unusual except late in the course of translocation breakpoint on the derivative 9 chromosome, the disease; when they are present, the prognosis is poor. The most commonly 177 blasts and promyelocytes are noted with most of the cells used staging systems have been derived from multivarimyelocytes, metamyelocytes, and band forms. The Sokal index identithe counts may be observed in patients followed without fied percentage of circulating blasts, spleen size, platelet treatment. Platelet counts are almost always elevated at count, age, and cytogenetic clonal evolution as the most diagnosis, and a mild degree of normocytic normoimportant prognostic indicators. It identified percentage of circulating blasts, spleen functions are usually normal at diagnosis and remain norsize, platelet count, age, and percentage of eosinophils and mal during the chronic phase. This ondary to basophilia is increased in later stages, causing system differs from the Sokal index by ignoring clonal pruritus, diarrhea, and fiushing. When applied to a data set of 272 patients an increased myeloid to erythroid ratio. Hyposegmented neutrophils may appear that has significant toxicity and a new targeted treat(Pelger-Huet anomaly). Blast cells can be classified as ment (imatinib) with excellent outcome based on 5-year myeloid, lymphoid, erythroid, or undifferentiated, based follow-up data. Therefore, physician experience and on morphologic, cytochemical, and immunologic feapatient preference must be factored into the treatment tures. The decision should focus on the outcomes, risks, and toxicities of the various Chromosomal Findings approaches. Hence the goal is complete 22 (22q-), designated as the Philadelphia chromosome, that molecular remission and cure. The Patient Patients should have acceptable endBefore imatinib mesylate, death was expected in 10% of organ function, be <70 years of age, and have a healthy, patients within 2 years and in ~20% yearly thereafter, histocompatible donor. Meawhich leads to inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of surement of busulphan levels revealed no significant proteins involved in Bcr/Abl signal transduction. It shows association between busulphan levels and regimenspecificity for Bcr/Abl, the receptor for platelet-derived related toxicity, but low levels were associated with an growth factor, and Kit tyrosine kinases. The complete transplants in which the preparative regimen is aimed at hematologic remission rate, at 18 months, of patients eliminating host lymphocytes rather than bone marrow. These results have led to a conpanied by a substantially higher transplant-related morsensus that molecular responses can be used as a treattality rate. Myelosuppression, although rare, in patients with advanced disease at the time of transplanmay require holding drug and/or growth factor support. Four mechanisms of resistance to imatinib have been Imatinib has also been combined with donor lymphocytes described to date. A role for toxicity profiles similar to imatinib with small but signiimatinib before stem cell collection to achieve minimal ficant differences. Therefore, we recomthe case, and splenectomy is now reserved for symptomend close monitoring of imatinib response, especially matic relief of painful splenomegaly unresponsive to in these patients (Table 14-4). Blast crisis following initial therapy with imatinib positivity at 6 months was regarded as an indication for carries a dismal prognosis even if treated with dasatinib additional therapy in the past, current studies utilize or nilotinib. Longo I Biology of Lymphoid Malignancies: Concepts of the Precursor Cell B Cell Neoplasms. These were easily subdivided into those of lymphoid or myeloid cancers arise from cells of the immune system at different origin based on morphologic characteristics. However, a stages of differentiation, resulting in a wide range of morspectrum of diseases that were formerly all called chronic phologic, immunologic, and clinical findings. When cytoSome malignancies of lymphoid cells almost always chemical stains became available, it was possible to present as leukemia. Using this system, lymphoid clinical pattern can change over the course of the illness. The distinction lymphoma Sezary syndrome between leukemia and lymphoma was made early, and Mantle cell lymphoma Smoldering adult T cell separate classification systems were developed for each. Imperfect form cells with basophilic and sometimes vacuolated morphologic systems were supplanted by imperfect cytoplasm were called L3. Major nancies was devised through a process of consensus develcytogenetic subgroups include the t(9;22). Specific energy radiation in early childhood increases the risk of lymphoma subtypes are dealt with in more detail later. In 2007, 15,340 new cases were diagnosed in the disease appears fairly stable, with 8190 new cases diagUnited States, but because of the prolonged survival nosed in 2007 in the United States. The rate lymphoma, nasal type of increase in the past few years seems to be decreasing. T cell lymphomas are more common in Asia with shorter latency and usually from transfusionthan in Western countries; certain subtypes of B cell transmitted virus. Infection of the stomach including infectious agents, chemical exposures, and medby the bacterium Helicobacter pylori induces the developical treatments. The virus is transmitted by Chronic hepatitis C virus infection has been associated infected lymphocytes ingested by nursing babies of with the development of lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma.

Purchase lanoxin mastercard
B symptoms (so-named because of their role in the Ann Arbor staging system described below) are defined as recurrent fever blood pressure medication diarrhea purchase 0.25mg lanoxin with amex, recurrent drenching night sweats, or unexplained loss of 10% body weight in a six-month period. Adapted from Skarin, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Atlas of Diagnostic Oncology, 1991. Since Hodgkin lymphoma spreads in a nonrandom fashion, and since treatment is designed according to extent of disease, it is most important to know the extent of disease. Radiotherapy is delivered to known areas of disease and immediately adjacent nodebearing tissue, taking into account the tendency for contiguous spread of the disease. More advanced disease is treated with repeated cycles of combination chemotherapy. Children do as well as adults, although the disease is rare under 10 years of age. With the improvement in prognosis, less aggressive treatment regimens are now being studied in an attempt to decrease the amount of therapy given to patients with favorable prognosis and thereby avoid some of the long-term side effects of therapy. Classification the classification of lymphoma has changed over the years with a better understanding of the underlying biology of the disease. Some forms of low grade lymphoma exhibit such indolent behavior that patients are not typically treated unless the disease is causing symptoms. They generally exhibit relentless (and in some cases very rapid) progression and are fatal if untreated. However, in contrast to low grade lymphomas, many patients can be cured with treatment. Most high grade lymphomas occur in middle age or later, but some (Burkitt lymphoma, for example) occur with appreciable frequency in children and young adults. The most common indolent lymphoma is follicular lymphoma (a B-cell lymphoma) and the most common aggressive lymphoma is diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Pathogenesis When a B cell passes through the germinal center of a lymph node and undergoes somatic hypermutation and class switching, it is particularly vulnerable to malignant transformation. Many lymphomas are the result of chromosomal translocations involving various oncogenes and the promoter for the IgH gene on chromosome 14. The result is a rather indolent lymphoma characterized by slow accumulation of malignant cells in lymph nodes resulting in lymph node enlargement. The t(8;14) that characterizes Burkitt lymphoma places the c-myc oncogene (chromosome 8) under the control of the IgH promoter (Figure 9. Overexpression of cmyc creates a strong proliferation signal and so Burkitt lymphoma is a very aggressive malignancy with an extraordinary growth rate (tumor nodules may double in size in one day). The common t(8;14) and variant t(2;8) and t(8;22) chromosomes in Burkitt lymphoma. The normal chromosomes are illustrated on the left and the abnormal c-myc-bearing chromosomes on the right. The second abnormal chromosome produced by each translocation (which may contain nonfunctional fragments of c-myc or immunoglobulin genes) is not represented, nor is the normal chromosome of each pair, which does not participate in the translocation. New genetics of Burkitt lymphoma and other nonHodgkin lymphomas, Am J Med 77:1083). Other factors that may contribute to the pathogenesis of lymphomas in humans include chronic infection and immunosuppression. Individuals may also present with B symptoms, pain, organ failure, or a variety of other symptoms, depending upon the kind of lymphoma and the sites of involvement. Patients with indolent lymphoma are more likely to be asymptomatic at diagnosis than patients with aggressive lymphomas. More than two thirds of patients with B-cell lymphoma have disseminated disease at diagnosis. Many have extranodal disease, especially in the bone marrow and gastrointestinal tract. These abnormalities include Coombs-positive hemolytic anemia, immunoglobulin deficiency and monoclonal gammopathy. Diagnosis and staging An adequate sample of tissue is essential to establish the correct diagnosis. Distinguishing one lymphoma subtype from another requires a skilled pathologist using a combination of morphology, immunophenotyping, and occasionally molecular diagnostics. Fine needle aspiration may help distinguish lymph nodes enlarged by lymphoma versus metastatic carcinoma or reactive processes, but accurate subtyping and characterization of lymphomas requires excisional biopsy. Within this broad category, subclassification of the different types of B cell lymphoma relies on the morphology, architectural organization, immunophenotype, and in some cases, the specific genetic aberrations of the malignant cells. Previous pathologic classification schemes relied primarily on the size and shape of the malignant cells and the architecture of the infiltrate. Some B cell lymphomas are named for the resemblance between the malignant clonal cells and a normal counterpart (geographic locale in the lymph node, immunophenotype, or morphology), as in mantle cell lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma. Generally speaking, the hematopathologist is assessing whether there are significant abnormalities in lymph node architecture (loss of the typical B and T cell zone pattern), aberrant locations or accumulations of B cells or T cells, or the presence of cells with atypical morphology. In some cases, it can be difficult to distinguish reactive and malignant conditions. As this rearrangement and use of specific V, D, and J cassettes is unique for every lymphocyte, a malignant lymphocyte population will show an aberrant monoclonality in this regard. Stage has a more important role in determining prognosis and treatment in Hodgkin lymphoma than in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. In some forms of indolent lymphoma, therapy can be postponed until the patient becomes symptomatic. Radiotherapy, either alone or in combination with chemotherapy, may help to palliate localized symptomatic disease. Non-Hodgkin lymphomas in children are typically aggressive cancers that have many features in common with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (discussed in chapter 8). An aggressive approach to the therapy of high grade lymphomas in children, using central nervous system treatment along with combination chemotherapy, has resulted in a remarkable improvement in the survival. Specific Diseases and Their Diagnosis In this final section, we will discuss a few representative lymphoid malignancies, and describe their presenting features and diagnostic strategies that separate them from benign/reactive conditions. Neoplastic In Chapters 1 and 8, we addressed the approach to high and low peripheral blood counts in the myeloid and erythroid lineages. One of the more common causes of reactive lymphocytosis conditions is acute infection with Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis). Infectious mononucleosis presents with impressive symptoms and signs in young adults: fever, sore throat, profound fatigue, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and axillae, rash, splenomegaly and, less often, hepatomegaly. Some of these clinical features also may be found in patients with cytomegalovirus and toxoplasma infections. More complicated manifestations such as splenic rupture, aseptic meningitis, respiratory distress as a result of enlarged tonsils, and severe hepatitis can be seen but are rare. Lymphocytosis with a preponderance of atypical lymphocytes is most frequently seen several days into the clinical illness. Elevation in liver enzymes is found in 80% of the cases, indicating mild hepatitis. In contrast, patients whose malignant clone shows little or no evidence of somatic hypermutation, presumably reflecting origin from a naive B cell, have a worse prognosis, with median survival in the 5-7 year range. By staining the blood, bone marrow, or lymph node sample with cocktails of antibodies against specific surface proteins that have different fluorescent dyes attached, the flow 186 cytometer can detect even relatively small clones with aberrant phenotypes. It can be confusing that in a disease we call chronic lymphocytic leukemia, patients very often exhibit lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly due to infiltration by leukemia cells. As is the case with other indolent lymphomas (particularly follicular center cell lymphoma), in a minority of cases transformation to a much more aggressive (and rarely curable) large cell lymphoma may occur. The presence of immature (blastic) lymphoid cells in the peripheral blood indicates acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (Chapter 8), which can be confirmed and further subtyped as B cell or T cell type by flow cytometry. Describe the morphology; location, biology, and function of normal plasma cells in the human body. Describe structure of immunoglobulins and the differences among the various immunoglobulin classes.