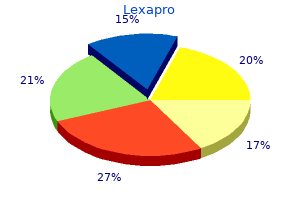
Lexapro
Buy cheapest lexapro
Giardiasis is more prevalent among children than among adults anxiety symptoms vibration discount generic lexapro canada, possibly because many individuals seem to have a lasting immunity after infection. However, chronic, symptomatic giardiasis is more common in adults than in children. Sources Infection typically results after ingestion of soil, water, or food contaminated with feces of infected humans or animals. However, foodborne outbreaks that were associated with vegetables and lettuce-based salads were reported in 2005 and 2007 and included 65 cases. Infected food handlers are very often implicated in giardiasis outbreaks, suggesting the ease of foodborne transmission. For example, an infected food handler preparing raw vegetables that were later served in an office cafeteria was the probable cause of nearly 30 cases. Giardia cysts are not killed by chlorine levels typically used to rinse produce post-harvest, and are especially difficult to wash off of complex food surfaces like leafy greens and berries. Diagnosis Giardia lamblia is frequently diagnosed by visualizing the organism, either the trophozoite (active reproducing form), or the cyst (the resting stage that is resistant to adverse environmental conditions) in stained preparations or unstained wet mounts of liquid stool, with the aid of a microscope. Commercial direct fluorescence antibody kits are available to stain the organism, with reported sensitivities and specificities reaching 100%. Organisms may be concentrated by sedimentation or flotation; however, these procedures reduce the number of recognizable organisms in the sample. When compared with microscopy, such tests have sensitivities and specificities ranging from 85% to 100%. Target Populations Giardiasis occurs throughout the population, although the prevalence is higher in children than in adults; especially in children 2 to 5 years old, in daycare, where a child-to-child passage rate as high as 50% has been noted. Other high-risk groups include individuals with certain antibody deficiencies and those with decreased gastric acidity. Food Analysis Food is analyzed by thorough surface cleaning of the suspected food and sedimentation of the organisms by centrifugation of wash material. Bad Bug Book Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Entamoeba histolytica For Consumers: A Snapshot 1. All species are characterized by a People who have a weak immune system or take life cycle that alternates between two medicines that lower the actions of the immune distinct stages. The cyst stage is the system (such as some drugs for rheumatoid infectious, but nonreplicative, form of the arthritis or cancer) are more at risk of illness than parasite that will develop in the intestine of are otherwise healthy people. Entamoeba is passed the host into active trophozoites capable of in the bowel movements of infected people and replicating. The cysts can survive symptoms do occur, they range from mild diarrhea freezing and are not always killed by to severe diarrhea that contains mucus and blood, chlorination; however, they do not survive and a swollen abdomen. If it goes to the liver, it can also cause fever, pain, and tenderness in the upper Entamoeba histolytica causes amebiasis (or right part of the abdomen, and nausea. In the United States, cases of Entamoeba histolytica infection are not common, and mortality is likely to be rare. Intestinal amebiasis manifests mostly as asymptomatic colonization, in which the parasite lives within the digestive system, but does not penetrate intestinal cells. In some people, the disease will progress into amoebic colitis after invasion of the intestinal mucosa. On rare occasions (2% to 20% of symptomatic infections), the disease will spread extraintestinally, mostly to the liver, causing amebic liver abscess, or to the brain, spleen, lungs, or genitourinary tract. The severity of the symptoms associated with intestinal amebiasis ranges from mild diarrhea to a severe, dysentery-like illness with mucus and blood in the diarrhea and abdominal distention. Amoebic liver abscess is characterized by fever, pain in the upper right abdomen, nausea, unintentional weight loss, and liver tenderness. Invasion of the intestine will cause symptoms that can last from a few days to several weeks, in the absence of treatment. Both cysts and trophozoites are passed in the feces, but trophozoites do not survive gastric acid. To become invasive, trophozoites secrete toxins that break down the intestinal protective mucus layer, destroy the colonic intestinal barrier, and counter the defense mechanisms of the host. Most infections, morbidity, and mortality occur in South and Central America, Africa, and Asia (Far East and Indian subcontinent). Sources As noted in the Organism section, above, cysts have several characteristics conducive to survival in the environment. Raw foods also may be a source of infection, after contamination by a food handler or by irrigation / rinse water, especially if the food is maintained in a moist environment. People who have chronic amebiasis or are asymptomatic can excrete several million cysts per day. During the acute phase of the illness, people tend to shed more trophozoites than cysts. Light microscopic examination of fecal specimens for cysts and trophozoites does not allow for such differentiation, unless red blood cells are identified inside trophozoites, a strong indication of invasive amebiasis. Biopsy, serology, antigen detection and molecular assays can be used for the specific diagnosis of E. In industrialized countries, this infection is most common among immigrants from endemic areas, travelers to developing nations, and in institutionalized populations. However, the procedure is not very sensitive, as less than 1% of the initial parasitic population may be recovered. Examples of Outbreaks In developed countries, amebic infections tend to cluster in households, in institutions housing people with developmental delayed, or among sexual partners. More recently, an outbreak of amebiasis was reported in the Republic of Georgia, with 177 cases recorded between May 26 and September 3, 1998, including 71 cases of intestinal amebiasis and 106 probable cases of liver abscess. Recent discoveries in the pathogenesis and immune response toward Entamoeba histolytica. Bad Bug Book Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Cryptosporidium parvum 1. The organism is transmitted via of body fluid lost from this illness can be dangerous oocysts. Otherwise healthy people who get this although it is susceptible to drying and illness usually get better in 2 days to 2 weeks. Even anyone who has severe or longerfilasting diarrhea, after a 90-minute contact time with seeing a health professional is very important. The illness levels of viable organisms is barely usually starts a week or a little longer after a person appreciable. Beside large amounts of watery diarrhea, symptoms Other notable characteristics are might include nausea, vomiting, cramps, and fever. The spread of Cryptosporidium can be A number of other Cryptosporidium prevented by washing fresh fruits and vegetables species (C. Oocysts are very resistant to chlorine (for example, bleach used for cleaning) and isolated from immunocompromised may not be killed, but can be inactivated by boiling in persons or children. This broader host range translates into more opportunities for pathogen spread and occurrence in the environment. Typically, human exposure occurs via ingestion of water contaminated with fecal material from an infected animal or food that was irrigated or washed with contaminated water. However, immunocompromised people have increased morbidity and mortality associated with cryptosporidiosis. Some infected people are asymptomatic; in others, symptoms may range from mild to profuse diarrhea, with passage of 3 to 6 liters of watery stool per day.
Cheap lexapro 20mg mastercard
Wienand anxiety symptoms pregnant order lexapro from india, Institute for Hygiene and Public Health, University of Bonn, Germany; fi N. Kathy Pond at the Robens Centre for Public and Environmental Health, University of Surrey provided English-language editing and Ana Isabel Guerreiro provided technical editing. Technical guidance on water-related disease surveillance page iii Several scientists carried out critical review functions and made valuable comments. Introduction Lead author: Martin Exner Over 30 million cases of water-related disease could be avoided globally each year through water and sanitation interventions. Investing in water supply and sanitation has produced benefits far greater than those directly related to the cost of treatment for water-related diseases (Bartram, 2002). Gastrointestinal infections are one of the principal causes of morbidity and mortality among children. For children under 5 years of age in developing countries it is estimated that a median of 3. Waterborne diseases with high potential for developing into epidemics, such as cholera, were brought under control through the works of John Snow (1854), Filippo Pacini (1854) and Robert Koch (1893), among others. Diseases such as hepatitis A, typhoid and paratyphoid, bacillary dysentery and infections by Escherichia coli are still significant health concerns in many countries of the Region, while endemic or imported cholera cases demand constant vigilance. Emerging pathogens in drinking-water have become increasingly important since the late 1980s. The newly identified and re-emerging water-related pathogens include Campylobacter spp. Such emerging pathogens in drinking-water have led to new demands in drinking-water hygiene, even in countries having achieved a high standard of water treatment since the late 1980s. In dependency on the route of transmission, waterborne pathogens must be subdivided into those that are transmitted via ingestion and those that are transmitted via inhalation or contact. It is important to distinguish between infections transmitted via ingestion and those transmitted via inhalation. Public health professionals need to be prepared for outbreaks and make contingency plans, including keeping abreast of new epidemiological insights. The challenges are particularly great in the eastern part of the Region, where strengthening primary health is a priority. In order to reduce the burden of water-related diseases in Europe, active involvement of all stakeholders is required. In particular, strengthening the relationship between public health Technical guidance on water-related disease surveillance page 3 services and the utilities managing the production and distribution of drinking-water should be seen as a priority challenge. The links between the two are detailed in the framework for safe drinking-water, as summarized in Fig 1. Primary health care promotes a holistic approach to health that makes prevention equally as important as cure. It aims to integrate health into all sectors, pursue collaborative models of policy dialogue, and increase stakeholder participation. In order to assist the cooperation between the different stakeholders involved in the implementation of the health framework, there is a need to strengthen understanding by primary health services of the approach followed by water utilities in their efforts to ensure safe water, and for understanding by the water utilities and other stakeholders of the techniques and approaches applied by (primary) health care services. The first section of these guidelines summarizes basic information on water-related pathogens and chemical contaminants. The second section introduces the different risk factors that affect drinking-water quality, from resource over treatment and distribution to the ultimate consumer and the steps taken by the water utilities to diminish the resulting risk through a multi-barrier approach. This section should allow health services to gain a fundamental insight into the basic approach to water safety from the viewpoint of a water utility, to identify the precise role of the (primary) health systems (in so far as they are not statutorily defined) and to interact in a Technical guidance on water-related disease surveillance page 4 meaningful way with water utilities and other stakeholders, particularly those tasked with environmental management. The third section of these guidelines then focuses on the specific management of health concerns relating to surveillance of water-related diseases. The difference between surveillance of drinking-waterborne infectious diseases and conventional surveillance systems is the integration of data from the drinking-water supply into the surveillance of infectious diseases. In order to promote a multisectoral approach, the guidelines outline basic epidemiological concepts and theoretical models relating to the specific challenges of waterborne disease surveillance. Guidance is offered on the correct formulation of surveillance programmes, including investigative activities undertaken to identify and evaluate risk factors associated with Technical guidance on water-related disease surveillance page 5 drinking-water. Counsel is offered on the setting up and operation of national surveillance systems, along with data and information management advice. Guidance will also be provided on evaluating existing surveillance systems and on how such systems could be improved. Health risks from microbial pathogens Lead authors: Friederike Dangendorf and Dirk Schoenen 2. The term also covers springs, wells or other collectors of water that are directly influenced by surface waters. Epidemiological definitions Water-associated diseases are classified into five main groups (according to Bradley, 1974): fi Waterborne diseases are caused by the ingestion of faecally contaminated water. Cholera and typhoid fever are classical examples of waterborne diseases, where only a few highly infectious pathogens are needed to cause severe diarrhoea. Shigellosis, hepatitis A, amoebic dysentery and other gastrointestinal diseases can also be waterborne. Pathogens are transmitted from person to person or by contact with contaminated surfaces. Eye and skin infections as well as diarrhoeal illnesses occur under these circumstances. A short list of the most important pathogens and their significance in water supplies is shown in Table 2. In particular, eye (trachoma) and skin infections (scabies), as well as diarrhoeal diseases occur under those conditions. They have spent one development cycle in aquatic molluscs, and another as fully grown parasites in other Technical guidance on water-related disease surveillance page 7 animal or human hosts. Because stagnating surface waters, such as reservoirs, are the preferred habitat of parasitic worms, the occurrence of water-based diseases such as dracunculiasis and schistosomiasis can be heavily influenced by anthropogenic activities. Insect vectors such as mosquitoes transmit diseases such as malaria, Chikungunya and other diseases. Waterborne pathogens and their significance in water supplies Pathogen Health Persistence Resistance Relative Important significance in water to infectivity animal supplies chlorine source Bacteria Campylobacter jejuni, C. High Multiply Low Moderate No Salmonella typhi High Moderate Low Low No Other Salmonella spp. High Short Low Moderate No Vibrio cholera High Short Low Low No Yersinia enterocolitica High Long Low Low Yes Viruses Adenoviruses High Long Moderate High No Enteroviruses High Long Moderate High No Hepatitis A High Long Moderate High No Hepatitis E High Long Moderate High Potentially Noroviruses and sapoviruses High Long Moderate High Potentially Rotaviruses High Long Moderate High No Protozoa Cryptosporidium parvum High Long High High Yes Entamoeba histolica High Moderate High High No Giardia intestinalis High Moderate High High Yes Helminths Dracunculus medinensis High Moderate Moderate High No Schistosoma spp. In order to evaluate the health risks of water-associated human-pathogenic microorganisms it is necessary to understand their ecology and epidemiology. In this chapter the ecology and epidemiology is described in detail for some of the most significant water-related infectious diseases. Diarrhoeal diseases 2 Diarrhoea occurs worldwide and causes 4% of all deaths and 5% of health loss due to disability. Diarrhoea is the passing of loose or liquid stools more frequently than is normal for the individual. Depending on the type of infection, the diarrhoea may be watery (for example in cholera) or passed with blood (in dysentery for example). Technical guidance on water-related disease surveillance page 8 events remains undetermined, especially when the episode is self-limiting. Cholera and dysentery cause severe, sometimes life-threatening forms of diarrhoea. Diarrhoea due to infection may last a few days, or several weeks (persistent diarrhoea). Severe diarrhoea may be life threatening due to fluid loss in watery diarrhoea, particularly in infants and young children, malnourished people and those with impaired immunity. The impact of repeated or persistent diarrhoea on nutrition, and the effect of malnutrition on susceptibility to infectious diarrhoea can be linked in a vicious cycle among children, especially in developing countries. Diarrhoea is a symptom of infection caused by a host of bacterial, viral and parasitic organisms, most of which can be spread by contaminated water. It is more common when there is a shortage of clean water for drinking, cooking and cleaning, and basic hygiene is important in prevention. Chemical irritation of the gut (such as that from magnesium sulfate or copper) or non-infectious bowel disease can also result in diarrhoea. Water contaminated with human faeces (for example from municipal sewage, septic tanks and latrines) is of particular concern.
Discount lexapro 20mg without prescription
In severe cases can anxiety symptoms kill you purchase lexapro 5 mg with amex, the normal balance of fluid and electrolytes can be restored by I. Severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance can be dangerous or deadly, in extreme cases, and needs medical attention. In dysentery, which is caused by some foodborne bacteria and other pathogens, diarrhea usually is severe and contains blood and mucus. They enter the bloodstream and travel to the cells of organs, where they are among the substances that enable the organs to function properly. Depending on the severity of the fluid and electrolyte imbalance, symptoms might include mild to severe weakness, confusion, and irregular heartbeat, among others. Laboratory tests can show if these symptoms are from an electrolyte imbalance, and if they are, the amounts of fluids and electrolytes you need to put your body back in balance. Some parasites (see definition) that live in freshwater can cause illness in humans if the water is used for drinking or for watering or rinsing fruits and vegetables, for example. Examples of hygienic behaviors in this book include handwashing, using clean cooking equipment, and keeping kitchen counters clean. They can become infected much more easily, get much sicker, and might not be able to get over the infection. Even foodborne illnesses that are mild, in most people, can be deadly to someone with a weak immune system. In some foodborne illnesses that cause diarrhea, this mucus is passed with the feces. A few types of fish and shellfish sometimes contain toxins that can cause neurologic symptoms. Depending on the toxin and the amount, problems may range from mild light-headedness that goes away by itself to paralysis. Worms that affect humans are too small to be seen with the naked eye at the life stage when they can cause an infection, but grow larger inside humans. Pasteurization applies a certain amount of heat for a certain amount of time, depending on the type of food or drink and the bacteria that are able to live and grow in it. And even though a food may be pasteurized, it still has to be stored properly afterwards; otherwise, harmful bacteria could grow in it. Toxins are poisons made by living things, such as the enterotoxins (see definition) made by some kinds of bacteria. Venoms are poisons that some animals, such as snakes, wasps, and lionfish, inject into other living things. Protozoans can act as parasites (definition appears above) and cause illness in humans. They produce more cysts, which then are passed through bowel movements into the outside world. Some of the more dangerous kinds of foodborne bacteria may be present in raw milk; for example, the types of E. For a few types of bacteria, the number is low, but, for many types, a fairly high number of bacterial cells has to be present in food to cause illness. If food is kept at 40fiF or below, it keeps bacterial cells from multiplying in food or greatly slows down the growth (with just a few exceptions). As important as refrigeration is, there are good reasons not to count on it as your only foodsafety measure. As noted, a few bacteria can multiply at refrigeration temperatures and even at average home-freezer temperatures. And unlike bacteria, which thrive on warmth, norovirus is most stable at cool storage temperatures. Because not everyone who is sick sees a health professional, some cases of illness go unreported. The numbers of cases probably would be substantially higher if unreported cases could be included.
Order genuine lexapro
However anxiety 8 year old buy lexapro discount, as the 42 study is based on drug sales data, there are many confounding variables that may influence the result, such as regional differences in prescribing patterns and policies, the age structure of the population and differences in drug purchasing behaviour. A similar study in the Canadian Province of Quebec, was also conducted by Barbeau et al. The obtained prevalences were then mapped according to the nine major hydrographic regions of Quebec. This area is also the largest user of various forms of pesticides, including herbicides, fungicides, mineral oils and insecticides. However, ecologic studies are rarely accepted as proof of causality because a number of competing interpretations of results is possible. Their main 43 limitation is that exposure and disease status are measured concurrently, therefore it is difficult to establish causation. The study found a significantly higher prevalence of a number of symptoms (plastic rigidity with cogwheel phenomenon, headache, fatigue, nervousness, memory complaints, and sleepiness) amongst the maneb-exposed workers. Another cross-sectional study, which was nested in a previous cohort study involving orchardists, examined symptoms of parkinsonism amongst exposed and unexposed workers. No associations were found for use of well water, farm employment or any specific pesticides. One of the major limitations with this study was the low percentage of the original cohort that participated in the cross-sectional study. Only 310 of the original 1300 subjects (24%) participated in the crosssectional survey as a large proportion were deceased (34%), could not be contacted (19%), were lost to follow-up (9%) or refused to participate (12%). A large cross-sectional study (n=4496) nested within the Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging examined environmental and lifestyle related factors (Baldereschi et al. Therefore, the welders may not have been representative of all welders in the community and 44 may have over-reported their welding exposures and/or symptoms. Welders were diagnosed with parkinsonism through videotaped footage rather than by physical examination by a neurologist and there was no mention of the validity of this method for measuring the outcome variable. Moreover, the study did not identify the prevalence of parkinsonism in the general community within the same geographic area but extrapolated data from an older study performed in a different and smaller geographic area (Schoenberg et al. In a case-control study, cases of the condition of interest are identified and their exposure status is determined. However, in order to determine if the exposure is associated with the condition of interest, the prevalence of the exposure in the population without the condition also needs to be established as a comparison. A control group is sampled from the entire source population that theoretically gives rise to the cases for this purpose. The review was limited to case-control studies to improve comparability between studies. The reference list of each of these journal articles was then reviewed for new case-control studies that had not been identified through the search of the databases. Seventy-one (71) peer-reviewed journal th articles were identified as at 4 of April 2002. Sixty-six articles were published in English, 1 in Chinese, 2 in French 1 in German and 1 in Japanese. The articles published in languages other than English were translated into English. The results from many of the studies were not directly compatible with each other due to differences in exposure definitions and measurement. Rather, the studies are summarised in table format (Tables B1-B6 in Appendix B) and the odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for each of the similar exposures from all the studies were plotted as a forest plot (Figures 2. Tables listing the bibliographic reference corresponding to each study number are listed in Appendix C. These may include:drinking well water contaminated with toxic substances, exposure to herbicides and pesticides associated with agriculture, and incidental agricultural exposure such as through pesticide spray drift. For example, detoxification pathways may be enhanced by low level exposure to contaminants common to urban environments. Significant positive associations were found with insecticide and herbicide exposure (Butterfield et al. The results for the 22 published case control studies that examined rural residency are presented in Table B1 (Appendix B) and are also displayed in Figure 2. Substantial variation in the estimates of risk associated with rural residency can be seen within each geographical region, suggesting that the variability between studies is not solely due to geographical differences, but also reflects differences between these individual studies. Further reasons to interpret the results of this study with caution include design limitations, such as a small sample size (38 cases and 76 controls consisting of two distinctly different control groups). The results of the 22 studies that examined well water as a potential risk factor are presented in Table B2 (Appendix B) and Figure 2. This may explain why well water has not been shown as a risk factor in all studies conducted in different geographical areas as not all groundwater would be uniformly contaminated. The authors identified China as a location where industrialisation has only occurred since 1949 and particularly in the two decades prior to the study. Some studies have also found statistically significant negative associations with certain types of farming (Tanner et al. Differences in results may, in part, be explained by geographical variability in farming practices between study areas. Whereas farming practices in western countries are likely to have included the use of pesticides for a longer duration. Farming is a diverse occupational field involving a multitude of different crops, herds and practices. After the effect due to occupational pesticide exposure was removed, farming still appeared to be a risk factor, independent of pesticide exposure. Possible dose-response relationships were seen in a Canadian study for the variables of agricultural work, field crop farming and grain farming (Semchuk et al. The results of the 21 studies examining exposure to farming as a variable are presented in Table B3 (Appendix B). Exposure Location Size 2 Grain Farming Canada 390 Market 2 Canada 390 Gardening Grain Farming 2 Canada 390 adjusted for Field farming adj 2 Canada 390 for herbicides Field crop 2 Canada 390 farming Hard Fruit 3 Canada 266 Orchard (women) Soft Fruit Orchard 3 Canada 266 (Women) Crop farming 3 Canada 266 (men) Soft fruit orchard 3 Canada 264 (men) Hard fruit orchard 3 Canada 264 (men) Hard Fruit 3 Canada 263 Orchard (women) Soft Fruit Orchard 3 Canada 263 (Women) Hard Fruit 3 Canada 263 Orchard (Men) Soft Fruit Orchard 3 Canada 263 (men) Crop farming 3 Canada 263 (men) Ever worked 3 Canada 179 (Orchard) 3 Orchard work Canada 179 15 Growing Fruit Taiwan 360 15 Growing Rice Taiwan 360 6 Wheat growing China 300 6 Corn growing China 300 6 Soybean raising China 300 6 Fruit growing China 300 6 Rice growing China 300 0. Non-significant, but elevated odds ratios have also been reported by some studies (Fall et al. The study had a number of strengths, such as the large sample size and use of a structured face to face interview and job exposure matrix to improve data quality and reduce recall bias. The results of the 26 studies examining exposure to pesticides as a variable are presented in Table B4 (Appendix B). A number of factors such as differences in types and severity of exposure and type of metal involved in the studies are likely to explain some of these conflicting results. Studies that divided the exposures into different categories according to length of exposure were more likely to find some significant associations (Gorell et al. This could possibly be a result of less rigorous protective measures used in a hobby situation compared to in a workplace.
Order lexapro 5 mg overnight delivery
Although eficigarettes have the bloodstream; and how additives to the efiliquid affect been used as a cessation device anxiety meaning cheap 5mg lexapro, the evidence supporting the the bioavailability of these compounds, among other confi effectiveness of eficigarettes as an aid for quitting convenfi siderations. Research is also needed to understand whether tional cigarettes remains extremely weak for adults (Bullen potential health risks may be ameliorated by changes in et al. Nicotine can cross the placenta and has known effects and toxicants, are not completely understood. Ingestion of eficigarette liquids containing nicotine can cause acute toxicity and possibly death if the 3. Eficigarettes can expose users to several chemicals, contents of refll cartridges or bottles containing including nicotine, carbonyl compounds, and volfi nicotine are consumed. Youth and Young Adults 125 A Report of the Surgeon General References Adriani W, Macri S, Pacifci R, Laviola G. Flavoring chemicals in Comparison of electronic cigarette refll fuid cytotoxfi eficigarettes: diacetyl, 2, 3fipentanedione, and acetoin in icity using embryonic and adult models. Electronic opmental in vivo nicotine exposure on prefrontal attenfi Cigarettes and Liquid Nicotine Data, 2016; < tion circuitry. Kids and vapor: a 4fiyear analysis of pediatric expofi American Efiliquid Manufacturing Standards Association. Shimato A, Sakakibara N, Soh Y, Mamiya T, Nagai T, Identifcation of toxicants in cinnamonfifavored et al. Extensive burn injury maternal smoking, childhood obesity, and metafi caused by fundamental electronic cigarette design faw. Cardiovascular toxicity of nicfi longfiterm behavioral effects of a single nicotine injecfi otine: Implications for electronic cigarette use. Perinatal nicotine expofi Continuous nicotine administration produces selective, sure eliminates peak in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agefidependent structural alteration of pyramidal neufi response in adolescent rats. Smoking predicts suicidfi the enhanced vulnerability of the adolescent brain ality: fndings from a prospective community study. Eficigarettes and cardiovascular disease risk; arette smoking among African Americans and Puerto evaluation of evidence, policy implications, and recfi Ricans from adolescence to young adulthood: associfi ommendations. Elevated risk of tobacco mouthpiecefibased computerized devices versus dependence among offspring of mothers who smoked direct observation. Variable and potentially fatal amounts decline of forced expiratory volume in one second in of nicotine in eficigarette nicotine solutions. Modulation of cell adhesion systems by prefi tidefiexpressing neurons in hypothalamus and amygfi natal nicotine exposure in limbic brain regions of dala. Insecticidal activities of leaf essential oils from stitute: a prospective 12fimonth randomized control Cinnamomum osmophloeum against three mosquito design study. A preliminary experifi Salminen O, Belozertseva I, Galankin T, Tuominen mental investigation of peer infuence on riskfitaking R, Zvartau E. Perinatal exposure to nicotine causes of the association between maternal smoking during defcits associated with a loss of nicotinic receptor funcfi pregnancy and offspring substance use and problems. Acrolein initiates rat urinary bladder carcinogenfi pregnancy and offspring externalizing problems: an esis. Adolescent brain development: a period of vulfi approach to modeling potential bystander exposures nerabilities and opportunities. Acrolein exposure is associated with increased now/2015/01/13/electronicficigarettefigymfiexplosionfi cardiovascular disease risk. Adult and perifi externalizing symptoms: bridging the behavior genetic adolescent rats differ in expression of nicotinic cholinfi and behavior teratologic divide. Explaining the effects of electronic cigarettes gata: interfirelationship with the serotonergic system. Dependence levels in users of elecfi smoking during pregnancy: impact on otoacoustic tronic cigarettes, nicotine gums and tobacco cigarettes. A proposal tronic cigarette cartridges and refll fuids: review of for a safe exposure level for diacetyl. International term effects of a nicotinefifree eficigarette compared to Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health a traditional cigarette in smokers and nonfismokers. Perinatal nicotine exposure impairs of electronic cigarette liquids and aerosol for the presfi ability of newborn rats to autoresuscitate from ence of selected inhalation toxins. Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence: 2008 who had achieved complete substitution of smoking. Evaluation of electronic cigarette use Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association of the United (vaping) topography and estimation of liquid consumpfi States. Acute impact of active and passive elecfi tronic cigarette use: comparison between frst and newfi tronic cigarette smoking on serum cotinine and lung generation devices. International Journal of Environmental Research cigarette smoking on complete blood count. Department of Health and Human among a large sample of exfismoking eficigarette users. Maternal parameters on particle concentration and size distribufi smoking during pregnancy and psychiatric adjustment tion in the mainstream of eficigarettes. Greater risk sensitivity of dorsolateral Health Effects of E-Cigarette Use Among U. Prenatal exposure to nicotine causes postfi ogens and toxicants in vapour from electronic cigafi natal obesity and altered perivascular adipose tissue rettes. Prenatal nicotine exposure enhances the trigemifi pendent genetically sensitive research designs. Nicotine exposure during selffimedicate attentional and emotional dysfuncfi adolescence leads to shortfi and longfiterm changes tions.
Order 20 mg lexapro
These experts help make plans for building anxiety relief purchase discount lexapro on line, maintaining, and renovating health-care facilities to ensure that the adverse impact of the environment on the incidence of health-care associated infections is minimal. The purpose of this guideline is to provide useful information for both health-care professionals and engineers in efforts to provide a safe environment in which quality health care may be provided to patients. The recommendations herein provide guidance to minimize the risk for and prevent transmission of pathogens in the indoor environment. Key Terms Used in this Guideline Although Appendix A provides definitions for terms discussed in Part I, several terms that pertain to specific patient-care areas and patients who are at risk for health-care associated opportunistic infections are presented here. Specific engineering parameters for these care areas are discussed more fully in the text. The use of personal respiratory protection is also indicated for persons entering these rooms. Immunocompromised patients are those patients whose immune mechanisms are deficient because of immunologic disorders. Immunocompromised patients who are identified as high-risk patients have the greatest risk of infection caused by airborne or waterborne microorganisms. Patients in this subset include those who are severely neutropenic for prolonged periods of time. Modes of Transmission of Airborne Diseases A variety of airborne infections in susceptible hosts can result from exposures to clinically significant microorganisms released into the air when environmental reservoirs. Once these materials are brought indoors into a health-care facility by any of a number of vehicles. Respiratory infections can be acquired from exposure to pathogens contained either in droplets or droplet nuclei. When droplets are produced during a sneeze or cough, a cloud of infectious particles >5 fim in size is expelled, resulting in the potential exposure of susceptible persons within 3 feet of the source person. Because these agents primarily are transmitted directly and because the droplets tend to fall out of the air quickly, measures to control air flow in a health-care facility. Strategies to control the spread of these diseases are outlined in another guideline. With this enhanced buoyancy, the spores, which resist desiccation, can remain airborne indefinitely in air currents and travel far from their source. Aspergillosis and Other Fungal Diseases Aspergillosis is caused by molds belonging to the genus Aspergillus. Clinical and epidemiologic aspects of aspergillosis (Table 1) are discussed extensively in another guideline. Increased levels of atmospheric dust and fungal spores have been associated with clusters of health-care acquired infections in immunocompromised patients. Patient-care items, devices, Last update: July 2019 21 of 241 Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Health-Care Facilities (2003) and equipment can become contaminated with Aspergillus spp. Environmental fungal pathogens: entry into and contamination of the healthcare facility Fungal pathogen Implicated environmental vehicle Aspergillus spp. There have been at least three outbreaks linked to contamination of the filtering systems from bird droppings98, 103, 104 Pigeon mites may gain access into a health-care facility through the ventilation system. However, viable particles of <2 fim diameter (and thus permissive to alveolar deposition) have been found in soil contaminated with bird droppings, particularly from pigeons. Substantial numbers of these infectious particles have been associated with chicken coops and the roosts of blackbirds. After the 1994 earthquake centered near Northridge, California, the incidence of coccidioidomycosis in the surrounding area exceeded the historical norm. Tuberculosis and Other Bacterial Diseases the bacterium most commonly associated with airborne transmission is Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Last update: July 2019 23 of 241 Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Health-Care Facilities (2003) Format Change [November 2016]: the format of this section was changed to improve readability and accessibility. These organisms can be shed from heavily colonized persons and discharged into the air. Other gram-positive bacteria linked to airborne transmission include Bacillus spp. Outbreaks and pseudo-outbreaks have been attributed to Bacillus cereus in maternity, pediatric, intensive care, and bronchoscopy units; many of these episodes were secondary to environmental contamination. In one epidemiologic investigation of bloodstream infections among pediatric patients, identical Acinetobacter spp. However, because water is the source of the organisms and exposure occurs in the vicinity of the aerosol, the discussion of the diseases associated with such aerosols and the prevention measures used to curtail their spread is discussed in another section of the Guideline (see Part I: Water). Airborne Viral Diseases Some human viruses are transmitted from person to person via droplet aerosols, but very few viruses are consistently airborne in transmission. Consequently, infection-control measures used to prevent spread of these viral diseases in health-care facilities primarily involve patient isolation, vaccination of susceptible persons, and antiviral therapy as appropriate rather than measures to control air flow or quality. The factors facilitating airborne distribution of these viruses in an infective state are unknown, but a presumed requirement is a source patient in the early stage of infection who is shedding large numbers of viral particles into the air. An outbreak of a Norwalk-like virus infection involving more than 600 staff personnel over a 3-week period was investigated in a Toronto, Ontario hospital in 1985; common sources. Airborne transmission may play a role in the natural spread of hantaviruses and certain hemorrhagic fever viruses. Last update: July 2019 26 of 241 Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Health-Care Facilities (2003) Table 4. Microorganisms associated with airborne transmission* Evidence for airborne transmission Fungi Bacteria Viruses Numerous reports Aspergillus spp. Potential for airborne transmission increases with patients who are effective disseminators present in facilities with low relative humidity in the air and faulty ventilation. More than 40 state agencies that license health-care facilities have either incorporated or adopted by reference these guidelines into their state standards. Diagram of a ventilation system* Outdoor air and recirculated air pass through air cleaners. Air is conditioned for temperature and humidity before it enters the occupied space as supply air. Infiltration is air leakage inward through cracks and interstitial spaces of walls, floors, and ceilings. Return air is largely exhausted from the system, but a portion is recirculated with fresh, incoming air. The air enters the distribution system for conditioning to appropriate temperature and humidity levels, passes through an additional bank of filters for further cleaning, and is delivered to each zone of the building. Filter Types and Methods of Filtration Filtration, the physical removal of particulates from air, is the first step in achieving acceptable indoor air quality. The performance of filters with fi90% efficiency is measured using either the dust-spot test or the weight-arrestance test. Filtration methods* Basic method Principle of performance Filtering efficiency Particles in the air are larger than the openings between the filter Straining Low fibers, resulting in gross removal of large particles. Particles enter into the filter and become entrapped and attached Interception Medium to the filter fibers. Small particles, moving in erratic motion, collide with filter fibers Diffusion High and remain attached. Particles bearing negative electrostatic charge are attracted to the Electrostatic High filter with positively charged fibers. This filtration system is adequate for most patient-care areas in ambulatory-care facilities and hospitals, including the operating room environment and areas providing central services. A metal frame has no advantage over a properly fitted wood frame with respect to performance, but wood can compromise the air quality if it becomes and remains wet, allowing the growth of fungi and bacteria. Filter Maintenance Efficiency of the filtration system is dependent on the density of the filters, which can create a drop in pressure unless compensated by stronger and more efficient fans, thus maintaining air flow. The pressure differential across filters is measured by use of manometers or other gauges.
Order lexapro visa
A proportion of the general population perhaps up to 50 per cent are slow acetylators anxiety jitters buy generic lexapro 20mg line. This rises to as high a level as 80 per cent among the chemically sensitive population. Their N-acetyltransferase activity is thought to be reduced, and this prolongs the action of drugs and other toxic chemicals, thus enhancing their toxicity. Slow acetylators have a build up of toxins in the system and rapid acetylators add acetyl groups so rapidly that they make mistakes in the process. Both slow and rapid acetylators are at increased risk for toxic overload if they are exposed to environmental toxins. Urinary bladder cancer appears to have the most consistent association with low acetyleation. Amino acid conjugation: the conjugation of toxins with amino acids occurs in this pathway. The amino acids commonly used in this pathway include glycine, taurine and glutamine, but arginine, and ornithine are also used. These amino acids help to excrete many toxic chemicals, called xenobiotics, from the environment. Amino acids are found in protein-rich foods if they are eaten in adequate amounts. Conjugation of bile acids in the liver with glycine or taurine is essential for the efficient removal of these potentially toxic compounds. Disturbed acylation by pollutant overload decreases proper levels 18 of bile in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in poor assimilation of lipids and fat-soluble vitamins, and disturbed cholesterol metabolism. Glycination Pathway Salicylates and benzoate are detoxified primarily through glycination. Benzoate is present in many food substances and is widely used as a food preservative. Patients suffering from xenobiotic overloads and environmental toxicity may not have sufficient amounts of glycine to cope with the amount of toxins they are carrying. People suffering from hepatitis, alcoholic liver disorders, carcinomas, chronic arthritis, hypothyroidism, toxemia of pregnancy, and excessive chemical exposure are commonly found to have a poorly functioning amino acid conjugation system. For example, using the benzoate clearance test (a measure of the rate at which the body detoxifies benzoate by conjugating it with glycine to form hippuric acid, which is excreted by the kidneys), the rate of clearance in those with liver disease is 50% of that in healthy adults Even in apparently normal adults, a wide variation exists in the activity of the glycine conjugation pathway. This is due not only to genetic variation, but also to the availability of glycine in the liver. Glycine, and the other amino acids used for conjugation, become deficient on a lowprotein diet and when chronic exposure to toxins results in depletion. Toluene, the most popular industrial organic solvent, is converted by the liver into benzoate, which, like aspirin and other salicylates, must then be detoxified by conjugation with the amino acid glycine (glycination). Glycine is a commonly available amino acid, but the capacity to synthesize taurine may be limited by low activity of the enzyme cysteine-sulfinic acid decarboxylase. Damage can occur to this enzyme directly by pollutants, or by overload/over-use resulting in depletion. Environmental medicine specialists may alkalinize over-acidic patients by administering sodium and potassium bicarbonate in order to facilitate these reactions. The principle amino acid methionine drives this pathway, which requires co-factors Vitamin B12, Folic Acid (B9) and Choline to function properly. Methylation eventually yields usable sulfate with the help of the trace mineral molybdenum. Sulfoxidation transforms toxic sulfite molecules into sulfate with the assistance of the mineral molybdenum. For example, they are often found in wine, dried fruit, dehydrated foods, seasonings, and salad dressings. Ironically, sulfites, which can be highly allergenic and can interfere with breathing in those who are sensitive to them, are also added to some asthma medications. Its effects in preventing estrogen-induced cholestasis (stagnation of bile in the gall bladder) have been demonstrated in pregnant women and those on oral contraceptives. In addition to its role in promoting estrogen excretion, methionine has been shown to increase the membrane fluidity that is typically decreased by estrogens, thereby restoring several factors that promote bile flow. Methionine is a major source of numerous sulfur-containing compounds, including the amino acids cysteine and taurine. According to environmental medicine specialist William Rae, the process most often disturbed in the chemically sensitive involves methylation reactions catalysed by S-adenosyl-L-methoninedependent enzymes. Methionine is the chief methyl donor to detoxify amines, phenols, thiols, noradrenaline, adrenaline, dopamine, melatonin, L-dopa, histamine, serotonin, pyridine, sulphites and hypochlorites into compounds excreted through the lungs. The activity of the methyltransferase enzyme is dependent on magnesium, and, due to the frequency of magnesium deficiency, supplementation with this nutrient will often stabilize chemically sensitive patients. Catechol-O-methyl transferase is the enzyme primarily responsible for breaking down the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. Risk may be increased for some neuropsychiatric disorders, imparied estrogen metabolism, increased sensitivity to pain, and late-onset alcoholism. Note: Epinephrine is the same as adrenaline, and norepinephrine is the same as noradrenaline. Minimizing Risks: Avoid excessive alcohol consumption; seek help if alcohol consumption is a health issue. Filtration of toxins is absolutely critical as the blood from the intestines contains high levels of bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, antigen-antibody complexes, and various other toxic substances. When working properly, the liver clears 99% of the bacteria and other toxins during the first pass. However, when the liver is damaged, such as in alcoholics, the passage of toxins increases by over a factor of 10. Sulfoxidation Sulfoxidation is the process by which the sulfur-containing molecules in drugs and foods are metabolized. It is also the process by which the body eliminates the sulfite food additives used 20 to preserve many foods and drugs. Various sulfites are widely used in potato salad (as a preservative), salad bars (to keep the vegetables looking fresh), dried fruits (sulfites keep dried apricots orange), and some drugs. Normally, the enzyme sulfite oxidase metabolizes sulfites to safer sulfates, which are then excreted in the urine. Those with a poorly functioning sulfoxidation system, however, have an increased ratio of sulfite to sulfate in their urine. The strong odor in the urine after eating asparagus is an interesting phenomenon because, while it is unheard of in China, 100% of the French have been estimated to experience such an odor (about 50% of adults in the U. This example is an excellent example of genetic variability in liver detoxification function. Those with a poorly functioning sulfoxidation detoxification pathway are more sensitive to sulfur-containing drugs and foods containing sulfur or sulfite additives. This is especially important for asthmatics, which can react to these additives with lifethreatening attacks. Molybdenum helps asthmatics with an elevated ratio of sulfites to sulfates in their urine because sulfite oxidase is dependent upon this trace mineral. Each day the liver manufactures approximately 1 quart of bile, which serves as a carrier in which many toxic substances are dumped into the intestines. In the intestines, the bile and its toxic load are absorbed by fiber and excreted. However, a diet low in fiber results in inadequate binding and reabsorption of the toxins. This problem is magnified when bacteria in the intestine modify these toxins to more damaging forms. Cholestasis has several causes, including obstruction of the bile ducts and impairment of bile flow within the liver. The most common cause of obstruction of the bile ducts is the presence of gallstones. Nearly 20% of the female and 8% of the male population over the age of 40 are found to have gallstones on biopsy and approximately 500,000 gall bladders are removed because of stones each year in the U.

