Kamagra Soft
Cheap 100 mg kamagra soft free shipping
This is then repeated on the Juvenile Primary Open-angle Glaucoma other side so that eventually the upper half of the canal wall is opened erectile dysfunction juice drink purchase kamagra soft online pills. Localization of the canal itself, however, is Glaucoma occurring between the ages of 4 and 10 years sometimes diffcult. Surgical treatment is often successful, although more than one operation may be necessary. Maximal tolerated medical therapy is one that may concentration of myocilin may increase resulting in a rise be used to control intraocular pressure, yet allows the patient in intraocular pressure. If, however, this does not control the intraocular pressure adequately, laser trabeculo plasty as described earlier, or surgery may be required. The importance of treatment and regular follow-up must be explained and emphasized. Surgery is commonly undertaken when medical therapy Management requires continued supervision by an oph fails to arrest visual feld loss, as in a non-compliant patient, thalmologist and consists of simple recordings of readings in a patient who cannot report for repeated review, or if the of applanation tonometry and status of the optic nerve head. Once the ganglion cells have been damaged and the vision carried by those Glaucoma-Filtering Operations nerve fbres lost, they cannot be replaced. Loss of vision Glaucoma-fltering operations are employed to control the in glaucoma is irreversible. This bleb is composed of spongy tissue, through controlled, and closely monitored. The initial treatment of glaucoma is generally instead of the normal drainage into the trabecular mesh medical or by laser procedures. In a corneoscleral incision the lips of the wound are defned for each patient with a chronic glaucoma, taking in good apposition and healing rapidly takes place. This is into account the intraocular pressure at which damage oc much less likely to occur if there is a gap between the lips curred, the family history, the extent of damage to the optic of the wound which becomes flled with loose scar tissue nerve head, visual feld, and the presence of systemic risk resulting in a fltering cicatrix. Very high intraocular pressures need to be lowered immedi ately with the use of intravenous acetazolamide or mannitol. Trabeculectomy Oral acetazolamide or glycerol take about half to one hour Trabeculectomy involves the creation of a lamellar scleral to control moderately high intraocular pressures. Lowering fap, under which, a piece of sclera which includes a short the intraocular pressure to near physiological levels allows length of the canal of Schlemm is excised, thus producing topical medication to become effective. Such an operation these systemic medications is not advisable, due to possibly also forms a fltering channel to the subconjunctival space life-threatening side-effects. If the wound heals and excessive scar tissue seals these are used as frst-line treatment for a raised intraocular the fap over the drainage hole, the pressure in the eye pressure. Reformation of the of these medications is often applied during the primary anterior chamber with balanced salt solution, air or visco trabeculectomy. The most glaucomas, and the fltering bleb that results is a dif presence of a draining bleb covered with thin conjunctiva fuse elevation of the conjunctiva showing microcystoid may lead to the subsequent development of blebitis, or changes at the limbus (Fig. This is most common if antifbro blastic agents have been used to enhance fltration and Complications ensure the success of a trabeculectomy. Cataract is a In the early postoperative period shallowing of the anterior common sequel, particularly if early changes are present chamber and hyphaema may be seen. The glaucoma progression analysis or In refractory glaucomas where a trabeculectomy has failed, the peridata programme analyse signifcant differences in or is likely to fail, valved or non-valved drainage devices threshold values at each location in the feld (Fig. Progression of a cataract often results in these tests It is important to remember that more eyes are lost by being labelled abnormal. The onset of retinal vascular delay in undertaking surgery than by surgical intervention. The prognosis thus depends largely on early diagnosis and the institution of Summary early and adequate treatment to forestall cupping of the Glaucoma is a chronic, progressive optic neuropathy with optic disc and loss of the visual feld. Continuous monitoring of intraocular pressure, optic There is a mismatch between the pressure in the eye and nerve head and perimetry will allow the detection of toler that which the axons of the ganglion cells or optic nerve can ance to medications or progression of the glaucoma. To determine the progression of visual feld defects the glaucomas are broadly classified as open or closed in glaucoma, one must establish a baseline by doing at angle glaucomas. Open angle glaucomas can be managed least three chartings of the visual feld in a newly diagnosed medically, but surgery may be necessary if not adequately patient of glaucoma. Angle closure glaucomas need an initial laser iri if the follow-up programmes and all parameters are the dotomy followed by medical or surgical therapy. If a change in the visual optic nerve head imaging and serial perimetry are parameters used to monitor the effect of treatment which is often lifelong. Retrieved August 12, total and pattern deviation of each examination in a row, 2010. Glaucoma: Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Ophthal available in the form of box plots which analyse changes in mology. Chapter 20 Diseases of the Retina Chapter Outline Anatomy and Physiology 309 Detachment of the Retina 330 the (Systemic) Vascular Retinopathies 310 Pathophysiology 331 Hypertensive Retinopathy 311 Predisposing Factors 331 Diabetic Retinopathy 312 Clinical Features 331 Retinopathy of Prematurity 317 Diagnosis and Management 331 Acquired Immune Defciency Syndrome 319 Congenital Abnormalities of the Retina 336 Retinopathy in Toxaemia of Pregnancy 319 Congenital Pigmentation of the Retina 336 Sickle Cell Retinopathy 319 Medullated Nerve Fibres 336 Lupus Erythematosus Retinopathy 320 Coloboma of the Retina and Choroid 336 Vascular Disorders of the Retina 320 Albinism 336 Obstruction/Occlusion of the Retinal Arteries 320 Phakomatosis 336 Obstruction of the Arterial Circulation 320 Angiomatosis of the Retina (von Hippel Lindau Disease) 337 Obstruction of the Venous Circulation 321 Tuberous Sclerosis (Bourneville Disease) 337 Coats Disease 323 Neurofbromatosis (von Recklinghausen Disease) 337 Medical Therapy in Retinal Vascular Diseases 324 Hereditary Dystrophies of the Central Retina and Choroid 337 Infammation of the Retina (Retinitis) 324 Sex-Linked Juvenile Retinoschisis 337 Purulent Retinitis 324 Stargardt Disease 337 Cytomegalovirus Infection 324 Dominant Foveal Dystrophy 338 Syphilis 324 Inverse Retinitis Pigmentosa 338 Sarcoidosis 325 Progressive Cone Dystrophy 338 Toxoplasmosis 325 Vitelliform Dystrophy of the Fovea 338 Toxocariasis 325 Reticular Dystrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium 338 Periphlebitis Retinae 325 Butterfy-Shaped Pigment Dystrophy of the Fovea 338 Retinitis from Bright Light (Photoretinitis) 326 Fundus Flavimaculatus 338 Degenerations of the Retina 326 Grouped Pigmentation of the Foveal Area 338 Myopic Chorioretinal Degeneration 326 the Hyaline Dystrophies 339 Age-Related Macular Degeneration 326 Pseudo-infammatory Foveal Dystrophy (Sorsby) 339 Macular Holes 327 Central Areolar Choroidal Atrophy 339 Pigmentary Retinal Dystrophy (Retinitis Pigmentosa) 327 Leber Congenital Amaurosis 339 Angioid Streaks 329 Lysosomal Storage Disorders 339 Benign Peripheral Retinal Degenerations 329 Degenerations Associated with Retinal Breaks 329 the retina is a component of what is clinically viewed divided into a number of zones for convenience of record as the fundus, and contains the photoreceptors that permit ing clinical fndings and to permit a precise localization of vision. Examination of the posterior the neurosensory retina is transparent, the background co part of the retina is undertaken with the use of a direct oph lour being provided by the retinal pigment epithelium and thalmoscope and by slit-lamp indirect biomicroscopy if vascular choroid, as described in Chapter 12. The venous or a more magnifed view with stereopsis by the use of a pressure is lowest near the disc, and there is a certain three-mirror contact lens. Within the macular re a momentary impedance to the outfow of blood during gion is a small, central depression called foveola, measuring systole, but the venous circulation recovers itself during the approximately 0. This pressure occurs during the diastolic area of a deeper red than the surrounding fundus, and in its phase and therefore has been called the negative venous centre there is nearly always a foveal refex, seen as an in pulse. If absent, the venous pulsation can be increased or tensely bright spot of light and is due to refection of light made manifest by increasing the intraocular pressure by from the walls of the foveal depression. The vitreous base straddles the ora serrata and is from the superior and inferior temporal arteries, and by frmly attached here. Occasionally, Retinal affections in general give rise to the following small arteries (cilioretinal) originating from the short symptoms, only some of which need be present in individ posterior ciliary arteries run inwards to enter the eye ual cases. There may be metamorphopsia, micropsia or mac and vein, which usually divide into two branches at or near ropsia. The contrast sensitivity is reduced in most patients the surface of the disc to form a superior and an inferior with a macular pathology. Each trunk usually divides into two, Clinical features in retinal pathologies are recorded as one of which sweeps up (or down) towards the temporal in Figure 20. The veins have a purplish tint and are duller and of other tissues such as the brain. Ophthalmoscopically what is seen is the ably originate from a state of anoxia which results in an blood column and not the vessel wall, which is normally increased permeability of the capillaries, the formation of transparent. All the retinal vessels may have a bright silvery multiple microaneurysms and local degenerative changes. Choroidal vessels are most easily visible in albinos tions larger than the disc, and, since they disappear rapidly, and in high myopes. They are formed by the In normal conditions, no pulsation can be seen in the arrest of axoplasmic fow at the edge of an ischaemic area. These hyaline or lipid deposits are gener ally seen as a cluster around a group of leaking microaneu rysms. In the macular region they tend to accumulate in a radial manner around the foveal centre, the arrangement mirroring the orientation of the fbre layer of Henle to form a fan or star-shaped fgure (macular fan/star).
Generic 100 mg kamagra soft mastercard
Ectopic beats are common in both mother and fetus and generally have no adverse effects on either erectile dysfunction hypogonadism order kamagra soft online now. However, investigations should be performed to exclude, anaemia, thyroid disease, together with an examination of cardiovascular and respiratory symptoms. The physiological stresses of pregnancy and delivery are thought to bring out an underlying potential cardiac arrhythmia. Risk factors include advanced maternal age, smoking, diabetes, obesity, hypertension and a positive family history. They should be referred to the Consultant Anaesthetic Antenatal clinc and offered an appointment. Close co-operation between the anaesthetist, cardiologist and obstetrician is important to ensure optimal management. The anaesthetic management plan will Author: J Ablett, A Elkington, L Williams, L MacKillop Date: Job Title: Consultant Obstetrician, Consultant Cardiologist, Consultant Review Anaesthetist, Consultant Obstetric Physician (J Radcliffe Hospital) Date: Policy Group Director Urgent Care Version: V6. For many of these women an epidural is the ideal labour analgesic and they should be expedited as medically necessary. Ergometrine causes vasoconstriction, Syntocinon vasodilatation and tachycardia while carboprost (haemabate) can cause bronchospasm and pulmonary hypertension. Both Carbetocin and Oxytocin should be diluted and given slowly, observing the effects. Depending on the cardiac condition ergometrine and carboprost may even be contraindicated. This could be provided by regional analgesia/anaesthesia but specific agents such as glycerol nitrate may be required. It may be appropriate for some of these women to be having an elective Caesarean section. The best way to provide a stable anaesthetic will be thought through as a guide in case of the need for emergency delivery. If delivery needs to be expedited within the proscribed period after administration of anticoagulant agents the risks and benefits of performing a block must be evaluated at the time, though this will be discussed at the antenatal assessment. This increases 10 fold if the mother has a cardiac anomaly and may be as high as 10% if both parents are affected. Thus a fetal cardiac scan should be performed at 24 weeks by Dr Suruchi Arora or Miss Surabhi Bisht. March 2008 Author: J Ablett, A Elkington, L Williams, L MacKillop Date: Job Title: Consultant Obstetrician, Consultant Cardiologist, Consultant Review Anaesthetist, Consultant Obstetric Physician (J Radcliffe Hospital) Date: Policy Group Director Urgent Care Version: V6. Jill Ablett, Consultant Obstetrician and Medical Lead Andrew Elkington, Consultant Cardiologist Lucy MacKillop, Consultant Obstetric Physician, John Radcliffe hospital, Oxford 26. Anaesthetic Referral All pregnant women with cardiac conditions need referral to the Anaesthetic Department. Fetal Medicine Referral Any woman with a congenital cardiac abnormality needs referral for a fetal cardiac scan at 24 weeks (Refer to Miss S Bisht or Dr Arora) back to top of page Author: J Ablett, A Elkington, L Williams, L MacKillop Date: Job Title: Consultant Obstetrician, Consultant Cardiologist, Consultant Review Anaesthetist, Consultant Obstetric Physician (J Radcliffe Hospital) Date: Policy Group Director Urgent Care Version: V6. In some cases it is appropriate to give Oxytocin in a lower dose, diluted in smaller volumes and / or infused slowly. Carbetocin is a long acting Oxytocin analogue which appears to cause relatively little cardiovascular disturbance. Ergometrine causes an increase in systemic vascular resistance and should be avoided in some cases of congenital heart disease (ischaemic heart disease, coarctation and pulmonary hypertension). Carboprost (haemabate) and misoprostol are contraindicated in patients with myocardial ischaemia. Carboprost may also cause bronchoconstriction Intravenous fluids General principles: Maintain normovolaemia Monitor input and output closely to avoid fluid overload Use volumetric fluid pump Author: J Ablett, A Elkington, L Williams, L MacKillop Date: July 2018 Job Title: Consultant Obstetrician, Consultant Cardiologist, Consultant Anaesthetist, Review July 2020 Consultant Obstetric Physician (J Radcliffe Hospital) Date: Policy Group Director Urgent Care Version: V6. The median importance Arrhythmias 15% ratings are refected in the Detailed content outline below. The Cardiovascular Disease Exam Committee and Cardiovascular Coronary Artery Disease 21. It is reasonable in mild infections to discontinue the inciting antibiotics and monitor for diarrhea resolution over the next 24-48 hours without initiating antibiotic therapy. Narrow antibiotic spectrum as much as possible and discontinue necessary antibiotics as early as medically safe. In early, mild diarrhea, it is reasonable to hydrate and monitor symptoms for 24-48 hours to determine if they resolve spontaneously. Continuum of Care Comparison Chart for Additional Precautions for Clostridium difficile D. Sample Information Sheet: Patients/Resident and Family Information about Clostridium difficile G. Contact, Droplet, Airborne) that are applied, in addition to Routine Practices, when infection, caused by microorganisms transmitted by these routes, is suspected or diagnosed. They include the physical separation of infected or colonized patients/residents from other individuals and the use of barriers. Cohorting: the assignment of a geographical area such as a room or a patient care area to two or more patients who are either colonized or infected with the same microorganism. In some instances, staffing assignments may be restricted to the cohorted group of patients/residents. Contact Precautions: the type of Additional Precautions used to reduce the risk of transmitting infectious agents via direct or indirect contact with an infectious person. Contamination: the presence of an infectious agent on the hands or on a surface, such as clothing, gowns, gloves, bedding, toys, surgical instruments, patient/resident care equipment, dressings or other inanimate objects. Diarrhea: Loose/watery bowel movements (conform to the shape of the container) and the bowel movements are unusual or different for the patient. Medical equipment /devices must be thoroughly cleaned before effective disinfection can take place. Endogenous flora: Microbial flora occupying niche(s) that are in or on the body of the host. Exogenous flora: Microbial flora normally existing externally to the body of the host. Hand hygiene relates to the removal of visible soil and removal or killing of transient microorganisms from the hands. Hand hygiene may be accomplished using soap and running water or an alcohol-based hand rub. High-Touch Surfaces: High-touch surfaces are those that have frequent contact with hands. Outbreak: An increase in the number of cases above the number normally occurring in a particular setting over a defined period of time. Patient/Resident Environment: the immediate space around a patient/resident that may be touched by the patient and may also be touched by the healthcare worker when providing care. In an ambulatory setting, the patient/resident environment is the area that may come into contact with the patient within their cubicle. This may be due to relapse of the initial infecting strain or due to reinfection with a new strain. Most recurrences present within one to three weeks after discontinuing antibiotic therapy, although recurrences can occur as late as two to three months later. Routine Practices: the system of infection prevention and control practices to be used with all patients during all care to prevent and control transmission of microorganisms in all health care settings. Routine Practices are based on the premise that all patients/residents are potentially infectious, even when asymptomatic, and that the same safe standards of practice should be used routinely with all patients/residents to prevent exposure to blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, mucous membranes, non-intact skin or soiled items and to prevent the spread of microorganisms.
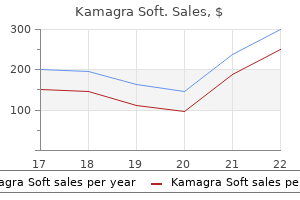
Generic kamagra soft 100 mg amex
Do not attempt to clear up after any accident with laboratory items or materials; Do not enter any room which is labelled containment level 3 on the door unless you are told that it is safe and are required to do so by a senior member of the laboratory staff; Never empty any laboratory waste containers unless you have been told to by a member of laboratory staff erectile dysfunction symptoms kamagra soft 100mg low price. Be very careful when putting your hands into bowls or other receptacles which contain glassware items, as some could be broken and could cause cuts. Autoclaving duties Do not attempt to use the autoclave until you have been taught how to do so by a senior member of laboratory staff and they are satisfied that you are competent to operate it on your own. Follow the operating instructions displayed near the autoclave at all times; Items requiring autoclaving should not be allowed to build up. They will be infectious and the risks are likely to get worse if not dealt with straightaway; If you have to stack waste containers or other materials awaiting autoclaving, do so carefully. If waste or other materials are spilt, report it to a senior member of the laboratory staff and your own supervisor at once and get instructions on how to deal with it. Do not try to do it yourself if you have not been trained to decontaminate a spillage; If pressure or temperature indications are incorrect, report it to a senior member of the laboratory staff. If there are any doubts, all of the material already in the chamber should be autoclaved again. Handling waste When collecting waste from disposal points, make sure that it is labelled showing where it has come from and properly bagged or otherwise safely contained according to standard operating procedures. If it is not, refuse to handle it; Be very careful when handling sharps containers because both the sharp points and the liquids can cause infection. Guidelines for maintenance staff and equipment service engineers in clinical laboratories 25 Much of the work in a clinical laboratory is concerned with handling specimens and materials that are infectious, and repair and maintenance staff will be required to handle equipment that has been used to process these materials. Although laboratory staff should ensure that the equipment is decontaminated and cleaned, maintenance staff and equipment service engineers may accidentally come into contact with infectious material. They should, therefore, always follow the general precautions as well as the additional instructions outlined below: For work in laboratories Maintenance work on building fabric, services, drainage, fixtures, fittings, plant or equipment, should usually be covered by a permit to work system. This should specify that appropriate cleaning and decontamination procedures have been carried out. Alternatively, where decontamination is not possible, you should be informed of this and receive special instructions concerning protective measures that you should take while working; Report to the laboratory safety officer to receive any such special instructions before commencing any work in the laboratory; You should wear the protective clothing deemed necessary by the laboratory or safety officer; Any tools or test equipment used in the laboratory should be inspected afterwards and, when considered necessary, they should be decontaminated before being returned to the workshop. You may need technical advice from laboratory staff about how to decontaminate equipment. Safe working and the prevention of infection in clinical laboratories and similar facilities Page 63 of 69 Health and Safety Executive Equipment to be sent to the workshop or elsewhere All equipment should be labelled to record whether any cleaning or decontamination has been carried out, and to inform those concerned of any special precautions that still need to be taken; these special precautions, which may include the use of protective clothing or equipment, should be closely followed by all maintenance and/or repair staff; Joints, seals and connections should not be opened or broken unless advice about the possible contents of pipes, tubes or containers has first been obtained from the laboratory staff. Guidelines for visitors to laboratories 26 Most visitors to a clinical laboratory will not be conversant with the general precautions or standard operating procedures associated with the workplace. Visitors should not be allowed to enter the laboratory area unless accompanied by a senior member of staff who will be responsible for their welfare. Visitors should: wear an approved coat or gown, properly fastened; be instructed not to touch anything while in the laboratory, unless their visit demands such action, in which case they should comply with the standard operating procedures. In some cases frequent hand washing may be necessary but visitors should, in any case, wash their hands thoroughly after removing their protective coat, before leaving the laboratory; not use personal items such as pens or pencils while in the laboratory if they have handled any laboratory equipment and should be instructed not to smoke etc before entering; not be taken into areas of the laboratory where they could become exposed to a risk of infection; not be left unsupervised while they are in the laboratory. It is the responsibility of the employer to decide where visitors may and may not go unless additional precautions are taken. Safe working and the prevention of infection in clinical laboratories and similar facilities Page 64 of 69 Health and Safety Executive References 1 Management of health and safety at work. Carriage of Dangerous Goods (Classification, Packaging and Labelling) and Use of Transportable Pressure Receptacles Regulations 1996. Department of Health and Human Services, are best-practice guidelines for the treat ment of substance use disorders. These recommenda tions are communicated to a consensus panel composed of experts on the topic who have been nominated by their peers. The members of each consensus panel represent substance abuse treatment programs, hospitals, community health centers, counseling programs, criminal justice and child welfare agencies, and private practitioners. Researchers and clinicians have begun tive disabilities; rural populations; individuals to question the acute care model of treatment who are homeless; and older adults. Psychiatry Middletown, Connecticut School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Gerard J. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Director Writer, chapters 1 and 2 Research Institute on Addictions University of Buffalo Co-Chair Buffalo, New York Paul D. Crawford Clinical Associate Chief Executive Officer Department of Psychiatry and Roxbury Comprehensive Community Behavioral Sciences Health Center Duke University Medical Center Roxbury, Massachusetts Durham, North Carolina Writer, chapters 1 and 5 Chris B. Johns Hopkins University School of Chicago, Illinois Medicine Writer, chapter 10 Baltimore, Maryland Writer, chapters 8 and 9 George Kolodner, M. Peyton Kolmac Clinic Principal Silver Spring, Maryland Peyton Consulting Services Writer, chapter 4 Newark, Delaware Writer, chapters 8 and 9 Felicity L. Division of Clinical and Services Research Academy for Educational Development National Institute on Drug Abuse Washington, D. Chief President Scientific Communications Branch Weinreich Communications National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Canoga Park, California Alcoholism Bethesda, Maryland Clarissa Wittenberg Director Harry B. Office of Communications and Public Liaison President/Chief Executive Officer National Institute of Mental Health Hands Across Cultures Bethesda, Maryland Espanola, New Mexico Consulting Members Richard K. Research Scientist Academy for Educational Development Division of Addiction Services Washington, D. University of Southern California Center for Communications Programs Alhambra, California Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, Maryland Patricia A. A panel of non-Federal clinical researchers, clinicians, program administrators, and client advocates debates and discusses its particular areas of expertise until it reaches a consensus on best practices. We are grateful to all who have joined with us to contribute to advances in the substance abuse treat ment field. Acting Deputy Administrator Assistant Surgeon General Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration H. Today, the same task requires two volumes, each devoted to a distinct audience, clinicians and administrators. A con A parallel development has been the fre tinuum of care ensures that clients can enter quent application of research findings into substance abuse treatment at a level appro practice in the field of substance abuse priate to their needs and step up or down treatment. Research has yielded new under to a different intensity of treatment based standing about the complexity of substance on their responses. Clinicians enhance the use disorders that takes into account bio capabilities of their programs when they are chemical processes, learning, spirituality, informed about and willing to refer clients to and environment. The is key to determining when they are ready collaboration between research and practice for the next appropriate level of care. A step-up behavioral interventions, relapse prevention or stepdown in treatment intensity in the training, motivational enhancement, and same program or a referral to a nonaffiliated case management are used in community provider can be disruptive for the client. Clinicians need to be thoroughly based principles that shape and guide familiar with local treatment options, includ substance abuse treatment. The consensus panel believes Clinicians should begin to establish a that these core services, such as group and therapeutic relationship as soon as clients individual counseling, psychoeducational present themselves for treatment. Any bar programming, monitoring of drug use, riers to treatment must be addressed. Based medication management, case manage on screening and assessments, clients should ment, medical and psychiatric examinations, be matched with the best treatment modal crisis intervention coverage, and orienta ity and setting to support their recovery. This concept is flexible, research and the experience of practiced cli and what might be considered enhanced nicians to address the issues of engagement services for some programs may be essential and retention. Clients can become distracted services for a program with a different client from recovery if family members continue population. When clinicians understand and Treatment Issues and prepare for these problems, their clients Many clients who enter substance abuse have a better chance of being retained in treatment drop out in the early stages and benefiting from treatment. Entry and tor in client retention is the quality of the engagement are crucial processes; how an relationship between client and counselor.
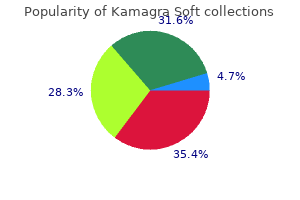
Buy 100 mg kamagra soft
These lenses form an aerial image that is inverted highest convex lens which allows clear vision must be cho laterally and vertically erectile dysfunction vacuum device generic 100 mg kamagra soft free shipping. The highly concave copy with the focusing lens of the direct ophthalmoscope Hruby lens has a power of 255 D and can also be kept at about 120 D, observe the retinal refex and then employed, but gives a low magnifcation and a small feld decrease the power of the lenses gradually, as the observer (Fig. A gradual reduction of the Such an examination is easier with full mydriasis but power of the focusing lenses permits the visualization of the disc can be visualized even through an undilated pupil. Fine changes in the posterior part of same optical conditions as the fundus of a hypermetropic the vitreous and retina and at the optic disc can be readily eye. The appearance of opacities in the vitreous or lens will studied binocularly under high magnifcation, areas of oe vary with their density and with the amount of light re dema are clearly outlined in the optical section, and diff fected from their surfaces; if they are very dense they will cult problems in diagnosis such as the difference between a appear black against the background of the red refex, but if cyst and a hole at the macula are clearly demonstrated. The they are semitransparent they will appear red or whitish ac examination provides a high quality, highly magnifed and cording to the relative amounts of light transmitted from the fundus and refected from their surface. A detached retina may, therefore, look red or white according to its degree of transparency, and if much light is refected from the P surface, details may be seen upon it. Slit-lamp Biomicroscopy the slit-lamp cannot be used to explore the eye beyond the A anterior parts of the vitreous because the beam of light is ordinarily brought to a focus in this region. If, however, the beam is made more divergent by eliminating the refractive infuence of the corneal curvature by using a contact lens with a fat anterior face, or (more simply) by interposing a high power concave or convex lens in front of the cornea, the posterior part of the vitreous and the central area of the fundus can be examined by the binocular microscope in the focused beam of light (Fig. Lenses for the examination of the fundus are of two types, contact and non-contact. The 160 D lens allows more magnifcation and appears in plane P; (B) a limited area of the fundus is seen. The convex Posterior fundus contact lenses nullify the power of lenses are initially held very close to the eye, between the the cornea. The posterior fundus can be directly visualized thumb and forefnger, the hand being stabilized by the through such lenses. The image produced is virtual and middle fnger resting on the forehead bar of the slit-lamp. Viewing the more peripheral retina requires the vation arms are aligned and the magnifcation is initially use of indirect contact lenses, which utilize angulated 103. The illumination is kept low, the slit beam at a width mirrors to bring the anterior retina into view. Goldmann three-mirror contact lens has three mirrors Once the fundal glow is visualized the lens is drawn away placed in the cone, each with a different angle of inclina from the eye till the posterior fundus comes into focus. The central part Refections that obscure visibility can be reduced by tilting of the contact lens allows a direct view of the posterior the lens slightly. This is maximal with a high by each mirror, bringing into focus a different area intensity of projected light, a good contrast between the (Fig. There are other lenses available for laser observed structure and background, a large angle of separa treatment of the retina, such as the panfundoscopic lens tion between observer and illumination axes and when and the transequatorial lens. Chapter | 12 Examination of the Posterior Segment and Orbit 141 because the choroid and pigmentary epithelium of the retina Examination of the Fundus do not extend up to the margin of the disc so that the sclera the details of the fundus should be examined systemati is seen through the retina. The patient is instructed to look straight ahead and the pigment around the margin of the disc due to the heaping up examiner approaches the eye with an ophthalmoscope or of the retinal pigmentary epithelium. The disc itself is not 178 D or 190 D lens from the temporal side so that the uniformly pink throughout its extent. The shape and the optic disc is usually paler and may be quite white, and colour of the disc, the arrangement of the vessels, their the temporal side is normally paler than the nasal. The cen pulsations if any, the colour of the choroidal refex (its uni tral vessels emerge from a funnel-shaped depression, the formity or tessellation), and gross abnormalities (white or physiological cup. The patient is then deep, the central part may be seen to be speckled with grey directed to look up, to the right, to the left and down. In this spots representing the meshes of the lamina cribrosa through manner the periphery of the fundus is brought into view. It may be brought into logical cup is best understood by comparing the ophthalmo view by telling the patient to look into the light; but it is scopic picture with a microscopic section vertically through best to fx the temporal edge of the disc and pass horizon the nerve head (Fig. Finally, the periphery of the fundus is investi in the centre, the white lamina shines through more brightly. The grey spots in the lamina, where they are seen, are due to With full dilation of the pupil it is possible to see almost up the non-medullated nerve fbres refecting less light than the to the oraserrata, especially if the sclera over the ciliary white connective tissue fbres. All fndings should in health and some experience is required in differentiating be recorded on a retinal chart (see Chapter 20). Diseases of the retina rarely occur the use of a red-free light enhances the visibility of in isolation, and are commonly associated with changes in haemorrhages and blood vessels in the retina as well as the adjacent structures such as the choroid, vitreous and optic defects in the nerve fbre layer, which may be seen as slits nerve. The retina is frequently affected by systemic diseases or wedges fanning upwards and downwards from the optic and these manifestations are termed retinopathies. In very dark-complexioned people the fundus is a darker red and in fair-skinned individuals it appears lighter in colour. Normally the choroidal blood vessels cannot be seen as the retinal pigment epithelium blurs any details, but is not suffcient to prevent the colour of the blood within the choroid manifesting itself. In people having a light pigmentation, the choroid and sometimes its larger ves R sels may be visible. Sometimes the pigment between the P choroidal vessels is particularly dense, or the pigment is defcient in the retinal pigmentary epithelium, while the C choroid is deeply pigmented; the choroidal vessels are then S seen to be separated by deeply pigmented polygonal areas (tigroid or tesselated fundus). The optic disc is generally pale pink in colour, nearly circular in shape and about 1. Retinal pigments and red cells absorb to the flm, with complete exclusion of the irradiating light. In the choroidal circulation, Fluorescein angiography is particularly helpful in ex fuorescein passes freely across the endothelium of the cap posing the depth of pathological involvement in diabetic illaries to the extravascular spaces. It gives a clear idea of the integrity of and the intact retinal pigment epithelium. Fluorescein dye appears first in the choroid, 1-2 s before the dye reaches the reti nal arterial circulation. When present, cilioretinal arteries fill along with the choroidal flush since both are supplied by the short posterior ciliary arteries. The arteriovenous phase of the angiogram comprises the time when the retinal arteries, capillaries, and veins contain fluorescein. In the early arteriovenous phase, thin columns of fluorescein are visualized along the walls of the larger veins (laminar flow). As the fluorescein dye begins to exit from the retinal arteries and capillaries, the co ncentration of fluorescein within the veins increases, resulting in a decrease in fluorescence of the arteries and an increase of fluorescence of the veins. The intensity of fluorescence diminishes slowly during this phase as fluorescein is removed from the bloodstream by the kidneys. The late phase of the angiogram demonstrates the gradual elimination of dye from the retinal and choroidal vasculature. Any other areas of late hyperfluorescence suggest the presence of an abnormality, usually the result of fluorescein leakage. Flowmetry, with the help of the scanning the vessels of the iris may be the frst sign of rubeosis. The sound is coupled to similar breakdown in the barrier occurs early in the course the eye by means of a saline bath or directly through a of retinitis pigmentosa and also in carriers of this disease. Indocyanine Green Angiography Indocyanine green stays within the choroidal circulation A-Scan and is stimulated by a longer wavelength of light than fuo the transducer is positioned so that the ultrasonic beam rescein dye. This provides a better resolution of the choroi passes through a chosen ocular meridian.
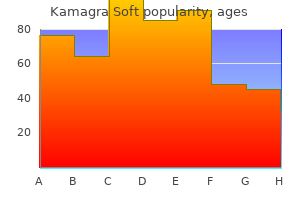
Buy kamagra soft 100mg visa
Multicellular behaviour and production of a wide variety of toxic substances support usage of Bacillus subtilis as a powerful biocontrol agent impotence 27 years old buy discount kamagra soft 100 mg on line. Killed Bacillus subtilis spores expressing streptavidin: a novel carrier of drugs to target cancer cells. Resistance of Bacillus endospores to extreme terrestrial and extraterrestrial environments. Langerhans-like dendritic cells generated from cord blood progenitors internalize pollen allergens by macropinocytosis, and part of the molecules are processed and can activate autologous naive T lymphocytes. Passive immunisation of hamsters against Clostridium difficile infection using antibodies to surface layer proteins. Recurrent Septicemia in an Immunocompromised Patient Due to Probiotic Strains of Bacillus subtilis. Clostridium difficile colonization in healthy adults: transient colonization and correlation with enterococcal colonization. Bacillus species: the dominant bacteria of the rhizosphere of established tea bushes. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in a region of Quebec from 1991 to 2003: a changing pattern of disease severity. Immunization with Bacillus spores expressing toxin A peptide repeats protects against infection with Clostridium difficile strains producing toxins A and B. Evaluation of Bacillus subtilis strains as probiotics and their potential as a food ingredient. Commensal gut flora reduces susceptibility to experimentally induced colitis via T-cell-derived interleukin-10. Characterization of the collagen-like exosporium protein, BclA1, of Clostridium difficile spores. Specialized peptidoglycan of the bacterial endospore: the inner wall of the lockbox. Sporicidal action of alkaline glutaraldehyde: factors influencing activity and a comparison with other aldehydes. Saccharomyces boulardii for the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in adult hospitalized patients: a single-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Complete genome sequence of the industrial bacterium Bacillus licheniformis and comparisons with closely related Bacillus species. Asymptomatic carriers are a potential source for transmission of epidemic and nonepidemic Clostridium difficile strains among long-term care facility residents. Fecal Flora Reconstitution for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection: Results and Methodology. A Novel Toxinotyping Scheme and Correlation of Toxinotypes with Serogroups of Clostridium difficile Isolates. Clostridium difficile infection: new developments in epidemiology and pathogenesis. Oral Poliovirus Vaccine: History of Its Development and Use and Current Challenge to Eliminate Poliomyelitis from the World. Influence of mode of delivery on gut microbiota composition in seven year old children. Infection of hamsters with epidemiologically important strains of Clostridium difficile. Gastrointestinal microbiome signatures of pediatric patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Probiotic formulations and applications, the current probiotics market, and changes in the marketplace: a European perspective. The multidrug-resistant human pathogen Clostridium difficile has a highly mobile, mosaic genome. Spores of Bacillus subtilis: their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. Sublingual vaccination with influenza virus protects mice against lethal viral infection. Molecular analysis of the pathogenicity locus and polymorphism in the putative negative regulator of toxin production (TcdC) among Clostridium difficile clinical isolates. Comparative phylogenomics of Clostridium difficile reveals clade specificity and microevolution of hypervirulent strains. Comparative genome and phenotypic analysis of Clostridium difficile 027 strains provides insight into the evolution of a hypervirulent bacterium. Identification of the immunodominant protein and other proteins of the Bacillus anthracis exosporium. Polymeric IgA Is Superior to Monomeric IgA and IgG Carrying the Same Variable Domain in Preventing Clostridium difficile Toxin A Damaging of T84 Monolayers. Prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea by Saccharomyces boulardii: a prospective study. The search for a better treatment for recurrent Clostridium difficile disease: use of high-dose vancomycin combined with Saccharomyces boulardii. Monoclonal antibodies for Bacillus anthracis spore detection and functional analyses of spore germination and outgrowth. A collagen-like surface glycoprotein is a structural component of the Bacillus anthracis exosporium. Polymorphism in the collagen-like region of the Bacillus anthracis BclA protein leads to variation in exosporium filament length. Complete genome sequence of the alkaliphilic bacterium Bacillus halodurans and genomic sequence comparison with Bacillus subtilis. An unusual mechanism of isopeptide bond formation attaches the collagenlike glycoprotein BclA to the exosporium of Bacillus anthracis. Mechanisms of killing of spores of Bacillus subtilis by iodine, glutaraldehyde and nitrous acid. Cefoperazone-treated mice as an experimental platform to assess differential virulence of Clostridium difficile strains. A novel fusion protein containing the receptor binding domains of Clostridium difficile toxin A and toxin B elicits protective immunity against lethal toxin and spore challenge in preclinical efficacy models. Genes of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus anthracis encoding proteins of the exosporium. Evaluation of formalin inactivated Clostridium difficile vaccines administered by parenteral and mucosal routes of immunization in hamsters. Field performance of transgenic elite commercial hybrid rice expressing Bacillus thuringiensis delta endotoxin. Toxin A of Clostridium difficile binds to the human carbohydrate antigens I, X, and Y. Characterization of the sporulation initiation pathway of Clostridium difficile and its role in toxin production. Enterotoxin-based mucosal adjuvants alter antigen trafficking and induce inflammatory responses in the nasal tract. Cutting edge: the mucosal adjuvant cholera toxin redirects vaccine proteins into olfactory tissues. Comparison of toxin and spore production in clinically relevant strains of Clostridium difficile. Characterisation of Clostridium difficile hospital ward-based transmission using extensive epidemiological data and molecular typing. Identification of a second collagen-like glycoprotein produced by Bacillus anthracis and demonstration of associated spore-specific sugars.
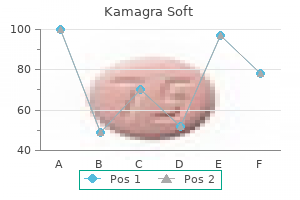
Indian Tree of Heaven (Tree Of Heaven). Kamagra Soft.
- How does Tree Of Heaven work?
- Diarrhea, menstrual disorders, asthma, cramps, epilepsy, fast heart rate, gonorrhea, malaria, tapeworms, or use as a tonic.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Tree Of Heaven.
- What is Tree Of Heaven?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96679
Purchase kamagra soft 100 mg free shipping
Linear ginkgo biloba erectile dysfunction treatment discount 100 mg kamagra soft with mastercard, spoke-like riders run towards A progressive type of congenital cataract, originally the equator. The opacities are tracted in the second and sometimes in the third month not progressive and do not lead to complete opacifcation of pregnancy. Their importance lies in their recognition as developed an immunological defence mechanism so that a developmental anomaly, for if they are seen when the extensive cellular parasitism occurs. There may be an accompanying retinitis, which appears as a fne pigmen Anterior Capsular (Polar) Cataract tary deposit (salt-and-pepper retinopathy) at the posterior pole. Other congenital anomalies occur in association with this may be developmental owing to delayed formation the cataract, particularly congenital heart disease (patent of the anterior chamber and, in this case, the opacity is ductus arteriosus), microphthalmos, micrencephaly, mental congenital. More commonly the condition is acquired, and retardation, deafness and dental anomalies. Unless all follows contact of the capsule with the cornea, usually after lens matter is removed, aspiration of the cataract may be the perforation of an ulcer in ophthalmia neonatorum. The area, a white plaque forms in the lens capsule, which some frequency of this combination with maternal rubella raises times projects forwards into the anterior chamber like a the serious question of medical termination of pregnancy pyramid (anterior pyramidal cataract). When this occurs it may well be that the the primary immunization schedule, and/or rubella vaccine subcapsular epithelium grows in between the capsular and to pre-pubertal girls or women who are to start a family and cortical opacities so that the clear lens fbres subsequently are found to be rubella antibody negative, are measures to growing from there lay down a transparent zone between reduce the morbidity of the teratogenic effects of congenital the two opacities. The possibility of other viruses traversing and the two together constitute a reduplicated cataract. Coronary Cataract Posterior Capsular (Polar) Cataract this represents a similar type of developmental cataract as the zonular, occurring around puberty. It is therefore situated this is due to persistence of the posterior part of the in the deep layers of the cortex and the most superfcial vascular sheath of the lens. Sometimes, however, of club-shaped opacities near the periphery of the lens, usu particularly in cases with a persistent hyaloid artery, the ally hidden by the iris, while the axial region and the ex lens is deeply invaded by fbrous tissue and a total cataract treme periphery of the lens remain free (Fig. Treatment of Developmental Cataract Before planning treatment, a detailed history and careful clinical evaluation including laboratory tests to look for the underlying aetiology (Table 18. This includes recording the intraocular pressure and fundus examination under dilatation to rule out associated diseases such as retinoblastoma. B-scan ultrasonography is useful in assessing the posterior segment of the eye to rule out an associated retinal detachment or retinoblastoma in a child with total cataract in whom the fundus is not visible. A-scan ultrasonography to record and compare the axial A B lengths of the two eyes should be done. The use of a contact lens requires the expert co of Bilateral, Non-hereditary Paediatric Cataract operation of interested parents and even with their Blood tests cooperation binocular vision may be diffcult to establish l Serum biochemistry for levels of blood glucose, calcium and amblyopia diffcult to avoid. Generally, l Screening for amino acids in the urine (if Lowe syndrome is intraocular lenses are favoured in children whose ocular suspected) growth is almost complete (over 2 years of age) and in those with unilateral cataract. The timing of surgery, surgical technique, type of the intraocular lens should be of a single-piece type, optical rehabilitation for aphakia (glasses, contact lens i. The implantation of anterior cham Treatment is not indicated in a developmental cataract ber intraocular lenses in children was discontinued in the unless vision is considerably impaired. If the cataract is mid-1980s due to major complications including secondary central and reasonably good vision can be obtained through glaucoma and corneal decompensation. The intraocular lens the clear cortex around it, the child should be kept under power is calculated according to the axial length and kera mydriasis if required with careful follow-up to monitor the tometry. If the opacity is large years old and 80% of emmetropic power in those less than or dense, an operation for removal of the cataractous 2 years of age to allow for any further growth of the eyeball. A decision on this issue depends Post-operative management includes careful follow-up upon whether vision with corrected refraction and retained for monitoring visual recovery, treatment of amblyopia and accommodation is to be preferred to probably improved evaluation for complications such as astigmatism, fbrinous vision after operation without accommodation. Moreover, the results of sur Besides the various forms of congenital cataract, abnor gery in unilateral cataract in children are universally malities in the shape and position of the lens occur, often poor, unless the operation is carried out as early as associated with other malformations of the eye (Fig. The critical Abnormal Shape or Size period for developing the fxation refex in both unilateral and bilateral visual deprivation disorders is In coloboma of the lens, there is a notch-shaped defect usu between 2 and 4 months of age. Any cataract dense ally in the inferior margin; less frequently it occurs in some enough to impair vision must be dealt with before this other part of the margin. It is due to defective development age and the earliest possible time is preferred, provided of part of the suspensory ligament. No posterior capsular Incarceration of the vitre Mainly advocated for opacifcation ous in the scleral incision. A total cataract is associated with a developmental anomaly related to persistence of the Familial primary vitreous and hyaloid arterial system. The posterior Autosomal dominant form capsule of the lens may be invaded by a fbro-vascular membrane, contracture of which leads to an elongation Autosomal recessive form (associated with iris coloboma, aniridia, microspherophakia, ectopia pupillae) of the ciliary processes which become visible through the pupil. In this disease, ectopia lentis becomes more marked Lenticonus is an abnormal curvature of the lens so that with age and gives rise to glaucoma. It is operative risks because of the tendency to venous thrombo more commonly posterior than anterior (Fig. Other signs include laxity of joints and a marfanoid rior lenticonus is seen in Alport syndrome. Clinical Features Ectopia Lentis Apart from poor vision, patients may complain of uniocular this is a congenital dislocation or subluxation of the lens, diplopia and glare. Loss of vision may its normal position is described as subluxation of the be noticed suddenly. Signs include an obvious lens dis lens if there is a partial displacement and dislocation of placement; however, sometimes this may not be visible the lens if there is a complete displacement of the lens through an undilated pupil. The condition is often heredi (iridodonesis) and lens (phacodonesis) accentuated by eye tary. The lens is small, but the edge is generally invisible movement, and a deep anterior chamber are other signs. The usual signs of subluxation the pupil should be dilated to look for the extent of dis are then seen. It is sometimes associated with arachnodac placement and assess whether the zonules are intact. Posterior displacement of the lens into the vitreous may cause lens-induced uveitis. Aetiopathogenesis the basic defect is breakage or weakening of the zonules Treatment (Table 18. The degree of displacement depends on If anteriorly dislocated, with inverse glaucoma, the patient whether this affects only a sector or local area or the entire must be treated as an emergency. Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant connec If the lens is subluxated, the extent is assessed and tive tissue disorder affecting the skeletal and cardiovascular refraction through the aphakic portion is performed to give systems and the eye. A defciency in the enzyme cystathionine If the vision is poor due to excessive lenticular astig synthetase gives rise to excessive amounts of homocystine matism or presence of the lens edge in the visual axis, in the urine and widespread abnormalities characterized by removal of the lens is required. Homocystine If any of these deformities cause great visual disability, in the urine is detected by the cyanide nitroprusside test. If opacifcation has occurred, control of the grading of nuclear hardness is useful to the cata the general condition may stay its progress, but once the pro ract surgeon in planning surgery by phacoemulsifcation. In senile cataract the progress of opacifcation may Grade Nucleus color cease spontaneously for many years, or refractive changes Grade 1 nucleus may result in temporary improvement of vision. In all cases, however, a careful examination of the Grade 2 slightly yellow patient should be made to exclude any specifc or constitu Grade 3 brown tional cause of the cataract; if any is found, it should be Grade 4 black, signifying an extremely hard nucleus treated. Before the era of microsurgery it was important to wait for total opaqueness of the lens before operating and in Retinal and optic nerve function must then be explored incipient cataract the condition of the patient would be since, if it is defective, operation may be valueless and much ameliorated during the tedious process of maturation the patient warned of possible disappointment. If the pupillary area is free, A bright focused light is then shone into the cataractous eye brilliant illumination will be found best. In this case, dark glasses are usually of and accurately, no matter how dense the cataract may be. He should also be asked to look at of incipient cataract the pupil should be dilated to allow a a distant light through a Maddox rod; if the red line is con thorough examination of the central and peripheral fundus at tinuous and unbroken, macular function is probably good. However, immature cata An entoptic view of the retina will often allow the pa racts are routinely successfully operated on today and the tient to supply valuable information.
Syndromes
- Do you prefer a provider focused on disease treatment, or wellness and prevention?
- Trans-Plantar
- Alkaptonuria
- Kidneys not able to filter fuilds and waste (chronic glomerulonephritis)
- Does it feel like something is in your eye now?
- Echocardiogram
- Squamous cell skin cancer
- Blood in the stool
- Adrenergic blockers
Discount kamagra soft on line
The third in this disease complex impotence urinary buy kamagra soft 100mg fast delivery, but disuse atrophy can not category pigs do not have muscle or fascial lesions, but be ruled out. This is a relatively common tumor of older animals especially rats and dogs, and, in this case, a bull. Histologically, there is a marked cellular increase (hyperplasia) of the anterior part (pars anterior) of the pituitary, but the cause is not known. It is targeted not only at those in the chemical and process industries, but also anyone likely to work with chemicals within industry and in the service sector. It embraces the entire life-cycle of chemicals during transport, storage, processing, marketing, use and eventual disposal and should appeal to chemists, occupational and environmental health practitioners and students, engineers, waste handlers, safety officers and representatives, and health care professionals. Clearly, more detailed texts or professional advice may need to be consulted for specific applications. Since the first edition in 1994 there have been no significant changes in the fundamentals of chemistry, physics and toxicology upon which the safe handling of chemicals are based. There has, however, been some increase in knowledge relating to the chronic toxicological and potential environmental effects of specific chemicals, and in legislation and government guidelines. There has been an increase in the controls applicable to the marketing and transportation of different classes of chemicals. Those applicable to major hazards have changed under the Control of Major Accident Hazard Regulations 1999. Increased concern as to the possible environmental impacts of chemical discharges and disposal has been accompanied by more comprehensive legislation for control. General safety legislation was expanded by the introduction of various separate regulations in 1993, including that dealing with management of health and safety at work; workplace health, safety and welfare; workplace equipment; and personal protective equipment. The opportunity has been taken to improve each chapter and to update the information. The main changes include an expansion of the terminology in Chapter 2 and provision of an introduction to basic chemical principles for non-chemists in a new Chapter 3. Chapter 5 on Toxic chemicals has been enlarged and the table of hygiene standards updated. Chapters 6, 7 and 8 on Flammable chemicals, Reactive chemicals and Cryogens, respectively, have been updated and expanded. The scope of Chapter 9 on Compressed gases has been widened to include additional examples together with the basic techniques of preparing gases in situ. Chapter 10 summarizes techniques for monitoring air quality and employee exposure. It has also been expanded to provide guidance on monitoring of water and land pollution. Considerations of safety in design (Chapter 12) are presented separately from systems of work requirements, i. The considerations for Marketing and transportation of hazardous chemicals are now addressed in two separate chapters (Chapters 14 and 15). Chemicals and the Environment are now also covered in two chapters (Chapters 16 and 17) to reflect the requirement that the impact of chemicals on the environment should be properly assessed, monitored and controlled. Although a substantial contribution to atmospheric pollution is made by emissions from road vehicles and other means of transport, and this is now strictly legislated for, this topic is outside the scope of this text. Chapter 18 provides useful conversion factors to help with the myriad of units used internationally. Whilst the hazards identified, and the principles and practice for the control of risks are universal, i. It is hoped that the improvements will help to achieve the objectives for which the text was originally conceived, i. The range of chemicals and chemical mixtures in common use in industry is wide: it is obviously impossible to list them all in a concise handbook, or to refer to all their proprietary names. Numerous sources not restricted to those in the Bibliography were searched for information and although not listed, to achieve conciseness, these are acknowledged. The multiplicity of data sources also means that minor variations occur due to differences in the procedures and methods for their determination; however they provide general guidance. Whilst the data quoted in this text has been carefully collated, its accuracy cannot be warranted. For this reason, and to avoid overlooking consideration of other chemical-specific hazards or location-dependent legislation, it is advisable to refer to a Chemical Safety Data Sheet before using any chemical. Act 1974, the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 1988, the Highly Flammable Liquids and Liquefied Petroleum Gases Regulations 1972, the Control of Pollution Act 1974 and the Environmental Protection Act 1990 are supplemented by a wide variety of other measures. Legislative controls tend to change frequently and it is important to ensure that a check is made on current requirements and constraints in any specific situation involving chemicals. It also provides a useful summary for those who may need to make only passing reference to the hazardous properties and potential effects of chemicals, such as general engineering students and occupational health nurses. Different hazards may be associated with the manufacture, storage, transport, use, and disposal of chemicals. Environmental hazards, through persistent or accidental losses of chemicals, may also be related to these operations. However, biological hazards arising from the working environment or from more specialized activities. This text deals solely with occupational, industrial and environmental hazards associated only with chemicals. It includes fires and explosions since they inevitably involve chemical compounds. Chemicals are ubiquitous as air, carbohydrates, enzymes, lipids, minerals, proteins, vitamins, water, and wood. These spanned a wide range of industrial and related premises as shown in Table 1. The most common sources of ignition (see Chapter 6) that year are shown in Table 1. One estimate suggests that the chemical industry contributes to 50% of all air pollution with proportions approximating to sulphur dioxide (36%), carbon dioxide (28%), nitrogen oxides (18%), carbon monoxide (14%) and black smoke (10%). Motor spirit refining is responsible for ca 26% of emissions of volatile organic compounds to the atmosphere. In 1996 there were over 20 000 reports of water pollution incidents with 155 successful prosecutions. In the workplace it is a management responsibility to ensure practices control the dangers, and it is for employees to collaborate in implementing the agreed procedures. Management must also prevent uncontrolled environmental releases and ensure all wastes are disposed of safely and with proper regard for their environmental impact. The aims of this book are to raise awareness and to help users identify, assess and control the hazards of chemicals to permit optimum exploitation whilst minimizing the dangers. Alternatively, prolonged or intermittent exposure may result in an occupational disease or systemic poisoning. Generally acute effects are readily attributable; chronic effects, especially if they follow a long latency period or involve some type of allergic reaction to a chemical, may be less easy to assign to particular occupational exposures. The possible permutations of effects can be very wide and exposure may be to a combination of hazards. For example, personnel exposed to a fire may be subject to flames, radiant heat, spilled liquid chemicals and vapours from them, leaking gases, and the pyrolytic and combustion products generated from chemical mixtures together with oxygen deficient atmospheres. However, whether a hazardous condition develops in any particular situation also depends upon the physical properties of the chemical (or mixture of chemicals), the scale involved, the circumstances of handling or use. Hazard recognition and assessment always start from a knowledge of the individual properties of a chemical.

Discount kamagra soft 100 mg fast delivery
Multiple different defects can lead to the same dis ease erectile dysfunction icd 9 code wiki buy genuine kamagra soft, especially in the case of inflammatory bowel disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Two major challenges lie ahead if the promise of Multiple Sclerosis new therapeutic approaches is to be fulfilled. First, we need reproducible and reliable serologic and clin Advances have been made in the treatment of ical methods of assessing the risk of a specific disease multiple sclerosis with the use of interferon beta-1a and copolymer I. The use of the criteria of the American College of Rheu timing of the use of these agents are still debated, a matology for a response in patients with rheumatoid recent study suggests that interferon beta-1a can de arthritis allows clinicians to compare the efficacy of lay the onset of frank disease when given after a first 114 episode of optic neuritis. The establishment specific inhibitor of T cells in vitro,127 although it may of international standards for screening tests for dia betes will enhance the reliability of these assays. Perhaps different ther apeutic interventions are needed at different stages disease cannot substitute for clinical trials, and these in the disease process. Psoria sis responded to treatment with interleukin-10 in sev Rheumatoid Arthritis eral small and short-term clinical trials. Initial results 144,145 126,131 138 Antagonism of inflammatory cytokines or protective cytokines with oral insulin have been disappointing, but the Inhibition of signaling cascades by small molecules146 results of systemic insulin are not yet available. Whether or not abnormal se Bone marrow ablation with donor stem cells rologic results should prompt treatment in the ab Bone marrow ablation without stem cells Sparing of target organs sence of clinical signs of the disease remains debatable. Alternatively, some autoim of active disease with antibodies against interleukin mune diseases may be sustained by memory cells that 10 may be effective. Pilot stud Four general approaches to therapy are being ex ies of reconstitution with autologous and allogeneic plored (Table 1): altering thresholds of immune ac stem cells are proceeding in patients with systemic tivation, modulating antigen-specific responses, re lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroder ma, and multiple sclerosis. The efficacy Interference with costimulation, signaling, chemo and safety of this approach are unknown. It is based on the concept that small chang allows the identification of subgroups of patients who es in the availability of proteins that control interac might benefit from particular approaches. Although tions between cells or participate in intracellular sig we will encounter both successes and setbacks, con naling can divert the immune system away from tinued studies of autoimmune diseases in humans autoreactivity. Perhaps this approach can only work dur ing the initial activation of autoreactive cells, because 1. Epidemiology and es milieu may be inflammatory and epitope spreading timated population burden of selected autoimmune diseases in the United States. Critical self-epitopes are key to the understand ance for autoimmune disease of less than 50 percent ing of self-tolerance and autoimmunity. Most peripheral specific therapies with cytokine or costimulatory B cells in mice are ligand selected. Colitis in trans ative disease in mice, caused by a point mutation in the Fas ligand. Cell genic and knockout animals as models of human inflammatory bowel dis 1994;76:969-76. Greatly accelerated lymphadenopathy and autoimmune disease in lpr inflammation and their relation to human inflammatory bowel disease. T-cell function and migration: two component controls chromatin degradation and prevents antinuclear auto sides of the same coin. C1q knock-out mice for the study of complement deficiency Cardiac expression of 52beta, an alternative transcript of the congenital in autoimmune disease. Recent developments in the understanding of the patho from viable motheaten mutant mice: implications for B cell tolerance. The origin of anti-nuclear of the autoimmune regulator protein: characterization of nuclear targeting antibodies in bcl-2 transgenic mice. The shared epitope hypothesis: ter induction of neonatal tolerance to H-2b alloantigens. J Exp Med 1996; an approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to 183:2523-31. Immunity American patients with rheumatoid arthritis do not have the rheumatoid 2000;13:277-85. J Hepatol 2000;32:538 B lymphocyte signaling thresholds critical for the development of B-1 lin 41. Sci of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy patients suggests common genetic ence 1999;285:2122-5. Immunologic determinants of susceptibility to experimental glo [Erratum, Nature 1999;399:84. Clin Immunol Antibody-mediated autoimmune myocarditis depends on genetically deter Immunopathol 1994;73:283-9. The aetiology of type 1 diabetes: an epidemiological per tory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in interleukin 1 receptor spective. N Engl J for interleukin 3 develop motor neuron degeneration associated with au Med 2000;343:23-30. Regulatory T cells in the control of autoimmu streptococcal and cardiac proteins. Diabetes induced by Coxsackie virus: initiation by bystander damage netics and cellular origin of cytokines in the central nervous system: insight and not molecular mimicry. Experimental autoim imental autoimmune myocarditis produced by adoptive transfer of spleno mune myasthenia gravis may occur in the context of a polarized Th1 or cytes after myocardial infarction. Is pathogenic humoral autoimmunity a Th1 and blocks tolerance induction of naive B cells. Thyroid-stimulating antibody ciated with complete deficiency of complement isotype C4A. Seishima M, Iwasaki-Bessho Y, Itoh Y, Nozawa Y, Amagai M, Kita and third-generation cephalosporins associated with immune hemolytic jima Y. Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C, but not phospholip anemia and/or positive direct antiglobulin tests. Transfusion 1999;39: ase D, is involved in pemphigus IgG-induced signal transduction. Assess drome suppress the inhibitory activity of tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Enhancement of protein S an tumor necrosis factor alpha: findings in open-label and randomized place ticoagulant function by beta2-glycoprotein I, a major target antigen of an bo-controlled trials. The World Health Or and its ligand gp39 in the development of murine lupus nephritis. Thrombo betes mellitus: report of the first international workshop for standardiza embolic complications after treatment with monoclonal antibody against tion of T cell assays. Treatment of systemic lupus ital heart block: demographics, mortality, morbidity and recurrence rates erythematosus by inhibition of T cell costimulation. Diabetes registries and early biological markers of insulin ologic effects of anti-interleukin-10 monoclonal antibody administration in dependent diabetes mellitus: Belgian Diabetes Registry. Rational use of new and existing disease-modifying blocking inflammation mediated by interleukin-1. Pharmacokinetics, safe oligomerized T cell epitopes: enhanced in vivo potency of encephalitogenic ty, and efficacy of combination treatment with methotrexate and lefluno peptides. Immunol mer acetate (Copaxone) induces degenerate, Th2-polarized immune re Today 1998;19:113-6. Induction of a non-encepha parison of copolymer-1-reactive T cell lines from treated and untreated sub litogenic type 2 T helper-cell autoimmune response in multiple sclerosis af jects reveals cytokine shift from T helper 1 to T helper 2 cells. Proc Natl ter administration of an altered peptide ligand in a placebo-controlled, ran Acad Sci U S A 2000;97:7452-7. Annu Rev Med 2000; tial of the myelin basic protein peptide (amino acids 83-99) in multiple 51:115-34. Commercial Relationships Policy: Presenters must state and display all applicable commercial relationships. Children in the convention center: Children under 18 years old must be accompanied by a parent or guardian at all times. Parents/guardians who bring children into paper sessions must remove them immediately if they become disruptive. Under no circumstances are children permitted in the exhibit hall during set-up or dismantle times.
Buy kamagra soft master card
Examples of these policies and procedures include: 31 erectile dysfunction proton pump inhibitors generic 100 mg kamagra soft overnight delivery,218,219 A sharps injury prevention program. Staff members carrying on activities in a health care setting who develop a communicable disease may be 243 subject to work restrictions. Exposures occur most commonly via inhalation 145 (respiratory) or direct skin contact. Over time, 151,317,321 without adequate controls, a sensitizer may cause asthma or chronic bronchitis. Respiratory symptoms increase in direct proportion to increased exposure time and higher concentrations of certain 317 chemicals, such as bleach and ammonia. Certain tasks, such as cleaning of toilet bowls, mirrors, sinks, and counter, as well as floor finishing tasks, regularly expose individuals to high concentrations of 145 volatile organic compounds. Irritants in health care settings associated with skin symptoms (irritant contact dermatitis) include water, soaps and detergents, most frequently in those who have underlying atopic dermatitis (allergy, eczema). A smaller number of people will develop allergic contact dermatitis where a particular allergen can cause an inflammatory response, usually hours to days later, which clinically may appear similar to irritant contact dermatitis. It is important that any health care provider who has a significant allergic, asthmatic, or dermatitis history, or who develops symptoms that may be related to work exposures, be assessed by occupational 322 health and safety. Exposure to workplace chemicals may be reduced through the use of engineering controls. Caution should be taken when cleaning and disinfection is performed in small and/or poorly ventilated spaces to reduce the risk of irritation to exposed skin and respiratory tract, and to ensure that exposure limits are not exceeded. Facilities should periodically conduct an occupational hazards assessment with respect to cleaning and disinfection of surfaces and equipment. The assessment should evaluate risks, and ensure that the safest cleaning agents, equipment and processes are selected; that appropriate training and access to personal protective equipment are in place; and that staff are aware of protocols to be 318 followed in the event of accidents, exposures or injuries. The use of automated dispensing systems or ready-to-use products is preferred over manual dilution and mixing, as automated systems reduce direct personal contact with concentrated products and reduce inhalation of volatile organic compounds from concentrated products. Automated systems also ensure that correct dilution ratios are obtained and eliminate the need for decanting. Applications of cleaning chemicals by aerosol or trigger sprays may cause eye injuries or induce or 141,144,222,317,323-331 compound respiratory problems or illness and must not be used. Repetitive movements, awkward work postures, heavy lifting, and application of high forces. Products that are lighter in weight, easily emptied and having proper handle length help reduce the risk of injury. Additionally, a variety of handle lengths should be available to ensure that differently sized cleaning staff have access 222 to appropriate ergonomically designed equipment. For more information about ergonomic design related to environmental cleaning, visit the Public Services Health & Safety Association website. There must be appropriate attendance management policies in place that establish a clear expectation that staff members do not come into work when acutely ill with a probable infection or symptoms of an infection. There must be procedures for the evaluation of staff members who experience sensitivity or irritancy to chemicals. Environmental Cleaning for Specialized Areas In this section, guidance is provided regarding cleaning and upkeep of specific facility areas including the cleaning of clean and soiled utility rooms, the upkeep of environmental cleaning equipment and supply rooms. Each client/patient/resident care area should be equipped with a room dedicated as a soiled utility room that may be used to clean soiled patient/resident 340 equipment that is not sent for central reprocessing. A separate room 80 shall be dedicated to the storage of clean supplies and equipment. A soiled utility room is used for temporary storage of supplies and equipment that will be removed for 80 341 cleaning, reprocessing or destruction, for the disposal of small amounts of liquid human waste, and 81 for rinsing and gross cleaning of medical instruments. Soiled utility rooms should: 80,81 Be physically separate from other areas, including clean supply/storage areas. If a soiled utility room is used only for temporary holding of soiled materials, the work counter and 81 clinical sink is not required; however, facilities for cleaning bedpans must be provided elsewhere. A clean utility/supply room for storing sterile supplies and equipment should: 80,81 Be separate from and have no direct connection with soiled workrooms or soiled holding areas. Toilet cleaning and disinfecting equipment should be discarded when the patient/resident leaves or sooner if required. In multi-bed rooms, a system should be developed for replacement of toilet brushes on a regular basis or as required. When choosing a tool for cleaning toilets, consideration should be given to equipment that will minimize splashing. To facilitate this, facilities shall have a sufficient number of rooms that are dedicated to the storage of cleaning equipment and supplies required for daily cleaning 80,340,341 (housekeeping closets) and are located conveniently throughout the facility. These rooms are 80,341 used for the storage, preparation and disposal of cleaning supplies and equipment, and are distinct from the clean utility/supply rooms described in 6. Facilities may also have centralized housekeeping rooms for storing bulky cleaning equipment and large 80,341 volume of supplies for distribution to local areas. At a minimum, there shall be at least one 80,340 housekeeping closet in all major care areas. In addition, housekeeping closets: Must be dedicated for use as a cleaning supply room where cleaning solution is prepared, and 80,341 dirty cleaning solution is disposed; and must not be used for other purposes. Infection prevention and control must assess construction and maintenance projects during planning, work, and after completion to verify that 31,86 infection prevention and control recommendations are followed throughout the process. Infection prevention and 31 control and occupational health and safety have the authority to halt projects if there is a safety risk. Cleaning is of particular importance both during construction and after completion of the construction project. This should be done as frequently as is necessary to avoid accumulation of dust and dispersion of dust to other areas of the facility, and at least daily. It is important that there is good liaison between the contractor, environmental services, infection prevention and control, and occupational health and safety. The level of cleaning that is expected during construction and at commissioning must be stated in the contract and the responsibility for cleaning 86 both the job site and adjacent areas shall be clearly defined. Where there is transport of construction materials (both clean and used materials) through the health care setting, a clear plan for traffic flow 86 that bypasses care areas as much as possible shall be established and adhered to . Until confirmed as a clean water source, all staff should assume that the water is contaminated. Immediate contamination may occur if the source of water harbours pathogenic bacteria. Regardless of the water source, the area will need to be cordoned off until cleaning and disinfection are completed. Persistent moisture following floods can lead to mould growth on plaster, drywall, carpeting and 124 86 furnishings. Wet carpets, if present, must be dried completely within 48 hours as the risk of mould growth increases substantially 86 after that point. If moisture persists beyond 48 hours, carpeting in a care area must be removed and 86 should not be replaced with carpeting (see 1. If the flooding involves a food preparation area, all food products that have come into contact with water must be discarded and the public health unit notified. Public health units must also be notified if vaccine refrigerators are involved in a flood or if flooding leads to a prolonged power outage that compromises food or vaccine refrigeration. Food service areas cannot re-open until the flood is controlled, the area has been cleaned, disinfected, and approval for food preparation has been obtained from public health units. Clean water Broken pipes, tub overflows, sink overflows, many Allow materials to dry appliance malfunctions, falling rainwater, broken completely before use. Gray water Overflow from a dishwater, washing machine or a Allow materials to dry Some degree of clean toilet bowl. Includes overflow Remove and discard wet Heavily and from a toilet bowl containing faeces, broken carpet, drywall, furniture and grossly sewer line, backed up sewage, all forms of ground other porous materials.

