Manforce
Generic 100mg manforce visa
However erectile dysfunction causes mnemonic buy manforce line, survival with temperatures of 46 ° C were recorded, and fatalities at significantly lower body temperatures have occurred. Heat regulation: the body absorbs heat in the same way as he reveals: conduction, convection, radiation and evaporation. For the function of thermal emission, undisturbed integrity of the skin, sweat glands function and autonomic nervous system is essential. Factors affecting the development of heat disorders: High temperature and humid environment, disturbed evaporation, increased physical activity, age, body weight (thickness), chronic alcoholism and a variety of acute and chronic diseases, medications and drugs. The most serious disorder associated with inadequate thermal regulation is heat stroke. Heat stroke, heat cramps, and heat exhaustion are the three main heat disorders of the human organism. The first type occurs in young people, while the other is not related to physical effort and is common in the elderly, chronically ill and young children. Etiology: Elevated temperature and humidity of the environment, increased body heat production (increased metabolism sepsis, thyrotoxic crisis, increased muscular activity exercise, convulsions, tetanus), decreased possibility of physical cooling, various drugs, and poisoning (cocaine, amphetamines. Clinical signs: Sudden onset, sometimes preceded by headache, dizziness and fatigue Increased heart rate 160-180 / min Blood pressure is often lowered Circulatory collapse, congestive heart failure Rapid breathing Disorientation precedes unconsciousness and convulsions Delirium, confusion, tremors, disturbed speech the feeling of burning Red, dry, hot skin Rapid growth of temperature to 40 41ºC Complications: Heart failure, pulmonary edema Permanent brain damage Renal (25-30%) Damage to the liver, usually transient 75 Damage to the lungs Destruction of muscle mass (rhabdomyolysis) Lethal outcome Prehospital Treatment: the removal of victims from the overheated environment Ceasing all medical interventions that can lead to temperature increase Wrap the victim in wet blankets and allow air circulation (fan) Immersion in water (not ice) Ice cooling the areas around main arteries (femoral, subclavian, carotid artery) In the case of loss of consciousness ensure airways endotracheal tube, laryngeal mask, airway, etc. Heat exhaustion It occurs due to excessive loss of fluids and electrolytes, resulting in hypovolemia and electrolyte disbalance. Occurs very often due to excessive sweating without replacement of water and salt. Clinical presentation: Low blood pressure Poorly palpable pulse the gradual development of malaise and weakness Nausea Excessive sweating Pale, clammy skin Fainting Treatment: Compensation of fluids and salts by the oral route. Heat cramps Heat cramps occur during physical exertion due to excessive intake of water without enough replacement of salt (so-called water intoxication) or due to loss of salt due to strong sweating during physical stress at high temperature (usually above 38 ° C. Take care of small children, the elderly and those with chronic or acute health disorders. Be aware that the lack of a sense of thirst may not be an indicator of good hydration (especially in the elderly. If these disorders are already present, it is necessary to act promptly to avoid further deterioration. Injuries caused by electricity Injuries caused by an electrical current are relatively rare. Some victims of electric shock die at the site of the accident, before it is even possible to provide help, while survivors often have severe injuries that demand quick and adequate treatment and have an uncertain outcome. A third occur in houses and appartments with children being the most frequent victims. It is estimated that a few hundred of these kind of injuries occur in the world every year, with 30% being lethal and 70% leaving severe morbidity in surivors. Injuries caused by electricity are divided into injuries caused by lightning, low and high voltage electricity. Unlike them, injuries caused by high voltage electricity (> 1000 V) along with cardiac arrest, cause very severe damage and destruction of tissue. High voltage electrical current causes the most serious consequences, however, death from low voltage current or so-called "home electricity" also often occur. The factors that determine the nature, seriousness and consequences of electric shock depend on: 1. Path of electric current At current of <1000 V, a direct mechanical contact is required for electric shock to occur. In contrast, with currents that are > 1000 V, the appearance of an electric arc usually causes an electrical impact. Resistance 2 of dry and well-keratinized, intact skin is around 20,000-30,000 Ω /cm, for palmar skin even 2 2 as high as 2. However, if the skin is damaged by abrasion, puncture or cutting wound, resistance can be reduced to 2 200-300 Ω / cm. Unfortunately, in these situations electrical shock, which usually causes less injury, can turn into life-threatening shock. The resistance of the skin can be reduced by prolonged exposure to the current flow, which occurs in alternating current of 50 Hz / sec. This type of power can produce tetanic contractions of skeletal muscles and prevent the release of electricity source and thus lead to prolonged exposure. This phenomenon usually occurs with passing of >14-16 mA current and can lead to dislocation of joints and fractures. With ≤15 mA alternating current it is often possible to release electruical conductor. The above-mentioned phenomena most often happens with alternating currents of > 50 mA, while with direct current this phenomenon is possible at 300-500 mA currents. Severe injuries and destruction of cell membranes of skeletal muscles and nerves occur with currents of > 0. A few seconds of prolonged contact can lead to thermal injuries of subcutaneous and deeper tissues. Since all tissues, regardless of the type, are sensitive to temperature exposure, there is thermal damage of all affected tissues on the path of the electrical current. The spread of electricity also has an impact on the type of possible injury and its 78 consequences. Transthoracic shock (hand-arm) has a higher probability of lethal outcome than vertical (hand-foot) or wide apart (leg-foot. Vertical shock, however, often causes heart damage due to the direct effects of electricity and spasm of the coronary arteries. Injuries from electrocution are the result of two effects: the direct effect of current on the cell membrane and the smooth muscles of the heart and blood vessels and conversion of electrical energy into heat as it passes through different tissues. In the light of this, an injury can be direct (primary) caused by the electricity or heat energy and delayed (secondary) caused by vascular blockages. Fractures and other injuries of musculoskeletal system due to tetanic contractions or falls are frequent. A premature formation of cataract of the eye is possible and even amaurosis blindness. However, if arrhythmias have not developed in the initial stages of injury it seems that such events are rare in the later course. Electrical contact with the head most often causes short-term unconsciousness, with the occurrence of transient convulsions similar to epileptic seizures. Common symptoms are confusion, deafness, amaurosis, headaches and retrograde amnesia. Lightning strike specifities Injuries from lightning strikes are the result of impact caused by an electric arc, rather than by direct contact. An enormous amount of electricity generates a very strong magnetic field around itself, which can induce electrical currents in the nearby body. This current is strong enough to cause heart disturbances and central nervous system damage. The temperature of the electric arc reaches ≤30000 ° K, which induces thermoacustical shock waves, called thunder. Shock waves reach a pressure of 4-5 atmospheres near the arc, while these pressures are much lower already at a distance of 1 m and are at value of 1-2 atm. This event can be very dangerous for people in the vicinity, as a voltage difference of about 1500-2000V between the feet of an individual can occur, with the emergence of the 2-3 A current that lasts for several μsek. Therefore, it is often necessary in trauma patients just to provide respiratory assistance and support. A lightning strike may cause a wide range of neurological injury, which may be the primary, as a result of the direct effect on the brain or secondary, as a result of cardiac arrest and hypoxia. Victims who survive lightning strike or successfully respond to resuscitation have a good prognosis, because subsequent cardiac arrest is not common. Unfortunately, bystanders are afraid to approach the victim, until a couple of minutes pass, fearing that they too may suffer from the "residual current". However, unless the victim is not on an isolated platform, there is no residual electricity after a few milliseconds.
Diseases
- Chromosome 18, trisomy
- Opsismodysplasia
- Lobster hand
- Hepatic veno-occlusive disease
- Microcephaly mental retardation spasticity epilepsy
- Hypophosphatasia, infantile
- Lymphatic neoplasm
- Neurofibromatosis type 2
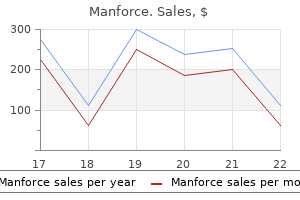
Purchase cheap manforce line
There is no cleft of the alveolar cleft in complete clefts of the primary palate the nasal floor or the alveolus erectile dysfunction treatment charlotte nc purchase manforce 100 mg without prescription. The markings are popular, but now largely given up because of its deleterious essentially the same as in the complete variant. On completion of the rotation incisions, it is possible gingivoperiosteoplasty has been used in this setting to close to lengthen the lip excessively unless one is meticulous in the alveolar defect and utilize the presumed potential of the planning and executing the rotation incision. A backcut is periosteum for bone formation to produce ?boneless bone seldom necessary. Some of these later develop Hsieh et al45 have reported a negative effect on growth severe cleft lip nasal stigmata. Other studies have also demonstrated closed alar dissection on these partial cleft lips. Microform Cleft Lip If the Cupid?s bow point is raised, however, a rotation is definitely required. In these patients with a trivial defi? this refers to a variant of cleft lip that primarily involves the ciency, the aim is to do only as much as is required to avoid vermillion. It has been variously called the mini cleft, forme? excess surgical trauma to minimize the scaring. However, one should ??Mini microform, where the cleft is confined to a assess the degree of continuity of muscle across this region vermillion notch with the Cupid?s bow points at the and if there is mild deficiency, this can be corrected by same level. If there is gross deficiency, then one ??Microform, where the cleft involves the vermillion and should perform a classical Millard?s procedure (Fig. In the mini microform lips, only a vermillion notch correction In developing countries, it is still not uncommon to find procedure, including scar excision, muscle build up, and a Z patients presenting for cleft repair later in life sometimes plasty on the mucosa, is required. In addition, there may be a Cupid?s bow that is level If these patients have a cleft lip with an unrepaired or pulled up. If the Cupid?s bow is level, then a mere scar cleft palate, the cleft palate repair should take precedence excision of the intervening tissue and a repair on the body of for optimal speech. In patients older than 3 years of age, a the lip excising a furrow or a scar is required. However, ??Deficiency of orbicularis oris muscle at the vermillion the vermillion in these older patients may be a little border that is preempted by retaining adequate muscle more difficult to manage as very often there is an excess bundle at the time of paring (Fig. These are then that needs to be trimmed carefully for an aesthetically sutured with nonabsorbable nylon sutures (6?0. However, as a simultaneous open rhinoplasty and septal repositioning these would be against the Langer?s lines, we use a Z using the approach of Trott and Mohan27with the sutural plasty on the mucosa, away from Noordhoff?s red line technique developed by the authors. Pulling up of the Cupid?s bow with resultant Prevention of Deformities notching, the immediate postoperative period does descend with time with a notch free lip if the rotation has been Preventable deformities following cleft lip repair include: adequate. This, we believe, can be eliminated by cleft lip repair unless care is taken at the primary proper alignment of the bony segments preoperatively repair to avoid it. However, should some Causes of a vermillion notch: amount of disparity remain, we perform an unequal ??Inadequate rotation of the Cupid?s bow. Z plasty as advocated by Jackson50 on the nasal layer, ??Inrolling of the skin and muscle edges. He releases the bony ??Inadequate rotation of the Cupid?s bow, causing tenting attachment of the lateral cartilage and also excises a up of the lip and the resultant pull causes notch on the part of the web. Unilateral Cleft Lip 59 on the angle of the back?up cut depending on the width of the columella, using a wider angle in a broader columella. Noordhoff-Chen Technique Noordhoff used a technique based on the Millard?s rotation advancement procedure but modified it in the following manner. The C flap was used either for the columella or the sill depending on the individual patient. Noordhoff addressed the vermillion mismatch (the vermillion on the cleft side is usually fuller than that on the noncleft side. This is in contrast to most other tissues which are all richer on the noncleft side. He retained a V?shaped Unsolved Problems extension from the otherwise discarded part of the cleft side vermillion and inset this into a cut made at the junction Despite the large strides in the correction of the lip and nose, of the wet and dry mucosa (Noordhoff?s red line) on the there remain certain problems that remain uncorrected. In the lip, there is a lateral vermillion deficiency that this helped in achieving a much better color match of the occurs especially when there is a gross alveolar disparity. However, care must be taken to meticulously this may be reduced significantly by presurgical molding. A nostril sill has not been produced effectively by any of the present methods of lip repair. Fisher?s Anatomic Subunit Repair Having trained with Noordhoff and Thompson, Fisher Mohler?s Modification of Millard?s devised a technique using a smaller triangle that is pre? Procedure cisely measured on the noncleft side (Fig. The majority of patients studied by accurate measurements with calipers to achieve adequate him belonged to this type. The disadvantages are that it is not an easy procedure extending into the base of the columella with a backcut at to master, and like all triangular flaps, the Cupid?s bow may right angles confined to the columella. The aim of this extension was to simulate the noncleft philtral column and to avoid a backcut on the lip. The resultant gap on the columella was covered the Pfeiffer and Afroze Incisions by the C flap. As a result, the advancement flap was inset more laterally and did not have to go as far across the base of Apart from the straight repair, Millard?s repair, and Triangular the columella as in the conventional Millard technique. This flap techniques, some surgeons prefer the Pfeiffer wavy technique is favored by Noordhoff and Chen. Reddy believes that this incision is versatile and gives good scars and also adequate lengthening of the lip. Hypertrophic scars are initially injected with Triamcinolone References intradermally with the use of silicone sheet or gel topically. Plast Reconstr Surg 1987; 80(4):511?517 Contractures are released; rerotation is necessary in 2. Studies in the pathologic anatomy Primary rhinoplasty diminishes the extent of the secondary of the unilateral hare?lip nose. St the authors perform a preschool rhinoplasty, and use a Louis: Mosby Year Book; 1991:3?4 sutural fixation technique for the cartilages; hitching the 6. Paring and approximation with needles and/ lower lateral cartilage on the cleft side to the upper lateral or suturing. Boston: Little Brown; is a stable fixation and usually there is no need for onlay 1976:79?88 cartilage grafts. Boston: Little Brown: 1976; 90?100 the preschool rhinoplasty if indicated is done at age 5? The at the same time to try and avoid additional surgeries for Unilateral Deformity. The Unilateral it is better to wait until the completion of the growth of the Deformity. The Unilateral secondary rhinoplasty is done after that so that there is a Deformity. Rotation advancement principle in cleft lip 9 on Secondary Rhinoplasty in Cleft Lip Nasal Deformity in closure. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd; 2010: It was Sir William Osler who said ?he who studies medicine 142?152 without a book sails an uncharted sea, but he who studies 15. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946) 1952;9(2):115?120 medicine without a patient does not go to sea at all. A triangular flap operation for the primary repair of Therefore, it is not from books that surgery can be learnt. Plast Reconstr Surg Transplant Bull One must apprentice with a surgeon who has mastered that 1959;23(4):331?347 particular operation. Augmentation of the Conference of the Association of Plastic Surgeons of India at nostril splint for retaining the corrected contour of the cleft lip Varanasi; 2008 nose. Repair of Long?term comparison of four techniques for obtaining nasal unilateral cleft lip. Elsevier; symmetry in unilateral complete cleft lip patients: a single Philadelphia, 2012:517?549 surgeon?s experience.
Cheap manforce 100 mg with mastercard
Administer diuretics: loop diuretic such as furosemide (Lasix) erectile dysfunction pills herbal cheap manforce 100 mg without a prescription, To achieve excretion of excess fluid, either a single thiazide di thiazide diuretic such as hydrochlorothiazide (Esidrix), or uretic or a combination of agents may be selected, such as potassium-sparing diuretic such as triamterene (Direnium), thiazide and spironolactone. Potassium deficit may occur, especially if client is receiving potassium-wasting diuretic. May be done to rapidly reduce fluid overload, especially in the presence of severe cardiac or renal failure. Mucous membranes dry, furrows on tongue, decreased tearing • Complete, sudden cessation of intake; or prolonged diminished and salivation intake of fluids. Levels may be higher than normal if sodium trations may mirror blood levels or be the opposite. Older adults (who are more likely to have serious and chronic conditions than young people) are at increased risk for de hydration, one of the most frequent causes of hospitaliza tion in adults ages 65 to 75 (Russo, 2012. Additional risk factors for dehydration include female gender, more than four chronic conditions, more than four medications, immo bility, and laxative use (Post, 2011. Palpate peripheral pulses; note capillary refill and skin color, Conditions that contribute to extracellular fluid deficit can re turgor, and temperature. Measure or estimate fluid losses from Fluid replacement needs are based on correction of current all sources such as gastric losses, wound drainage, and deficits and ongoing losses. Measure Although weight gain and fluid intake greater than output may edematous areas such as abdomen and limbs. Ascertain clients beverage preferences, and set up a 24-hour Relieves thirst and discomfort of dry mucous membranes and schedule for fluid intake. Turn frequently, gently massage skin, and protect bony Tissues are susceptible to breakdown because of vasoconstric prominences. Bathe every other day using mild Skin and mucous membranes are dry with decreased elasticity soap. Provide safety precautions, as indicated, such as use of side Decreased cerebral perfusion frequently results in changes in rails where appropriate, bed in low position, frequent mentation or altered thought processes, requiring protec observation, and soft restraints if required. Investigate reports of sudden or sharp chest pain, dyspnea, Hemoconcentration and increased platelet aggregation may cyanosis, increased anxiety, and restlessness. Refer to listing of predisposing or contributing factors to de termine treatment needs. Note: Dehydration is the most common fluid and electrolyte imbalance in older adults (Russo, 2007. Depending on the avenue of fluid loss, differing electrolyte and metabolic imbalances may be present and require correc tion. For example, use of glucose solutions in clients with underlying glucose intolerance may result in serum glucose elevation and increased urinary water losses. Enteral replacement can provide proteins and other needed elements in addition to meeting general fluid requirements when swallowing is impaired. Serum sodium range: 135 to 145 mEq/L of impulses and is essential for maintaining acid-base b. Use of certain drugs—hypoglycemia medications, bar infusion of sodium-free solutions biturates, antipsychotics, aminophylline, morphine (may b. Dilutional hyponatremia—water gains stimulate pituitary gland to secrete excessive amounts i. Sodium/Water Deficit Sodium less than 135 mEq/L, urine specific gravity elevated, and serum osmolality normal. It plays a key role in maintaining fluid balance—where may not occur until level is less than 120 mEq/L. Normal range for adult female is 39% to 45%; normal adult male range, 44% to 56% (Matheny 2012. Concen to sodium loss from a nonrenal source, unless sodium-wasting trations may mirror blood levels or be the opposite. Severe hyponatremia can cause neurological dam age or death if not treated promptly. Co-occurring hypochloremia may produce slow and shallow respirations as the body compensates for metabolic alkalosis. Encourage foods and fluids high in sodium such as milk, meat, Unless sodium deficit causes serious symptoms requiring im eggs, carrots, beets, and celery. Note: Too rapid or excessive administration of hypertonic solutions can be lethal. Sodium chloride Used to replace deficits in the presence of chronic or ongoing losses. Note: May be contraindi cated in clients with liver disease because nephrotoxicity may occur. May be done to restore sodium balance without increasing fluid level when hyponatremia is severe or response to diuretic therapy is inadequate. Predisposing or Contributing Factors disease; excessive ingestion or infusion of sodium; salt a. Excessive water losses: polyuria (as may occur with diabetes water near-drowning insipidus); use of osmotic diuretics (such as mannitol); pres c. Insufficient water intake: administration of tube feedings ence of fever, profuse sweating, vomiting, diarrhea or high-protein diets with minimal fluid intake, self b. It plays a key role in maintaining fluid balance—where be accompanied by severe neurological signs. Is reduced in presence particles (sodium, glucose, and urea) in plasma, reflecting fluid of extracellular fluid excess and less than 200 mOsm/L with balance. Normal values are not fixed; kidneys vary rate of excretion to match dietary intake (Matheny, 2012) but generally range from 15 to 250 mEq/L/day. Identify client at risk for hypernatremia and likely cause such Early identification and intervention prevents serious complica as water deficit or sodium excess. Deep, labored respirations with air hunger suggest metabolic acidosis due to hyperchloremia, which can lead to cardiopul monary arrest if not corrected. Assess these parameters are variable, depending on fluid status, and presence and location of edema. Sodium imbalance may cause changes that vary from confusion and irritability to seizures and coma. Maintain safety and seizure precautions, as indicated, such as Sodium excess and cerebral edema increase risk of convulsions. Assess skin turgor, color, and temperature and mucous Water-deficit hyponatremia manifests by signs of dehydration. Avoid use of mouthwash that Promotes comfort and prevents further drying of mucous contains alcohol. Give free May prevent hypernatremia in client who is unable to perceive water to client receiving enteral feedings. Recommend avoidance of foods high in sodium such as Reduces risk of sodium-associated complications. Refer to listing of predisposing or contributing factors to determine treatment needs. Monitor serum electrolytes, osmolality, and arterial blood Evaluates therapy needs and effectiveness. Replacement of total body water deficit will gradually restore sodium and water balance. Restriction of sodium intake while promoting renal clearance lowers serum sodium levels in the presence of extracellular fluid excess. Other: sweat losses (heavily perspiring person acclimated to carbenicillin, steroids; licorice abuse heat); liver disease b. It works with other electrolytes, such as chloride (as well as potassium) depletion. Used to deter mine how well lungs are able to move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. Changes associated with hypokalemia include abnormalities in both conduction and contractility. Encourage cough Respiratory muscle weakness may proceed to paralysis and and deep-breathing exercises; reposition frequently.
Purchase manforce
Vestergaard (2002) reported results from a meta-analysis of 25 studies pertaining to smoking history and Graves disease (hyper thyroidism) impotence definition buy manforce overnight delivery, Graves disease with ophthalmopathy, and various forms of hypothyroidism. Current smoking was strongly associated with risk of developing Graves disease (odds ratio 3. One study showed an increasing risk with increasing number of cigarettes per day in current smokers. Some studies were limited to women; in other studies, the number of men was relatively small (20% of the total sample. Nevertheless, there was some indication in the two studies that allowed sex-specific analyses that the association was stronger in women than in men. Stronger associations for never smokers and current smokers were seen with Graves disease with ophthalmopathy (for never smokers, the odds ratio was 4. The only study that presented sex-specific analyses reported a stronger effect in women than in men. Fewer studies are available regarding smoking and hypothyroidism (defined as Hashimoto thyroiditis, clinical hypothyroidism, subclinical hypothyroidism, or autoimmune thyroiditis), and the overall association with hypo thyroidism was weaker (odds ratio around 1. Several prospective studies provided data regarding the risk of developing multiple sclerosis in relation to smoking history in women (Table 12. Villard Mackintosh & Vessey (1993) also found an association with smok ing history and multiple sclerosis in the Oxford Family Planning Association cohort. In a small study using self-reported multiple sclerosis in a population-based study in Norway, the overall asso ciation with ever smokers (risk ratio 1. Two recent reviews have summarized studies of smoking history in relation to risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (Albano et al. The association with smoking history appears to be stronger in patients positive for rheumatoid factor than in patients negative for rheumatoid factor and stronger in men than in women. There is also some evidence of associations with pack years or smoking duration, but more variable effects have been seen with the amount smoked per day (Albano et al. The severity of rheumatoid arthritis may be increased in smokers, as evidenced by increased disability and risk of extra articular manifestations, including vasculitis and interstitial lung disease, but not of joint swelling (Albano et al. A recent meta-analysis examined the association between smoking and the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in seven case– control and two cohort studies (Costenbader et al. Larger studies specifically designed to assess sex differences are needed to understand the effect of smoking across the spectrum 144 Chemical/Physical Agents and Autoimmunity of autoimmune diseases. Although a positive correlation between alcohol intake and the degree of liver injury has been reported, there is a high degree of variability in the development and severity of disease between individuals with similar levels of abusive ethanol consumption, and only a small percentage of alcoholic patients develop cirrhosis or hepatitis. Heavy drinkers without significant liver disease had significantly lower titres of IgA antibodies against acetaldehyde modified erythrocyte protein and IgG antibodies against oxidized or malondialdehyde-modified low-density lipoproteins, compared with patients with alcoholic liver disease (Viitala et al. These studies suggest that multiple mechanisms or genetic factors may be involved in the disease process. In support of this, two studies using the National Academy of Sciences – National Research Council twin registry in the United States concluded that there was genetic predisposition to organ-specific complications of alcoholism based on the significant concordance rates in monozygotic twins (Hrubec & Omenn, 1981; Reed et al. Gene polymorphisms encoding for the enzymes responsible for ethanol metabolism, oxidative stress, and proinflammatory/immune responses have been investi gated (Bataller et al. A genetic analysis of individuals participating in a study evaluating liver disease in northern Italy suggested that heavy drinkers with cirrhosis or alcoholic liver disease had a higher frequency (0. A study in alcoholic patients in Japan reported an increase in the frequency of individuals homozygous for the C1 allele in men with alcoholic cirrhosis (Yamauchi et al. In contrast, there was no difference in either C1 or C2 allelic distribution in an earlier study conducted in Caucasian men (Carr et al. Cytokine gene polymorphisms have also been suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. The í511 146 Chemical/Physical Agents and Autoimmunity allele 2 was found at a higher frequency in patients with cirrhosis than in heavy drinkers without liver disease. Jarvelainen and colleagues (2001) demonstrated that in Finnish males, expression of one T allele was associated with both alcoholic hepatitis and cirrho sis. There is conflicting evidence as to whether variations in the genes encoding for manganese superoxide dismutase represent a risk factor for alcoholic liver disease (Degoul et al. The data on cytokine and metabolic enzyme gene polymorph isms in the human population as well as experimental studies with ethanol-fed rodents are indicative of the importance of inflamma tion, oxidative stress, and endotoxin in the pathogenesis of alcohol induced liver damage. Chronic ethanol exposure has been associ ated with the formation of alcohol-modified proteins, leading to autoantibody formation and immune-mediated damage to the liver. Circulating antibodies recognizing acetaldehyde–malondialdehyde adducts have been found in Wistar rats fed an ethanol-containing liquid diet (Xu et al. Immunization with acetaldehyde adducts in conjunction with ethanol feeding stimulated ex vivo lymphocyte proliferation in B6 mice, but not in several other strains (Shimada et al. The antibodies generated by these alcohol-modified proteins may also respond to unmodified self-proteins, leading to a breaking of tolerance and autoimmune pathology. Obese strain chickens spon taneously develop a disease very similar to Hashimoto thyroiditis. They were the first model that showed that exposure to iodine affects the course of disease. Depletion of iodine after hatching, achieved by injections of potassium chlorite, reduced thyroid infiltration. In contrast, the onset of spontaneous thyroiditis was hastened by adding sodium iodide to the diet. This effect, however, was reduced by administration of antioxidants, suggesting that reactive oxygen intermediates are one mechanism by which iodine contributes to cell injury. The Biobreeding/Worcester rat has been widely used as a model for studying spontaneous diabetes mellitus, but it also develops autoimmune thyroiditis. Administration of excess iodine accelerates the appearance of the lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid and the production of thyroid-specific autoantibodies. The incidence of diabetes is very low, but many of the animals develop autoimmune thyroiditis. Iodinated thyroglobulin is more antigenic than the same molecule lacking iodine, suggesting another mechanism by which iodine enhances thyroiditis. Several studies have evaluated the effects of excessive iodine intake in humans, and antithyroid antibodies and iodine-induced hypo and hyperthyroidism have been reported following long-term iodine treatment for endemic goitre (Boyages et al. Although a few epidemiological analyses have been published, they are often confounded by the absence of a clear-cut diagnosis. Clinical outcomes can be the result of immunoallergic, pseudoallergic, or autoimmune-like mechanisms. However, a comprehensive review of adverse autoimmune responses and autoimmune diseases associated with therapeutic agents is beyond the scope of this monograph, and only a few examples will be discussed below. Table 13 provides an abbreviated list of therapeutic drugs that have reportedly been associated with autoimmune reactions. When considering drug-induced autoimmunity, it is important to differentiate two situations. On the other hand, one given agent is associated with only one given type of autoimmune disease. In the latter case, the disease can be organ specific and then closely mimic the spontaneous disease, except that cessation of the offending agent leads to the progressive recovery of clinical and then biological manifestations of the disease. The disease can also be systemic and consists of clinical manifestations and biological/immunological changes markedly different from those of spontaneous diseases. Interestingly, drug-induced systemic autoimmune-like reactions often resemble systemic hypersensitivity reactions, and this further illustrates overlapping mechanisms between immunoallergic and autoimmune-like reactions. Hydralazine inhibits the covalent 150 Chemical/Physical Agents and Autoimmunity binding reaction of the complement protein C4, and susceptibility to hydralazine-induced lupus, as in idiopathic systemic lupus erythema tosus, may depend partly upon genetically determined C4 levels (Sim & Law, 1985; Speirs et al. Adoptive transfer of T cells made autoreactive by treatment with either hydralazine or procainamide causes a lupus like disease (Yung et al. The possibility of a lupus-inducing effect of the drug on T cell development in the thymus has been suggested (Quddus et al. Studies of the specificities of B cells that respond to chroma tin-reactive T cells at the initiation of this autoimmune process demonstrated a rapid and robust expansion of anti-chromatin-secret ing B cells, thus indicating the presence of a normal immune reper toire that includes non-tolerant autoreactive B cells that respond to strong T cell drive and are readily manifested if Fas-mediated activation-induced cell death is inhibited (Ayer et al. Because of a high incidence of adverse events and the strong association with several autoimmune-like phenomena, including myasthenia, pemphigus, and Goodpasture disease, the clinical use is limited. The adverse effects of D-penicillamine in animals are similar to those observed in humans. A study on the effects of D-penicillamine in various strains of mice indicated that D-penicillamine facilitates the induction of autoantibodies in animals with an inherent suscep tibility to autoimmunity (Brik et al. Studies using the popliteal lymph node assay demonstrated that D-penicillamine is capable of inducing an antigen.
Turnerae diffusae folium (Damiana). Manforce.
- Dosing considerations for Damiana.
- How does Damiana work?
- Headaches, bedwetting, depression, nervous stomach, constipation, sexual problems, boosting mental and physical stamina, and other conditions.
- What is Damiana?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96689
Effective manforce 100mg
However guaranteed erectile dysfunction treatment order 100 mg manforce with mastercard, there is insufficient published evidence to its efficacy in establishing the risk of ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death. Back to Top Date Sent: 3/24/2020 995 these criteria do not imply or guarantee approval. Utility of current risk stratification test for predicting major arrhythmic events after myocardial infarction. Prediction of fatal or near-fatal cardiac arrhythmia events in patients with depressed left ventricular function after an acute myocardial infarction. Back to Top Date Sent: 3/24/2020 996 these criteria do not imply or guarantee approval. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Date Sent: 3/24/2020 1006 these criteria do not imply or guarantee approval. Criteria | Codes | Revision History x Adult Standers x Pediatric Standers Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington and Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington Options, Inc. Supported standing programs are routinely used by therapists as part of a postural management approach in children with severe developmental disabilities (e. These in turn, may prevent or reduce the children?s musculoskeletal problems, increase their independence, and enhance their functional abilities (Gudjonsdottir 2002, Caulton 2003. The is insufficient evidence to date to determine the efficacy of standers in reducing risk of fractures among children who are unable to stand independently due to severe developmental disabilities. In addition, it used bone mineral density, an intermediate outcome, as the primary end point. Back to Top Date Sent: 3/24/2020 1022 these criteria do not imply or guarantee approval. A randomized controlled trial of standing program on bone mineral density in non-ambulant children with cerebral palsy. The use of use of standers to reduce fracture risk does not meet the There is insufficient evidence to date to determine the efficacy of standers in reducing risk of fractures among children who are unable to stand independently. A more important clinical outcome would be the effect of the program on reducing the risk of bone fracture. The compliance rate was only 44%, and the 6 months results showed a net benefit of treatment equal to +15. These may be used by patients with mild to severe disabilities such as spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury, cerebral palsy, muscle dystrophy, or other neuromuscular conditionsthat do not enable the individual to stand independently. They can be used at home, in the workplace, extended care units, assisted living centers, nursing homes, andrehabilitation facilities. Prolonged standing has been investigated over the years for its possible benefits for patients with spinal cord injuries and other disabilities. It is suggested that standing and weight bearing activities may increase bone mineral density and muscle strength, reduce abnormal muscle tone and spasticity, improve circulation, reduce lower limb swelling, improve bowel and bladder function, prevent pressure sores, as well as other potential benefits. Many of these benefits, however, are not supported by good quality evidence (Eng 2001, Bagley 2004, Bernhardt 2012. The common types include sit to stand, prone, upright, prone, multi-positioning standers, and standing wheelchairs. Some systems can be changed by the user from a sitting to a standing position; others require the assistance of another person to change its position. Passive or static standers that remain in one place and cannot be self-propelled, 2. Mobile or dynamic standers that can be propelled by the user if 2013 Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington. Back to Top Date Sent: 3/24/2020 1023 these criteria do not imply or guarantee approval. Active standers that can create reciprocal movements of the arms and legs while the patient is standing. There is insufficient evidence to date, to determine the efficacy of standing devices on health outcomes of patients with disabilities or health conditions that render them unable to stand independently. In addition to undergoing the usual stroke care, the patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive 14 consecutive treatment with the use of Oswestry standing frame, or to receive 14 consecutive treatments but without access to the Oswestry standing frame. The results of the trail showed no statistically significant difference between the study groups in any of the primary or secondary outcome measures or for resource savings. The following trial was selected for critical appraisal: Bagley P, Hudson M, Forster A, Smith J, et al. A randomized trial evaluation of the Oswestry Standing Frame for patients after stroke. Back to Top Date Sent: 3/24/2020 1024 these criteria do not imply or guarantee approval. Criteria | Codes | Revision History x CyberKnife Robotic Radiosurgery System x Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy x Multiple Brain Metastatic Lesions (5 or more brain metastatic lesions) x Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington and Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington Options, Inc. Back to Top Date Sent: 3/24/2020 1042 these criteria do not imply or guarantee approval. Criteria | Codes | Revision History Radiosurgery can be defined as the stereotactic (precision) delivery of multiple cross-fired radiation beams to a point or volume within a configured space (Chang 2003. Stereotactic radiosurgery may also be described as a method to destroy targets using single high doses of focused ionizing radiation, administered using stereotactic guidance (Niranjan 2001. It is a combination of minimally invasive technologies administered by a multidisciplinary team consisting of surgeons, oncologists, medical physicists, and engineers. It then evolved to target benign tumors and vascular malformations in surgically inaccessible locations. These indications are continuously expanding with the rapidly evolving technology of radiosurgical systems. Currently it has become an alternative to microsurgery and conventional radiation therapy in the treatment of many lesions in the base of the skull. It is used for vascular, tumor, and functional brain surgery, including arteriovenous malformations, pituitary adenomas, acoustic neuromas, and meningiomas, as well as brain metastases. Radiosurgery was initially limited to the brain because of the requirement of a stereotactic frame attached to the skull to provide a coordinate system for tumor localization. Recent advances however, allow radiosurgical treatment throughout the body without such frames. A variety of methods have been developed to provide a reference system for the localization study to determine the target coordinates, including fixed frame and frameless systems, removable frame systems, and rigid masks. Treatment can be repeated any number of times with equal precision as the target is calculated from the position of gold markers. Isodose distributions, dosage prescription and calculation Setup and quality assurance testing Simulation of prescribed arcs or fixed portals Stereotactic intervention or treatment itself Gamma knife, the prototype of stereotactic radiosurgery was first clinically used in 1967. It developed rapidly from the earlier A-units to B units, and in 1999 to Model C that has a robotic engineering. With the gamma knife, the patient?s head is placed within a large metal collimator consisting of a dome-shaped shell with holes that transmit the radiation to the center point. A stereotactic frame is anchored to the skull with four screws that penetrate the outer table to position the head so that the desired target is at the center of the collimator. The use of the frame limited the use of the gamma knife to head lesions, and to patients who could tolerate the rigid frame fixation. Moreover, the use of fractionated treatments that extended for several days was impractical with the frame fixation (Giller 2005. The CyberKnife is a recently developed frameless stereotactic system that consists of a modified linear accelerator mounted on a robotic arm that moves slowly around the patient. It delivers several beams of radiation at each of many stopping points while minimizing radiation exposure of surrounding tissue (Quinn 2001. Stereotactic precision is achieved without a rigid frame by means of two diagnostic x-ray cameras mounted in the CyberKnife vault and are used to acquire real-time images of the patient?s internal anatomy during treatment. Any patient motion is detected by these images, and the information is used by the robot to compensate and keep the linear acceleration on target. Treatment time ranges from 45-60 minutes and can be given in one fraction, or several fractions with smaller doses given over several days, depending on the condition being treated and the size of the affected area. The use of the CyberKnife for radiosurgery of organs other than the brain is more challenging and requires several technical refinements. When used for spinal lesions for example, it requires the placement of internal small 2-mm stainless steel screws in the spinal lamina adjacent to the target site as ?fiducial markers? (Giller 2005. It is non-invasive, and can treat poor surgical candidates, and tumors inaccessible to surgery, Moreover, it can safely deliver higher doses of radiation than those used in conventional radiotherapy, while sparing the surrounding tissues from the high levels of radiation. It can thus be more effective in treating radioresistant and recurrent tumors and may be used as a boost to conventional radiotherapy. On the other hand, its was reported that its efficacy is lower and risk of complications higher in larger tumors, or those that were previously treated with radiation.
Buy generic manforce on-line
Clonidine was determined to be nonparticulate sizes of different steroids and the effect of dilution erectile dysfunction pills photos cheap 100 mg manforce mastercard, re when examined by light microscopy, clonidine mixed viewed the relative neurotoxicities of the steroids. Their with equal parts of each of the 3 corticosteroids did not results showed Dexamethasone and betamethasone result in increased clumping or increased particle size sodium phosphate were pure liquid. Fur larger particles was significantly greater in the meth ther, dexamethasone 4 mg/mL solution had no measur ylprednisolone and the compounded betamethasone able particles, and there was no apparent aggregation preparations compared with the commercial beta in the solution. The the commercial betamethasone and triamcinolone, al particles were densely packed with extensive aggrega though betamethasone had a smaller percentage of the tion observed. The betametha betamethasone with lidocaine decreased the percent sone 6 mg/mL solution contained long, rod-shaped age of the larger particles, whereas increased dilution particles of varying sizes. The particles formed extensive of methylprednisolone 80 mg/mL with saline increased aggregates. One study comparing Celestone safer with no significant difference in the effectiveness Soluspan and Kenalog (2244) showed Kenalog to be (2137. Formulations of commonly used epidural steroids superior to Celestone at one and 2 weeks after injection are shown in Table 43 and the pharmacologic profile of (2244. In a study evaluating the cervical transforaminal commonly used epidural steroids is shown in Table 44 epidural injections (2250), the effectiveness of dexa (890,1029,1990,2001,2218,2219,2220,2232-2277. In a study assessing the comparison ies (921,983,2244,2249-2252) and in 2 randomized trials of 2 doses of corticosteroids in epidural steroid injec (232,233. The randomized trials showed no significant tions (2252), there was no significant difference in the difference between methylprednisolone 40 mg com outcomes either with 40 mg of methylprednisolone or pared to 6 mg of either commercial betamethasone or 80 mg, both showing comparable results, with a less non-particulate compounded betamethasone. This philosophy there was no significant difference when compared to was also reaffirmed in another study (2251) evaluating the effect of local anesthetics with any of the steroids. The long-term data the groups at one week after the second transforaminal are available only from randomized trials. Among the doses of 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 nonparticulate dexamethasone phosphate was shown mg, or 40 mg, all of them were equal except the 5 mg to be close to the safety and effectiveness of particular dosage. The authors (2251) recommended a minimal methylprednisolone acetate in the treatment of lumbar effective dose of corticosteroid of 10 mg equivalent of radiculopathy (921. In another study of selective nerve triamcinolone in transforaminal epidural steroid injec root blocks with betamethasone and triamcinolone tions for patients with lumbar radiculopathy. However, in another study compar of action of various steroids, multiple animal and human Table 43. Depo-Medrol Kenalog Celestone Soluspan Decadron Triamcinolone Betamethasone, Dexamethasone Methylprednisolone acetonide Sodium Phosphate, and sodium phosphate Single-dose vials Single-dose Betamethasone Acetate Single-dose vials vials Injectable Suspension Amount of steroid 40 mg/mL 80 mg/mL 40 mg/mL 6 mg/mL 4 mg/mL Polyethylene glycol 3350 29. Com showed that sedation with midazolam accentuated the monly observed effects of corticosteroids include sup suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal axis. Equivalent doses, antiinflammatory potency, Hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal function may be sup sodium retention capacity, and duration of adrenal sup pressed for approximately 8 days from the commence pression are illustrated in Table 44. Duration of adrenal ment of chemotherapy cycles with administration of suppression with epidural injections is an important dexamethasone for first 8 days of chemotherapy (2266. This However, even topical steroid application on a long-term has been variously described as one to 3 weeks for depo basis may cause Cushing?s syndrome and adrenocortical methylprednisolone and epidural dexamethasone, 2 to insufficiency (2267. An evaluation of patients receiv 3 months with multiple epidurals of triamcinolone, and ing long-term intraarticular corticosteroids tests of the one to 2 weeks with intramuscular betamethasone. In an hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal axis 5 to 7 weeks after evaluation of pituitary adrenal axis function following a the last injection revealed suppression in some patients. Only a few patients exhibited separa raminal epidural injections, though no trials have tion for up to 2 weeks. Caution 3 weeks; however, adrenal response to adrenocortico must be exercised in the use of particulate steroids in tropic hormone was suppressed for 5 weeks. Thus, they transforaminal epidural injections and specifically for concluded that a single dose of methylprednisolone is cervical transforaminal epidural injections, particularly capable of altering adrenocortical function in dogs for if sharp needles are used. In an assessment of epidural Among multiple issues crucial in performing triamcinolone on the suppressive effect of pituitary interventional techniques, bleeding risk and periop adrenal axis in human subjects (2273), it was shown that erative management of patients on anticoagulants the median suppression was less than one month and and antithrombotic therapy is one of the major ones all patients had recovered by 3 months. The majority of the guidelines drawal being associated with a 3-fold higher risk of developed thus far are not based on appropriate evi major adverse cardiac events which was magnified in dence, due to the paucity of evidence in this area. Car patients with intracoronary stents with the conclusion diovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are among that aspirin discontinuation in such patients should be the leading causes of morbidity and mortality (2283 advocated only when bleeding risk clearly overwhelms 2287); and chronic persistent pain is the leading cause that of atherothrombotic events. In a study of the of disability and functional impairment across the evaluation of incidence of death and acute myocardial globe (46-49,2288-2290. It has been tinuation among both medically treated and percu estimated that a significant proportion of patients taneous coronary intervention treated patients with with cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, or peripheral acute coronary syndrome, supporting the possibility of vascular disease, receiving antithrombotic therapy un clopidogrel rebound effect. It has been described that dergo surgical interventions including interventional more than two-thirds of the sudden cardiac events techniques. The data on even though continuation of antithrombotic therapy cerebrovascular events are not known; however, acute is considered as ?safe? (944,2315,2316. Based on the coronary syndrome is linked with pro-inflammatory multiple guidelines published with evidence derived and pro-thrombotic conditions that involve an increase from case reports, it has been the generally accepted in fibrinogen, C-reactive protein, and plasminogen to stop antiplatelet therapy and is considered as stan activator inhibitor (2338. However, there is setting, the risk of acute coronary syndrome is further also significant disagreement among the guidelines. Studies assessing the result in spinal cord injury but only occurs with pro risk of maintaining antiplatelet therapy have shown cedures that involve placing a needle into the spinal increased surgical blood loss of 2. However, no increase in surgical mortality the exterior spine such as medial branch blocks. In a systematic platelet agents in the perioperative period are gener review and meta-analysis of the hazards of discon ally higher than those of maintaining them through tinuing or not adhering to aspirin regimens among the perioperative period. Thus, Chassot et al (2331) patients at risk for coronary artery disease (2291) non recommended that it is necessary to modify the ap compliance or withdrawal of aspirin treatment was proach of withdrawing patients from all antiplatelet associated with significant complications in those with agents 7 to 10 days before surgery, except when bleed or at moderate to high risk for coronary artery disease. After a comprehen this study showed aspirin non-adherence or with sive literature review, they (2135) also proposed that S196 www. Thus, interventional epidural hematoma; and rapid assessment and surgical pain physicians managing these patients are con or nonsurgical intervention to manage patients with fronted with the complex issue of weighing the risks epidural hematoma can avoid permanent neurologi of hemorrhagic complications when continuing the cal complications. Even though data to avoid bleeding and epidural hematomas and/or suggest that the traditional attitude of discontinu to continue antiplatelet therapy clopidogrel (Plavix), ing the medication 7 days before interventions poses ticlopidine (Ticlid), or prasugrel (Effient) during in considerable risk, multiple guidelines recommend terventional techniques to avoid cerebrovascular and these polices and it has been a general practice to dis cardiovascular thromboembolic fatalities. An evaluation Based on the comprehensive review of the by Manchikanti et al (944) of over 18,000 procedures evidence, it has been shown that most commonly, epi with over 12,000 encounters and over 3,000 patients, dural hematomas appear spontaneously. In addition, showed no significant prevalence of adverse events there has been a large number of epidural hematoma observed in those who continued with or ceased reports in patients after regional anesthesia. In addition, another issue re hematoma or bleeding instances have been reported lated to interventional pain management is that most with interventional techniques in patients without reports are related to regional anesthesia for surgical antiplatelet therapy, discontinued antiplatelet therapy, procedures, with few reports of epidural hematoma and continued platelet therapy. However, Manchikanti in patients undergoing interventional techniques for et al (2314), in a survey, showed epidural hematoma chronic pain with or without antithrombotic therapy in 29 patients with discontinuation of antiplatelet continued or discontinued. In contrast thrombolic ture and assessment of all the factors, Manchikanti et complications were much higher when antithrombotics www. For low risk or multiple drugs should be taken into consideration paravertebral interventional techniques and cau and may or may not be discontinued based on dal, it may be stopped for one day in patients with clinical judgment of individual risk and benefits normal renal function. In this regard, the simultaneous use of to 5 days for those with creatinine less than 50 mL multiple agents that possess anticoagulant proper per minute. They may or may not be discontinued prior to in recommended one injection for diagnostic as well as terventional techniques. Platelet aggregation inhibitors including ticlopi tions in a series irrespective of a patient?s progress dine (Ticlid), clopidogrel (Plavix), and prasugrel or lack thereof; whereas, others suggest 3 injections (Effient) may be continued or discontinued prior to followed by a repeat course of 3 injections after 3-, interventional techniques (evidence fair. Based on patient factors and managing cardiolo who propose that an unlimited number of injections gist?s opinion, if a decision is made to discontinue, with no established goals or parameters should be the current recommendations are that they may be available. A limitation of 3 mg per kilogram of body discontinued for 7 days with clopidogrel and prasu weight of steroid or 210 mg per year in an average grel and/or 10 to 15 days with ticlopidine (evidence person and a lifetime dose of 420 mg of steroid also fair. The comprehensive review of the literature in tion of 3 days may be effective (evidence limited. Assessment of bleeding risk of interventional techniques: A best evidence synthesis of practice patterns and periopera tive management of anticoagulant and antithrombotic therapy. Further, multiple well controlled trials have interlaminar and limited for transforaminal) illustrated no significant difference with local anes-. Moderate to severe pain causing functional thetic alone, or in combination with local anesthetic disability.

Buy manforce with visa
Short Study Long-term Number of Intervention or Follow-up Outcome term Characteristics relief Comment(s) Patients Comparator vs erectile dysfunction doctors orange county cheap manforce 100mg line. Investigations into the assessment of vari cluded in Table 5 of the systematic review by Atluri et al ous causes of thoracic pain are less frequent. All 3 studies (1346,1347,1989) were performed by Even though the description of the involvement the same group, with utilization of the same methodol of thoracic facet joints as a cause of chronic mid back ogy, with controlled comparative local anesthetic blocks and upper back pain dates back to 1987 (1986), thoracic with 80% pain relief based on the duration of local facet joint pain patterns were not described until 1994 anesthetics with lidocaine administered first, followed and 1997 by Dreyfuss et al (1987) and Fukui et al (1988. These studies evaluated not only the Based on the postulates of Bogduk (1472), tho prevalence but also false-positive rates with confidence racic facet joints have been shown to have an abundant intervals. There was no significant difference among nerve supply (15,16,1471,1960,1961,1987,1988,1991 the 3 studies with prevalence or false-positive rates. The 1993); been shown to be capable of causing pain selection criteria, inclusion, and exclusion criteria of the similar to that seen clinically, in normal volunteers with patients was the same in all 3 studies. Consequently, controlled local anesthetic prevalence of facet joint pain in patients suffering blocks of thoracic facet joints or medial branch blocks are with chronic upper or mid back pain involving thoracic employed to diagnose facet joint pain (1996. The evidence without somatization disorder without any significant is good for the diagnosis of thoracic pain of facet joint differences between the patients with psychological origin with controlled diagnostic blocks. Sedation as a confounding the prevalence and false-positive rates of facet joint factor was evaluated in the cervical and lumbar spine S168 www. Diagnostic accuracy of thoracic facet joint nerve blocks: An update of the assessment of evidence. In contrast to radiofre the evidence for the diagnostic accuracy of con quency neurotomy where pain returns when the axons trolled, dual diagnostic blocks with at least 80% concor regenerate requiring repetition of radiofrequency pro dant relief criterion standard thoracic facet joint nerve cedures, the mechanism of return of pain in therapeutic blocks is good. Our litera agnostic thoracic facet joint nerve blocks are indicated ture search showed one new publication (258), which is in patients with somatic or nonradicular upper back or a 2-year result of a previous publication by Manchikanti mid back pain, with lack of obvious evidence for dis et al (803. The observational report (2001) Interventions of medial branch blocks was performed by the same Facet joint pain originating from the thoracic group of investigators. Manchikanti et al (258,803,1990) spine is generally managed with conservative manage in the randomized trial evaluated 100 patients with 50 ment; however, after failure of conservative manage patients in each group receiving local anesthetic with ment, therapeutic facet joint interventions including or without steroids. The authors assessed the outcomes medial branch blocks and radiofrequency neurotomy with numeric pain scores, Oswestry Disability Index, have been described (242,258,487,803,1381,1383,1998 opioid intake and return to work status. Significant pain relief was defined as greater evidence for therapeutic thoracic medial branch blocks than 50% relief along with greater than 50% improve (16,1995), whereas evidence for radiofrequency neu ment in functional status. The results showed 80% of the rotomy of thoracic facet joint nerves was indeterminate patients with significant improvement at the end of one (16,1995. The majority of patients experi mechanism of radiofrequency neurotomy is by denatur enced significant pain relief for 46 to 47 weeks requiring ing of the nerves. Thus, the pain returns when the axons approximately 3 to 4 treatments with an average relief regenerate requiring repetition of the radiofrequency of 14 to 16 weeks per episode of treatment over a period lesioning. Over a period of 2 years they experienced an application of a strong electric field to the tissue that approximately 86 weeks of relief and also required 6 surrounds the electrode. The evidence for therapeutic medial branch blocks Among these, Stolker et al (2002) published a pro is fair in managing chronic mid back or upper back pain spective outcome study in 1993 assessing 40 patients of facet joint origin after the diagnosis is established with thoracic pain with radiofrequency neurotomy that with controlled, comparative local anesthetic blocks. Study Pain Relief Results Study Short Long-term Characteristics Participants Outcome Measures 6 12 term relief Comment(s) 3 mos. Significant vs vs P P P trial showed 83% pain relief was defined as 81% 83% positive results > 50% relief. Significant with long-term functional improvement was follow-up > 40% reduction of Oswestry Disability Index. Prospective 55 consecutive evaluation patients, Measured numeric pain Manchikanti et al, showed positive all meeting scores, Oswestry Disability 2006 (2001) results on a diagnostic Index, employment status, 71% 71% 71% P P P P, F long-term basis criteria for and Pain Patient Profile at 3, 7/13 for procedures thoracic facet 6, 12, 24, and 36 months. The results showed positive atic reviews with our search criteria showing the effec response in 68% of patients in the thoracic region with tiveness of thoracic intraarticular injections. Further, 85% of pain relief was illustrated for 9 months in 18 of 28 patients (64%. Radiofrequency neurotomy may be performed Based on one high quality, double-blind, random with conventional heat radiofrequency, pulsed radio ized trial and one observational report, medial branch frequency, or cooled radiofrequency. Results of randomized and observational studies of thoracic radiofrequency neurotomy. Study Pain Relief Results Study Short Long-term Outcome Characteristics Participants 3 6 12 term relief Comment(s) Measures Methodological mos. Stolker et al, 1993 40 patients with Pain relief with Prospective (2002) thoracic pain were numeric rating N/A N/A 64% N/A P P evaluation with P evaluated scale positive results. The results showed that while at intrathecal delivery systems are primarily effective for baseline patients reported moderate to severe leg nociceptive or mixed pain. Table 41 shows results of published studies of dominant leg pain of neuropathic radicular origin. Among the observational studies 11 of 12 showed group achieved at least 50% pain relief. In the 2 long-term stud that collected outcome data from patients implanted ies, 80. In showed that at 3 months after implantation of the per a prospective, population based controlled cohort study, Table 41. Results of published studies of effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation in post lumbar surgery syndrome. Pain Relief Results Study Methodological Short Long Study Patients Characteristics Quality Scoring? Spinal cord stimulation for patients with failed back surgery syndrome: A systematic review. There er than 10% of patients in any group achieved success were no significant differences between medication at any follow-up on the composite primary outcome costs. As described above, ths study has been criticized encompassing less than daily opioid use and improve for design and outcome measures. Taylor et al (2009) found pain and function, but with higher rates of daily opi that initial health care acquisition costs were offset oid use. The primary outcome measure was also cre ated by the authors and was composite score of opioid 1. After adjusting for costs, including produc the most common adverse event reported S174 www. They provided used in the treatment of recalcitrant chronic cancer limited evidence for the effectiveness of intrathecal or non-malignant pain after all other methods have infusion systems in managing chronic non-cancer pain. Consequently, various types of in claim there is a lack of effectiveness based on a lack trathecal infusion systems have been developed for the of randomized trials (150,2073-2076. However, these management of chronic intractable pain with opioids guidelines have come under scrutiny due to their and other agents (27,225,262,277,898,1506,2077,2098 incomplete review of the literature and exclusion of 2112. Even then, there is a paucity of literature in ref recent high quality published studies, outdated as erence to intrathecal infusion systems for long-term sessment criteria, inconsistent conclusions, and failure management of chronic non-cancer pain with a lack to comply with current standards for producing high of randomized trials. Systematic reviews must be up quality objective guidelines for various interventional dated frequently in today?s atmosphere of increased techniques (103,112,115,150,2074-2076. However, a effective and safe in controlling refractory painful common theme among all the systematic reviews conditions that have failed multiple other treatment is that there is a paucity of good quality publica modalities, both in cancer and non-cancer related tions for intrathecal infusion therapy, especially for conditions. While the literature has sig for intrathecal infusion systems is limited to a moder nificant heterogeneity of patient types, medications, ate recommendation for non-cancer pain based on and devices, all of them conclude that there is effec the current moderate evidence derived from 15 ob tive pain relief. Apart from the systematic reviews servational studies for chronic non-cancer pain. They described by Patel et al (2077), Hayek et al (225), and subsequently concluded that intrathecal drug delivery Falco et al (27), Noble et al (2103) included 16 stud remains a valuable therapy for chronic painful condi ies with 2,801 patients. Their outcomes showed 25% tions, both cancer and non-cancer related, and is often relief in 56. Turner et al up, there were 65% in the minimal to moderate dis (506) in a systematic review included 6 observational ability range. Those that pain improved on average across all studies, but in the severe disability range decreased to 30% and with increased opioid consumption over time, and 22%, respectively, at the 6 and 12 month follow-up. Simpson et al (2105) in a systematic review looked Other reported events that were infrequent included at intrathecal opioids with controlled studies and case catheter kinking and fractures. The conclusion was that intrathecal pain in patients who have not found effective relief infusion for pain and spasticity appears effective for with other therapies. However, drug and device com Roberts et al study (2106) assessed 88 patients plications are common.

Order manforce without prescription
Defines the problem erectile dysfunction medicine order manforce 100 mg overnight delivery, providing opportunity to answer ques tions, clarify misconceptions, and problem-solve solutions. Allows client to deal with reality and strengthens trust in care givers and information presented. Client should understand that this includes ongo ing periodic evaluation for change (Neal, 2009. Review drug therapy, use of herbal products, and diet, such as Some clients may prefer to treat with complementary therapy increasing intake of fruits and soybeans. Note: Nutrients known to inhibit prostate enlargement include zinc, soy protein, es sential fatty acids, flaxseed, and lycopene. Herbal supple ments that client may use include saw palmetto, pygeum, stinging nettle, and pumpkin seed oil. However, a recent study found no difference in efficacy or side effects be tween saw palmetto and a placebo, indicating a need for further research as to benefit versus variability of potency or purity of botanical products (Bent, 2006. Recommend avoiding spicy foods, coffee, alcohol, long auto May cause prostatic irritation with resulting congestion. Address sexual concerns—during acute episodes of prostatitis, Sexual activity can increase pain during acute episodes but may intercourse should be avoided but may be helpful in treat serve as massaging agent in presence of chronic disease. Note: Medications, such as finasteride (Proscar), are known to interfere with libido and erections. Alternatives include terazosin (Hytrin), doxazosin mesylate (Cardura), and tamsu losin (Flomax), which do not affect testosterone levels. Provide information about sexual anatomy and function as it Having information about anatomy involved helps client under relates to prostatic enlargement. Encourage questions and stand the implications of proposed treatments because they promote a dialogue about concerns. Review signs and symptoms requiring medical evaluation— Prompt interventions may prevent more serious complications. Discuss necessity of notifying other healthcare providers of Reduces risk of inappropriate therapy, such as the use of de diagnosis. Reinforce importance of medical follow-up for at least 6 months Recurrence of hyperplasia and infection caused by same or dif to 1 year, including rectal examination and urinalysis. Discuss personal safety issues and potential environmental Recent research reports increased risk of falls in presence of changes. Kidney damage from long-standing blockage low midline incision made through the bladder. Mortality: Prostatectomy is a relatively low-risk procedure cantly bothered by these symptoms (generally stated as 0 or less than 1% and usually associated 2. Cost: In 2010, the direct costs for treatment of prostate can scope introduced through the urethra. Common symp Kegel exercises: Pelvic muscle exercises intended to improve toms include nausea, vomiting, and confusion. Procedure, prognosis, therapeutic regimen, and rehabilita treatment, and rehabilitation needs. Assist client to assume normal position to void; for example, Encourages passage of urine and promotes sense of normality. Record time, amount of voiding, and size of stream after the catheter is usually removed 2 to 5 days after surgery, but catheter is removed. Note reports of bladder fullness, inabil voiding may continue to be a problem for some time because ity to void, and urgency. Encourage client to void when urge is noted but not more than Voiding with urge prevents urinary retention. Limit Maintains adequate hydration and renal perfusion for urinary fluids in the evening once catheter is removed. Instruct client in perineal exercises, such as tightening buttocks Helps regain bladder sphincter control, minimizing incontinence. Advise client that dribbling is to be expected after catheter is Information helps client deal with the problem. Pro incontinence is usually temporary, but stress incontinence— vide and instruct in use of continence pads when indicated. Measure residual volumes via suprapubic catheter, if present, Monitors effectiveness of bladder emptying. With bladder irrigations, monitoring is essential for estimating blood loss and accurately assessing urine output. Note: Following re lease of urinary tract obstruction, marked diuresis may occur during initial recovery period. Note: Hypertension, bradycardia, and nausea or capillary refill, and dry mucous membranes. Weigh dressings, if Signs of persistent bleeding may be evident or sequestered indicated. Encourage increased fluid intake, preferably water, to 2000 to Helps maintain fluid volume while flushing bladder of blood 2500 mL/day unless contraindicated by medical condition. Observe urethral and suprapubic catheter drainage, noting Bleeding is not unusual during first 24 hours for all but the excessive or continued bleeding. Continued or heavy bleeding or recur rence of active bleeding requires medical evaluation and intervention. Evaluate color, consistency of urine, for example: Bright red with bright red clots Usually indicates arterial bleeding and requires aggressive therapy. Dark burgundy with dark clots and increased viscosity Suggests venous source, which is the most common type of bleeding and usually subsides on its own. Avoid taking rectal temperatures and use of rectal tubes or May result in referred irritation to prostatic bed and increased enemas. Coagulation studies and platelet count May indicate developing complications that can potentiate bleeding or clotting. Maintain traction on indwelling catheter; tape catheter to inner Traction on the 30-mL balloon positioned in the prostatic ure thigh. Document period of appli Prolonged traction may cause permanent trauma and prob cation and release of traction, if used. Prevention of constipation and straining for stool reduces risk of rectal-perineal bleeding. Presence of drains and suprapubic incision increases risk of infection, as indicated by erythema or purulent drainage. Change suprapubic/retropubic and perineal incision dressings Wet dressings cause skin irritation and provide medium for frequently, cleaning and drying skin thoroughly each time. Provides protection for surrounding skin, preventing excoriation and reducing risk of infection. May be given prophylactically because of increased risk of infec tion with prostatectomy. Keep tubing Maintaining a properly functioning catheter and drainage free of kinks and clots. Decreases irritation by maintaining a constant flow of fluid over the bladder mucosa. Give client accurate information about catheter, drainage, Allays anxiety and promotes cooperation with necessary pro bladder spasms, and potential for voiding difficulties. Note: Depending on the degree of preoperative urge incontinence, postoperative urge incontinence may be present for weeks or months (Mills, 2011. Provide comfort measures, such as position changes, back rub, Reduces muscle tension, refocuses attention, and may enhance Therapeutic Touch, and diversional activities. Promotes tissue perfusion and resolution of edema and enhances healing in perineal approach. Administer antispasmodics, such as: Oxybutynin (Ditropan), flavoxate (Urispas), B & O suppositories Relaxes smooth muscle to provide relief of spasms and associ ated pain. Propantheline bromide (Pro-Banthine) Relieves bladder spasms by anticholinergic action. Usually discontinued 24 to 48 hours before anticipated removal of catheter to promote normal bladder contraction. Demonstrate problem-solving skills regarding solutions to difficulties that occur. Be honest in answers to clients the nerve plexus that controls erection runs posteriorly to the questions. In procedures that do not in volve the prostatic capsule, impotence and sterility are usu ally not consequences.
Purchase manforce with american express
Medical Management Objectives of management are to determine the cause erectile dysfunction herbs order manforce 100mg overnight delivery, to administer therapy for the specific cause (when known), and to detect signs and symptoms of cardiac tamponade. Bed rest is instituted when cardiac output is impaired until fever, chest pain, and friction rub have disappeared. Ask patient to hold breath to help in differentiation: audible on auscultation, synchronous with heartbeat, best heard at the left sternal edge in the fourth intercostal space where the pericardium comes into contact with the left chest wall, scratchy or leathery sound, louder at the end of expiration and may be best heard with patient in sitting position. Diagnosis Nursing Diagnoses • Acute pain related to inflammation of the pericardium P Collaborative Problems/Potential Complications • Pericardial effusion • Cardiac tamponade Planning and Goals the major goals of the patient may include relief of pain and absence of complications. Nursing Interventions Relieving Pain • Advise bed rest or chair rest in a sitting-upright and lean ing-forward position. Perioperative Nursing Management 511 Monitoring and Managing Potential Complications • Observe for pericardial effusion, which can lead to cardiac tamponade: arterial pressure falls; systolic pressure falls while diastolic pressure remains stable; pulse pressure narrows; heart sounds progress from being distant to imperceptible. Reassure patient and continue to assess and record signs and symptoms until physician arrives. Evaluation Expected Patient Outcomes • Is free of pain • Experiences no complications For more information, see Chapters 29 and 30 in Smeltzer, S. Perioperative Nursing Management Preoperative Concerns P Surgery, whether elective or emergency, is a stressful, complex event. Surgery may also be classified according to the degree of urgency involved (emergency, urgent, required, elective, and optional. Whatever its classification, current surgery involves many more ambulatory procedures than ever before and administra tive processes that are new to nursing and other health care staff. However, perioperative nursing concerns still focus on the patient and his or her well-being. Inpatient or outpatient, all surgical procedures require a comprehensive preoperative nursing assessment and interventions to prepare the patient and family before surgery. Informed con sent is required for invasive procedures, such as incision, biopsy, cystoscopy, or paracentesis; procedures requiring sedation and/or anesthesia; nonsurgical procedures that pose more than slight risk to the patient (arteriography); and pro cedures involving radiation. Assessment: Inpatient Surgery • Obtain a health history and perform a physical examination to establish vital signs and a database for future comparisons. Decayed teeth or dental prostheses may become dislodged during intubation for anesthetic delivery and occlude the airway. Assessment: Ambulatory Surgery • Obtain the health history of the ambulatory or same-day surgical patient by telephone interview or at preadmission testing. Ask about recent and past health history, allergies, medications, preoperative preparation, and psychosocial and demographic factors. Also monitor 514 Perioperative Nursing Management elderly patients for dehydration, hypovolemia, and electrolyte imbalances, which can be a significant problem in the elderly population. Nursing Diagnoses • Anxiety related to the surgical experience (anesthesia, pain) and the outcome of surgery • Risk for ineffective therapeutic management regimen related to deficient knowledge of preoperative procedures and pro tocols and postoperative expectations • Fear related to perceived threat of the surgical procedure and separation from support system • Deficient knowledge related to the surgical process Planning and Goals the surgical patients major goals may include relief of pre operative anxiety, adequate nutrition and fluids, optimal res piratory and cardiovascular status, optimal hepatic and renal function, mobility and active body movement, spiritual com fort, and knowledge of preoperative preparations and postop erative expectations. Nursing Interventions Reducing Anxiety and Fear: Providing Psychosocial Support P. Be a good listener, be empathetic, and provide information that helps alleviate concerns. Managing Nutrition and Fluids • Provide nutritional support as ordered to correct any nutri ent deficiency before surgery to provide enough protein for tissue repair. Perioperative Nursing Management 515 • Instruct patient that oral intake of food or water should be withheld 8 to 10 hours before the operation (most com mon), unless physician allows clear fluids up to 3 to 4 hours before surgery. Promoting Optimal Respiratory and Cardiovascular Status • Urge patient to stop smoking 2 months before surgery (or at least 24 hours before. Supporting Hepatic and Renal Function • If patient has a disorder of the liver, carefully assess various liver function tests and acid–base status. Maintain patients body in proper alignment when P patient is placed in any position. Respecting Spiritual and Cultural Beliefs • Help patient obtain spiritual help if he or she requests it; respect and support the beliefs of each patient. Individuals from some cultural groups may not make direct eye contact with others; this lack of eye contact is not avoidance or a lack of interest but a sign of respect. Correct use of communication and interviewing skills can help the nurse acquire invaluable information and insight. Perioperative Nursing Management 517 Providing Preoperative Patient Education • Teach each patient as an individual, with consideration for any unique concerns or learning needs. Include descriptions of the procedures and explanations of the sen sations the patient will experience. Provide a tele phone number for patient to call if questions arise closer to the date of surgery. P Teaching the Ambulatory Surgical Patient • For the same-day or ambulatory surgical patient, teach about discharge and follow-up home care. Education can be pro vided by a videotape, over the telephone, or during a group meeting, night classes, preadmission testing, or the preoper ative interview. Explaining Pain Management • Instruct patient to take medications as frequently as pre scribed during the initial postoperative period for pain relief. Preparing the Bowel for Surgery • If ordered preoperatively, administer or instruct the patient P to take the antibiotic and a cleansing enema or laxative the evening before surgery and repeat it the morning of surgery. Preparing Patient for Surgery • Instruct patient to use detergent–germicide for several days at home (if the surgery is not an emergency. Perioperative Nursing Management 519 • Remove jewelry, including wedding rings (if patient objects, securely fasten the ring with tape. Transporting Patient to Operating Room • Send the completed chart with patient to operating room; attach surgical consent form and all laboratory reports and nurses records, noting any unusual last-minute observations that may have a bearing on the anesthesia or surgery at the front of the chart in a prominent place. Attending to Special Needs of Older Patients • Assess the older patient for dehydration, constipation, and malnutrition; report if present. Attending to the Familys Needs • Assist the family to the surgical waiting room, where the surgeon may meet the family after surgery. P Evaluation Expected Patient Outcomes • Reports decreased fear and anxiety • Voices understanding of surgical intervention Postoperative Nursing Management the postoperative period extends from the time the patient leaves the operating room until the last follow-up visit with the surgeon (as short as a day or two or as long as several months. During the postoperative period, nursing care is directed at reestablishing the patients physiologic equilib rium, alleviating pain, preventing complications, and teach ing the patient self-care. Careful assessment and immediate intervention assist the patient in returning to optimal func tion quickly, safely, and as comfortably as possible. Ongo ing care in the community through home care, telephone Perioperative Nursing Management 521 follow-up, and clinic or office visits promotes an uncompli cated recovery. Postanesthesia care in some hospitals and ambulatory sur gical centers is divided into three phases. The nurse also performs a baseline assessment followed by checking the surgical site for drainage or hemorrhage and connecting all drainage tubes and monitoring lines. After the initial assess ment, the nurse monitors vital signs and assesses the patients general physical status at least every 15 minutes, including assessment of cardiovascular function with the above assess ments. The nurse maintains airway patency and supplemental oxygen; maintains cardiovascular stability with prevention, prompt recognition, and treatment of hemorrhage, hyperten sion, dysrhythmias, hypotension and shock; relieves pain and anxiety; and controls nausea and vomiting. The nurse also notes any pertinent information from the patients history that may be significant (eg, hard of hearing, blind, history of seizures, diabetes, allergies to certain medications or other sub stances. Usually, the nurse makes sure they are transported home safely by a responsible person. Nursing Management in Same-Day Surgery • Inform the patient and caregiver (ie, family member or friend) about expected outcomes and immediate postoperative changes anticipated in the patients capacity for self-care. Provide caregiver Perioperative Nursing Management 523 with verbal and written instructions about what to observe the patient for and about the actions to take if complica tions occur. Follow-up telephone calls from the nurse or surgeon may be used to assess patients progress and to answer any questions. Postoperative Nursing Management in Home Care •The home care nurse assesses the patients physical status (eg, respiratory and cardiovascular status, adequacy of P pain management, surgical incision) and the patients and familys ability to adhere to the recommendations given at the time of discharge. The 524 Perioperative Nursing Management patient and family are instructed about signs and symptoms to report to the surgeon. Perioperative Nursing Management 525 Nursing Interventions Maintaining Patent Airway • Check the orders for and apply supplemental oxygen. Assess respiratory rate and depth, ease of respirations, oxygen sat uration, and breath sounds. Maintain hard rubber or plastic air way in patients mouth or nose until gag reflex resumes.

