Bactrim
Cheap bactrim 480mg otc
Therapeutic ment of Beta-2-microglobulin adsorbent for direct hemoperfuplasma exchange performed in tandem with hemodialysis sion antibiotics in breast milk buy bactrim american express. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis associated b2-microglobulin in patients with dialysis-related amyloidosis in with amyloidosis: efficacy of plasma exchange. There is rapid loss of renal function with the histologic finding of crescent formation in over 50% of glomeruli. These cells comprise proliferating parietal epithelial cells and infiltrating macrophages and monocytes. Symptoms include malaise, intermittent fever, weight loss, respiratory distress, and diffuse pain in joints and can culminate in mortality. The current management is combination therapy consisting of high-dose corticosteroids and cytotoxic immunosuppressive drugs (cyclophosphamide and rituximab). Two randomized trials indicate that rituximab is an effective alternative to cyclophosphamide in new or relapsing patients. Other drugs that have been used include leflunomide, deoxyspergualin, tumor necrosis factor blockers, calcineurin inhibitors, mycophenolate mofetil, and antibodies against T-cells. Later subset analysis in two trials consisting of 62 patients found benefit in patients who were dialysis-dependent at presentation but not those with less severe acute kidney injury. Plasmapheresis therapy for diffuse alveolar hemorTcherakian C, Guillevin L; French Vasculitis Study Group. Plasma exchange for renal vasculitis and idiopathic rapidly Flossmann O, Tesar V, Vanhille P, de Groot K, Luqmani R, progressive glomerulonephritis: a meta-analysis. The three principles are to rapidly remove circulating antibody, to stop further production of antibodies, and to remove offending agents (hydrocarbon fumes, metallic dust, tobacco smoke, infections [influenza A], cocaine, etc). In general, the disease does not relapse in a successfully treated patient and therefore such patients do not require chronic immunosuppression. The presence or absence of antibody should not be used to initiate or terminate therapy, because antibody is not demonstrable in a few patients with the disease and may be present in patients without active disease. Alveolar hemorrhage in anti-basement membrane antibody disease: a series of 28 cases. Clinical and morphological aspects of the managebrane antibody disease: analysis of prognostic significance of ment of crescentic anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody clinical, pathologic and treatment factors. Acquired disease can be idiopathic or secondary to malignancy, thymoma, autoimmune or infectious diseases, certain drugs, and chemicals. Patients present with bleeding and bruising (most common), along with anemia and/or infection. Hematopoietic growth factors and androgens are sometimes used as adjunctive therapies. Diagnosis and manageReferences of the identified articles were searched for additional ment of acquired pure red cell aplasia. Treatment of erythropoietin-induced pure red tation after pretransplant isoagglutinin reduction with donor-type cell aplasia: a retrospective study. Pure red cell aplasia following immunotherapy in aplastic anemia and pure red cell aplasia. Complete remission of idiopathic incompatible allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Apheresis: Principles and Pracperipheral blood stem cell transplantation successfully treated tice, 3rd edition. Persistent skin inflammation may be associated with a relative lack of T-regulatory cells in the skin. Treatments for third-line or under investigation are interferon-g, omalizumab, allergen immunotherapy, probiotics, Chinese herbal medications, and antimetabolites. In parallel, decreased skin infiltration by inflammatory cells and improved skin architecture were observed. Double-filtration apy, and plasma exchange and plasmapheresis for articles published plasmapheresis for the treatment of patientswith recalcitrant in the English language. Knobler R, Berlin G, Calzavara-Pinton P, Greinix H, Jaksch P, Laroche L, Ludvigsson J, Quaglino P, Reinisch W, Scarisbrick J, 1. Apheresis in the treatment of recalcitrant atopic derBohbot A, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Dreno B, Enk A, French L, matitis: case series and review of the literature. Guidelines on the use of extracorporeal photopherement of severe atopic dermatitis. Philadelphia: ElsevImprovement of treatment-refractory atopic dermatitis by immuier. Prednisone suppresses antibody production and down-regulates Fc-receptor-mediated hemolysis in the spleen. Splenectomy, despite being underutilized, is perhaps the most effective and best-evaluated second-line therapy, but there are only limited data on longterm efficacy. In patients who have severe disease, the most effective and best-evaluated treatment is rituximab in the standard lymphoma dose and is now recommended first-line therapy, although complete and sustained remissions are uncommon. Alemtuzumab plus cyclosporine treatment terms warm/cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia, cold agglutinin of the autoimmune hemolytic anemia in an adult bowel transdisease, plasma exchange/plasmapheresis for reports published in plant. How I treat autoimmune hemolytic anemias searched for additional cases and trials. A case report of tive analysis of 30 severe autoimmune hemolytic anemia refractory warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia treated with plaspatients treated by whole blood exchange transfusion. Cold agglutinins in patients undergoing cardiac surA life-threatening paediatric case of acute autoimmune haemogery requiring cardiopulmonary bypass. Hematology, Basic Principles and Pracprospective study of 37 courses of therapy in 27 patients. Plasma term efficacy of the complement inhibitor eculizumab in cold exchange and rituximab treatment for lenalidomide-associated agglutinin disease. Autoimmune pathogenesis and autoplasma exchange: a case report and review of the literature. Patients treated with therapeutic plasma exchange: a tory, and fatal primary autoimmune hemolytic anemias. A new cold autoagof clinical outcome data with respect to evidence-based mediglutinin specificity: the third external loop of band 3. Cold agglutinin syndrome in pediatric blood cell antigens occur frequently with hemolysis among pediliver transplant recipients. Excessive cytokine production is thought to be a major cause of severe babesiosis and is associated with tissue pathology that can lead to significant end-organ damage and can result in persistent relapsing disease or death (all-cause mortality <1% of clinical cases and about 10% in transfusion transmitted cases). The detection of IgM is indicative of recent infection while IgG titer of 1:1,024 or greater usually signify active or recent infection.
Best bactrim 960 mg
R&D bacteria used for bioremediation bactrim 960 mg amex, Beerse, Belgium, 3Analytical Sciences, Janssen R&D, Beerse, Belgium, inornatipennis, C. Culicoides of Allied Health Sciences, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and milnei was the potential host for the development of Mansonella perstans Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, 6Research Institute for Chromatography, microflariae. Culicoides the neglected tropical disease onchocerciasis, or river blindness, is caused milnei has been demonstrated to be the major vector of M. Current this part of Cameroon and its activity takes place essentially in the night estimates indicate that 17 million people are infected worldwide, the with the most prominent peak between 9 and 10 pm. Today there are no non-invasive tests from this study offer opportunities to carry out transmission surveys for available that can detect ongoing infection and that can be used for Mansonellosis due to M. Stuyver2, Michel flariasis cases: 8 individuals; non-endemic controls: 20 individuals). This Mandro3, Germain Abhafule3, Deogracias Rossy3, Swabra Nakato1, work resulted in the identifcation of the plasma metabolites inosine Joseph F. Siewe1, Robert Colebunders1 and hypoxanthine as biomarkers for flarial infection, and of the urine 1University of Antwerp, Wilrijk, Belgium, 2Janssen R&D, Beerse, Belgium, metabolite cis-cinnamoylglycine as specifc biomarker for O. These large-scale validation approaches are necessary prior to is excreted in the urine of infected individuals as a biomarker for active the defnition of an intended use for any of these markers. A promising drug target is the flarial when comparing the entire population (with and without epilepsy endosymbiotic bacteria, Wolbachia, which can be depleted with antibiotics (P=0. Doxycycline induced Sultani Matendechero, Mwatha Stephen, Ngugi Jeremiah, signifcant reductions in Wolbachia after continuous treatment for 7 or Wyckliff Omondi, Cecilia Wandera 14 days, whilst drug removal after 7 days led to non-signifcant reduction Neglected tropical medicine, Nairobi, Kenya after 7 days washout. It we have robustly validated an in vitro co-culture system which may be has affected over 120 million in the world and about 3. The target population were aged Alain Javel1, Carl Fayette1, Franck Monestime1, Ellen Knowles2, two years and above but excluded pregnant women. Data was collected and aggregated using registers and tally 1 2 sheets then analyzed using Microsoft Excel and Epi-Info. Two counties in 2016 partners proposed a two-phase microplanning protocol in fve communes compared to 3 in 2017 achieved the 80% recommended coverage. Retrospective pre-testing was used to evaluate microplanning Cade Howard9, Zebedee Kerry10, Leanne Robinson10, Myra Hardy11, workshops. In each country, acceptability of the treatments was assessed with a survey of 400 randomly selected participants (age fi14 yrs) within four months of treatment. We aimed to develop consensus criteria for the diagnosis of scabies to 545 facilitate this integration. We conducted an iterative, consensus (Delphi) study involving international experts in the diagnosis of scabies. Kartey-Attipoe1, generation and ranking a long list of possible features (rounds 1 2), to Sampsom Otoo1, Joseph Otchere1, Bruno Gomes2, Dziedzom K. Reimer2 Panel participants (n=30) were predominantly highly experienced clinicians, representing a range of clinical settings and all continents. Adoption of the criteria may require the best sampling method that can capture high numbers was supported by 96. Gravid anophelines diagnosis of scabies have been established with very high agreement. The are good indicators for assessing transmission due to close contact with 2018 criteria for the diagnosis of scabies can be used as part of integrated humans through blood meals. Additionally, indoor resting collection was similarly effcient in the Northern region (8. Screening of mosquitoes for approach is designed to ensure effective mass drug administration, explore infection showed, 3. Term of reference for National trainers was refned and bound strict to every trainer. This study emphasizes the need for leaders of decentralized health be used to identify areas of persistent transmission for further intervention. In Gashaka, Republic of Tanzania, 3National Institute for Medical Research, Dar Es Ov16 prevalence ranged from 0-23%, with 11 schools having 0 positives. Salaam, United Republic of Tanzania In Bekwarra, Ov16 prevalence ranged from 0-13% with 5 schools having 0 positives. The intervention was piloted in a village in Central Java, (pieces of clothes impregnated with insecticide) are a new, cheap and Indonesia using a pre/post design with both qualitative and quantitative effective tool to control tsetse fies. However, in the context of vector control, community based and behaviours related to gastrointestinal and helminth-related disease approaches are often recommended because the action is implemented were assessed before and after the intervention through a questionnaire near to the daily activities of the affected people. A community-led intervention is being performance is an effective health education tool. The results provide implemented since 2017 in three villages in the Kwilu province. The wayang kulit intervention is evaluated through the Action-Research methodology and production provides a signifcant additional component for an integrated, data is collected with different qualitative and quantitative methods. However, it remains to evaluate if this approach is feasible at a bigger scale, cost effective and appropriate to Anne Karing1, Karim Naguib2 reach the elimination objective for 2020. The health ministry, through its Community Health Uvon2, Jean-Paul Tambwe2, Gary J. Two types of social incentives were distributed 3 la Sante, Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Washington to dewormed adults in the form of colorful bracelets and ink. This strategy has been supported by the results of included a household visit to recruit subjects). Findings show that offering a 3-year community trial conducted in the Republic of Congo, where bracelets incentivizes deworming treatment take-up (8. In June 2014, we started a parallel treatment adoption when compared to ink and calendars. Among 438 individuals who were examined Claudio Fronterre1, Rachel Pullan1, Jorge Cano1, Emanuele both in 2014 and 2017, 149 were positive at baseline; 69 of those Giorgi2 149 (46. Soil-transmitted helminth caused by three species of nematode worms: Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia infections were monitored using Kato-Katz method. Whilst highly practical, these diagnostics are less useful for describing ongoing 553 transmission intensity, particularly after treatment. The output of this research can lead of Health, Suva, Fiji, 3University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia to better informed implementantion strategies for the elimination of lymphatic flariasis. Women were less likely to be mf positive (2% vs 6% in men) on potential ways to achieve. Policy and leadership is sustainable were mild, not affecting normal daily activities of work or school. Budget is largely sustainable, fatigue (32%), headache (10%), nausea (9%), dizziness (7%) and muscle however domestic funding and government ownership of budgets is weakness (7%). In order to ensure sustainability is important to develop transition plans which should outline the exact roles and responsibilities played by partners and government stakeholders, and should detail how these responsibilities can slowly transition over time. The objective was to verify the accuracy of the Constanza Cortez1, Siomara Vargas1, Fredi Cifuentes1, Francisco reported coverage. The survey was Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Chile cluster-based and took place in two health districts, purposely selected. Data collection was paper-based and quantitative and qualitative interview Trypanosoma cruzi is the etiological agent of Chagas Disease, a public techniques. Previous studies showed that probenecid number of 3,454 individuals were surveyed. The median age of the survey participants was 23 years the effect an antimalarial drug, interestingly until now presence of gap old. This fnding the administrative coverage previously reported in Bali was higher than also suggest the presence of functional gap junction membrane channel survey coverage, leading to conclusion of an over reporting. The chemosensitization of probenecid to benznidazole these results showed in contrary an under reporting.
Diseases
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- Acral dysostosis dyserythropoiesis
- Tracheoesophageal fistula
- Crigler Najjar syndrome
- Acitretine antenatal infection
- Lowe syndrome
- Wagner Stickler syndrome
- Diastrophic dysplasia
- Hepatitis D
960 mg bactrim sale
Probable Mode of Transmission: Ingestion infection specialist discount bactrim 960mg on line, inhalation (occupational exposure to farmers) Known Distribution: Worldwide; rare in N. Pulmonary syndromes are usually chronic, often occurring in persons with other underlying pulmonary disease. Subjective: Symptoms Lymphadenitis (painless enlargement of the lymph nodes of the neck), usually unilaterally; skin and soft tissue infections edema, erythema; pulmonary infection chronic, productive cough with fever and weight loss; accompanied by malaise, night sweats and hemoptysis. Other Syndromes: Therapy based on site of disease, organism and susceptibility testing results. No Improvement/Deterioration: Reevaluation and repeat culture and susceptibility testing. Follow-up Actions Wound Care: Local care (clean, dry, protect, topical antibiotics) to prevent secondary bacterial infection. Consultation Criteria: Management of chronic pulmonary infection usually requires specialty consultation. Although the acid-fast bacilli can be detected in lesional or sputum smears or biopsy material, culture is required to confirm diagnosis. Cryptococcosis is found worldwide but symptoms are most common in the immunosuppressed and are not acutely life-threatening. Blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis are endemic fungal infections that should be included in a differential diagnosis so individuals with potential infections may be removed or referred to higher echelons of care. In adults, disease commonly occurs in diabetics, the immunocompromised, and after antibiotic treatment for other disorders. Disseminated, life-threatening infection can also occur in severely immunocompromised persons. Subjective: Symptoms Oral thrush: Usually asymptomatic; may cause mouth discomfort or difficulty swallowing. Vaginal thrush: Itching, dyspareunia (pain with intercourse) and change in the odor or consistency of vaginal discharge. Intertrigo nystatin powder or clotrimazole or miconazole cream twice daily until resolved. Alternative: Oropharyngeal candidiasis clotrimazole troches (lozenges), 10 mg 5/day, oral fluconazole, 50-200 mg/day, itraconazole, 100-200 mg/day, or ketoconazole, 200 mg/day. Esophageal candidiasis itraconazole 100-200 mg/day, or intravenous amphotericin B, 0. Patient Education General: this is a superficial infection that should resolve with standard therapy. It can occur in healthy people, but could indicate other disease such as diabetes or immunocompromise. Medications: Topical antifungals have virtually no adverse effects associated with their use. The oral azoles, fluconazole, itraconazole, and ketoconazole are all well tolerated. These drugs may interact with other drugs processed through the liver, causes the levels of drugs such as oral diabetes, seizure, and anticlotting medications. Ketoconazole that is used long-term may affect steroid hormones, causing irregular menses in women and decreased libido or breast tissue enlargement in men. Malaise, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and infusion site phlebitis (vein inflammation) may also occur. Intravenous use of amphotericin B is associated with infusion-related fever, headache, chills, myalgias, and rigors. Prevention and Hygiene: None necessary No Improvement/Deterioration: Further evaluation is necessary if infection does not resolve within two weeks. Follow-up Actions Return evaluation: If lesions do not resolve consider alternate treatment. However, those with recurrent thrush, disseminated infection or who require intravenous amphotericin B therapy should be referred to the appropriate higher echelon of care. Most individuals seeking care for this infection have progressive pulmonary disease or cutaneous lesions. Subjective: Symptoms Acute pulmonary infection produces fever, cough, and pleuritic chest pain. Chronic pulmonary disease can also include hemoptysis, weight loss, and skin lesions. These begin as red papules or nodules that enlarge and then ulcerate or become verrucous. Using Advanced Tools: Lab: Large (8-15 mm), thick-walled, broad-based, budding yeast cells may be visible on Gram stain of sputum or lesion. Itraconazole can be used in all other infections at a dose of 200-400 mg/day po, 5-59 5-60 usually for 6-12 months. Alternative: Ketoconazole 400-800 mg/ day or fluconazole 400-800 mg/ po day Patient Education General: Acute pulmonary infection may resolve untreated in 1-3 weeks. Follow-up Actions Wound Care: Local care to prevent secondary bacterial infection. Return evaluation: Observe patients over a 1-2 year period for resolution of infection. About 1% of those infected develop chronic pulmonary disease or disseminated infection to the meninges, skin, bone, or soft tissue. It has frequently been reported in service members training at Fort Irwin, California. Incidence peaks during dry periods following rains, usually in summer and fall, and is often associated with wind and dust storms. Risk Factors: Filipinos, blacks, Hispanics, pregnant women, immunocompromised patients are at higher risk for dissemination and severe disease. Subjective: Symptoms Cough (usually dry), fever, pleuritic chest pain, malaise, headache, anorexia, myalgia and often rash; severe disease may present with a sepsis-like syndrome. Large joint pain may occur after asymptomatic infection, especially in white females (desert rheumatism). Using Advanced Tools: Ophthalmoscope: Patients with meningitis may have papilledema on funduscopy. This can be followed with fluconazole 400-800 mg/day to complete 3-6 months of therapy. Alternative: Itraconazole (400-600 mg/day) may be used in non-meningeal infections. Some authorities add intrathecal amphotericin B in the initial therapy of meningeal disease. Patient Education General: Acute pulmonary disease will likely resolve untreated in 6-8 weeks. Medications: See Candidiasis section for adverse effects of intravenous amphotericin B and azole antifungals. Follow-up Actions Return evaluation: Patients should be evaluated frequently for progressive disease. Evacuation/Consultation Criteria: Evacuate and refer all patients to a specialist for care. Risk Factors: Outbreaks may occur with the removal of debris containing contaminated bird or bat droppings. Outbreaks in military personnel have been documented after clearing barracks and bunkers. Subjective: Symptoms Acute (days): Malaise, fever, chills, anorexia, myalgias, cough, pleuritic chest pain. Assessment: Differential Diagnosis (see respective topics) Acute pulmonary infection influenza Chronic pulmonary infection tuberculosis, other fungal infections Plan: Treatment Primary: Therapy is not needed in asymptomatic or acute pulmonary infection unless associated with hypoxemia or symptoms longer than one month. Itraconazole 200 mg daily for 6-12 weeks, can be given in those cases that do not spontaneously improve/resolve. For severe infection, including acute or chronic pulmonary disease, disseminated disease or meningitis, give amphotericin B 0. This therapy can be changed to intraconazole 200 mg once or twice daily, for 6-24 months when clinically stable or continued for 3-4 months (35 mg/kg total amphotericin B). Alternative: Ketoconazole 200-800 mg/day can be used as an alternative to itraconazole. Patient Education General: Most acute pulmonary infections resolve spontaneously in 3-4 weeks. Prevention and Hygiene: Encourage others to avoid areas where patient was exposed.
Best order for bactrim
In general zinnat antibiotic discount 480 mg bactrim, worms in mammals Table 1 lists the species of Dracunculus which have been are regarded as D. Dracunculus has from a wide range of mammals both from parts of the world a very short patent period, at the most a few weeks, and an where dracunculiasis is endemic and from parts where it is not emerging worm is not easy to see in fur-bearing carnivores (Fig. This is well illustrated by the situation in North America, where there are one or two reports of infection in wild carnivores and domestic dogs each year, mostly from states in the southeastern United States and from southern Ontario, Canada. A human case of guinea worm disease, with an emerging aNote that some authorities have recognized only two species: D. The worm is often wound on a stick, a practice which is believed to in mammals and D. The taxonomic status of this North American parasite is also worthy of investigation. It was described by Leidy in a short account in 1858 and confirmed as a different species (D. This supposition is suplength of the gubernaculum and number of preanal papillae ported by the higher prevalence found by surveys of the human from males of D. However, when more males of population than by the dissection of dogs culled during the 1920s the latter species were described (116), these differences were in Bukhara, Uzbekistan (Fig. However, worms are still found not found to be valid, and the species was never accepted by all in dogs in the former areas of endemicity of Uzbekistan (99) and authorities. It is significant that the disease has not from North America (see reference 146 for one such case; returned to Uzbekistan in the 70 years since it was eliminated Spearman et al. Nor An isolated autochthonous human case of dracunculiasis has has it returned to Egypt, Iran, Gambia, or Guinea, where it been reported from Japan (105), and similar older cases ocdisappeared decades ago. Infections in reptiles appear to be due to separate species (see Preemergent female worms can move easily through the reference 116). The host reaction results in the tion (123), and aspirin was found elsewhere to be equally formation of a burning, painful blister, which bursts in a few effective (Muller, unpublished). Ivermectin is effective against days to give a shallow ulcer, and there is then a marked inmany other nematodes but had no action in one trial, nor in fiammatory response against the cuticle of the entire worm, experimental infections (55, 96). The bacteriologically sterile blister treatment with mebendazole was associated with aberrant mifiuid contains larvae surrounded principally by polymorphonugration of the worms, which were more likely than usual to clear neutrophils with macrophages, lymphocytes, and eosinoemerge at places other than the lower limbs. Unfortunately, the track of the In recent years, the understanding has grown that biological worm becomes secondarily infected in about half of all cases, and technical feasibility is not the only criterion to consider and patients become severely incapacitated. Costs and benefits area of Nigeria, 58% of patients, mostly in the 15to 49-yearare no less important (52). The benefits of dracunculiasis eradold working-age group or of school age, were disabled for an ication, in contrast to those of smallpox and polio, will accrue average of 12. In another study in patient besides palliative treatment; most patients live in poor, Benin there was 0. Female worms sometimes burst in the tissues, resulting in walking to a health facility; and most recover spontaneously a very large pus-filled abscess and severe cellulitis. For example, a large teaching females or males elicit a slight infiammatory reaction and hospital in Nigeria never saw dracunculiasis cases in the Casometimes calcify, showing up on a roentgenogram. Because few cases were reported, there is little evidence of acquired immunity and the same the disease was often considered an exotic curiosity rather than individual can be reinfected many times. However, in areas of endemicextrusion of larvae is indicative of an Arthus reaction followed ity its social, economic, nutritional, and educational conseby a delayed hypersensitivity response (117). Diagnosis Disability Patients in an area of endemicity have no doubt about the diagnosis when, or just before, the blister forms from the local Dracunculiasis is rarely fatal; studies in India based on meditching and then sharp pain and often general allergic sympical records suggest a case fatality rate of 0. Once the blister has burst, cold is probably a generous estimate, because only persons with water will encourage the release of larvae, which can be seen severe complications usually seek treatment from health facilmicroscopically under low power. The proportion of patients permanently disabled by are not useful in practice because it has not been proved that the disease is also small; a number of studies have found it to they can detect prepatent infections, mainly because of the lack be less than 1% (94, 132, 142). However, antibodies can be dethe social impact of guinea worm disease is mainly attribtected in patent infections by enzyme-linked immunosorbent utable to the temporary disability suffered by the patient. Two assay or dot-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, using longitudinal studies in Nigeria (5, 143) found that 58 to 76% of whole-worm antigens. The most specific reaction appears to be patients were unable to leave their beds for approximately a for detection of immunoglobulin G4 (17). The more able to detect prepatent infections up to 6 months before severe and protracted disability is associated with secondary emergence (11), in which case it could have practical imporinfection of the lesion; this occurs in roughly half the cases tance. The impact of this temporary disability is reinforced by the seasonal pattern of worm emergence, often peaking at stages of the agricultural year when labor is in maximum demand. The particularly when combined with a clean dressing and antibimiddle section shows the corresponding variation in cases of otic ointment to prevent secondary bacterial infection (115). The pattern typical of the There is no evidence that any chemotherapeutic agent has a forest zone to the south is shown in the bottom section of Fig. Months are January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, and December, from left to right, respectively. This seasonality means that a whole a worm, 34% of patients still had some difficulty performing community can be laid prostrate simultaneously and household everyday activities, usually due to pain attributable by its locamembers can be prevented from substituting for one another tion and the date of onset to the episode of dracunculiasis. Indeed, it has been claimed While this disability is not necessarily permanent, it extends that the effect of the disease on agricultural productivity can be beyond the incapacity occurring during worm emergence. The impact of guinea worm disease does not end when the Some attempts to estimate the economic impact of dracunworm is out and the sufferer returns to work. A study in Ghana culiasis have simply multiplied the number of days of labor lost (88) found that, between 12 and 18 months after emergence of by the mean value of production per day or by the wage rate. From such a simplification, it is a small step to multiply the loss in their families. Children miss school when they have guinea per household to derive an estimated cost for a whole region. As a result, ern Nigeria sustained an annual loss of $20 million due to school attendance suffers during the peak season (22, 60, 62, guinea worm disease. In spite of its simplistic argument, this 92, 124), and schools in areas of endemicity often have to close study was extremely effective in mobilizing the support of sefor 1 month in each year as a result. It is, therefore, surprising that a recent cost-benefit analstrategies by which households respond to illness (such as ysis of the eradication effort by the World Bank (104) considers abandoning other tasks and using additional labor), which only the benefits from incidence reduction during the camqualitative studies have found to be common in peasant farmpaign; their estimate of a 29% economic rate of return for the ing (23, 38). A more sophisticated approach is to examine the global campaign, which they estimate to have cost some $90 impact on actual production (24) or even to include the incimillion to date, is certainly pessimistic. Deep wells are rarely implicated in transHowever, there is also a cost to the coping strategies, which mission (31, 118); few cyclops are found in them, probably cannot be measured using this approach. The simplistic ponds and sometimes shallow or step wells are the main approach used for the Nigerian study mentioned above may be sources of the disease, and the epidemiology of dracunculiasis more accurate than it seems. Nutrition, Education, and Perpetual Benefits Numerous studies have illustrated the predominant role of ponds in dracunculiasis transmission in various parts of Nigeria Such economic calculations do not take into account the (57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 100, 127), Ghana (112, 138), Burkina Faso unequal distribution of costs within the family and the way in (70), Togo (129), Uganda (77), Pakistan (86), India (98), and which disease, by impacting more on the production of some what is now Uzbekistan (171). Table 2 shows the findings of Steib and found that, in households where more than half the adult Mayer (147) for a village in Northeast Burkina Faso, which members had suffered from dracunculiasis in the previous year, illustrate the large number of ponds which can be found in a the children under 6 years old were nearly three times as likely single village, even in a semiarid, Sahelian setting, and the to be malnourished, as indicated by wasting. Peak transmission seasons for dracunculiasis in 14 African countries Occurrence in month:a Country Jan Feb Mar Apr May June July Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Mauritania X X X X Chad X X X X X Mali X X X X X Niger X X X X X Burkina Faso X X X X X X Cameroon X X X X X X Sudan X X X X X X Uganda X X X X X Ethiopia X X X X X Ivory Coast X X X X X X X Ghana X X X X X X X Benin X X X X X X Togo X X X X X Nigeria X X X X X X X X aAbbreviations: Jan, January; Feb, February; Mar, March; Apr, April; Aug, August; Sept, September; Oct, October; Nov, November; Dec, December. Other types of human-made ponds, sometimes larger than quence for the design of eradication programs. For example, in 1990 the excavated for community water storage on the Mossi plateau of national case search conducted in all 8,068 villages of Burkina central Burkina Faso (101); small dams in northern Ghana (152); Faso found cases in only 2,621 (101).
Cheap bactrim 960 mg without prescription
As a result of the Merger virus paralyzing children discount 480mg bactrim, our ownership of OphthaliX, immediately post-Merger, became approximately 8% of the outstanding shares of common stock. In addition, that certain License Agreement granted to OphthaliX by us and a related services agreement was terminated. Our current capital expenditures are made solely within Israel and primarily consist of the acquisition of computers and related communications equipment. Business Overview We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on developing orally bioavailable small molecule therapeutic products for the treatment of cancer, liver and inflammatory diseases and erectile dysfunction. We also co-develop specific formulations of cannabis components for the treatment of cancer, inflammatory, autoimmune, and metabolic diseases. Overproduction or inappropriate production of certain cytokines by the body can result in disease. We believe our pipeline of drug candidates represent a significant market opportunity. On September 10, 2019, we entered into a collaboration agreement with Univo, a medical cannabis company, to identify and co-develop specific formulations of cannabis components for the treatment of cancer, inflammatory, autoimmune, and metabolic diseases. We agreed to pay Univo a total of $500,000 through two installments and issued to Univo 19,934,355 ordinary shares through a private placement, representing approximately 16. We believe that our drug candidates have certain unique characteristics and advantages over drugs currently available on the market and under development to treat these indications. Moreover, we believe characteristics of Piclidenoson, as exhibited in our clinical studies to date, including its good safety profile, clinical activity, simple and less frequent delivery through oral administration and its low cost of production, position it well against the competition in the autoimmune-inflammatory markets, including the rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis markets, where treatments, when available, often include injectable drugs, many of which can be highly toxic, expensive and not always effective. Our recent findings also demonstrate that a biological predictive marker can be utilized prior to treatment with Piclidenoson, which may allow it to be used as a personalized medicine therapeutic approach for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. None of our product candidates have been approved for sale or marketing and, to date, there have been no commercial sales of any of our product candidates. Our Strategy Our strategy is to build a fully integrated biotechnology company that discovers, in-licenses and develops an innovative and effective small molecule drug portfolio of ligands that bind to a specific therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer, liver and inflammatory diseases and erectile dysfunction. We generally focus on drugs with global market potential and we seek to create global partnerships to effectively assist us in developing our portfolio and to market our products. Using this approach, we have successfully advanced our product candidates for a number of indications into various stages of clinical development. Specific elements of our current strategy include the following: Successful development of our existing portfolio of small molecule orally bioavailable drugs for the treatment of various diseases. We intend to continue to develop our existing portfolio of small molecule orally bioavailable drugs, both for existing targeted diseases, as well as other potential indications. Our drug development will continue to focus on cancer, liver and inflammatory diseases and erectile dysfunction. We intend to focus most prominently on advancing our product candidates that are in the most advanced stages, i. Use our expertise with our platform technology to evaluate in-licensing opportunities. We continuously seek attractive product candidates and innovative technologies to in-license or acquire. We believe that by pursuing selective acquisitions of technologies in businesses that complement our own, we will be able to enhance our competitiveness and strengthen our market position. We will then seek to grow our product candidate portfolio by attempting to in-license those various candidates and to develop them for a variety of indications. Our existing product candidates are almost all directed at diseases that have major global markets. Our intent is to continue to develop products that target diseases that affect significant populations using our platform technology. We believe further that this strategy will increase the likelihood of advancing clinical development and potential commercialization of our product candidates. We have entered into several out-licensing arrangements with leading pharmaceutical companies in the Far East, Canada and Europe. We intend to continue to commercialize our product candidates through out-licensing arrangements with third parties who may perform any or all of the following tasks: completing development, securing regulatory approvals, manufacturing, marketing and sales. If appropriate, we may enter into co-development and similar arrangements with respect to any product candidate with third parties or commercialize a product candidate ourselves. Figure 1: Piclidenoson anti-inflammatory mechanism of action 52 Set forth below are general descriptions of the inflammatory diseases with respect to which Piclidenoson is currently undergoing, or is in preparation for clinical trials. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic autoimmune-inflammatory disease that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks flexible synovial, or joints, on both sides of the body. This symmetry helps distinguish rheumatoid arthritis from other types of arthritis, which is the general term for joint inflammation. Although the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, autoimmunity plays a pivotal role in both its chronicity and progression. The inflammatory cells migrate from the blood into the joints and joint-lining tissue. There, the cells produce inflammatory substances that cause irritation, wearing down of cartilage, or the cushioning material at the end of bones, swelling and inflammation of the joint lining, which is caused by excess synovial fluid, the development of pannus, or fibrous tissue, in the joint, and ankylosis, or fusion of the joints. Joint inflammation is characterized by redness, warmth, swelling and pain within the joint. As the lining expands due to inflammation from excess fluid, it may erode the adjacent bone, resulting in bone damage. Rheumatoid arthritis can also produce diffuse inflammation in the lungs, membrane around the heart, the membranes of the lungs, and white of the eye, and also nodular lesions, most common in subcutaneous tissue. In psoriasis, immune cells move from the dermis to the epidermis, where they stimulate keratinocytes, or skin cells, to proliferate. These cytokines and antimicrobial peptides signal more inflammatory cells to arrive and produce further inflammation. In other words, psoriasis occurs when the immune system overreacts and mistakes the skin cells as a pathogen, and sends out faulty signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells. But in psoriasis, new skin cells move rapidly to the surface of the skin in days rather than weeks. There are five types of psoriasis: plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular and erythrodermic. The most common form, plaque psoriasis, is commonly seen as red and white hues of scaly patches appearing on the top first layer of the epidermis, or skin. In plaque psoriasis, skin rapidly accumulates at these sites, which gives it a silvery-white appearance. Plaques frequently occur on the skin of the lower back, elbows and knees, but can affect any area, including the scalp, palms of hands, soles of feet and genitals. In contrast to eczema, psoriasis is more likely to be found on the outer side of the joint. Psoriasis is a chronic recurring condition that varies in severity from minor localized patches to complete body coverage. Fingernails and toenails are frequently affected, known as psoriatic nail dystrophy, and can be seen as an isolated symptom. Psoriasis can also cause inflammation of the joints, which is known as psoriatic arthritis. Pre-Clinical Studies of Piclidenoson the information below is based on the various studies conducted with Piclidenoson, including preclinical studies. Pre-clinical studies are a set of experiments carried out in animals to show that a certain drug does not evoke toxicity. The toxicity of Piclidenoson has been evaluated following 28-day, 90-day, six-month and nine-month good laboratory practice repeated-dose toxicity studies in male and female mice (28-day, 90-day and six-month), dogs (single-dose only), and monkeys (28-day, 90-day and nine-month). Even though the dose of Piclidenoson in these studies was escalated to an exposure that is many folds higher than the dose used in human clinical studies, no toxic side effects were identified.
Syndromes
- Endoscopy -- camera down the throat to see burns in the esophagus and the stomach
- Spray your clothes with insect repellant.
- Congenital syphilis
- Difficulty using the arms and hands or legs and feet due to weakness
- Hereditary IgA deficiency
- Learn stretching exercises for your neck and upper body. Stretch every day, especially before and after exercising. A physical therapist can help you learn how to stretch correctly.
- Headache
- Turner syndrome
- Glaucoma
- Opening of the surgical cut site
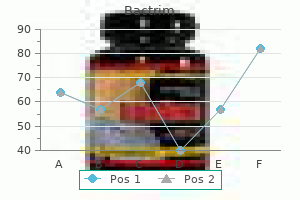
Cheap 480mg bactrim with amex
A considerable number of international bodies are involved in work on chemical safety antibiotic kidney pain buy bactrim with a mastercard. In many countries work programmes for the promotion of chemical safety are in place. Such work has international implications, as chemical risks do not respect national boundaries. However, a significant strengthening of both national and international efforts is needed to achieve an environmentally sound management of chemicals. Strengthening of national capabilities and capacities for management of chemicals; f. In addition, the short final subsection G deals with the enhancement of cooperation related to several programme areas. The six programme areas are together dependent for their successful imp lementation on intensive international work and improved coordination of current international activities, as well as on the identification and application of technical, scientific, educational and financial means, in particular for developing countries. To varying degrees, the programme areas involve hazard assessment (based on the intrinsic properties of chemicals), risk assessment (including assessment of exposure), risk acceptability and risk management. Increased coordination of United Nations bodies and other international organizations involved in chemicals assessment and management should be further promoted. The broadest possible awareness of chemical risks is a prerequisite for achieving chemical safety. The principle of the right of the community and of workers to know those risks should be recognized. Industry should apply adequate standards of operation in all countries in order not to damage human health and the environment. There is international concern that part of the international movement of toxic and dangerous products is being carried out in contravention of existing national legislation and international instruments, to the detriment of the environment and public health of all countries, particularly developing countries. In resolution 44/226 of 22 December 1989, the General Assembly requested each regional commission, within existing resources, to contribute to the prevention of the illegal traffic in toxic and dangerous products and wastes by monitoring and making regional assessments of that illegal traffic and its environmental and health implications. The Assembly also requested the regional commissions to interact among themselves and to cooperate with the United Nations Environment Programme, with a view to maintaining efficient and coordinated monitoring and assessment of the illegal traffic in toxic and dangerous products and wastes. Assessing the risks to human health and the environment hazards that a chemical may cause is a prerequisite to planning for its safe and beneficial use. Among the approximately 100,000 chemical substances in commerce and the thousands of substances of natural origin with which human beings come into contact, many appear as pollutants and contaminants in food, commercial products and the various environmental media. Fortunately, exposure to most chemicals (some 1,500 cover over 95 per cent of total world production) is rather limited, as most are used in very small amounts. However, a serious problem is that even for a great number of chemicals characterized by highvolume production, crucial data for risk assessment are often lacking. It could be made cost-effective by strengthening international cooperation and better coordination, thereby making the best use of available resources and avoiding unnecessary duplication of effort. However, each nation should have a critical mass of technical staff with experience in toxicity testing and exposure analysis, which are two important components of risk assessment. Several hundred priority chemicals or groups of chemicals, including major pollutants and contaminants of global significance, should be assessed by the year 2000, using current selection and assessment criteria; b. To produce guidelines for acceptable exposure for a greater number of toxic chemicals, based on peer review and scientific consensus distinguishing between healthor environment-based exposure limits and those relating to socio-economic factors. Promote mechanisms to increase collaboration among Governments, industry, academia and relevant non-governmental organizations involved in the various aspects of risk assessment of chemicals and related processes, in particular the promoting and coordinating of research activities to improve understanding of the mechanisms of action of toxic chemicals; c. Encourage the development of procedures for the exchange by countries of their assessment reports on chemicals with other countries for use in national chemical assessment programmes. Give high priority to hazard assessment of chemicals, that is, of their intrinsic properties as the appropriate basis for risk assessment; b. Industry should provide data for substances produced that are needed specifically for the assessment of potential risks to human health and the environment. Such data should be made available to relevant national competent authorities and international bodies and other interested parties involved in hazard and risk assessment, and to the greatest possible extent to the public also, taking into account legitimate claims of confidentiality. Governments, through the cooperation of relevant international organizations and industry, where appropriate, should: a. Develop criteria for priority-setting for chemicals of global concern with respect to assessment; b. Review strategies for exposure assessment and environmental monitoring to allow for the best use of available resources, to ensure compatibility of data and to encourage coherent national and international strategies for that assessment. Most of the data and methods for chemical risk assessment are generated in the developed countries and an expansion and acceleration of the assessment work will call for a considerable increase in research and safety testing by industry and research institutions. It should be noted that there are considerable costs, often not possible to quantify, that are not included. The Conference secretariat has estimated the average total annual cost (1993-2000) of implementing the activities of this programme to be about $30 million from the international community on grant or concessional terms. Major research efforts should be launched in order to improve methods for assessment of chemicals as work towards a common framework for risk assessment and to improve procedures for using toxicological and epidemiological data to predict the effects of chemicals on human health and the environment, so as to enable decision makers to adopt adequate policies and measures to reduce risks posed by chemicals. Strengthening res earch on safe/safer alternatives to toxic chemicals that pose an unreasonable and otherwise unmanageable risk to the environment or human health and to those that are toxic, persistent and bio-accumulative and that cannot be adequately controlled; b. Promotion of research on, and validation of, methods constituting a replacement for those using test animals (thus reducing the use of animals for testing purposes); c. Promotion of relevant epidemiological studies with a view to establishing a cause-andeffect relationship between exposure to chemicals and the occurrence of certain diseases; d. Promotion of ecotoxicological studies with the aim of assessing the risks of chemicals to the environment. International organizations, with the participation of Governments and non-governmental organizations, should launch training and education projects involving women and children, who are at greatest risk, in order to enable countries, and particularly developing countries, to make maximum national use of international assessments of chemical risks. International organizations, building on past, present and future assessment work, should support countries, particularly developing countries, in developing and strengthening risk assessment capabilities at national and regional levels to minimize, and as far as possible control and prevent, risk in the manufacturing and use of toxic and hazardous chemicals. Technical cooperation and financial support or other contributions should be given to activities aimed at expanding and accelerating the national and international assessment and control of chemical risks to enable the best choice of chemicals. For the safe transport of dangerous goods, including chemicals, a comprehensive scheme elaborated within the United Nations system is in current use. Globally harmonized hazard classification and labelling systems are not yet available to promote the safe use of chemicals, inter alia, at the workplace or in the home. Classification of chemicals can be made for different purposes and is a particularly important tool in establishing labelling systems. There is a need to develop harmonized hazard classification and labelling systems, building on ongoing work. A globally harmonized hazard classification and compat ible labelling system, including material safety data sheets and easily understandable symbols, should be available, if feasible, by the year 2000. Governments, through the cooperation of relevant international organizations and industry, where appropriate, should launch a project with a view to establishing and elaborating a harmonized classification and compatible labelling system for chemicals for use in all United Nations official languages including adequate pictograms. Such a labelling system should not lead to the imposition of unjustified trade barriers. The new system should draw on current systems to the greatest extent possible; it should be developed in steps and should address the subject of comp atibility with labels of various applications. Evaluate and, if appropriate, undertake studies of existing hazard classification and information systems to establish general principles for a globally harmonized system; b. Develop and implement a work plan for the establishment of a globally harmonized hazard classification system. The plan should include a description of the tasks to be completed, deadline for completion and assignment of tasks to the participants in the coordinating group; c. The Conference secretariat has included the technical assistance costs related to this programme in estimates provided in programme area E. They estimate the average total annual cost (1993-2000) for strengthening international organizations to be about $3 million from the international community on grant or concessional terms. Governments and institutions and non-governmental organizations, with the collaboration of appropriate organizations and programmes of the United Nations, should launch training courses and information campaigns to facilitate the understanding and use of a new harmonized classification and compatible labelling system for chemicals. In strengthening national capacities for management of chemicals, including development and implementation of, and adaptation to , new classification and labelling systems, the creation of trade barriers should be avoided and the limited capacities and resources of a large number of countries, particularly developing countries, for implementing such systems, should be taken into full account. The following activities, related to information exchange on the benefits as well as the risks associated with the use of chemicals, are aimed at enhancing the sound management of toxic chemicals through the exchange of scientific, technical, economic and legal information. The London Guidelines for the Exchange of Information on Chemicals in International Trade are a set of guidelines adopted by Governments with a view to increasing chemical safety through the exchange of information on chemicals. Special provisions have been included in the guidelines with regard to the exchange of information on banned and severely restricted chemicals. The export to developing countries of chemicals that have been banned in producing countries or whose use has been severely restricted in some industrialized countries has been the subject of concern, as some importing countries lack the ability to ensure safe use, owing to inadequate infrastructure for controlling the importation, distribution, storage, formulation and disposal of chemicals.
Purchase bactrim 960 mg line
Active hepatic capsulitis munication: Gnathostoma infective stage larvae in caused by Paragonimus westermani infection antibiotic withdrawal buy generic bactrim 480 mg line. IdenAnisakiasis of the colon presenting as bowel obstructification of anisakid nematodes from the Southern Baltic tion. Overview of the epidemiologiparasites and microsporidia in irrigation waters used for cal situation on echinococcosis in the Mediterranean crop production. Effect Human cystic echinococcosis in Kyrgystan: an epideof high hydrostatic pressure on Cryptosporidium parvum miological study. Hygiene and restraint of pigs is terization of Giardia spp isolated from drinking water associated with absence of Taenia solium cysticercosis in Canada. ParaZimmerman J, Hallam A, Bush E, Faulkner C, and McCord gonimiasis: a view from Columbia. Efficacy of common laboratory disinfecimmunity in pigs against experimental cysticercosis. Inactivation of on Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts (vol 67, pg 5526, infective larvae of Angiostrongylys costaricensis with 2001). Few people, even in the medical establishment, knew much about Cyclospora and Cryptosporidium until recently. At one time it was thought that Cyclospora was a blue-green alga because it appeared to share some structural and chemical features with this group of prokaryotes. Later observations revealed that Cyclospora is a eukaryotic organism related to the coccidian parasites Cryptosporidium and Isospora and more distantly related to the microsporidia Septata and Enterocytozoon. As recent outbreaks have demonstrated, however, immunocompetent individuals are also at risk for infection. When the oocysts (infectious stages) of Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora, and Isospora are ingested by an individual, they pass to the small intestine where they excyst, releasing sporozoites. These cells invade the enterocytes (epithelial cells lining the small intestine) and undergo a cycle of asexual reproduction to form merozoites. When the merozoites are released from the enterocytes, they disperse to infect other intestinal cells. There may be one or many cycles of this type of asexual reproduction and then a cycle of sexual reproduction producing gametes. Fertilization results in the formation of oocysts, which are then passed out with the feces. In some protozoa, such as Cryptosporidium, the oocysts are immediately infective to another host while in others. Cyclospora and Isospora, the oocysts must mature for several days or longer before becoming infective. When these are ingested and reach the small intestine, the spore contents are injected directly into an enterocyte. These parasites then multiply within the host cells and carry on many cycles of asexual reproduction. Eventually spores are passed out with the feces and are ready to infect another host (3). Depending on the age and immune status of the host, the number of spores or oocysts ingested, and the pathogenicity of the parasites, these protozoa can cause asymptomatic infections, a self-limited diarrhea (usually lasting about 2 or 3 weeks), or a prolonged, severe diarrheal illness which may persist for months. It has been hypothesized that invasion of the intestinal cells stimulates the release of cytokines which activate phagocytes. These cells then release soluble factors which increase intestinal secretions of chloride and water, thereby causing symptoms of diarrhea. Cryptosporidium is the best studied of this group of parasites, but some fundamental questions concerning its pathogenicity remain, such as the possible production of an enterotoxin. Although the small intestine is the main site of infection, in some heavily parasitized patients, especially in the immunocompromised, the colon and liver may be also be affected. Dissemination to other parts of the body has only been observed regularly with Septata. Surveys to determine the prevalence of oocysts in stool samples generally report a higher incidence of infection in persons from Asia, Latin America, and Africa than in those from Europe and North America. Therefore, many people in these countries have been exposed to this parasite during their lifetime. The other protozoa have been reported to cause diarrhea, at a lower frequency, in the same groups of people. Since the infective stages of these protozoa are present (at concentrations as high as 1,000,000/gram) in feces, some type of fecal contamination is responsible for new cases of diarrhea. Person-to-person transfer may occur in families and institutional settings such as daycare facilities. Although the infant was asymptomatic and the woman had washed her hands before preparing the salad, enough oocysts were transferred to the food to cause illness in more than half of the estimated 50 persons attending a social function (10). Cryptosporidium oocysts have also been isolated from cider made from apples which had fallen on the ground in a cow pasture (9) and from raw vegetables in Costa Rica (12). However, current methodology was not sensitive enough to detect oocysts on fresh fruit associated with these outbreaks. Efforts are underway to modify these assays so that low concentrations of Cryptosporidium and Cyclospora oocysts can be detected in foods. Cryptosporidium is notorious for its lack of host specificity, with most isolates from mammals capable of infecting many different mammalian species. In fact, a number of waterborne outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis in developed countries have resulted from contamination of drinking water sources with runoff from agricultural lands where infected cattle have grazed. Cyclospora oocysts, identical to those observed in human samples, have been isolated from fecal samples from baboons and chimpanzees in Africa (17). In addition, the investigation of the Chicago Cyclospora outbreak indicated that rodent or bird feces may have contaminated the drinking water supply for a dormitory. No cross connections between water and sewage pipes in the building were detected. But the drinking water, stored in a rooftop tank, was not adequately protected from the environment, and animal feces were observed on the rim of the tank. Cyclospora has also been isolated from stool specimens from members of a Peruvian family with diarrhea and from ducks bred by the family (18). High temperatures are known to be lethal to these protozoa and therefore boiled water and adequately heat-processed foods should be safe to consume. Cryptosporidium oocysts are also notoriously resistant to chlorination, as seen in outbreaks involving chlorinated drinking water. Laboratory experiments demonstrated that oocysts suspended for up to 2 hours in 1. As these data demonstrate, it is possible to eliminate Cryptosporidium and probably other oocystand spore-forming protozoa from food and water with appropriate conditions of heat and freezing. However, viable oocysts and spores persist in contaminated foods that are eaten fresh, such as fruits and salad ingredients, and in contaminated drinking water. Chlorination will not destroy the oocysts in water, and filtration systems may have an inadequate pore size to exclude oocysts or may become clogged or overwhelmed during certain seasons, such as spring, when snow melts and rains may be heavy. Although much research has been devoted to Cryptosporidium, methods for its control and elimination are not yet adequate. Further research is also necessary to refine methods for the detection of the other protozoa and to determine conditions necessary to destroy their spores and oocysts. Understanding intestinal spore-forming protozoa: cryptosporidia, microsporidia, Isospora, and Cyclospora.
Order generic bactrim online
Potential barriers included use of traditional healers antibiotic xacin buy bactrim 960 mg visa, Indonesia, 5National Malaria Control Program, Ministry of Health, Jakarta, distrust of public sector health staff and interventions for their potentially Indonesia, 6Malaria Elimination Initiative, Global Health Group, University stigmatizing effects. During the trial, perceptions of malaria risk were closely related of information for estimating the burden of malaria, identifying remaining to presence of illness in the community. Reasons for participating included hotspots, and developing risk maps for targeting scarce resources. We effective recruitment, the opportunity to learn, feeling unwell, and level of extracted routinely collected monthly health facility data from January disease in the community. Most refusals were attributed to being busy or 2013 until December 2016 to describe risk factors, identify hotspots, away from home. When considering improvements, members suggested and generate spatial risk maps of malaria in Aceh Besar and Aceh Jaya they be informed of visits in advance to prepare, more interventions districts, in Aceh Province, Indonesia. The community of residencies, and parasitological data, including date of febrile, date preferences identifed during the trial led to an increase in efforts to inform of diagnosis and date of treatment were assembled from Primary Health communities in advance and better coordination of the clinical teams to Center registry books. Case locations were geo-located based on village increase acceptance of trial interventions. Brown1, altogether with other species of Plasmodium malaria infections, such as Petra F. Most individuals with positive malaria were forest-related of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands workers (96. Multivariable logistic regression will be used to establish socioGhana has made many strides in the fght against malaria. Residents in the rural area were less informed of malaria and its preventive measures than Sophia Hocini1, Francois Rerolle1, Andrew Lover1, Emily Dantzer1, those in the urban areas. Their knowledge was associated with increased Bouasy Hongvanthong2, Rattanaxay Phetsouvanh3, Adam Bennett1 odds for malaria. Malawi-Liverpool-Wellcome Trust Clinical Research Programme, Blantyre, Both health service and societal perspectives were explored. Sensitivity analyses exploring the impact of variation in vaccine Medicine, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, costs, vaccine coverage rate and coverage of 3 doses and 4 doses showed Thailand, 3Mahidol Vivax Research Unit, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, vaccine implementation would be cost-effective across a wide range of Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, 4Department of Entomology, scenarios. This host cell tropism is believed to be mediated by the (189-859) deaths for the four-dose schedule, per 100 000 fully vaccinated reticulocyte binding protein family of the parasite. We also found that treatment of erythrocytes with trypsin or chymotrypsin signifcantly reduces binding activity. To reduce dosing frequency, we tested a mature schizonts and localized at the apical end of merozoites. These development steps are crucial for the possibility of elimination and eradication of malaria through the use of parasite to complete its life cycle and transmission to a new vertebrate the vaccine. However, the functions of phosphatases involved in gametogenesis to the success of any clinical study. Here, we present a Plasmodium berghei protein, of volunteers on clinical trial procedures and what makes them opt for Ser/Thr Protein Phosphatase 5 (Pb. Almost two-thirds developments of ookinetes in vitro and oocysts in vivo are completely (62%) of the volunteers to participate because they wanted to know their blocked. More than 90% of the volunteers strongly approved study development in the gametocytes exfagellation and ookinetes conversion. These results and the high degree of conservation storage of urine, stool and blood samples up to 15 years for further of Pb. In conclusion, attractive target for the development of novel drugs to block the spread the results of the study indicated that volunteers hold a positive perception of malaria, and might be a potential novel transmission blocking vaccine of the study procedures. This implies that community members are aware of the importance of undergoing a 426 medical checkup and failing to fulfll this need recruitment and retention of volunteers in the clinical study will be a challenge. Bharti4, Quique Bassat5, Alfredo predominantly IgG1 and IgG3, with lower IgG2 and IgG4. Lluis Company, Barcelona, Spain, (including malaria cases and controls) were analyzed. The isolates were adapted to laboratory culture and 1 1 1 1 after minimal in vitro cultivation were characterized for their invasion Daming Zhu, Weili Dai, Holly McClellan, Dennis Braden, phenotypes by analysing their ability to invade enzymatically-treated Patricia A. Importantly, antibody combinations against these three antigens induced high-titer invasion-blocking antibodies in a human challenge trial; elicited potent strain-transcending inhibition at lower IgG concentrations however, the vaccine failed to provide protection even against homologous in a synergistic or additive manner, thus validating the vaccine potential challenge. Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology and Jawaharlal Nehru University, o New Delhi, India, 3International Centre for Genetic Engineering and the results indicate that the complex was stable for 72 hours at 4 C. Currently we have cloned and Investigacao em Saude de Manhica, Mozambique, Mozambique expressed 17 humAbs from 16 clonal groups. Current Erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium falciparum is an indispensable step for epitope evaluation indicates some humAbs recognize similar epitopes to its blood-stage life cycle and successful transmission to new human hosts. Notable four humAb are more potent inhibitory and is an attractive step to identify critical invasion ligands that could antibodies compared to any of the previously characterized murine mAbs. The potential of passive transfer thus imperative to identify conserved vaccine targets that could generate of inhibitory humAbs into non-human primates or humans can confrm broadly-neutralizing anti-parasitic antibodies. Mendoza1, treated cells in a sialic acid independent manner and showed varied Justine Shiau1, Neeraja Punde2, Ashutosh K. Pathak1, Demba Sarr1, sensitivities to trypsin and chymotrypsin treatment, implying the usage of Courtney Murdock1, Donald Champagne1, Evelina Angov3, Donald alternate invasion pathways. Our study strongly suggests the inclusion require 3+ injections to induce modest levels of protection. To achieve this result, the feld is utilizing recent advances in vaccine adjuvant and delivery technologies. Our lab pioneered the use of a self429 assembling matrix as a non-immunostimulatory vaccine adjuvant. First, we optimized the (1) injection route and (2) Mueller2, Wai-Hong Tham2, Christopher L. Compared to conventional delivery of these Medical Biology, the University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, 3The two antigens, we found gel-depot delivery works best via intradermal and Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Parkville, Australia, subcutaneous routes. These studies receptor 1 (TfR1) on reticulocytes, mediates the successful invasion of host are the frst phase of our long-term goal of generating a functional cells. Paired iggh and iggl were cloned into IgG1 expression vector, expressed and purifed. The acute challenge model allows rapid, sensitive detection of both complete and partial protection. This strategy should be considered Malaria is caused by parasites of the genus Plasmodium that are as a frst line approach for broadening the repertoire of liver stage vaccine transmitted to humans by the bites of Anopheles mosquitoes. Here we repeatedly infected six Aotus monkeys with blood stages of the homologous P. Maiga1, Issaka immunity was achieved after the second homologous Sal1 infection in 4 Sagara1, Sara A. Standard Membrane Feeding Assays and Direct but a positive correlation vs peak parasitemia (r = 0. These experiments provide a conditions, by allowing mosquitoes to feed directly on the skin of vaccine template for testing the effcacy of candidate blood stage P. Olsen, Kevin Zhou, Sean collected mosquitoes, and oocyst counts in midguts by microscopy 7 days C. Infection was determined by dissection and oocysts counts 7 days post Subunit T cell vaccine development for malaria is faced with a problem feeding. Several factors could contribute to highly immunogenic but completely non-protective. Coding sequences are designed to eliminate signal sequences and are cloned in-frame as ubiquitin fusion proteins to minimize the induction of antibody responses. Their rate is slightly Sidibe1, Aboubacar Tembely1, Mariam Doumbia1, Diango Cisse1, higher than for us and this could be explained by the fact that they did Sekou F. Mass production is needed in many cases and it is imperative to use high quality mosquitoes 436 to ensure good entomological outcomes from the vaccine trials. Assadou1, Mamady rate, adult mosquito size, adult longevity and sex ratio of mosquitoes. In Kone1, Kourane Sissoko1, Boubacar Traore1, Jordyn Manucci2, Jen total, 50 3-day old females were used in each of 3 replicate experiments.
480mg bactrim with amex
The adult flies live for only a few days antimicrobial resistance and antibiotic resistance buy bactrim 960mg without a prescription, but since the flies do not all emerge from the pupal stage at the same time, populations of Gasterophilus spp. Little is known about the effect of stomach infestation by Gasterophilus larvae on the health of equines. Ulceration of the nonglandular portion of the stomach was the most frequent lesion. Abscesses, rupture of the stomach, and peritonitis can occasionally occur (Soulsby, 1982). Human infestation is apparently rare; only a single case was reported during the period from 1989 to 2001 (Royce et al. The larvae rarely develop beyond the first stage, and only exceptionally do they reach the stomach. The common clinical form is a dermal affliction similar to cutaneous larva migrans, with superficial serpiginous tunnels within the tegument that look like red stripes on the surface of the skin. Accordingly, the best time for treatment is May, June, or July (the end of spring and beginning of summer) because two generations can be eliminated at once. In this case, the treatment needs to be applied in February (winter) to eliminate the previous generation and in August (summer) to eliminate the new generation. The larvae are deposited in packets, either on the animals or in their vicinity, and they then penetrate intact skin and produce a furuncular lesion. The larvae mature in 7 to 9 days, abandon the animal, and pupate for 10 to 12 days. When the adults emerge 11 to 17 days later, the females lay their eggs, and thus the cycle is completed. In humans, the infestation is found only in children who spend time outdoors, in whom it causes small subcutaneous abscesses, irritability, fever, and dehydration. The fly is attracted by skin wounds, where it deposits its larvae, but it also does so in natural orifices of humans, sheep, bovine cattle, and other domestic animals, including fowl (especially geese). Human infestation does not appear to be frequent; during the 1990s, only five cases were reported. The following sites were involved: the eye (one case), vulva (in an elderly woman), orotracheal region (in an elderly intubated man), ear (one case), and scalp (in a child) (Ciftcioglu et al. Facultative or Semispecific Myiases A large variety of dipterans can be facultative parasites of animal and human tissue. These flies, which normally lay their eggs or larvae on decomposing meat or animal or human remains, can sometimes invade the necrotic tissue of wounds in live animals. The larvae of these dipterans do not penetrate healthy skin and rarely invade recent wounds that have been kept clean. Their medical importance lies in the fact that the larvae of some species do not always restrict themselves to feeding on necrotic tissue but can occasionally penetrate deeply and damage healthy tissue. One such species is Lucilia (Phaenicia) sericata, whose larvae do not usually cause serious damage but can sometimes destroy healthy tissue surrounding wounds and can also invade the human nasal fossae in large numbers. The most susceptible breed is the merino, and the highest incidence rates are in Australia, Great Britain, and South Africa. In hot, humid summers, when the population of calliphorine flies is at its peak, this myiasis often affects the development of sheep and causes losses in both wool and meat production. The most common site of larval invasion is the ano-vulvar or ano-preputial region, where the skin often becomes excoriated from soft feces and urine, the smell of which attracts the flies. According to some authors, a lesion is not required in order for invasion to occur; during hot summers with abundant rain followed by sunshine, the matted wool can become rotten and attract swarms of flies. When the density of calliphorine flies is low, their larvae breed in carcasses or garbage containing scraps of meat. The situation changes when climatic conditions favor a rapid increase in the fly population, at which point the larvae also invade contaminated wounds and damp, dirty wool. The development cycle of these flies can be completed in a few weeks, and, under highly favorable conditions, within a single week. In areas where calliphorine flies are a problem for sheep, all wounds should be treated immediately and the animals should be protected with larvicides or repellents. According to reports published in different parts of the world between 1989 and 2001, the most common larvae that produce facultative human myiases belong to the genera Lucilia, Sarcophaga, Parasarcophaga, Phormia, and Paraphormia. Lucilia larvae appear to be the most frequent: of 14 human myiases reported over approximately two years in Brisbane, Australia, 10 were caused by L. These myiases, because of their nature, affect wounded, bedridden, or otherwise debilitated people who are unable to take care of themselves. Cases have also been reported in apparently healthy individuals, such as a cattle-rancher in Korea who had five larvae in the auditory canal which did not appear to be bothering him, and an urban case acquired in Spain. The larvae of Sarcophaga also appear to be a frequent cause of facultative human myiases. Two nosocomial infestations were described in Spain: one in a 77-year-old woman with radionecrotic wounds and another in an 87-year-old man with dementia (Merino et al. One infestation was reported in Japan, with nine larvae in the eye of a debilitated patient. In India, 64 cases of myiases in the nasal cavity, hands, and toes of leprosy patients were reported, from whom the larvae of Sarcophaga haemorrhoidalis, Chrysomya bezziana, Callitroga americana, and Musca domestica were recovered (Husain et al. In Israel, larvae from the same fly were found in the auditory canal of four children, resulting in pain, pruritus, and secretions. A case of Parasarcophaga argyrostoma larvae in the gangrenous toe of an elderly man was described in England, and in Japan, an intestinal myiasis caused by Parasarcophaga crassipalpis was reported. Since the identification of some of these larvae is difficult, polymerase chain reaction techniques have been developed for this purpose (Vincent et al. Accidental Myiases Accidental myiases are caused by numerous species of flies that normally lay their eggs or larvae on decomposing organic matter and accidentally deposit them on the food or wounds of humans or animals, giving rise to intestinal or cutaneous myiases. Most eggs or larvae ingested in this way are destroyed in the digestive tract, but some of them survive and continue their larval development. Often, the ingested larvae are eliminated in feces without causing any damage or symptoms. In other cases, however, there can be abdominal pain and nausea, and, in very intense infestations, damage to the intestinal mucosa and bloody diarrhea. Myiases have been described in the urinary tract (cystomyiasis), but they are rare. These infestations have occurred mainly in immobilized elderly patients suffering from incontinence. In other cases, however, secondand third-stage larvae have been found in the bladder. Finally, two cases of cutaneous myiasis caused by Musca domestica were described in England, as was a third case, attributed to the same species, in a leprosy patient in India. Role of Animals in the Epidemiology of the Disease: Animals play an essential role in the epidemiology of the flies that cause obligate myiases; without their animal hosts, the flies could not exist. Man is only an accidental host of these larvae, and in some myiases, such as those caused by O. The obligate myiases occur in humans when there is a high incidence of animal myiases, typically in the spring or summer. The victims are usually people who live in rural areas where both the flies and the natural hosts of their larvae are abundant. Control: Human obligate myiases are controlled by eliminating or reducing infestations in the animal reservoirs. The primary means of achieving this goal is preventive treatment of the animals at risk with insecticides or repellents to keep them from becoming infested, or, once they are infested, curative treatment with insecticides to eliminate the larvae before they abandon the host and begin to pupate. With both animals and humans in areas where myiases are common, any wound should be treated as soon as possible and watched closely until it forms a scar. Particular care should be taken with bedridden patients who have wounds and cannot protect themselves from flies. To prevent the disease in man, both personal and environmental hygiene should be observed, including steps to eliminate the breeding sites of flies.

Generic 480 mg bactrim overnight delivery
Poor inhaler technique results in an inadequate delivery of medicaton to the airways and an increased depositon of medicaton in the mouth bacteria fermentation safe bactrim 960 mg, resultng in poor symptom control. Management of exacerbations Guidelines for the management of exacerbatons of asthma provide a step-wise management programme based on the symptoms and the response to beta-2-agonists, involving a combinaton of controllers and relievers to relieve the symptoms and reduce infammaton (see htp:// Asthma educaton includes being sensitve to the partcular informaton needs and difcultes of individual patents. Atending to their fears, exploring their expectatons and sharing informaton underpin a partnership approach to guided self-management. Specifc informaton should be provided on the conditon and the reliever and controller medicaton. Verbal informaton should be supported by writen informaton and contact details for the local asthma support group. One excepton to this rule is when it is linked with an inherited defciency of alpha-1-anttrypsin. Pathophysiology Pathological changes include chronic infammaton, an increased number of infammatory cells and structural changes as a result of injury and repair. Bronchodilator medicatons form the basis of symptom relief and improvement of exercise tolerance. These include beta-2-agonists, antcholinergic agents and methylxanthines, which may be used in combinaton. Inhalatonal treatment is preferred both for its efectveness and to minimise side efects. Long-actng inhaled antcholinergics reduce the rate of exacerbatons and improve the efectveness of pulmonary rehabilitaton. Up to 75% of exacerbatons are infectve (bacterial or viral); other causes include air polluton, increased comorbidity and poor medicaton adherence (Miravitlles 2010). In additon, patents may also experience chest tghtness, fuid retenton and confusion. However, this has to be balanced against the risk of complicatons from their regular use. Oxygen therapy is indicated for the management of hypoxaemia; an oxygen saturaton of over 90% is acceptable. Rapid assessment units, early discharge and hospital at home programmes are increasingly being developed to support the treatment of patents with acute exacerbatons at home. Patents with advanced disease experience poor symptom control, isolaton, guilt, stgma, anxiety and depression (Andenaes et al. Palliative care Palliatve care is an approach to care that, through the preventon and relief of sufering, seeks to improve the quality of life of patents and their families facing problems associated with life-threatening illness. Conversatons of this nature develop over tme and should be encouraged when the patent is stable and able to partcipate fully in exploring possible treatment interventons, such as mechanical ventlaton. In additon to communicaton needs, the patent may also require nursing care to address breathlessness, relaxaton and breathing exercises, sputum clearance, cough, smoking cessaton, oxygen and medicaton management, anxiety and depression, pain, nutritonal support and social, psychological and emotonal support. Bronchiectasis is usually localised to one lung segment or lobe but may spread over tme to other parts of the same lung as a result of unresolved infectons. A prompt treatment and resoluton of infectve exacerbatons, the preventon of further infectons, Part 2 Adult Medical and Surgical Nursing possibly with the prolonged use of antbiotcs, and bronchial clearance underpin treatment plans (Drain & Elborn 2011). The abnormal gene is subject to autosomal recessive inheritance, meaning that both parents must be carriers for the conditon to be inherited by their child. Assessment and management As a consequence of the multsystem involvement, patents require management of gastrointestnal, pancreatc and hepatc complicatons in additon to respiratory problems. Poor secreton clearance from the airways results in recurrent infectons, damage to the bronchi, the development of bronchiectasis and respiratory failure. The respiratory tract is colonised with bacteria that must frequently be treated combinatons of antbiotcs; resistance is a signifcant challenge. With bronchiectasis and as a result of exacerbatons, there is progressive scarring of the lungs and colonisaton with pathogens. Antbiotc resistance develops, and management of exacerbatons requires the involvement of a microbiologist to explore treatment optons. Over the past decade, however, early diagnosis and signifcant advances in treatment have resulted in more patents surviving early adulthood. As respiratory symptoms increase with loss of lung functon, intensive nutritonal support is needed. When respiratory failure and end-stage lung disease develop, patents are assessed for lung transplant, but many do not meet the criteria. End of life care may be especially challenging as patents may be focused on lung transplantaton and unable to consider death and dying. Pathophysiology When the lungs fail to maintain sufcient arterial oxygenaton or carbon dioxide eliminaton, respiratory failure can occur. Low amounts2 of carbon dioxide as a result of hyperventlaton result in hypocapnia or respiratory alkalaemia. In type I respiratory failure, hypoxaemia is present but there is no associated hypercapnia. Assessment and management Type I respiratory failure is managed by oxygen therapy and treatment of the underlying conditon. However, oxygen therapy should be reduced as the patent shows clinical improvement. Hypercapnia may play a more limited role in triggering inspiraton, but instead a fall in oxygen concentraton will trigger inspiraton. Medicaton management also includes inhaled and possibly intravenous bronchodilators, beta-2agonists and antcholinergic agents, and intravenous and inhaled cortcosteroids. Diuretcs may be required, and opiates and anxiolytcs may be necessary for breathlessness and anxiety. Part 2 Adult Medical and Surgical Nursing Oxygen therapy and ventilation Oxygen is a drug that is prescribed to correct hypoxaemia. Venturi masks are a more accurate means of delivering oxygen than nasal prongs, but this must be balanced against patent comfort. Oxygen must be used with care because, for some patents, their respiratory drive depends on their degree of hypoxia rather than the usual dependence on hypercapnia. Uncontrolled oxygen therapy can therefore lead to a suppression of respiratory drive, carbon dioxide narcosis and respiratory arrest. Ideally, oxygen is delivered via a facemask at an inspiratory fow rate of between 24% and 35%. The management of dyspnoea, airway clearance and impaired gas exchange is essental. Administraton of bronchodilators, cortcosteroids, diuretcs and possibly opiates and anxiolytcs should be as prescribed. Lung cancer Defnition Lung cancer refers to malignancies that originate in the airways or pulmonary parenchyma. Epidemiology Lung cancer is the third most common form of cancer across Europe and is the most lethal (Wilking & Jonsson 2008). For those patents who are diagnosed early and before symptoms occur, the 5-year survival is greater.