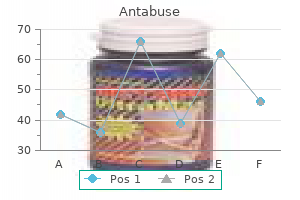
Antabuse
Buy cheap antabuse 250mg
Several of their experience with prospective Regulation is the major regulations that afect the franchisees and contact information for industry are listed below medicine 20th century purchase antabuse now. Medium and the Furthermore, hair salons must comply trend is Increasing Federal regulations with the Health and Safety in Salons are subject to advertising and Employment Act of 1992. Under federal identify workplace hazards such as and state law, ads that mislead or deceive exposure to chemicals and they must take consumers are unlawful. Franchisers must manufacture products, the cosmetic provide information about subjects like products it sells are subject to regulation franchiser-initiated lawsuits against by the Food and Drug Administration franchisees. These regulations principally franchisees that have left the franchise in relate to the safety of ingredients used, the past year; franchise turnover proper labeling, advertising, packaging information; the dangers of buying and marketing. There are also various statewide state-licensed barber or cosmetology regulations for the treatment of school. Programs usually comprise nine wastewater that may contain chemicals months of training. This cosmetology training may be credited regulation is designed to encourage nail toward a barbering license and vice versa salons to discontinue using nail polishes and a few states combine the two that contain these chemicals due to their licenses. Estheticians, as well, are harmful efects on nail technicians and required to train an average of 600 hours customers. Industry Assistance the Hair and Nail Salons industry does not Cosmetology Salon Professionals each receive any industry-specifc government provide education services, government assistance in the form of subsidies or advocacy and charitable outreach for Level & Trend otherwise. The American Skin the level of receive indirect assistance from various Association works to advance research and Industry Assistance industry trade associations. The Professional promote skin health and public awareness is None and the Beauty Association and the Association of of skin disease. Note: For a full description of the ratios refer to the Key Statistics chapter online. This removes the impact of changes in interest royalties, dividends and the sale of fxed the purchasing power of the dollar, leaving only the tangible assets are excluded. It is derived by adding imports to trade is determined by ratios of exports to revenue and industry revenue, and then subtracting exports. Imports/domestic demand: low is less than partners, managers and executives within the industry. Multiple technological change; and the level of customer establishments under common control make up an acceptance of industry products and services. When tough strategic, budget, sales and marketing decisions need to be made, our suite of Industry and Risk intelligence products give you deeply-researched answers quickly. If you require a specifc treatment or you may be required to attend for several hours time please contact your local salon for an and we ask you to be patient. When to see a dermatologist Rosacea Seeking early treatment can help to reduce the Medications appearance of common symptoms. It can be used long term and is patients feel more comfortable and confident about their available in a gel, cream and lotion formulation. Early and ongoing treatment of Antibiotics (topical, oral) rosacea can help to control symptoms and prevent Rosacea is often treated with antibiotics, either in a topical worsening of the condition and the possibility of formulation that is applied directly to affected skin or in a disfigurement. Oral antibiotics include Different forms of rosacea tetracycline, minocycline, erythomycin, clindamycin, and There are four forms of rosacea, which are defined by the others. In addition, there may some swelling, burning either over-the-counter or prescription-strength. They can make rosacea worse if used for of rosacea that is marked by persistent redness and longer periods. This oral agent may be prescribed if rosacea is severe or if Severe (Phymatous) In some individuals, rosacea may symptoms do not respond to antibiotics. Ocular rosacea In addition to skin symptoms, rosacea may Sodium sulfacetamide and sulphur also affect the eyes and eyelids. It may cause redness to Sodium sulfacetamide and sulphur are typically used in the surrounding skin tissue but also burning or stinging, combination to treat redness and inflammation. Laser resurfacing, dermabrasion or cosmetic Rosacea does not improve or resolve on its own, and surgery may be used to reduce the tissue overgrowth untreated rosacea can worsen over time. Your family doctor or dermatologist can prescribe various forms of treatment and recommend which skin care products and cosmetics are appropriate. Sticking with the treatment recommended by your doctor will improve symptoms within a few weeks. Rosacea (row-zay-sha) is a chronic skin condition that A number of lifestyles factors can cause rosacea to flare primarily affects the face. These triggers vary from person to person, so it is both redness or blushing that comes and goes initially. Over important and helpful to find out which ones make your time, the redness may become persistent and more rosacea symptoms flare up. The most common sites for symptoms are the better manage your condition and to avoid things that cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. Products with fragrance, alcohols, abrasives or Bumps, tiny pus-filled pimples, and enlarged blood other irritating ingredients. Rosacea symptoms can vary from one For more information on: Food and Drinks: person to another, and there is no predicting severity. Hot drinks, such as soup and hot chocolate Causes of Rosacea There is no known cure for rosacea, although it can be Caffeinated beverages, such as tea or coffee managed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle Managing Rosacea Spicy seasonings such as pepper, paprika, red changes. It is characterized by thick, Overheating the body can trigger flushing red bumps around and on the nose, which develop when Divide vigorous exercises into shorter sessions the oil-producing glands and the surrounding connective Stay cool while working out tissues becoming enlarged. This is a more severe form of rosacea that occurs mostly when it remains untreated. Medications Rhinophyma develops in some men who have rosacea, Certain medications that cause flushing can and very rarely in women with rosacea. Extended use of Rosacea usually develops in adults between ages 30 and prescription-strength cortisone creams on the 50. It affects both men and women, although it seems to face can worsen rosacea symptoms. It tends to affect people with fair skin, such as Stress, or emotional upset, is one of the most advance the science and art of medicine and surgery related to those of northern and eastern European descent (for common triggers associated with rosacea the care of the skin, hair and nails; provide continuing example Celtic, English, and Scottish), although rosacea flare-ups. Manage stress by getting enough professional development for its members; support and advance patient care; provide public education on sun protection and can develop in those of any skin type. Temperature extremes this brochure has been produced with the assistance of an Quick facts about rosacea Extremely hot or cold weather unrestricted educational grant from: Rosacea affects over two million Canadians. Exposure to wind It is a chronic skin condition that does not go away but Hot baths, showers and saunas can be controlled. How to cite this document: Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion (Public Health Ontario). Publication history: 1st edition: 1998 (Ministry of Health and Long-term Care) 2nd edition: 2009 (Ministry of Health and Long-term Care) 3rd edition: November 2018 1st Revision: July 2019 Guide to Infection Prevention and Control in Personal Service Settings i Summary of Revisions First published: November 2018 the evidence in this document is current to November, 2018. Summary of changes in 1st revision: Date of Implementation Description of Major Changes Page(s) Removed requirement for single-use disposable blades to be Jun-19 97 sterile. Guide to Infection Prevention and Control in Personal Service Settings iv Contents Preamble. A recent online survey in Ontario obtained responses from 1,270 respondents between the ages of 16 and 35 and found the self reported prevalence of tattoos among this age group (both sexes) to be 48%, and of body piercings (excluding earlobe piercings) to be 65%. Only 26% of respondents reported having no tattoos or body piercings, although over half of these expressed an intention to obtain tattoos or body piercings in the future. Other services that are growing in popularity include holistic services such as colon hydrotherapy and sensory deprivation. Infections may be transmitted even if skin penetration does not occur (see Appendix A: Personal Services and Infection Risks). Recommendations were derived from legislation and regulations and were developed by consulting existing best practice documents, seeking expert opinion, and Guide to Infection Prevention and Control in Personal Service Settings 1 conducting a review of select primary literature.
Generic antabuse 250mg fast delivery
Meshed grafts have a number of advantages over sheet grafts: (1) meshed grafts will cover a larger area with less morbidity than non-meshed grafts; (2) the contour of the meshed graft can be adapted to fit in a regular recipient bed; (3) blood and exudate can drain freely through the inter stices of a meshed graft; (4) in the event of local ized bacterial contamination symptoms after miscarriage order antabuse visa, only a small area of Fig 3. A piece of cardboard is placed on the defect and the meshed graft will be jeopardized; (5) a meshed moisture blot is traced. The cutout pattern is then placed on the graft offers multiple areas of potential reepi skin graft donor site and outlined. Phase 2 coincides with the onset of Richard and colleagues67 compared the Tanner fibrovascular ingrowth and vascular anastomoses and Bioplasty skin graft meshing systems with respect between the graft and the host. Both systems delivered dealing with skin grafts to the penis and scrotum, approximately 50% of the anticipated skin expan which are particularly difficult to immobilize and sion, leading the authors to recommend harvesting dress, Netscher and associates85 suggest wrapping skin grafts larger than needed to compensate for the graft area in nonadherent gauze mesh over the eventual shortage. The Ingenious ways to mesh skin grafts when a mesher foam maintains penile length and gently but firmly is not available have been reported. The authors cite ease of application and safe and effective therapy for recalcitrant leg ulcers. Balakrishnan88 prefers Lyofoam, a Meek grafts are useful alternatives to meshed grafts semipermeable, nonwoven polyurethane foam when donor sites are limited, and are particularly dressing. The foam is easy to apply directly on well suited for grafting granulating wounds and the graft and is biologically inert. Wolf Graft take is said to be excellent even in difficult and coworkers90 confirmed the effectiveness of rub beds. Yeh and colleagues82 compared this al92 modify a cutoff disposable syringe to affix the technique with the microskin method in a rat model, silk threads of their graft dressings. Other healing parameters were similar infusion bottle on which multiple radial slits are between the two groups. Other suggested fixation methods for grafts Graft Fixation 94 include silicone rubber dressings and silicone Adherence of the graft to its bed is essential for gel sheets,95 rubber band stents,96 transparent skin graft take. A thin fibrin layer holds the graft to gasbag tie-over dressings,97 Coban self-adherent the bed and forms a barrier against potential infec wrap,98 thin hydrocolloid dressings,99 and assorted tion. Proponents of fibrin glue say that it improves graft survival, reduces blood loss, speeds reconstruc Allografts tion by allowing large sheet-graft coverage, and 111 Traditionally cadaver allografts have been the produces better esthetic results. Cadaver ence at the University of Texas Southwestern skin serves as temporary wound cover, reduces pain Medical Center bears out this assertion: A thin and fever, restores function, increases appetite, layer of fibrin glue improves graft take consider controls fluid loss, and promotes wound healing. As ably, particularly in the head and neck and mobile the grafts revascularize, they form a barrier against body parts. The open-wound technique of donor site man As discussed above, Chinese investigators have agement is associated with prolonged healing time, successfully used combinations of allografts and autografts for coverage of open wounds. Most authors recommend autograft is cut into small pieces and placed in the dressing the donor site of a skin graft to protect it slits of meshed allografts, or is laid down in alternat from trauma and infection. As rejection unfolds, Allen and coworkers118 compared bacterial epidermal cells in the autograft gradually replace the allograft. The advantages a dramatic decrease in bacterial colonization, lead of xenografts are relatively low cost, ready availabil ing the authors to conclude that it was the antibi ity, easy storage, and easy sterilization. Disadvan otic, not the dressing, that had a sterilizing influ tages are lack of antimicrobial activity, no proof that ence. Skin grafts have no intrinsic bactericidal they promote reepithelialization, potential for properties. Op-Site and Tegaderm showed rapid, relatively painless healing and low infection rates. Recommendations from the authors were for Op-Site or Jelonet for dressing small donor areas and for Vaseline gauze to cover large wounds. Zapata include Xeroform, Biobrane, and fine mesh gauze Sirvent134 compared Biobrane and Scarlet Red and impregnated with Scarlet Red or Vaseline. Semiocclusive dressings are Tavis et al135 agree that Biobrane reduces pain, impermeable to bacteria and liquids, so fluid tends limits infection and desiccation, and optimizes heal to collect beneath the dressing and must be drained ing times, although its expense is considerable. Poulsen and colleagues136 found Jelonet superior Feldman and colleagues129 evaluated the effec to Op-Site in the treatment of partial-thickness burns tiveness of various donor site dressings in 30 patients both in terms of speed of healing (7 vs 10 days) and with respect to healing, pain, infection, and residual scars (8% vs 21%). Biobrane of use, and less discomfort with Xeroform, particu was more comfortable than Xeroform, but was larly with movement. The rate of epithelialization, graft are more numerous and show greater arboriza degree of pain, and convenience of use were mea tion than those in normal skin. The Kaltostat-treated patients had fifth or sixth postgraft day, and subsequently the slower healing times (15. Primary contraction is passive and prob parallel group comparison in 80 patients. Owen and Dye142 area as a result of primary contraction; a medium report that topical application of 2% lignocaine gel thickness graft, about 20%; and a thin split-thickness to graft donor sites controlled discomfort during the graft, about 10%. Split-thickness grafts, on the other hand, difference in time of reepithelialization or patient contract whenever circumstances allow. Unless split comfort between this inexpensive material and the thickness skin grafts are fixed to underlying rigid more costly hydrocolloid dressings. A contracted wound is often tight and the skin graft is white, but once applied to the immobile and there is distortion of surrounding nor recipient area it becomes pink over the next few mal tissue. There is blanching on pressure with prompt manipulated somewhat by adjusting the thickness capillary refill. The contrac below the level of the surrounding skin, but by the tion-inhibiting effect of dermis depends more on 14th to 21st postgraft day it becomes level with the the percentage of dermis included in the graft than surrounding surface. By day 30, however, these wounds by graft orientation, amount of epidermis, or had contracted more than conventional autografts. The extent of reinnervation depends on ber of myofibroblasts, and wounds contract less than how accessible the neurilemmal sheaths are to the comparable nongrafted sites. Bertolami and Donoff150,151 studied the effect of Skin grafts are initially hyperalgesic and slowly dermis on the actinomycin content of granulating regain normal sensation. If the warmth sensi decreased collagen synthesis, which in turn may be bility had recovered, the threshold was lower than involved in preventing wound contraction. Seven grafts showed no thermal sensibil Oliver and associates156,157 highlight the impor ity at all. Haro and colleagues160 confirmed poor return of tance of the collagen matrix in inhibiting wound contraction. The matrix was prepared for grafting sensitivity in grafts by means of immunohistochemi by adding azide to destroy the cells and trypsin to cal methods. These grafts, cell no sensitivity whatsoever, and pain sensation had free and noncollagenous-protein-free, resist wound developed only in the 15-month-old grafts. Although contraction as well as full-thickness skin grafts, sug deep and superficial nerve plexuses regenerated, gesting that dermal cells and noncollagenous pro no sensory corpuscles were detected in grafted skin teins are not part of the inhibitory process. It may be possible, ings and speculate that the failure of regeneration therefore, to store nonantigenic dermal substitutes of sensory corpuscles may be related to the degen produced from banked cadaveric skin or xenoge eration of periaxonal corpuscular elements.
Purchase cheap antabuse
The fracture line passes obliquely from anteroproximal to posterodistal on lateral radiographs symptoms electrolyte imbalance buy generic antabuse 250mg line. When displaced, the sharp proximal bone fragment often pierces the triceps and overlying skin, creating an open fracture. A more comprehensive classification system, based on the presence of intercondylar extension and fracture comminution, is used more commonly in adults. Anatomic reductionwith stablefixation in adultsis bestachieved with plate-and-screw fixation(see table). External fixators are used when rapid stabilization of the elbow is required (eg, vascular disruption), when an open wound is associated with significant soft tissue injury or loss, or when plate-and-screw fixation is precluded by extensive bone loss or comminution. External fixator pins are placed laterally into the distal humerus and dorsally into the ulna. Skin incisions that are followed by blunt dissection to bone under direct visualization help prevent injury to the radial nerve. Ulnar pins are inserted with the forearm in 30 degrees of supination to permit forearm rotation. Describe the classification and management of supracondylar fractures in children. The Gartland classification of supracondylar humerus fractures in children is based on the degree of displacement. Fracturesareclassifiedasundisplaced,minimallydisplaced,displaced>5 mmbutproximaltothe elbow joint, and entrapped (usually between the olecranon and trochlea). Acute fractures are differentiated from chronic tension stress injuries (little league elbow). Chronic stress fractures are treated conservatively with brief immobilization and activity modification. Transcondylar fractures usually are seen in older adult patients as a consequence of osteoporotic bone. The fracture line passes between the articular surface and the old epiphyseal line, traversing the coronoid and olecranon fossae. Excessive callus formation in the coronoid or olecranon fossa may result in loss of motion. Condylar fractures are rare in adults, representing <5% of all distal humerus fractures. Lateral condylar fractures, which include the capitellum and lateral epicondyle, are more common than medial condylar fractures. Jupiter describes Milch fractures as high or low, based on extension of the fracture line into the supracondylar region. Closed treatment of initially nondisplaced fractures in a long-arm cast is associated with a loss of reduction. Usually they result from forces directed against the posterior aspect of a flexed elbow that cause the ulna to impact the trochlea. The resultant force splits the condyles, which are pulled apart by the flexor (medial) and extensor (lateral) muscle masses. The Jupiter classification describes the shape and direction of the fracture as high T, low T, Y, H, medial lambda, or lateral lambda. Older adult patients with osteoporotic bone and comminuted articular fractures may be managed with either closed treatment (cast/traction) or total elbow arthroplasty using a semiconstrained device. What are typical functional outcomes after an intraarticular distal humerus fracture Approximately 70% of patients have a good or excellent outcome; 25% have a fair outcome; and 5% have a poor outcome. Other typical outcomes are the following: mean flexion arc, 112 degrees; pronation and supination, 75 degrees each; grip strength, 80% of the contralateral side. Treatment of nondisplaced fractures involves placing the elbow in maximal flexion and forearm pronation to allow for the radial head to act as an internal splint. However, extreme flexion in the face of soft tissue edema can cause vascular compromise and subsequent compartment syndrome. Immobilization at 90 degrees of flexion in a long-arm cast decreases the risk of compartment syndrome but is associated with loss of fracture reduction. Provisional fixation with Kirschner wires simplifies placement of small-fragment cancellous bone screws (directed posteriorly to anteriorly) or Herbert screws (placed anteriorly to posteriorly and buried below the articular surface). Trochlear fractures are rare injuries produced by coronal shear forces directed against the trochlea by the coronoid process. Often associated with capitellar fractures, trochlear fractures are distinguished by a double-arc sign on lateral distal humerus radiographs. One arc represents the lateral ridge of the trochlea, and the other arc represents capitellar subchondral bone. Displaced fractures with significant osseous fragments are exposed through an extended lateral Kocher approach and stabilized via cancellous or Herbert screws. Colton modified the original Schatzker classification system of olecranon fractures to include the following classes: undisplaced, displaced, oblique, and transverse fractures; comminuted fractures; and fracture-dislocations. Treatment of undisplaced fractures involves immobilization in a long-arm cast with the elbow in 45 to 90 degrees of flexion for approximately 3 weeks. Radiographic evaluation 5 to 7 days after cast application is needed to rule out fracture displacement. Joint stiffness and loss of motion are common, particularly in older adult patients who undergo prolonged immobilization. Displaced fractures or fractures associated with a loss of active elbow extension are commonly treated with tension band wiring, 3. Approximately 85% of patients have no complaints at long-term follow-up; 50% will show arthritic changes compared with 11% in the uninjured extremity. Approximately 22% of plates used for fixation require removal, and up to 50% of tension band wires will need to be removed. Three types of coronoid fractures, based on fragment size, were described by Regan and Morrey. Therefore, most type I fractures represent shear fractures of the tip of the coronoid. Summarize the mechanisms of injury and general management of radial head fractures. Radial head fractures result from indirect trauma (eg, fall onto an outstretched hand) when longitudinal forces drive the radial head into the capitellum. A mechanical block to motion or elbow instability is an indication for operative intervention. In children 90% of proximal radial fractures involve either the physis or the radial neck and are associated with fractures of the olecranon, coronoid, and medial epicondyle. Radial head excision in children is associated with a high incidence of overgrowth and poor outcome. Elbow dislocations are classified based on the position of the ulna and radius relative to the distal humerus. Several types of elbow dislocations are recognized: posterior, posterolateral, posteromedial, medial, lateral, anterior, and divergent. Posterolateral elbow dislocations account for 11% to 28% of injuries to the elbow and are more common than other types of elbow dislocations. The incidence of posterolateral dislocations is highest in the 10 to 20-year-old age group and frequently is associated with sports-related injuries. Divergent elbow dislocations are rare and consist of two types: anteroposterior and mediolateral (divergent).
Order 250 mg antabuse otc
Daily maintenance with topical metronidazole can absolutely decrease relapses and allow for longer intervals between fare-ups symptoms of colon cancer purchase antabuse 500 mg fast delivery. Another topical option is to use a prescription medication that combines benzoyl peroxide with erythromycin (an antibiotic), the same one that is more typically recommended for those with acne. There is some research showing it can be as or more effective than topical metronidazole. Azelaic acid, in concentrations of either 15% or 20%, is an interesting, versatile ingredient that is prescribed not only for rosacea but also for acne and brown skin discolorations. Overall, azelaic acid is considered a very effective and safe therapy for rosacea. On average, twice-daily application of azelaic acid has shown results in reducing the rosacea symptoms of redness, faking, and papules that are similar to once-daily application when using metronidazole. One study demonstrated that azelaic acid was as effective as metronidazole but was tolerated better by patients. Yet oral antibiotics truly make a difference in the appearance of rosacea, and the frustration about what to prescribe has confounded the medical world. This antibiotic is prescribed at a level where it does not cause bacterial resistance, but can still make a signifcant improvement in the appearance of rosacea symptoms. Both Renova (active ingredient tretinoin) and Differin (adapalene) would be two of the more typical options that can be prescribed. If you decide to go this route, pay attention to the way your skin is reacting, and discontinue use if it becomes more red and irritated than when you started. These catalysts can include hot liquids, spicy foods, exposure to extreme temperatures (including cooking over a hot stove), alcohol consumption, sunlight, stress, saunas, hot tubs, smoking, rubbing or massaging the skin, irritating cosmetics, and anything else that overstimulates the skin and blood vessels. The cost of each treatment session can range from $300 to $700, though some clinics offer package deals make individual treatments less expensive. It is important to keep in mind that none of this is a cure, and that continued success would require using topical and/or oral methods to keep the condition at bay. Psoriasis is identifed by the presence of thickened, scaly areas of skin sometimes accompanied by papules (small, solid, often-infamed bumps that, unlike pimples, do not contain pus or sebum). These bumps are usually slightly elevated above the skin surface, sharply distinguishable from normal skin, and can be red to reddish brown in color. Dotted over the various parts of the face and body, the lesions are usually covered with small whitish silver scales that stick to the cystlike swelling; if scraped off, the skin may bleed. The extent of the disease varies from a few tiny patches to generalized involve ment of most of the skin from head to toe. What makes psoriasis so frustrating is that no one knows for certain exactly what causes the problem, although recent studies suggest it may be related to an immune system problem. Referred to as an immune-mediated disorder, it triggers infammation and sets off a trigger that causes the skin to make too many cells at breakneck speed. Many feel this theory holds the most water because immunosuppressant medications can reduce or eliminate psoriatic lesions. Psoriasis is the recurring, persistent growth of too many skin cells that are not able to shed properly, accompanied by red, oozing patches of skin. A normal skin cell matures in 28 to 45 days, while a psoriatic skin cell takes only 3 to 6 days. Stress, skin irritation, injury, and health problems such as fus and viruses have been reported to precede a recurrence. Climate may also play a factor, with dry, cold weather triggering recurrences and sunny warm weather improving it or even causing remission. Too much alcohol, smoking, and obesity may also play a role but no one is sure why. Sadly, there is no cure for psoriasis, but there are many different treatments, both topi cal and systemic, that can be added to your skin-care routine to obtain optimal results. Manifesting in a variety of ways, psoriasis of the nails can include pitting, lifting of the nail away from the nail bed, white discolorations, and ridges. Although there have been important advances in the treatment of psoriasis as it pertains to the skin, options for dealing with the way it affects the nail are barely researched. While a number of treatment alternatives currently exist for nail disease, the general gross lack of clear evidence regarding these choices often makes it diffcult to select the most effcient, safe, and optimal treatments. It is even more important for those with psoriasis; because this skin condition is an infammatory condition, reducing infam mation becomes even more critical. In essence you need to follow the skin-care routine for your skin type in terms of dryness or oiliness as recom mended in this book. Following those steps will help you create a healthy starting point for the other medications your doctor may select for you. As a rule, the best place to start is with treatments that pose the least risk and have the least side effects. Topical prescription creams and lotions are the preferred way to begin as they generally are the most benign and can be extremely helpful. Due to its immune suppressing and skin cell-damaging effects, ultraviolet radiation can control psoriasis. A curve ball in treatment is that the body can become resistant to the medications and lesions can start showing up again after a long period of remission, requiring a new round of experimenting to fnd what works. Of the various therapies available to treat psoriasis, it is generally best to start with those that have the least-serious side effects, such as topical steroids (cortisone creams), coal-tar creams or shampoos, or sulfur-based creams and shampoos, along with careful exposure to sunshine. If those methods are not successful, you can proceed to the more serious treat ments involving oral medications. All of the treatments, both topical and oral, are often used in varying combinations for the best results. Frequently, several combination treatments are used in rotation to reduce the potentially harmful side effects of each one or the decrease in or lack of effectiveness. Discovering whether any of these will work for you, alone or in combination, takes patience and a systematic, ongoing review and evaluation of how your skin and health are doing. It is also important to be aware of the consequences of the varying treatment levels. For example, continued long-term use of topical cortisone creams can cause skin thinning, stretch marks, and built-up resistance to the cortisone medication itself, so that it actu ally becomes an ineffective treatment. Oral steroids can have serious withdrawal effects, including increased bouts of psoriasis. Several systemic psoriatic treatments can cause liver problems, nausea, and severe irritation. Each option has its own set of pros and cons that need to be researched and discussed at length with your physician. Daily, short, nonburning exposure to sunlight clears or improves psoriasis in many people.
Discount 500 mg antabuse with mastercard
Therapists must be aware of certain pathologies and their associated sites of pain referral symptoms vitamin b deficiency order antabuse 250mg overnight delivery. What are the components of the physical examination in the abdominal region when screening for visceral disorders The components of the physical examination of the abdominal region are inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation. Inspection is the process of visually looking at the body for symmetry, alignment, skin color, and scars present. Normal bowel sounds are made by movement of the intestines as food and liquid pass through. Bowel sounds occur frequently, on the order of every 2 to 5 seconds, although there is a lot of variability. Palpation in the abdominal region is usually deep palpation (firm pressure) and is used to assess for tenderness and presence of visceral organs. Percussion is used to determine the size, shape, and density of tissue using sound. The examiner listens for sounds that can range from tympani to a flat sound based on the tissue. Tissue density can range from high to low with percussive sounds ranging from flat, dull, resonant, hyperresonant, and tympanic. A dull sound indicates the presence of a solid mass under the surface such as the heart. A more resonant (vibrating) sound indicates hollow air-containing structures, such as the lungs and the hollow viscera of the abdomen. Tissues can also have abnormal fluid or a mass altering the typical sound heard in that anatomic location. In addition to producing different notes, percussion can also produce different sensations in the fingers, such as vibration. Texture the surface characteristics of the skin and hair are noted (brittle, coarse, thick, thin, roughened, or smooth) Moisture Assess the moisture content of the skin, hair, and mucous membranes; are they moist and supple or dry and cracked Skin temperature Palpate the head, face, trunk, arms, hands, legs, and feet to assess the local skin temperature and the distribution of heat Characteristics When a mass or enlarged organ is discovered, record its size, shape, consistency, of masses mobility, surface regularity, and presence or absence of expansile or transmitted pulsation Precordial cardiac Palpate the precordium (portions of the body over heart and lower chest) for signs thrust of heart action Crepitus During examination of the bones, joints, tendon sheaths, pleura, and subcutaneous tissue, feel for crepitation Tenderness Discomfort or pain on palpation of accessible tissues and over major organs should be noted; how much pressure is required to induce the uncomfortable sensation Thrills Palpate the precordium for thrills; if bruits (abnormal sounds) are heard in the major arteries, palpate them for thrills Vocal fremitus Palpation of vocal vibrations through the chest wall provides important information about the underlying pleura and lung 9. The adult liver is normally not palpable below the right anterior inferior costovertebral margin (acute angle created between the vertebral column and the twelfth rib). To palpate for hepatomegaly the examiner uses the tips of the fingers with two hands inferior to the ribs in the midclavicular line. How strong is the evidence to support the tests for palpation and percussion of the liver There is minimal evidence to support the use of palpation and percussion of the liver for hepatomegaly. This test is performed with the patient in the supine position and the examiner placing his or her hands on the right upper abdominal quadrant at the inferior costal margin. The patient inspires and the examiner palpates deeply in the subcostal region with the fingertips. The test is considered positive if pain is perceived during inspiration or the patient stops inspiration because of discomfort. The examiner percusses the posterior axillary line from the distal end of the lung to the middle anterior costal margin. The examiner places his or her fingers over the eighth or ninth intercostal space, in line with the left anterior axillary line, and performs percussion during normal breathing and at full inspiration. The right hand then palpates the costal margin and underneath the ribs to feel the spleen. In isolation, palpation and percussion tests for splenomegaly have minimal evidence to support their use and predictive value. When palpation and percussion are performed together does the evidence support the use of these tests There is moderate evidence to support the use of percussion and palpation tests of the spleen together. Sullivan and Williams (1976) reported sensitivity at 88% and specificity at 83% with a positive likelihood ratio of 5. When performing this percussion test the patient can either be in prone or sitting. Next, the examiner provides a percussive thump with the other hand, allowing the kidney to vibrate. A positive test is noted by either costovertebral tenderness or reproduction of back/flank pain signaling a red flag for renal involvement. If the patient experiences no pain after the thump is performed, then renal involvement is ruled out. As the patient inhales the anterior hand is pushed firmly and deeply beneath the costal margin in an effort to trap the kidney. The left kidney is usually not palpable because of its position beneath the bowel. The diagnostic accuracy of this test is unknown as it appears to have not been tested. The test is positive if pain is reproduced in the subcostal region, flank, or lateral aspect of the abdomen. What are the clinical findings related to appendicitis and the medical screens that would be utilized Alvarado score assesses the components of a physical examination for acute appendicitis. If the patient reports the following, he or she receives one or two points for each. Scores <5 were less likely to be acute appendicitis, and scores >6 were more likely. What are the clinical signs and causes of an iliopsoas (liacus or psoas) abscess, and what tests can be used to screen for this disorder Unilateral involvement can be associated with appendicitis, but it can be bilateral with generalized peritonitis.
500 mg antabuse with amex
Anterior and posterior forces then are placed on the proximal humerus medicine zofran order antabuse amex, and the direction and degree of translation are determined. The posterior force is then released; if the patient experiences pain and apprehension, then the test is considered positive. What are the sensitivity and specificity values of commonly performed shoulder instability tests Anterior translation of 25% or less of the humeral head diameter is considered normal. In addition to the load-shift test, posterior instability can be assessed with the jerk test. The arm is brought into a horizontally adducted position, and posterior slippage is noted. What radiologic studies and views are best suited for confirming or evaluating shoulder instability The Hill-Sachs lesion is a compression fracture of the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head. It results from impact to the anteroinferior rim of the glenoid during an anterior dislocation of the shoulder. A reverse Hill-Sachs lesion involves a compression fracture of the anteromedial humeral head as the result of a posterior dislocation. The detection of a Hill-Sachs lesion is prognostically important because patients with a Hill-Sachs lesion may be prone to redislocation. A Bankart lesion is an avulsion or detachment of the anterior portion of the inferior glenohumeral ligament complex and glenoid labrum off the anterior rim of the glenoid. Although a Bankart lesion can contribute to increased translation of the humeral head, complete dislocation requires associated capsular injury. Observation usually reveals a prominent coracoid process and a flattening of the anterior aspect of the shoulder. What is the suggested initial medical treatment for anterior shoulder dislocation Acute glenohumeral dislocations should be reduced as quickly and gently as possible because early relocation quickly reduces stretch and compression of neurovascular structures, minimizes the degree of muscle spasm that must be overcome to reduce the joint, and prevents progressive enlargement of the humeral head defect in the locked dislocation. Postreduction management after traumatic anterior shoulder dislocation is controversial. A 10-year prospective study by Hovelius comparing immobilization with no immobilization found no difference in recurrence rates. What is the most common complication in managing a traumatic anterior dislocation Other complications include fractures of the humerus, vascular injuries, neural injuries, and rotator cuff tears (more common in patients >40 years). Several factors have been identified as contributing to recurrence and instability. Patients under the age of 20 years may have a recurrence rate up to 80%, whereas after the age of 40 the rate drops to under 10%. Males have a higher recurrence rate than females, and most recurrences are seen within 2 years of the initial traumatic dislocation. If dislocation occurs a second time in younger patients, the chance of frequent recurrence is almost 100%. What is the incidence of associated rotator cuff tears in patients older than 40 years The incidence of rotator cuff tears after acute dislocation in patients older than 40 years ranges from 35% to 86%. The reason for the variability in numbers is the unknown amount of rotator cuff pathology before the initial dislocation. With dislocation of the humeral head anteriorly, the anterior and/or posterior structures are disrupted. With dislocations in younger patients, the anterior capsuloligamentous complex tends to disrupt because it is less strong than other tissues of the shoulder. In older patients, the posterior structures (rotator cuff and greater tuberosity complex) are weaker by attrition and tend to disrupt, leaving the anterior capsuloligamentous complex intact. After an initial period of immobilization, a regimen of shoulder rehabilitation should be implemented. Strengthening of the shoulder musculature is of paramount importance to improve dynamic stability. Because the capsular stabilizing structures are compromised, the shoulder has a greater dependence on dynamic stabilizing mechanisms. The scapula must provide a stable base on which the humerus can rotate and maintain the glenoid in a position that provides maximal congruence with the humeral head. The core scapular exercises are scaption, protraction, retraction, and seated press-up. Once scapular stability is addressed, emphasis is placed on reestablishing the strength of the rotator cuff musculature, which is the main dynamic stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint. Exercises should be performed in the scapular plane, which provides the greatest congruence between the humeral head and glenoid and minimizes the stress placed on the anterior capsule. Activation of the teres minor and infraspinatus draws the humeral head posteriorly and thus unloads the stress on the damaged anterior structures. Reduction is accomplished by longitudinal forward traction on the arm with the elbow bent, accompanied by anterior pressure on the humeral head. The arm then is brought into an adducted, externally rotated, and internally rotated position to reduce the humeral head back into the glenoid fossa. Principles of nonoperative treatment include pain management, activity modification, and a shoulder strengthening program involving the scapular and rotator cuff musculature. Nonoperative treatment produces superior results in posterior instability compared with anterior instability. Integral to the strengthening program is the periscapular and rotator cuff musculature. Aggressive physical therapy with strengthening of the scapular stabilizers and rotator cuff musculature frequently provides sufficient dynamic stability. If the patient does not respond to conservative treatment, an inferior capsular shift should be included as part of the surgical procedure. Describe the modern surgical management of patients for whom operative treatment is advisable. The success and/or failure rate for each is quite variable and highly dependent on the skill of the surgeon. How does the outcome of immediate surgical stabilization compare to the nonoperative management of shoulder instability in the young, healthy adult Kirkley conducted a prospective randomized clinical trial comparing the effectiveness of immediate arthroscopic stabilization versus immobilization and rehabilitation in first time, traumatic anterior shoulder dislocations. The standard of care in the overhead athlete is early repair of the capsular structures. Early stabilization in athletic high-risk patients should diminish progressive soft tissue and bony damage. Patients complain of popping and sliding of the shoulder, especially with overhead activities. Aprospective,randomizedevaluationofarthroscopicstabilizationversusnonoperativetreatmentin patients with acute, traumatic, first-time shoulder dislocations.
Purchase antabuse cheap online
Relevant legislation may state or territory Acts and local regulations relating include: to skin penetration state or territory and local health and hygiene regulations occupational health and safety 6 medications that deplete your nutrients antabuse 500 mg. Infection control must use of personal protective equipment include: equipment sterilisation and disinfection use of disposable equipment. Adverse effects may include: erythema or inflammation arising from hair removal treatment or products scarring allergic reactions of skin or body to treatment or products reactions of client to electrical current, treatment or product. Home-care advice may care of treatment area include: management of hair growth product recommendations. The use of non-ionising radiation for cosmetic treatments is currently subject to licensing under the Queensland Radiation Safety Act 1999, and accreditation of equipment, premises and operator under the Tasmanian Radiation Protection Act 2005. The Western Australian Radiation Safety Act 1975 imposes limitations restricting the use of Class 4 lasers for cosmetic treatments, including hair removal, to medical practitioners. With regard to other states and territories, no licensing, regulatory or certification requirements apply to this unit at the time of endorsement. They exercise judgement in planning and implementing an appropriate treatment program to safely achieve desired hair reduction outcomes for each client. Pre-Requisites Prerequisite units Employability Skills Information Employability skills this unit contains employability skills. The following examples are appropriate for this unit: direct observation of learners performing a range of tasks over sufficient time to demonstrate handling of a range of contingencies, including: setting up and taking down equipment organising preventive maintenance completing clinical procedures checklists providing and documenting safe client care procedures identifying potential hazards complying with treatment environment safety procedures written and oral questioning appropriate to the language and literacy level of the learner, to assess the required skills and knowledge of this unit third-party reports from technical experts. Risks may include: incomplete hair removal or regrowth darkening of the skin (hyperpigmentation) lightening of the skin (hypopigmentation) blistering and scarring changes in the skin texture crusting or scabbing hair changes. Preventive maintenance must documentation, including: include: relevant equipment safety standards equipment service history schedule for recommended testing and maintenance regular testing. Control panel may include: power settings pulse settings time settings emergency control delivery systems. This unit describes the process of applying complex understanding of skin and hair biology and wound healing to evaluate client suitability for the application of light technologies for hair reduction performed in a beauty industry treatment environment. The therapist designs a staged program of multiple treatments that will safely achieve optimum outcomes for the client. The use of non-ionising radiation for cosmetic treatments is currently subject to licensing under the Queensland Radiation Safety Act 1999, accreditation of equipment, premises and operator under the Tasmanian Radiation Protection Act 2005. Contraindications may sun-tanned skin include: artificially tanned skin pregnancy some herbal remedies active herpes simplex active impetigo active eczema active acne photo-sensitive medication hypertrophic and keloid scars tattoos in the treatment area psoriasis in the treatment area certain circulatory conditions inappropriate hair type and colour. Post-treatment skin cold compress cooling products may cryogen sprays include: cold gels. Treatment program may energy settings (fluence) include: planning frequency of treatments. Client assessment must client requirements include: client characteristics: Fitzpatrick skin types one to six skin condition specific hair reduction treatment area or areas pain tolerance heat tolerance client relevant medical history contraindications patch test outcomes. The use of non-ionising radiation for cosmetic treatments is currently subject to licensing under the Queensland Radiation Safety Act 1999 and accreditation of equipment, premises and operator under the Tasmanian Radiation Protection Act 2005. They exercise judgement in planning and implementing an appropriate treatment program. Optimum outcomes are usually achieved across a treatment program that involves multiple treatments. Safe practice protocols must control panel treatment settings include: treatment after care (cold compress). Treatment program plan may treatment area include: follicle type and distribution hair type: single, compound straight, curved fine, coarse lanugo, vellus, terminal equipment selected planned treatment parameters based on patch test results, including: wavelengths to be used pulse duration energy settings (fluence) treatment duration products equipment follow-up procedures contraindications relevant medical history and medications outcomes of previous temporary and permanent hair reduction treatments. Immediate post-treatment cold compress skin cooling products may cryogen sprays include: cold gels. Unit Descriptor Unit descriptor this unit describes the performance outcomes, skills and knowledge required to apply the principles of nail science and recognise skin disorders as they apply to nail treatments on hands and feet. Application of the Unit Application of the unit this unit applies to beauty workers, beauty therapists and nail technicians who apply an understanding of the main functions and role of the skin on the hands and feet, the structure of the nails, and the recognition of skin disorders as they relate to contraindications to the provision of a range of nail services in nail salons and beauty salons. Required skills the following skills must be assessed as part of this unit: technical skills to: respond to possible skin or nail damage situations identify client characteristics, and recommend and perform a service, including: preparation of service area preparation of products and equipment preparation of client literacy skills to source, read and apply relevant information on skin science and skin disorders to the design and performance of nail services communication skills to translate information on skin science and skin disorders when providing advice, responding to questions, and providing information and reassurance to clients on nail services. Required knowledge the following knowledge must be assessed as part of this unit: relevant health and hygiene regulations and requirements relevant occupational health and safety regulations and requirements principles of nail science as they relate to nail treatments nail science in relation to nail treatments and procedures, including: anatomy of skin and nails skin and nail disorders contraindications to both natural and artificial nail treatments effects on nail of ingredients and equipment in a range of treatment products provision of post-treatment advice workplace product, treatment and equipment range and manufacturer instructions and safety data sheets. Critical aspects for Evidence of the following is essential: assessment and evidence applying relevant workplace policies and required to demonstrate procedures competency in this unit applying federal, state or territory, and local health and hygiene requirements and regulations and skin penetration legislation applying principles of nail science as they apply to nail or beauty treatments, including: structure and function of lower arms and legs as they relate to manicure and pedicare services appearance and gross anatomy of normal human skin appearance and gross anatomy of normal human nails skin and nail disorders contraindications to natural nail or artificial nail treatments effects of ingredients in a range of treatment products for both natural and artificial nails on natural nails applying a range of natural and artificial nail treatments providing home-care advice for artificial nail services. The following examples are appropriate for this unit: observation of learners performing a range of tasks in an actual or simulated work environment, over sufficient time to demonstrate handling of a range of contingencies, including: applying knowledge of structure of the skin and nails during natural and artificial nail services promoting skin and health care written and oral questioning appropriate to the language and literacy level of the learner, to assess knowledge and understanding of principles of nail science as they apply to nail or beauty treatments completion of workplace documentation relevant to nail treatments third-party reports from experienced beauty professionals in the workplace. Unit Descriptor Unit descriptor this unit describes the performance outcomes, skills and knowledge required to perform a range of manicure and pedicare services. The manicure or pedicare service is performed in response to client consultation and assessment, conducted and recorded on a treatment plan. Application of the Unit Application of the unit this unit applies to services offered in nail salons and beauty salons in the beauty industry. The manicure or pedicare service could be an individual treatment or form part of a series of manicure or pedicare treatments that have been designed to meet client requirements. The unit applies to nail technicians and other beauty workers who interpret observations and information, and follow known routines in order to plan and perform manicure and pedicare services that meet client requirements. Required knowledge the following knowledge must be assessed as part of this unit: infection control procedures and universal precautions workplace policies and procedures in regard to manicure and pedicare services appearance of contraindications and adverse effects effects of changes created by complementary nail shapes and colour polish or varnish application workplace product range effects and benefits of a defined range of workplace manicure and pedicare products care and cleaning requirements for manicure and pedicare implements correct and environmentally sound disposal methods for all types of waste and in particular for hazardous substances. The following examples are appropriate for this unit: direct observation of learners performing a range of tasks in an actual or simulated work environment, over sufficient time to demonstrate handling of a range of contingencies, including: preparing clients for manicure and pedicare services selecting manicure and pedicare products and applying nail care techniques and products according to manufacturer instructions providing home-care advice according to client needs written and oral questioning appropriate to the language and literacy level of the learner, to assess knowledge and understanding of the provision of manicure and pedicare services, including the safe use of products and equipment and relevant health regulations completion of workplace documentation, including treatment plans relevant to the provision of manicure and pedicare services completion of self-paced learning materials, including personal reflection and feedback from trainer, coach or supervisor review of portfolios of evidence and third party workplace reports of on-the-job performance by the candidate. Clients may include: new or regular clients with routine or special needs male or female clients people from a range of social, cultural and ethnic backgrounds and with varying physical and mental abilities. Contraindications may bacterial, viral or fungal infections include: warts inflamed skin visible non-normal nails rashes blisters, corns and calluses heel fissures bunions hammer toes circulatory problems. Appropriate professional may medical practitioner include: complementary therapist podiatrist. Equipment must include: sanitising tray or unit for implements, with appropriate strength solution. Equipment may include: nail clippers or scissors emery board, rasp, and file orange stick or cuticle pusher exfoliation cream paraffin wax bath buffer foot spa vibrating and whirlpool electric spa machine towels water bowls cleaning pod. Application of the Unit Application of the unit Gel nail application services are performed in response to client consultation and assessment, conducted and recorded on a treatment plan. They could be an individual treatment or form part of a series of regular treatments that have been designed to meet client requirements. The unit applies to nail technicians and other beauty workers in nail salons and beauty salons, who interpret observations and information, and follow known routines in order to plan and perform gel nail services that meet client requirements. Methods of assessment A range of assessment methods should be used to assess practical skills and knowledge. Treatment plan may include: required service areas requiring special treatment products selected for service recommended home-care products use of electric file tools, implements and equipment follow-up procedures. Contraindications may damaged natural nails from ineffective removal of artificial nails include: bacterial, viral or fungal infections warts inflamed skin visible non-normal nails rashes blisters corns calluses. Unit Descriptor Unit descriptor this unit describes the performance outcomes, skills and knowledge required to perform a range of acrylic nail enhancement services to enhance the appearance of fingernails and toenails. The service is performed in response to client consultation and assessment, conducted and recorded on a treatment plan. Application of the Unit Application of the unit this service is offered in nail salons and beauty salons. It could be an individual treatment or form part of a series of regular nail treatments that have been designed to meet client requirements. The unit applies to nail technicians and other beauty workers who interpret observations and information and follow known routines in order to plan and perform acrylic nail services that meet client requirements.
Order genuine antabuse online
Acne is inuenced by 3 factors generating comedonal and inammatory papule formation treatment gout generic antabuse 500 mg free shipping. They are the formation of a Supercial Chemical keratinous plug, increased sebum production, and increased growth of commensurate microorganism, in particular Pro Peels for Acne Vulgaris pionibacterium acnes. Androgens help to stimulate sebaceous gland activity, the most commonly used chemical peel is glycolic acid (Ta leading to lling of the comedones with sebaceous material, ble 1). This is an alpha-hydroxy acid, which has a hydroxyl which provides a medium for endogenous bacteria to grow. Many acne treatments are issued a pregnancy rating on glycolic acid, epidemiological available to physicians for treating acne that specically in studies have not detected any fetal abnormalities when gly colic acid was used on pregnant patients. In this article, we focus on 2 commonly used nonlaser therapeutic home use at lower concentrations (5-20%) and pH 4-6 com options for supercial exfoliation: supercial chemical peels pared with ofce use, where it is used at its highest soluble concentration of 70% and a pH of 1 to 2. Because the resolve of comedones ranges between 2 and 6 use applications are as a wash used once or twice a day. If patients have no current medical acne regimen, an appropriate topical antibiotic and/or topical retinoid should be supplemented. Patients on oral retinoids are not recommended to undergo supercial peeling procedures be cause there may be severe irritation. These patients are more prone to develop postpeel worsening of papular and pustular lesions secondary to the postoperative wound care. Patient perception of successful treatment and realistic expectations also are addressed. If these patients desire to proceed with the procedure, a test site could be peeled to check for possible reactions or the peeling compound may be started at lower concentrations and ti trated up as tolerated. The physician should also assess if the patient has any history of oral herpes simplex virus infections and start appropriate antiviral prophylaxis14 to ensure no cutaneous eruptions develop after the ensuing exfoliation (Fig. After the physician determines that the patient is a good candidate for supercial peeling, one option is to initi ate treatment at home with a glycolic acid solution for home use as well as either topical retinoid and/or topical or oral antibiotic treatment depending on their current regimen (Ta ble 2). The peel is performed by cleaning the face with a gentle cleanser, followed by stripping away any surface oils 214 S. Uebelhoer demonstrate that supercial chemical peels can benet many different skin types. After the procedure, the patient undergoes a postpeel reg imen of an emollient for dryness and crusting and a combi nation of sunscreen and/or occlusive moisturizer (white petrolatum) to prevent any further irritation (Table 3). Com plications after the peel of which to be aware are urticarial eruptions or perioral dermatitis (Fig. The patient should know these complications and notify the treating physician if they develop so appropriate treatment can be started. For urticarial eruptions, we recommend starting treatment with an oral antihistamine, such as hydroxyzine or loratadine. If Figure 2 Complication of herpes simplex labialis in patient after glycolic acid peeling. This gure was published in Mark Rubin (ed): Table 2 Glycolic Acid Peel/Acne Wash Procedure Procedures in Cosmetic Dermatology Series: Chemical Peels (Pro Instructions cedures in Cosmetic Dermatology), Volume 1. After your initial consultation, start washing your face routinely with a skin regimen that includes your glycolic acid cleanser. Two weeks prior to your peel you should begin a skin given to you by your physician. At this moment, the glycolic retinoids, such as retinol acid is neutralized with a buffered bicarbonate solution or Waxing, depilatories, electrolysis cool water. This neutralization of the acid prevents further Masques, loofahs and other sponges corneocyte adhesion, which prevents peeling to deeper layers Hair dyeing, permanent wave or straightening of the epidermis. During the procedure, most patients de treatments Other resurfacing or exfoliating treatments velop a burning sensation, which is normally relieved after Use of the above products/treatments prior to your peel washing off the solution and made bearable during applica may increase the reactivity of the skin to the glycolic tion by using a fan to blow cool air over the face. We have reviewed your medical history and have been clinical trials demonstrating the efcacy of this tech discussed the following areas: nique on Caucasian16,17 as well as darker skin types (Fig. In gen If there is any additional information that has not been eral, it took the former group 3 to 4 peels to achieve a de discussed, please contact your physician prior to you crease of 50% of acne lesions, whereas the latter required up peel. As a reminder, if you do have a history of herpes to 9 treatments to obtain a similar general response. In this simplex (cold sores) you whould be on a preventive oral study, 20% of patients experienced some worsening of their antiviral medication. The peel procedure can induce an acne after treatments associated with the erythema and dis episode of herpes lesions on patients who have had comfort as described above, but in general most patients were them previously. At the day of your appointment to have the peel, coworkers18 observed glycolic peeling with 30% to 50% con please come to the ofce fully cleansed face; no makeup, aftershave or cologne should be applied. They used the greater concentration in patients with oilier skin types and achieved an objective improvement in the Supercial Chemical Peel/Acne Wash Postprocedure Instructions. This table was adapted from a section published in Procedures in majority of patients examined after 11 treatments. These pa Cosmetic Dermatology Series: Chemical Peels (Procedures in tients developed similar complications as mentioned previ Cosmetic Dermatology), Volume 1, Mark Rubin, Page 32, Copy ously without any noted hyperpigmentation. Supercial chemical peels and microdermabrasion for acne vulgaris 215 Figure 3 Patient with type V skin comparing baseline (A) with skin after 3 glycolic acid peels, one at 20% and the other two at 35% (B). Patients that develop either of these complications is encountered, we generally perioral dermatitis can be treated with oral tetracyclines till recommend discontinuation of any future glycolic acid con the eruption clears. In between ofce peels, the patient is encouraged to continue glycolic acid topically as well as Table 3 Glycolic Acid Peel/Acne Wash Postprocedure Instructions any other acne regimen. Peeling usually occurs over the rst It may take up to 1 week for the appearance of your skin day after treatment (Figs. Some patients see benets of you may experience some of the following: stinging, post peel procedures for up to 5 months (Fig. These sensations will gradually diminish over the course of the week as the skin returns to its the other commonly used ofce peel is salicylic acid. If swelling occurs, use cold incorrectly labeled as a beta-hydroxy acid, which would in compress with ice for 15 minutes on and 15 minutes off, dicate a hydroxyl group at the second carbon from the car intermittently as needed. Instead, it is a benzoic acid Following these guidelines will help accelerate the with a hydroxyl group at the atom adjacent to the carboxyl renewal process: containing carbon. This compound would more appropri Apply the postprocedure moisturizer twice daily for 3 to ately be termed o-hydroxybenzoic acid. It is ingested orally 7 days until the skin returns to its normal appearance without complications in its acetylated form, aspirin. Although no studies day after the peel because you are more sensitive to the have demonstrated topical salicylic acid use in pregnant pa sunlight. Furthermore, systemic salicylic Scratch the skin acid causes platelet coagulation problems in nursing infants Pick the skin of women undergoing salicylic acid peels or patients of anti Use a masque on the skin coagulation. In-ofce salicylic acid peels are generally performed at this table was adapted from a section published in Cosmetic Der matology Series: Chemical Peels (Procedures in Cosmetic Derma 20% to 30% concentration with home use between 0. Uebelhoer Figure 4 Patients with urticarial (A) and perioral dermatitis (B and C) after glycolic acid peeling. This gure was published in Mark Rubin (ed): Procedures in Cosmetic Dermatology Series: Chemical Peels (Pro cedures in Cosmetic Dermatology), Vol ume 1. The practitioner can quantify the topical application amount to patients are sent home with a salicylic acid solution-based the amount of white precipitate left behind. After this product to test compliance and safety of applying the prod 4-minute application, the substrate may then be easily uct. A fan may be used during this thus allowing the physician to apply a more homogenous procedure to allow patients some comfort with the burning application. Just like glycolic acid, salicylic acid can be used sensation of supercial peeling as with glycolic acid applica in all skin types. Fur many physicians recommend hyperpigmentation prophy thermore, salicylic acid is a volatile compound; therefore, laxis for both glycolic and salicylic acid peels with topical after 4 minutes of topical application, there is usually no hydroquinone. This is especially important for patients of Figure 5 Patient 2 weeks after 70% glycolic acid peel (B) compared with baseline (A). Supercial chemical peels and microdermabrasion for acne vulgaris 217 Figure 6 Baseline (A) compared with postprocedure day 1 (B) after 70% glycolic acid peel. As discussed earlier in this text, it is im compared with glycolic acid, which displayed new acne le perative to assess skin types before chemical peeling and sions after discontinuation of peeling.