Residronate
Order genuine residronate
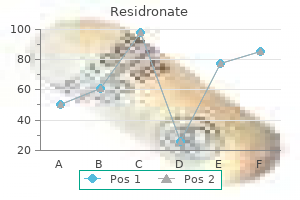
The study confirmed a relationship between arcuate artery Doppler indices and downstream decidual vascular pathology medications given for bipolar disorder proven 35 mg residronate. Impedance to flow in the umbilical and uterine arteries during the third trimester was not different between patients with good glycemic control and those with poor control 29. In contrast, impedance was significantly higher in patients with pre-eclampsia than in those without pre eclampsia, regardless of glycemic control. It was concluded that Doppler investigation may be clinically useful only in diabetic pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia. Diabetic Diabetic Author Doppler study non-diabetes vasculopathy control Olofsson et al. The aim of Doppler ultrasound studies of the fetal middle cerebral artery and aorta is to examine whether the compromised fetus of a diabetic pregnancy demonstrates the same features of circulatory redistribution as seen in fetal hypoxemia due to uteroplacental insufficiency. With the exception of three pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia and/or intrauterine growth restriction, the uteroplacental and fetoplacental circulations were essentially normal. It is of particular interest that normal Doppler results in the uterine and umbilical arteries and the fetal middle cerebral artery and aorta were also observed in five of six patients with diabetic nephropathy 31. Cordocentesis, performed within 24 hours before delivery, demonstrated these fetuses to be hypoxemic and acidemic. It was concluded that fetal acidemia in pregnancies complicated by diabetic nephropathy is not a consequence of impaired placental perfusion, and the degree of metabolic derangement may be obscured by the apparent normal growth of these fetuses and their failure to demonstrate blood flow redistribution. They found no significant association between impedance to flow in the fetal aorta and fetal outcome. They concluded that fetal aortic Doppler velocimetry cannot be used as a means of assessing impending fetal compromise in offspring of diabetic mothers. This disease is characterized by a thickening of the interventricular septum and ventricular walls and by systolic and diastolic dysfunction, which may result in congestive heart failure. Figure 1: Real-time and M-mode tracing of a fetus of an insulin-dependent diabetic mother at 36 weeks of gestation. The interventricular wall septal thickness is increased (10 mm compared to the expected mean of 5 mm for this gestation) Figure 2: Flow velocity waveforms across the tricuspid valve in a fetus of an insulin-dependent diabetic mother at 32 weeks of gestation. These findings, which were unrelated to maternal glycosylated hemoglobin levels, suggest that, even in well-controlled maternal diabetes mellitus, there is fetal interventricular septal hypertrophy that affects cardiac diastolic function. The cardiomegaly and cardiac dysfuncion increased with gestation but they were evident from as early as 20 weeks. Since the diabetic control in these pregnancies was good, it was suggested that fetal cardiomegaly may be the consequence of increased insulin sensitivity of the fetal myocardium. This hypothesis is supported by the data of Thorsson and Hintz, showing a reduction from fetus to adult in the number and affinity of insulin receptors 36. The lower ratio between early and active ventricular filling at the level of the atrioventricular valves in fetuses of diabetic mothers may be due to impaired development of ventricular compliance, possibly secondary to cardiac wall thickening. In addition, the ratio may be influenced by reduced preload, as a consequence of the polycythemia, and therefore increased blood viscosity in fetuses of diabetic mothers. Thus, in a Doppler study of 37 fetuses of insulin dependent diabetic mothers, immediately before an elective Cesarean section, the ratio between early and active ventricular filling was significantly and independently affected by both the interventricular wall thickness and fetal hematocrit 37. Ventricular diastolic filling increased with gestation in both groups but the increase was delayed in the diabetic group. It was concluded that, in fetuses of well controlled diabetic pregnancies, altered cardiac morphology is evident early in pregnancy, before any obvious alteration in cardiac function. In the fetuses of diabetic mothers, compared to normal pregnancies, there was a lower ratio between early and active ventricular filling at the level of the atrioventricular valves, a higher percentage of reverse flow during atrial contraction in the inferior vena cava, and a higher proportion of cases with pulsations in the umbilical vein. These findings, demonstrating impaired development of cardiac and venous blood flow patterns from as early as at 12 weeks of gestation, were more evident in pregnancies with poorer glycemic control but they were also found in the presence of good metabolic control. Peak velocities at the level of the aortic and pulmonary outflow tracts were significantly higher in fetuses of diabetic mothers than in normal fetuses 34. The most likely explanations for the increased peak velocities are increased cardiac contractility (also found in postnatal studies in infants of diabetic mothers) and increased intracardiac flow volume due to the relatively large size of such fetuses, since cardiac output is a function of fetal weight. These findings suggest that the mechanisms inducing fetal distress in diabetic pregnancies (where the development of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy plays a pivotal role in the genesis of fetal distress) are different from those in fetuses with intrauterine growth restriction, where the change in cardiac function is secondary to the alteration in peripheral resistance. In neonates from normal pregnancies, the ratio between early and active ventricular filling at the level of the atrioventricular valves increases during the first few days of postnatal life; the early wave is usually higher than the active one, resulting in a ratio between early and active ventricular filling that is higher than one. In newborns of diabetic mothers, there are no changes in this ratio during the first 5 days of life and its value remains lower than one44. These anomalies might explain the relatively high incidence of transitory tachypnea and pulmonary edema in neonates from diabetic pregnancies. The cardiac hypertrophy of fetuses of diabetic mothers resolves during the first year of postnatal life. However, it is possible that the cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction observed in intrauterine life may affect cardiac function in adult life. However, increased impedance, as in non-diabetic pregnancies, identifies a group at high risk for subsequent development of pre-eclampsia and/or intrauterine growth restriction. There is contradictory evidence concerning a possible increase in impedance in pregnancies with maternal vasculopathy. This is presumably because, in diabetes, there may be acute fluctuations in fetal blood pH, since the latter is associated with the maternal glucose concentration. Furthermore, unlike intrauterine growth restriction, in diabetes metabolic derangements in the fetus may lead to acidemia without hypoxemia. Therefore, the classic redistribution seen in fetal hypoxemia due to uteroplacental insufficiency may not occur even in severely compromised fetuses, and it is therefore important not to be misled by apparently normal fetal Doppler results. This disease is characterized by a thickening of the interventricular septum and cardiac dysfunction, which may be evident from as early as 12 weeks of gestation. Fetal pancreatic b-cell function in pregnancies complicated by maternal diabetes mellitus. The role of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 in the control of human fetal growth. Fetal acidosis and hyperlacticaemia diagnosed by cordocentesis in pregnancies complicated by maternal diabetes mellitus. Fetal polycythemia and thrombocytopenia in pregnancies complicated by maternal diabetes mellitus. Metabolic effect of constant hypertonic glucose infusion in well oxygenated fetuses. Arterial hypoxemia and hyperinsulinemia in the chronically hyperglycemic fetal lamb. Effects of chronic fetal hyperglycemia upon oxygen consumption in the ovine uterus and conceptus. The effect of chronic fetal hyperglycemia on substrate uptake by the ovine fetus and conceptus. Fetal heart rate and umbilical artery velocity variability in pregnancies complicated by insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Comparison of umbilical Doppler velocimetry, nonstress testing, and biophysical profile in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Doppler velocimetry discordancy of the uterine arteries in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Doppler umbilical artery velocimetry in pregnancy complicated by insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy and the assessment of umbilical artery waveforms using pulsed Doppler ultrasonography. Ishimatsu J, Yoshimura O, Manabe A, Hotta M, Matsunaga T, Matsuzaki T, Tetsuou M, Hamada T. Umbilical artery blood flow velocity waveforms in pregnancy complicated by diabetes mellitus. Doppler velocimetry of the umbilical artery in pregnancies complicated by insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Doppler flow velocimetry of the uterine and uteroplacental circulation in pregnancies complicated by insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Predictive value of uterine Doppler waveform during pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Uterine arcuate artery Doppler and decidual microvascular pathology in pregnancies complicated by type I diabetes mellitus.
Quality 35mg residronate
Remove bristles with a very sticky tape position that is lower than the heart using such as adhesive tape or duct tape medicine you cant take with grapefruit cheap 35mg residronate visa. Be prepared to administer mouth-to-mouth symptoms and may include topical steroid resuscitation and cardiopulmonary therapy, systemic antihistamines, and resuscitation if necessary. Wound infection can occur but can be and acts as a neurotoxin and neuromuscular easily prevented by cleaning the skin using blocking agent. Venom is not affected by hot water povidone-iodine and topical antibiotic therapy. Systemic antibiotics may be needed for established secondary infections that first need culturing, aerobically and anaerobically. Each distributed in all regions and is usually found species has a radial shape and long spines. Penetration of the sea urchin spine can cause the shell is most often symmetrical in a spiral intense local pain due to venom in the spine or coil, colorful, with a distinct head, one to two from another type of stinging organ called the pairs of tentacles, two eyes, and a large flattened globiferous pedicellariae. Numbness, generalized weakness, paresthesias, nausea, vomiting, and cardiac dysrhythmias have been reported. Remove large spine fragments gently, being very careful not to break them into small fragments that remain in the wound. Caution should be used to prevent scalding the skin which can easily occur after a brief period in water above 122F (50C). Topical antibiotic ointment should be used to Image reprinted with permission from: Edmonds, C. It has a highly Some small fragments may be absorbed by developed venom apparatus: venom is contained the body. Surgical removal, preferably with in darts inside the proboscis which extrudes a dissecting microscope, may be required from the narrow end but is able to reach most of when spines are near nerves and joints. Allergic reaction and bronchospasm can be body; involvement of the mouth and lips is controlled with subcutaneous epinephrine severe. There are no visual disturbances, and respiratory distress, specific antivenins available. Do not apply a loose breathing reptile which has adapted to its aquatic constricting band or ligature. Some authorities recommend incision of Sea and have been seen 150 miles from land. Otherwise, the river mouths as sea snakes are more numerous procedure may be ineffective. Incision and suction by inexperienced true snake, usually 3 to 4 feet in length, but may personnel has resulted in inadvertent reach 9 feet. Transport the patient to a medical facility while ensuring that the patient is breathing adequately. Cone shell venom results in paralysis or Image reprinted with permission from: Edmonds, C. Patient should be admitted to a treatment facility and monitored closely for respiratory or cardiovascular complications. Local anesthetic with no epinephrine may be injected into the site of the wound if pain is severe. Respiratory arrest may result from injects a poison that has 2 to 10 times the generalized muscular paralysis; intubation toxicity of cobra venom. The bites usually and mechanical ventilation may be appear as four puncture marks but may range required. The neurotoxin poison is a heat stable nonenzymatic protein; hence, bites should a. Monitor renal function and fluid balance not be immersed in hot water as with venomous anticipating acute renal failure. Because of the possibility of delayed respiratory distress and failure, plus smoky symptoms, all sea snake-bite victims colored urine from myoglobinuria, which may should be observed for at least 12 hours. If symptoms of envenomation occur within 4 one hour, antivenin should be administered First Aid and Treatment as soon as possible. Antivenin is available from the the dependent position with splints and Commonwealth Serum Lab in elastic bandages. Transport all sea snake-bite victims to a regarding dosage and sensitivity testing treatment facility as soon as possible, on the accompanying package insert regardless of their current symptoms. Sensory reversal of hot and cold irritants on the surface of certain sponges or sensation when touching or eating objects of exposure to the minute sharp spicules can cause extreme temperatures may occur. In severe cases, respiratory failure and 4 First Aid and Treatment cardiovascular collapse may occur. Vinegar or a 3 to 10-percent acetic acid Complete recovery will occur in the majority of should be applied with saturated cases with neurological symptoms persisting for compresses as sponges may be secondarily months or years. Antibiotic ointment is effective in reducing from endemic areas with international travelers the chance of a secondary infection. Table 22-5 lists some of toxins found in fish and shellfish and their potential sources. The poisoning is common in reef Scombrotoxin Tuna, bonito, skipjack, mackerel, fish between latitudes 35N and 35S around (histamine-like mahi mahi reaction) tropical islands or tropical and semitropical shorelines in Southern Florida, the Caribbean, the West Indies, and the Pacific and Indian Bivalve shellfish (mussels, clams, Saxitoxin Oceans. Fish and marine animals affected scallops) accumulate toxin from (neurologic include barracuda, red snapper, grouper, sea dinoflagellate during red tides effects) bass, amberjack, parrot fish, and the moray eel. Symptoms may begin immediately or within several hours of ingestion and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, itching and Table 22-5. Known to be Poisonous 22-26 4 First Aid and Treatment A rapid bacterial production of histamine and saurine (a histamine-like compound) produce the symptoms of a histamine reaction: 1. Treatment is largely supportive and nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, facial symptomatic. If the time since suspected flushing, urticaria (hives), headache, pruritus ingestion of the fish is brief and the victim (itching), bronchospasm, and a burning or is fully conscious, induce vomiting (syrup itching sensation in the mouth. Symptoms may of Ipecac) and administer purgatives begin one hour after ingestion and last 8 to 12 (cathartics, laxatives) to speed the hours. In addition to the symptoms described Prevention Immediately clean the fish and above, other complications which may preserve by rapid chilling. Do not eat any fish require treatment include hypotension and that has been left in the sun or in the heat longer cardiac dysrhythmias. Antiemetics and antidiarrheal agents may be required if gastrointestinal symptoms Oral antihistamine. Atropine may be needed to control 22-5 lists some of toxins found in fish and bradycardia. Calcium gluconate, diazepam, and An extremely potent neurotoxin called methocarbamol can be given for muscle tetrodotoxin is found in the viscera, gonads, spasm. Amytriptyline has been used successfully puffer fish, porcupine fish, and ocean sunfish. Typical fish causing scombroid avoid contact with the visceral organs known to poisoning include tuna, skipjack, mackerel, concentrate the poison. Fish that cause the first sign of poisoning is usually scombroid poisoning are found in both tropical tingling around the mouth, which spreads to the and temperate waters. Neurological findings may progress to stumbling gait (ataxia), generalized weakness, and paralysis. The victim, though paralyzed, remains conscious until death occurs by respiratory arrest with a 50 to 60 % mortality rate if untreated. Provide supportive care with airway sensation in the throat, swollen tongue and management and monitor breathing and bronchospasm may also be an individual circulation. Proliferation (solution of baking soda) may be helpful of these dinoflagellates during the warmest since the poison is acid-stable. Provide supportive treatment with close colorless, so that poisonous mollusks may be observation and advanced life support if unknowingly consumed. Poisonous shellfish cannot be detected by the poisoning is related to the quantity of appearance, smell, or discoloration of either a poisonous shellfish consumed and the silver object or garlic placed in the cooking concentration of the dinoflagellate water. The toxic varieties of dinoflagellates are common in the following 4 Bacterial and Viral Diseases from Shellfish areas: Northwestern U.
Buy cheapest residronate
It would also rule out terminal complement component deficiencies in a person with recurrent Neisseria infections medicine hat weather residronate 35mg amex. If the titers are low, then obtaining pre and postvaccination titers should determine the ability of that person to mount a significant antibody response at that point in time. This, however, does not indicate that this person is able to mount a significant antibody response at the present point in time against new antigens. Markedly elevated preimmunization antibody titers, however, make it almost impossible to interpret antipolysaccharide antibody responses. Infections with viruses or intracellular microorganisms should prompt quantitative and qualitative evaluation of cell-mediated immunity. Phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A are T-cell mitogens; pokeweed mito-gen is a T-dependent B cell stimulator. Response to alloantigen (mixed lymphocyte culture or mixed lymphocyte response) tests the ability of naive T cells to mount a response to new antigens. Unfortunately, there is no one antigen to which 100% of the population would be positive. Early (<24 hours) induration might indicate an Arthus reaction (most commonly seen with tetanus especially if a high concentration is used). A delayed reading (>48 hours) might render a borderline positive (5 to 6 mm induration) as a negative (<5 mm induration). Nevertheless, the majority of immunodeficiencies in both children and adults are secondary rather than primary. Antibody response to pneumococcal vaccination as a function of preimmunization titer. Host defense pathways: role of redundancy and compensation in infectious disease phenotypes. These studies are useful for the evaluation of patients with suspected immune deficiency disorders and autoimmune, allergic, or malignant diseases. The chapter is directed at general concepts and appropriate applications of methods used to characterize and quantify immuno-globulins and specific antibodies; evaluate lymphocyte phenotype and function; study neutrophil function, assay complement, as well as molecular methods used to enhance these other studies and make a definitive genetic diagnosis. Specific immunoglobulins (antibodies) are normally produced following antigenic stimulation, yielding a variety of antibody molecules, all of which react with varying strengths to the specific antigen. This type of response is referred to as polyclonal because it involves multiple B-cell clones. The basic molecular structure of the immunoglobulin consists of two identical heavy chains (,,,, or ) and two identical light chains ( or ) that together form a monomer (see Chapter 1). There are five different classes or isotypes of immu-noglobulin that are determined by the heavy chain used in the molecule. The Fab portion of the molecule provides the antigen-combining sites, and the Fc portion contains the other sites of biologic function, such as complement component binding. IgG, the most prevalent immu-noglobulin in serum, is found as a monomer and constitutes the major antibody class produced in secondary antibody responses. Both IgE, the antibody of the allergic response, and IgD, a principal B-cell surface immunoglobulin, are also present in serum as monomers but are found in very low concentrations. IgA is found in serum and secretions as a dimer, together with a J chain and secretory component. The secretory component is synthesized by mucosal epithelial cells and joined to the dimeric IgA molecule as it passes through these cells. IgM, normally present in serum as a pentamer, is the immunoglobulin class produced early during a primary antibody response to an antigen. Evaluation of immunoglobulins consists of qualitative and quantitative tests that are useful for evaluating immunoglobulin classes and their subclasses and/or antigen-specific antibody. Age dependent change in the levels of immunoglobulins must be taken into account when interpreting results. Decreases in the level of a serum protein, such as an immunoglobulin, can result from impaired synthesis, altered utilization, and/or increased loss. Immu-noglobulin molecules of a particular class or subclass all share the same chemical structure, are recognized by a common structure in the constant region of the heavy (or light) chain, and, as such, can behave similarly in an immunoas-say. Binding of the antigen to specific antibodies is also defined by a qualitative aspect of strength of the binding between antibody and antigen (defined by affinity for one interaction and avidity for the combined affinities in the case of multiple epitopes), making quantitative measurement of specific antibodies more difficult. The sample (solution) to be tested is placed on a buffer-saturated support medium. Serum electrophoresis normally yields five bands consisting of albumin, alpha-1, alpha 2, beta, and gamma globulin fractions (Fig. These bands can be assessed with a densitometer that generates a tracing from which the relative percentage of each fraction is determined. Immunoglobulins normally fall in the gamma globulin band, although they also migrate into the beta and alpha-2 globulin bands. This semiquantitative technique is useful for assessing total protein status and can be used to screen for monoclonal immunoglobulins, although this technique may miss low-level monoclonal antibodies seen in early myelomas. The electrophoretic pattern and densitometric tracing demonstrate the five major bands (albumin plus alpha-1, alpha-2, beta, and gamma globulins) from a normal serum sample. This has been used primarily for the characterization of monoclonal immunoglobulins, but in the clinical laboratory, this method is now largely replaced by immunofixation electrophoresis. Polyclonal immunoglobulins give a diffuse band, a monoclonal immunoglobulin produces an intense narrow band typically within the diffuse band in the background, and oligoclonal immunoglobulins yield multiple bands of increased intensity against the background. The test currently represents the standard clinical laboratory approach for identification of monoclonal or oligoclonal immunoglobulins. Demonstrates a normal pattern with antibodies to the major heavy-chain and light-chain proteins. A clonal immunoglobulin would result in a darker staining band in a heavy-chain and light-chain zone. Double gel diffusion is another semiquantitative test that evaluates the relationship between specific antibodies or antigens in solutions. Comparison between a reference material and unknown serum allows a comparative assessment for identity, partial identity, or nonidentity. Although it lacks the detection sensitivity of many quantitative methods, the test is technically easy, can be performed with antigen preparations that are only partially purified, is highly specific, and serves as a useful screening test for the presence of an antibody or antigen particularly in a heterogeneous sample. Single radial immunodiffusion allows quantification of a protein (antigen) by adding serum (or other fluid) to wells cut into agarose that contains a specific antiserum. Thus, the diameter of this ring is proportional to the concentration of the protein (antigen) being evaluated because the concentration of the antiserum is constant throughout the gel. The concentration of the unknown is then determined by plotting the precipitin ring diameter on a concentration curve produced from a series of standards with known protein (antigen) concentration. Nephelometry is a method to quantify proteins in a solution that is based on the scattering of light from soluble immune complexes generated by the addition of specific antibody to the sample being tested. In contrast to precipitin reactions, nephelometry is performed in slight antibody excess, and this procedure is readily amenable to automated instrumentation. Nephelometry is the standard method for quantifying immunoglobulin in most clinical laboratories because of the high-volume capabilities of modern nephelometers. The competitive binding test can also be reversed by using a fixed concentration of purified antigen together with labeled antibody to evaluate for specific antibody concentrations in an unknown sample.
Purchase residronate 35mg mastercard
Simple foods like breast milk or pH balance until diarrhoea ceases 85 medications that interact with grapefruit cheap generic residronate uk, mostly spon strength buffalo milk, boiled potato, rice, chicken taneously. Antimicrobials in diarrhoea One or more antimicrobial agent is almost routi Salmonella food poisoning is generally a self nely prescribed to most patients of diarrhoea. Antibiotics have been widely However, such drugs have a limited role in the used, but may be harmful rather than beneficial. Approval has also been granted (b) Slightly loose, smaller volume stools, frequen in 33 countries for various conditions. Side effects are flatulence, abdominal (iii) Pancreatic enzyme deficiency pain, defecation urgency and headache. Clinical experience with rifaximin is in blind loops/diverticulitis may be treated with limited, and efficacy for empirical treatment of tetracycline or metronidazole. Cotrimoxazole, or a cultures or lyophillised powders, that are intended fluoroquinolone or colistin may be used in acute to restore and maintain healthy gut flora or have cases and in infants. Diarrhoeal illnesses and antibiotic use are associated with alteration in the (iii) Shigella enteritis: only when associated with population, composition and balance of gut blood and mucus in stools may be treated with microflora. Cotrimoxazole and pathogenic, mostly lactic acid forming bacteria ampicillin are alternatives, but many strains are and yeast is believed to help restore this resistant to these. Several reviews and metaanalysis of clinical (v) Yersinia enterocolitica: common in colder trials have suggested that probiotics significantly places, not in tropics. Antimicrobials are regularly useful in: controlled trials have been carried out in health care setting in developed countries, while data from (i) Cholera: Though only fluid replacement is life community based studies carried out in resource saving, tetracyclines reduce stool volume to nearly poor countries is minimal. Cotrimoxazole is an alternative, especially strains, either alone or in combination, have been in children. Lately, multidrug resistant cholera used in different studies, but the protective effect strains have arisen. These can be treated with has been more or less similar, though collation norfloxacin/ciprofloxacin. While probiotics appear to be useful adjuncts to conventional therapy of acute infectious (ii) Campylobacter jejuni: Norfloxacin and diarrhoea, and are loudly promoted as well as other fluoroquinolones eradicate the organism frequently prescribed, convincing evidence of their from the stools and control diarrhoea. This prevents them from being Erythromycin is fairly effective and is the preferred accepted as a standard component of diarrhoea drug in children. Stronger evidence of efficacy has emerged (iii) Clostridium difficile: produces antibiotic against antibiotic-associated diarrhoea, but there associated pseudomembranous enterocolitis. Natural curd/yogurt is an metronidazole, while vancomycin given orally is abundant source of lactic acid producing an alternative. Migration appears to have an important immune component of inflammatory cells into bowel wall is interfered triggered by a variety of factors. Given during active phase of the disease Ulcerative colitis It involves only the colon starting from the anal canal. It may remain restricted to the rectum or it reduces number of stools, abdominal cramps extend proximally in a contiguous manner to variable extent and fever, but is less effective than corticosteroids; upto caecum. The lesions are mucosal and may be diffuse may be employed for mild to moderate exacer or confluent. Maintenance therapy Majority of patients have ileocaecal disease upto ascending colon, but in some it may be restricted to the small intestine, with 1. The primary transmural, complications like perforation, abscess, fistula, value of sulfasalazine is in maintaining remission strictures, etc. Upto 1/3rd patients suffer intolerable with sulfapyridine linked through an azo bond, adverse effects. Folic acid supplementation Drug interactions Coated mesalazine may should always be given during its use. The with coumarins, furosemide, spironolactone, absorbed sulfapyridine moiety appears to be methotrexate and rifampicin are possible. Adverse effects Coated mesalazine is much In more severe disease with extraintestinal mani better tolerated than sulfasalazine. Side effects festations and for rapid relief therapy may be noted are nausea, diarrhoea, abdominal pain and initiated with i. It is during steroid therapy is continued to prevent contraindicated in renal and hepatic impairment. Thus, it has a limited role in severe CrD and in patients not responsive to or not tolerating azathioprine. Infliximab produces substantial toxicity, chronic immunosuppression must be weighed in including acute reactions, formation of antibodies and each patient before instituting therapy with these lowering of resistance to infections. Because of long latency of response, they drug for selected patients with refractory disease. Nonspecific antidiarrhoeal drugs Azathioprine this purine antimetabolite is the these drugs can be grouped into: most effective and most commonly used A. It is indicated in steroid dependent, streroid-resistant and relatively severe A. Although, azathioprine has its own consistency and frequency of stools and give an impression adverse effect potential, the same is rated lower of improvement, but do not reduce the water and electrolyte than that of prolonged steroid therapy. It is indicated in the short luminal transit and allow more time for the term treatment of acute secretory diarrhoeas. No tolerance develops to contrast to loperamide/diphenoxylate, it is not their constipating action. The antidiarrhoeal Anticholinergics Atropinic drugs can reduce bowel motility action is most prominent, but because it is and secretion, but have poor efficacy in secretory diarrhoeas. Abuse liability is rated a long plasma t (90 min) as well as potent antisecretory/ low, and overdose will produce disturbing antimotility action on the gut. Loperamide is Antimotility drugs can be used to induce contraindicated in children < 4 yr. Fixed dose combination of antidiarrhoeals with infective diarrhoeas because they delay clearance antihistaminics. The stools are relatively small volume, liquid but not watery, frothy and are preceded by griping pain in abdomen. Their advent microorganisms, which selectively suppress the changed the outlook of the physician about the growth of or kill other microorganisms at very power drugs can have on diseases. This definition excludes of the few drugs which can cure, and not just other natural substances which also inhibit micro palliate disease. As a class, they are one but are needed in high concentrations (ethanol, of the most frequently used as well as misused lactic acid, H2O2). Chemotherapeutic agent Initially this term Drugs in this class differ from all others in was restricted to synthetic compounds, but now that they are designed to inhibit/kill the infecting since many antibiotics and their analogues have organism and to have no/minimal effect on the been synthesized, this criterion has become recipient.
Buy discount residronate 35mg on line
This patient has renal impairment medicine you can take during pregnancy purchase residronate toronto, half life of cefotaxime is likely to be prolonged. Since the patient has distressing urinary symptoms and is febrile, empirical antimicrobial treatment should be started after urine has been collected for bacteriological testing. The first line antimicrobials for this purpose are fluoroquinolones, cotrimoxazole, amoxicillin clavulanate, an oral 1st or 2nd generation cephalosporin, or nitrofurantoin. Nitrofurantoin is usually not preferred because it needs at least 7 days treatment, and often causes nausea and gastric pain. It relieves symptoms of bladder and uretheral irritation and can be given with the selected antimicrobial drug. Because this patient has suffered >3 episodes of cystitis within one year, she should be advised long term prophylactic therapy. The suitable prophylactic drug for her is cephalexin 250 mg once daily at bed time, because it is not contraindicated in pregnant women. Though this patient is not presently pregnant, she may conceive during use of the prophylactic drug. The other recommended prophylactic drugs, viz cotrimoxazole, nitrofurantoin and norfloxacin are all contraindicated during pregnancy. However, chemotherapy should be started immediately, because the culture and sensitivity tests take 6 weeks or more and defering treatment for such a long time may jeopardise outcome. This is a defaulted patient who has taken isoniazid and rifampin only for 3 months. For the initial 2 months, he should be given all 5 first line drugs, viz isoniazid 300 mg + rifampin 600 mg + pyrazinamide 1. Streptomycin should be stopped after that and the 4 oral drugs given for another 1 month. Pyrazinamide should be discontinued and 3 drugs rifampin, isoniazid and ethambutol should be continued for 5 more months. The regimen may be modified when the culture and sensitivity report becomes available. Since the patient had taken the standard multidrug therapy for the prescribed one year, and had responded clinically, the most likely cause of relapse is reactivation of dormant (persister) bacilli. As such, he should be treated with the same drugs, viz rifampin 600 mg + clofazimine 300 mg once a month alongwith dapsone 100 mg + clofazimine 50 mg daily for one year. The treatment of choice for Candida esophagitis is oral fluconazole 100 mg/day for 3 weeks, because it is highly effective and well tolerated. These may be treated with itraconazole 200/day or voriconazole 200 mg twice daily. Uncontrolled diabetes is an important predisposing factor in the causation of esophageal candidiasis, and appears to have played a role in this patient. Since the patient already had a complication of diabetes (Candida infection) it is desirable to shift her to insulin therapy (at least till the esophagitis is fully cured). The dose and frequency of insulin injections should be guided by repeated blood glucose monitoring. The intensity of action of glibenclamide (if continued in this case) is likely to be affected unpredictably. Thus, even if this drug is continued, close monitoring of blood glucose level and dose adjustment of the sulfonylurea is required. Therefore, it would be prudent to give prophylactic medication to further cut down chances of acquiring the infection. While majority of asexual schizonts are killed by chloroquine and the fever subsides, some survive and multiply to cause fever again. As broughtout above, recrudescence indicates chloroquine-resistance, which is particularly likely in this case, because the infection appears to be contacted from an area where chloroquine resistance among P. As such, she should be treated with an alternative drug effective against chloroquine-resistant P. Quinine 600 mg three times a day for 7 days along with doxycycline 100 mg once daily for 7 days. Artesunate 100 mg twice daily for 3 days, along with a single dose of sulfadoxine 1500 mg + pyrimethamine 75 mg. The primaquine therapy should be continued to complete the 14-day course, so as to totally eradicate the P. It was correctly changed to oral route once the patient improved, because oral bioavailability of metronidazole is nearly complete. Experience has shown that a single 10-day course of metronidazole is generally enough to kill all viable amoebae in the liver abscess, though the abscess cavity may persist for few weeks and heal spontaneously. Since the patient has improved clinically, visualization of persisting abscess cavity on ultrasound is not in itself an indication to extend/repeat metronidazole therapy. Since amoebic liver abscess is always secondary to colonization of colon by amoebae (which may be asymptomatic) and because metronidazole does not effectively eradicate cyst forming trophozoites from the colon (it is completely absorbed in the upper intestine, and very little reaches the colonic lumen), a luminal amoebicide should be given along with or after metronidazole. This patient of neurocysticercosis is suitable for treatment with anthelmintic drug, because there are multiple active parenchymal cysticerci in the cerebral cortex which in addition to seizures can cause other focal reactions in the brain. Planned killing of the cysticerci under corticosteroid cover may prevent future episodes of the reaction and may abolish the cause of seizures, so that long term antiseizure therapy can be avoided. The preferred drug is carbamazepine; start with 200 mg 3 times a day, increase by 200 mg/day if the seizures recur till they are fully suppressed or a maximum of 1200 mg/day dose is reached. To this patient, it should be given in a dose of 400 mg twice daily with milk or fat-rich food (to enhance absorption) for 15 days. Carbamazepine induces praziquantel metabolism and lowers its blood level, but not that of albendazole. Dexamethasone (which has to be given) also lowers praziquantel blood levels, but increases albendazole absorption. This is essential to suppress the inflammatory reaction to the dying cysticerci killed by albendazole therapy. A solution (Retinol) (W,I) Ethambutol (W,I) Co-trimoxazole (W,I) Ether, anaesthetic (I) (Trimethoprim + Sulphamethoxazole) Ethinylestradiol (W,I) Cyclizine (W) Ethinylestradiol + Levonorgestrel (W,I) Cyclophosphamide (W,I) Ethinylestradiol + Norethisterone (W,I) Cycloserine (W) Ethionamide (W) Cyclosporine (W,I) Ethosuximide (W) Cytosine arabinoside (cytarabine) (W,I) Ethyl alcohol 70%, (Ethanol) (W,I) D Etoposide (W,I) D. Antiemetics Domperidone (X) Promethazine, Doxylamine (morning sickness, Ondansetron Dicyclomine, Prochlorperazine other types of vomiting) Metoclopramide 2. Laxatives Senna, Bisacodyl, Docusates Dietary fibre, Ispaghula (constipation) Saline purgatives Lactulose 4. Cold-cough remedies Codeine, Dextromethorphan Xylometazoline Bromhexine, Expectorants Oxymetazoline Nasal drops Budesonide 7. Antiallergics Cetirizine, Loratadine Chlorpheniramine Fexofenadine, Astemizole (X) Promethazine 8. Antibacterials Cotrimoxazole, Fluoroquinolones Penicillin G, Ampicillin (systemic bacterial (X), Tetracycline (X), Doxycycline Amoxicillin-clavulanate infections) (X), Chloramphenicol (X), Cloxacillin, Piperacillin Gentamicin, Streptomycin (X), Cephalosporins Kanamycin (X), Tobramycin (X), Erythromycin Clarithromycin, Azithromycin, Clindamycin, Vancomycin, Nitrofurantoin 9. Antitubercular Pyrazinamide, Streptomycin (X) Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol 10. Antiamoebic Metronidazole, Tinidazole Diloxanide furoate, Paromomycin Quiniodochlor 11.
Buy generic residronate 35mg line
It does happen symptoms carbon monoxide poisoning 35 mg residronate free shipping, however, that atopic individuals are more prone to these events, not patients with shellfish allergy in particular, but those with atopy in general. The reason for this has not been completely established, but it is hypothesized that atopic individuals have a lower threshold for degranulation (not only to radiocontrast but to other direct-acting mast cell secretagogues as well). This regimen is recommended for an individual who has had a previous anaphylactic reaction to radiocontrast who must receive this diagnostic agent again. A nonionic, iso-osmolar dimer is probably the drug of choice when radiocontrast must be administered to a patient who has experienced a previous reaction. Systemic mastocytosis Systemic mastocytosis can be a cause of severe episodes of anaphylaxis, and these episodes usually present as idiopathic events. However, they can clearly be triggered by agents known to degranulate mast cells, especially opioids. In its classic form, systemic mastocytosis is due to a gain-of function tyrosine kinase mutation in the c-kit receptor (a growth receptor on the mast cell), which produces an autoactivation of the receptor, resulting in spontaneous mast cell degranulation. Recently, patients who are clinically indistinguishable from classical mastocytosis patients have been described as those who do not have all the classic biopsy findings for this condition. There is no definitive therapy at present available for patients with mastocytosis. They are treated in a similar fashion as patients with idiopathic anaphylaxis to prevent bothersome symptoms (such as urticaria) or life-threatening events. Disorders involving hypotension the most common condition confused with anaphylaxis is the vasodepressor reaction (vasovagal syncope). The vasodepressor reaction is characterized by hypotension, pallor, nausea, vomiting, weakness, and sweating. The characteristic bradycardia associated with vasodepressor reactions has been used as a differential diagnostic feature to distinguish them from anaphylaxis. However, this single feature may not be trustworthy and may be insufficient alone to distinguish a vasodepressor reaction from an anaphylactic event. Thus, perhaps the most important distinguishing feature between the two types of events is the absence of cutaneous symptoms (other than sweating) in the vasodepressor response. The absence of cutaneous features distinguishes these from episodes of anaphylaxis. Disorders involving flushing Since flushing occurs relatively frequently in anaphylactic episodes, a number of other causes of flushing should be considered. In the wet form, there is associated sweating mediated by sympathetic cholinergic nerves that supply sweat glands in the skin. It is characteristic of postmenopausal flushing and the flush produced by ingestion of capsaicin. The dry form involves direct vasodilatation without stimulation of the sweat glands and produces a dry flush as is seen in the carcinoid syndrome. Other forms of dry flush include those due to niacin, nicotine, catecholamines, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Dry flushing can also occur due to pheochro-mocytoma, rosacea, hypoglycemia, mastocytosis, and niacin ingestion. It causes a nonelevated intense erythema more frequently distributed across the trunk, neck, and face, occurring minutes after the ingestion of alcohol. Symptoms usually peak 30 to 40 minutes after ingestion and usually subside within 2 hours. One form occurs when alcohol is taken simultaneously with certain drugs and in patients with certain illnesses. Conditions predisposing to alcohol-induced flush include lymphoreticular neoplasms, the hypereosinophilic syndrome, and mastocytosis. The second form of alcohol-induced flush is due to a deficiency in acetaldehyde dehydrogenase-2. In patients with a deficiency of this enzyme, there is accumulation of acetalde-hyde, which results in mast cell degranulation. Perhaps the most common of these, and the one that resembles anaphylaxis to the greatest degree, is scombroidosis. This condition is produced by the ingestion of histamine contained in spoiled fish. Histamine is the major chemical involved in the production of symptoms, but all symptoms are not caused by histamine alone. The ingestion of histamine-contaminated spoiled fish is more toxic than the ingestion of equal amounts of pure histamine; therefore, other chemicals have been incriminated. The most likely is cis-Urocanic acid, an imidazole compound similar to hista-mine. Cis-Urocanic acid can also cause mast cell degranulation, thus perhaps to some extent augmenting the response. Histamine is produced by histidine-decarboxylating bacteria that cleave histamine from histidine in spoiled fish. This histamine production occurs shortly after the death of the fish and therefore can occur on the fishing vessel, at the processing plant, in the distribution system, or in the restaurant or home. Such contaminated fish cannot be distinguished by their appearance or smell, and cooking does not destroy the histamine. The onset of symptoms in scombroidosis occurs within a few minutes to several hours after the ingestion of fish. Symptoms include urticaria, flush, angio-edema, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a fall in blood pressure. The most common manifestation is face and neck flush accompanied by a sensation of heat and discomfort. Nonorganic problems that are psychologically based have also been confused with episodes of anaphylaxis. Panic attacks, except for flush and sweating, are usually devoid of cutaneous manifestations but can be characterized by tachycardia, gastrointestinal symptoms, and shortness of breath. There is no pruritus or true airway obstruction, and the absence of urticaria and angioedema is usually a telltale sign. Undifferentiated somato-form anaphylaxis is a term used to describe patients who present with manifestations that mimic anaphylaxis but who lack confirmatory findings and fail to respond to standard therapy. They often have psychological characteristics of other undifferentiated somatoform disorders. Anaphylaxis can be a result of an underlying disease and not actually due to exposure to an external agent. Such illnesses include systemic masto-cytosis (see above), urticaria pigmentosa, basophilic leukemia, acute promy-elocytic leukemia treated with tretinoin, and hydatid cyst. A separate set of disorders present with features suggestive of anaphy-laxis but are pathophysiologically distinct. For example, patients with hereditary angioedema present with acute swelling and occasionally exhibit an erythematous, serpiginous rash that can resemble urticaria. This rash accompanied by upper airway obstruction can be confused with an anaphylactic episode. The capillary leak syndrome can present with angioedema, gastrointestinal symptoms, shock, and hemoconcentration. Serum tryptase By far, the most commonly employed biomarker used to confirm a diagnosis of anaphylaxis is the measurement of total serum tryptase. The constitutively secreted tryptase is, for the most part, an immature form of tryptase, beta-protryptase.
Order residronate 35mg overnight delivery
Burnishers When the carving is complete medicine misuse definition cheap 35mg residronate with mastercard, the dentist may use burnishers to smooth and polish the restoration. Carvers After the amalgam is condensed, it must then be carved to approximately the same original anatomical tooth structure. Carvers have sharp cutting edges that are used to shape, form, or cut tooth anatomy into amalgam restorations. Figure 16-8 illustrates these instruments that come in assorted shapes and sizes in double ended designs. The Interproximal and #1/2 Hollenback were designed for carving mesial, distal, interproximal, lingual and facial tooth surfaces, Figure 16-7. Plastic instruments can be rounded working ends and come in single and steam sterilized and used on composites and double-ended types. Some advantages to using plastic A variety of double-ended instruments make instruments are that they will not discolor or up this instrument group. They are used to contaminate the composite restoration, and transport and place dental cements, resins, composite resin material will not cling to the temporaries, and insulating and pulp-capping materials. Cement and Insulating Base Instruments the instruments in this group are used for mixing and handling restorative resin and various temporary restorative, insulating, and pulp-capping materials. Another instrument frequently used with etching and bonding procedures associated with composite resins is a disposable brush that has a reusable handle (Fig. Single-use disposal brushes are being used more frequently, aiding in good infection control practices. Some of these spatulas can cause referred to as calcium hydroxide (Dycal) discoloration in the material being mixed. They are used to mix, carry, and selection of a mixing spatula is not critical place insulating bases, and are available as a except when preparing a permanent anterior single-ended or double-ended, shown in composite restoration. This can be prevented by using the spatulas provided by the manufacturer when working with it. The single ended #322 and #324 are suitable for mixing materials other than composites. Instruments in a diagnostic exam pack consist of a dental mirror, explorer, periodontal probe and cotton forceps are usually used in all dental specialties. Aspirating Syringe this syringe is used in dentistry to inject a local anesthetic. The aspirating syringe differs from most syringes in that it is designed to inject anesthetic from a carpule (Fig. The parts of an aspirating syringe consist of a threaded tip where the needle attaches, a barrel where the carpule is placed, a piston rod (plunger) with a harpoon attached that embeds itself into the rubber stopper of the carpule, a finger grip, and a thumb ring (Fig. Once the harpoon is engaged into the rubber stopper of the anesthetic carpule, the dentist can apply inward or outward pressure on the stopper by exerting pressure on the thumb ring. Pulling the thumb ring outward also pulls the plunger outward producing an aspirating effect; pushing inward forces the anesthetic solution through the needle. Aspirating Syringe Needle the aspirating syringe needles used in dental t r e a t m ent are sterile and disposable. They are designed for a single use, and are available in different gauges and lengths (Fig. This hub is positioned to the rubber dam punch is used to make permit the needle to extend inward to penetrate necessary spaced holes in the rubber dam the rubber seal portion of a loaded anesthetic material. These features let the operator select and adjust the wheel to punch the desired diameter hole in the rubber dam. The last five remaining holes correspond to the teeth that are included in the isolation. When placing the needle onto the syringe, remove only the cap that covers the syringe end on the needle. Generally, the Corpsman prepares the anesthetic syringe with a short needle (13/16 inch in length) for maxillary injections, and a long needle (1-3/16 inches in length) for mandibular injections. The tip of the needle has a beveled angle, which is turned toward the alveolus to accurately deposit the solution. These instruments prepare and maintain the position of thin sheets of latex rubber (rubber dam material). The rubber dam itself is used to isolate a designated tooth or teeth in the mouth before certain operative, endodontic and preventive dentistry procedures are performed. It also keeps fluids, tissues, and the tongue away from the operating site and prevents the patient from accidentally swallowing or aspirating debris. To maintain a snug fit the clamp is narrower than the diameter of the around the neck of the tooth, a rubber dam corresponding tooth. These clamps are made of spring around the tooth, it is necessary to spread the steel in various sizes (Fig. The working ends have small projections that fit into two corresponding holes on the rubber dam clamps. This sliding lock device locks the handles in positions while the provider Figure 16-20. Clamp # Area of use in the mouth 0 Primary teeth 2 Small bicuspids W3 Bicuspids and small molars 7 Mandibular molars W8A Partially erupted molars 9 Anterior teeth 2 1 2 Anterior teeth Table 16-1. Most of the rubber dams used today are determination, select a rubber dam clamp for a U-shaped. A simple and secure method is to put both ends of a piece of floss together and place them on a flat surface. Next, place the two loose ends through the looped end and carefully pull the loose ends through the loop until the floss is secured tightly over the bow of the clamp (Fig. To save valuable chair side time, place Hold the clamp with the bow facing upward the rubber dam following the administration of and away from the forceps. Locking the forceps handles is necessary to maintain the tension required to keep the clamp attached to the forceps. Pass the rubber dam forceps, with the working end covered, with the palm of the hand and the clamp pointed toward the placement position of the tooth. To stabilize the clamp, all the tips of the clamp must be in contact with the tooth to establish a facial lingual balance. Exercise care to ensure that the clamp tips do not impinge on the gingival Figure 16-24. Caution is advised to stabilize the clamp from the standard pattern for these items. The firmly on the tooth before the clamp forceps are first step is to punch the hole for the tooth to be loosened. Next, determine what additional holes remove the forceps and attach the clamp until must be punched. An To prepare the rubber dam material, the exception to this is root canal therapy when only rubber dam punch is needed to make the the involved tooth is exposed. A ragged hole or Placement tag will tear easily as the dam is placed over the crowns of the teeth. A ragged hole also may the rubber dam material and clamp can be cause leakage of moisture around the tooth. Place the rubber dam Ideally, the rubber dam material is marked frame on the outside of the dam with the bow of with predetermined markings of an average arch the frame facing out. The rubber dam material should appear the normal shape of the arch and spacing baggy on the frame rather than tight to allow alignment of the teeth. Pass the material, always check the oral cavity for any rubber dam and attached frame to the dentist for missing, misaligned, or extra teeth. Holding the edges of dam material between the holes) between the the rubber dam with the fingers, use the forceps teeth without tearing the material. Continue the placement as in the the tooth assists in bringing a single thickness second method. The last two methods of rubber of the dam through the proximal contact when dam placement are valuable when a rubber dam the floss is carried through. Floss placed on the must be placed by one individual rather than rubber dam itself tears the dam and requires the two. After the restoration is placed, remove the passing of two thicknesses of the dam through rubber dam.
Buy residronate on line amex
Pure carbolic acid has the advantage of penetrating little more deeply than is actually applied medications hyperthyroidism purchase residronate discount. The touched part becomes whilte immediately, but the normal epithelium recovers rapidly. The acid should not touch the conjunctiva to prevent adhesions (symblepharon) between the lids and eyeball. It prevents complications of spontaneous perforation which usually occurs in the centre of the cornea involving the visual axis. Therapeutic full thickness or penetrating keratoplasty is done as the last resort. The epithelium is usually intact and therefore the fluorescein staining is negative. Evacuation of pus is done first by a sterile autoclaved fine needle or knife before starting the topical antibiotic treatment as for corneal ulcer. If perforation is small in the pupillary area and there is no prolapse of iris: i. Optical iridectomy the pupil is extended to the periphery by a slit-like iridectomy. Full thickness keratoplasty is preferred treatment when the ulcer has healed and the vision is markedly reduced. Tattooing with gold (brown) or platinum (black) is advised for cosmetic purpose only in firm blind eyes usually. A piece of blotting paper of the same size, soaked in fresh 2% platinum chloride solution is kept over the opacity. On removing this filter paper, few drops of fresh 2% hydrazine hydrate solution are applied over the area which in turn becomes black. It is important to note that hypopyon is sterile as the leucocytosis is due to the toxins and not by actual invasion of the bacteria. Pneumococcus, Pseudomonas pyocyanea, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Gonococcus, Moraxella, fungus, etc. Chronic dacryocystitis is a continuous source of infection particularly of Pseudomonas pyocyanea and pneumococcus bacteria. In case of a corneal ulcer there is always associated iridocyclitis due to the liberation of toxins by the bacteria, which diffuses into the anterior chamber via the endothelium. This results in dilatation of the blood vessels and outpouring of leucocytes which become enmeshed in the fibrin network. In severe cases, it may completely fill the anterior chamber thus obscuring the iris. The hypopyon is sterile and it usually gets absorbed when hypopyon corneal ulcer is adequately treated with routine treatment for corneal ulcer. The opacity is greater at the advancing edge in one particular direction than centre. The tissues breakdown on the side of the densest infiltration (yellow crescent) and ulcer spreads in size and depth. Marked iritis with cloudy aqueous (hypopyon), conjunctival and ciliary congestion is usually present. Panophthalmitis may occur due to rapid growth and spread of the virulent organisms. Perforation may heal resulting in leucoma, adherent leucoma, anterior staphyloma or occlusio pupillae causing marked visual impairment. Treatment It is a well-known surgical rule that pus anywhere in the body has to be removed. Early and intensive treatment of corneal ulcer as mentioned earlier is started at once after culture and sensitivity. Secondary glaucoma is the most common cause of failure of treatment in elderly persons. Etiology It is commonly caused by Candida albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Fusarium, Cephalosporium, Streptothrix actinomycosis, etc. Fungal corneal ulcer Symptoms these are same as for the bacterial ulcer but they are less prominent than equal-sized bacterial ulcer. There is mild pain, irritation, watering and presence of yellow patch in the cornea. It is dry in appearance with small satellite lesions around the ulcer due to the stromal infiltration with delicate feathery, finger-like hyphate edges protruding into adjacent stroma. Predisposing factors Non-specific Systemic immunosuppressives, local or systemic steroids therapy 4. Diagnosis Scraping of the ulcer at the margin and inoculation of media should be done promptly. As the organism is often situated deep within the stroma, corneal biopsy may be taken at times. Topical antifungals are to be instilled for a long-time, as the response is often delayed. Cycloplegics such as atropine is used to prevent posterior synechiae formation and to control iritis by paralysing the ciliary muscle. Therapeutic full-thickness keratoplasty is much better solution in cases of non-healing fungal keratitis. Deep marginal ulcer may occur rarely in cases of polyarteritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus due to antigen-antibody complexes. Etiology It occurs as a result of degenerative process due to ischaemia of cornea. Characteristic white overhanging edges are seen as the ulcer spreads below the epithelium and superficial layers of stroma.