Piroxicam
Order piroxicam overnight delivery
The other two parasites are surroundings arthritis diet dogs 20mg piroxicam overnight delivery, personnel hygiene (washing hands found in central and south America (Acha and of children after they play with pets), proper disSzyfres 2006). The infection occurs due to the paraDog and foxes act as definitive hosts for sites belonging to the species Echinococcus E. The metacestode infection is comIntermediate host: Rodents monly known as hydatidosis. Although throughout their life, but the disease causes rare, but disease is malignant and highly fatal significant economic losses in most of the food among infected human beings. Large-sized hydatid cysts can cause symptoms in the animals due to pressure atrophy of the affected organ(s) (Schwabe 1986). The cysts are responsible for reduced growth and milk production especially in dairy animals. In human beings, radiography along with serological confirmation is routinely used for diagnosis of the parasite (Figs. The parasite has been recorded across the globe but is commonly found in eastern Asia (Viroj 2005) viz. Ingestion of larvae from cyclops (copepod; first intermediate host) or frogs can lead to infection in humans, pigs and mice (Fukushima and Yamane 1999; Nithiuthai et al. Second stage larvae (spargana) during their migration in these hosts (reptiles-snakes; mammals such as pigs and human beings) cause the disease (Mueller 1974; Fig. Use of infected frog as a bandage and pressing it on the ulcers, skin and the infection generally remains asymptomatic eye could lead to transmission of the parasite in intermediate and definitive hosts but could through mucous membranes (Mueller 1974; cause weight loss and emaciation in cats. But acciTaeniasis is a true zoonotic infection dental ingestion of eggs of the parasite (Euzoonoses) where pig and cattle act as inter(T. Pigs and human beings can become infected after ingestion of eggs shed by human carriers. Sewage farming is another important risk factor for neurocysticthe infection occurs due to T. The cysticerci have Neurocysticercosis is an important public health tendency to develop in the brain tissue leading to issue and is responsible for neurological disorneurocysticercosis (Garcia et al. Small cysts can be seen in many organs Cysticercosis is mainly diagnosed at the time of such as skeletal muscles and some visceral post mortem examination in pigs (Figs. Oribatid mites act as intermediate time before consumption can help prevent the host where cysticercoid stage occurs. The parasite infects gastrointestinal asymptomatic but there might be abdominal system and may cause abdominal pain, diarpain, diarrhoea and general fatigue in some rhoea, weakness, etc. Rodents act as principal and rare human infections occur after accidenhost for these parasites but the parasite could tal ingestion of food contaminated with infected infect humans, particularly children (Goswami arthropod (Acha and Szyfres 2006). The parasite has been recorded from site generally remains asymptomatic but could many parts of the world (Marangi et al. The life cycle of parasite is direct with the infection through faecal oral route in humans, but rat may play role in the transmission of the disReferences ease due to contamination of human food with rat faeces. Case report epidemiology and molecular characterization of coeand literature review. In: Singh G, Prabhakar S Ishimoto K (2007) Dipylidium caninum infection in (eds)Taeniasoliumcysticercosis:frombasictoclinical an infant. An overview of the epidemiology, transmission, clinical manifestations and diagnosis of zoonotic nematodes is presented, along with methods of prevention and control. Angiostrongylosis is endemic in south Asia, Pacific islands, Australia, China and Caribbean islands. Zoonotic ascariasis due to Ascaris suum has been widely reported in North America and some European countries. Baylisascaris procyonis, the intestinal roundworm of raccoons has been reported to cause severe neurologic disease in man. The provision of safe food and water in the non-industrialised countries is of utmost importance for the prevention and control of these diseases. Till date, seven cases of paratenic host (Roberts and Janovy 2005) or due acanthocephlus have been reported (Roberts to incidental consumption of intermediate host and Janovy 2005; Berenji et al. The definitive Roberts and Janovy 2005) and Acanthocephalus hosts become infected after eating the intermerauschi (Marquards et al. The morphological parameters of pain, perforation of the intestine, fatigue, diarthe parasite have been described in detail by rhoea, anorexia, irritability and intermittent burndifferent authors (Lawlor et al. Angiostrongylus costaricensis caumove more slowly and travel shorter distances ses abdominal eosinophilic granulomas in Cen(Moore et al. The crustaceans (prawns and land Humans should avoid ingestion of intermediate crabs), predacious land planarians (fiatworms in or paratenic host. These first stage larvae are eaten up Order: Strongylida by snails and slugs, and further develop into Superfamily: Metastrongyloidea infective larvae (third stage). Man and rats become infected after consuming infected snail or contaminated vegetables. The cycle is completed when definitive host ingest infective larvae the disease can be diagnosed after detection of released from slugs (Fig. The other important symptoms include headache, neck stiffness, paraesthesia, vomition and nausea (Wang et al. Fish and some occurs due to accidental ingestion of the parasite cuttlefish act as paratenic hosts (Caramello et al. Human beings become infected after consumption of third stage larvae present in infected salt-water fish or cephalopod mollusc 5. In fish, larvae generally localise on the surface of visceral organs, body cavity and occasionally on the 5. Other definitive hosts the disease can occur due to Anisakis, Pseudoinclude birds, reptiles and amphibians (Fig. The dislead to urticaria, angioedema and anaphylactic ease is common in Japan (about 2000 cases/year) shock associated with other gastrointestinal but cases have also been recorded from northern symptoms (Caramello et al. Further changes include invasion of the gut wall, and eosinophilic granuloma, or perforation which 5. The parasite larvae may lead to liver atrophy, perforations of the stomach wall, visceral adhe5. In marine mammals, parasites have been the adult parasites are present in stomach of found embedded in gastric mucosa tumours marine fish (whales and dolphins). Ascariosis occurs due to Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum; two closely related species 5.
Cheap piroxicam
Information for management purposes should receive priority support in view of the intensity and magnitude of the changes occurring in the coastal and marine areas arthritis pain relief elbow discount piroxicam 20 mg without prescription. Develop and maintain databases for assessment and management of coastal areas and all seas and their resources; b. Conduct regular environmental assessment of the state of the environment of coastal and marine areas; d. Prepare and maintain profiles of coastal area resources, activities, uses, habitats and protected areas based on the criteria of sustainable development;. Cooperation with developing countries, and, where applicable, subregional and regional mechanisms, should be strengthened to improve their capacities to achieve the above. The role of international cooperation and coordination on a bilateral basis and, where applicable, within a subregional, interregional, regional or global framework, is to support and supplement national efforts of coastal States to promote integrated management and sustainable development of coastal and marine areas. States should cooperate, as appropriate, in the preparation of national guidelines for integrated coastal zone management and development, drawing on existing experience. A global conference to exchange experience in the field could be held before 1994. The Conference secretariat has estimated the average total annual cost (1993-2000) of implementing the activities of this programme to be about $6 billion including about $50 million from the international community on grant or concessional terms. States should cooperate in the development of necessary coastal systematic observation, research and information management systems. They should provide access to and transfer environmentally safe technologies and methodologies for sustainable development of coastal and marine areas to developing countries. They should also develop technologies and endogenous scientific and technological capacities. International organizations, whether subregional, regional or global, as appropriate, should support coastal States, upon request, in these efforts, as indicated above, devoting special attention to developing countries. Coastal States should promote and facilitate the organization of education and training in integrated coastal and marine management and sustainable development for scientists, technologists, managers (including community-based managers) and users, leaders, indigenous peoples, fisherfolk, women and youth, among others. Management and development, as well as environmental protection concerns and local planning issues, should be incorporated in educational curricula and public awareness campaigns, with due regard to traditional ecological knowledge and socio-cultural values. International organizations, whet her subregional, regional or global, as appropriate, should support coastal States, upon request, in the areas indicated above, devoting special attention to developing countries. Full cooperation should be extended, upon request, to coastal States in their capacity-building efforts and, where appropriate, capacity-building should be included in bilateral and multilateral development cooperation. Consulting on coastal and marine issues with local administrations, the business community, the academic sector, resource user groups and the general public; c. Identifying existing and potential capabilities, facilities and needs for human resources development and scientific and technological infrastructure;. Supporting "centres of excellence" in integrated coastal and marine resource management; h. Supporting pilot demonstration programmes and projects in integrated coastal and marine management. Land-based sources contribute 70 per cent of marine pollution, while maritime transport and dumping-at-sea activities contribute 10 per cent each. Many of the polluting substances originating from land-based sources are of particular concern to the marine environment since they exhibit at the same time toxicity, persistence and bioaccumulation in the food chain. There is currently no global scheme to address marine pollution from land-based sources. Degradation of the marine environment can also result from a wide range of activities on land. Human settlements, land use, construction of coastal infrastructure, agriculture, forestry, urban development, tourism and industry can affect the marine environment. Approximately 600,000 tons of oil enter the oceans each year as a result of normal shipping operations, accidents and illegal discharges. With respect to offshore oil and gas activities, currently machinery space discharges are regulated internationally and six regional conventions to control platform discharges have been under consideration. The nature and extent of environmental impacts from offshore oil exploration and production activities generally account for a very small proportion of marine pollution. A precautionary and anticipatory rather than a reactive approach is necessary to prevent the degradation of the marine environment. This requires, inter alia, the adoption of precautionary measures, environmental impact assessments, clean production techniques, recycling, waste audits and minimization, construction and/or improvement of sewage treatment facilities, quality management criteria for the proper handling of hazardous substances, and a comprehensive approach to damaging impacts from air, land and water. Any management framework must include the improvement of coastal human settlements and the integrated management and development of coastal areas. States, in accordance with the provisions of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea on protection and preservation of the marine environment, commit themselves, in accordance with their policies, priorities and resources, to prevent, reduce and control degradation of the marine environment so as to maintain and improve its life-support and productive capacities. Apply preventive, precautionary and anticipatory approaches so as to avoid degradation of the marine environment, as well as to reduce the risk of long-term or irreversible adverse effects upon it; b. Ensure prior assessment of activities that may have significant adverse impacts upon the marine environment; c. Integrate protection of the marine environment into relevant general environmental, social and economic development policies; d. Develop economic incentives, where appropriate, to apply clean technologies and other means consistent with the internalization of environmental costs, such as the polluter pays principle, so as to avoid degradation of the marine environment;. Improve the living standards of coastal populations, particularly in developing countries, so as to contribute to reducing the degradation of the coastal and marine environment. States agree that provision of additional financial resources, through appropriate international mechanisms, as well as access to cleaner technologies and relevant research, would be necessary to support action by developing countries to implement this commitment. Activities (a) Management-related activities Prevention, reduction and control of degradation of the marine environment from land-based activities 17. In carrying out their commitment to deal with degradation of the marine environment from landbased activities, States should take action at the national level and, where appropriate, at the regional and subregional levels, in concert with action to implement programme area A, and should take account of the Montreal Guidelines for the Protection of the Marine Environment from Land-Based Sources. To this end, States, with the support of the relevant international environmental, scientific, technical and financial organizations, should cooperate, inter alia, to: a. Consider updating, strengthening and extending the Montreal Guidelines, as appropriate; b. Assess the effectiveness of existing regional agreements and action plans, where appropriate, with a view to identifying means of strengthening action, where necessary, to prevent, reduce and control marine degradation caused by land-based activities; c. Initiate and promote the development of new regional agreements, where appropriate; d. Develop means of providing guidance on technologies to deal with the major types of pollution of the marine environment from land-based sources, according to the best scientific evidence;. Incorporating sewage concerns when formulating or reviewing coastal development plans, including human settlement plans; b. Building and maintaining sewage treatment facilities in accordance with national policies and capacities and international cooperation available; c. Locating coastal outfalls so as to maintain an acceptable level of environmental quality and to avoid exposing shell fisheries, water intakes and bathing areas to pathogens; d. Promoting environmentally sound co-treatments of domestic and compatible industrial effluents, with the introduction, where practicable, of controls on the entry of effluents that are not compatible with the system;. Promoting primary treatment of municipal sewage discharged to rivers, estuaries and the sea, or other solutions appropriate to specific sites; f. Establishing and improving local, national, subregional and regional, as necessary, regulatory and monitoring programmes to control effluent discharge, using minimum sewage effluent guidelines and water quality criteria and giving due consideration to the characteristics of receiving bodies and the volume and type of pollutants. As concerns other sources of pollution, priority actions to be considered by States may include: a. Establishing or improving, as necessary, regulatory and monitoring programmes to control effluent discharges and emissions, including the development and application of control and recycling technologies; b. Promoting risk and environmental impact assessments to help ensure an acceptable level of environmental quality; c. Promoting assessment and cooperation at the regional level, where appropriate, with respect to the input of point source pollutants from new installations; d. Eliminating the emission or discharge of organohalogen compounds that threaten to accumulate to dangerous levels in the marine environment;. Reducing the emission or discharge of other synthetic organic compounds that threaten to accumulate to dangerous levels in the marine environment; f. Promoting controls over anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen and phosphorus that enter coastal waters where such problems as eutrophication threaten the marine environment or its resources; g.
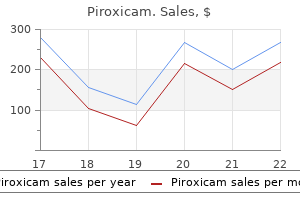
| Comparative prices of Piroxicam | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Family Dollar | 410 |
| 2 | Best Buy | 551 |
| 3 | Burger King Holdings | 203 |
| 4 | Subway | 662 |
| 5 | Army Air Force Exchange | 488 |
| 6 | Tractor Supply Co. | 770 |
| 7 | PetSmart | 320 |
| 8 | Office Depot | 709 |
| 9 | Hy-Vee | 494 |
Discount piroxicam 20 mg on-line
Sirolimus-induced angiotion of adverse reaction to intravenous immune serum globulin infuedema reactive arthritis in feet discount 20mg piroxicam mastercard. Severe anaphylactic reaction after not responding to antihistamines and/or corticosteroids. Provocative challenge with induction of general anesthesia: subsequent evaluation and managelocal anesthetics in patients with a prior history of reaction. Intolerance to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs might precede by years the onset of chronic urticaria. Clopidogrel hypersensitivity synlactic reactions to iodinated contrast material. Hypersensitivity reactions to cancer cryoglobulinaemia-related vasculitis following treatment of hepatitis C chemotherapeutic agents [in Japanese]. Complementary and imab therapy are common in young children with inflammatory bowel alternative remedies: an additional source of potential systemic nickel disease. Guillain-Barre and Miller Fisher following intravenous phytonadione (vitamin K1): a 5-year retrospecsyndromes occurring with tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonist thertive review. Peripheral neuropathy in two N-acetylcysteine: a prospective case controlled study. Transagainst patent blue during sentinel lymph node removal in three melplantation. Anaphylaxis to isosulfan a humanized murine antibody after anaphylaxis to a chimeric murine blue. A phase I study of visilidyes during the perioperative period: reports of 14 clinical cases. Whether the upper or plied policy of the Department of Vetlower extremities, the back or abdomerans Affairs to administer the law inal wall, the eyes or ears, or the carunder a broad interpretation, condiovascular, digestive, or other system, sistent, however, with the facts shown or psyche are affected, evaluations are in every case. When after careful conbased upon lack of usefulness, of these sideration of all procurable and assemparts or systems, especially in self-supbled data, a reasonable doubt arises report. This imposes upon the medical garding the degree of disability such examiner the responsibility of furdoubt will be resolved in favor of the nishing, in addition to the etiological, claimant. Every element fortable at home or upon limited activin any way affecting the probative ity. Otherwise, the lower ratchange in evaluation is to be made, the ing will be assigned. Disability from injuries to the muspensation may be assigned, where the cles, nerves, and joints of an extremity schedular rating is less than total, may overlap to a great extent, so that when the disabled person is, in the special rules are included in the approjudgment of the rating agency, unable priate bodily system for their evaluato secure or follow a substantially tion. Dyspnea, tachycardia, nervousgainful occupation as a result of servness, fatigability, etc. Both the use of ability, this disability shall be ratable manifestations not resulting from servat 60 percent or more, and that, if there ice-connected disease or injury in esare two or more disabilities, there shall tablishing the service-connected evalbe at least one disability ratable at 40 uation, and the evaluation of the same percent or more, and sufficient addimanifestation under different diagtional disability to bring the combined noses are to be avoided. The rating, however, is based or of one or both lower extremities, inprimarily upon the average impaircluding the bilateral factor, if applicament in earning capacity, that is, upon ble, (2) disabilities resulting from comthe economic or industrial handicap mon etiology or a single accident, (3) which must be overcome and not from disabilities affecting a single body sysindividual success in overcoming it. Total disability will regarded where the percentages rebe considered to exist when there is ferred to in this paragraph for the servpresent any impairment of mind or ice-connected disability or disabilities body which is sufficient to render it are met and in the judgment of the ratimpossible for the average person to ing agency such service-connected disabilities render the veteran unemployfollow a substantially gainful occupaable. Marginal employment shall not tion; Provided, That permanent total be considered substantially gainful emdisability shall be taken to exist when ployment. The following will be earned annual income does not exceed considered to be permanent total disthe amount established by the U. Deability: the permanent loss of the use partment of Commerce, Bureau of the of both hands, or of both feet, or of one Census, as the poverty threshold for hand and one foot, or of the sight of one person. Marginal employment may both eyes, or becoming permanently also be held to exist, on a facts found helpless or permanently bedridden. Department of Veterans Affairs that (b) Claims of all veterans who fail to all veterans who are unable to secure meet the percentage standards but who and follow a substantially gainful occumeet the basic entitlement criteria and pation by reason of service-connected are unemployable, will be referred by disabilities shall be rated totally disthe rating board to the Veterans Servabled. When the perA veteran may be considered as uncentage requirements are met, and the employable upon termination of emdisabilities involved are of a permaployment which was provided on acnent nature, a rating of permanent and count of disability, or in which special total disability will be assigned if the consideration was given on account of veteran is found to be unable to secure the same, when it is satisfactorily and follow substantially gainful emshown that he or she is unable to seployment by reason of such disability. The resulting difadvancing age or intercurrent disference will be recorded on the rating ability, may not be used as a basis for sheet. Age, as such, time of entrance into the service is not is a factor only in evaluations of disascertainable in terms of the schedule, ability not resulting from service, i. Conjectural analogies will be not in any instance influence the offiavoided, as will the use of analogous cers in the handling of the case. Fairratings for conditions of doubtful diagness and courtesy must at all times be nosis, or for those not fully supported shown to applicants by all employees by clinical and laboratory findings. In view of the number of atypical inAll correspondence relative to the instances it is not expected, especially terpretation of the schedule for rating with the more fully described grades of disabilities, requests for advisory opindisabilities, that all cases will show all ions, questions regarding lack of clarthe findings specified. Findings suffiity or application to individual cases ciently characteristic to identify the involving unusual difficulties, will be disease and the disability therefrom, addressed to the Director, Compensaand above all, coordination of rating tion and Pension Service. Claims in regard to which the converted to the nearest degree divisschedule evaluations are considered inible by 10, which is 50 percent. If there adequate or excessive, and errors in the are more than two disabilities, the disschedule will be similarly brought to abilities will also be arranged in the attention. The combined value, exTable I, Combined Ratings Table, reactly as found in table I, will be comsults from the consideration of the effibined with the degree of the third disciency of the individual as affected ability (in order of severity). The comfirst by the most disabling condition, bined value for the three disabilities then by the less disabling condition, will be found in the space where the then by other less disabling conditions, column and row intersect, and if there if any, in the order of severity. Thus, a are only three disabilities will be conperson having a 60 percent disability is verted to the nearest degree divisible considered 40 percent efficient. Thus, ceeding from this 40 percent efficiency, if there are three disabilities ratable at the effect of a further 30 percent dis60 percent, 40 percent, and 20 percent, ability is to leave only 70 percent of respectively, the combined value for the efficiency remaining after considthe first two will be found opposite 60 eration of the first disability, or 28 perand under 40 and is 76 percent. The indiwill be combined with 20 and the comvidual is thus 72 percent disabled, as bined value for the three is 81 percent. The same procefirst be arranged in the exact order of dure will be employed when there are their severity, beginning with the four or more disabilities. All disabilities are appearing in the space where the colthen to be combined as described in umn and row intersect will represent paragraph (a) of this section. This version to the nearest degree divisible combined value will then be converted by 10 will be done only once per rating to the nearest number divisible by 10, decision, will follow the combining of and combined values ending in 5 will be all disabilities, and will be the last proadjusted upward. Thus, with a 50 percedure in determining the combined cent disability and a 30 percent disdegree of disability. This procedure will facilitate a the bilateral factor applies, and simiclose check of new and unlisted condilarly whenever there are compensable tions, rated by analogy. In the selecdisabilities affecting use of paired extion of code numbers, injuries will gentremities regardless of location or erally be represented by the number asspecified type of impairment.
Order genuine piroxicam on-line
Illnesses caused by recreational water exposure can involve the gastrointestinal tract fungal arthritis in dogs piroxicam 20 mg on-line, respiratory tract, central nervous system, skin, ears, or eyes. Cryptosporidiosis may cause life-threatening infection in immunocompromised children and adolescents. Swimming is a communal bathing activity by which the same water is shared by dozens to thousands of people each day, depending on venue size (eg, small wading pools, municipal pools, water parks). The largest outbreaks of waterborne disease tend to affect children younger than 5 years disproportionately, occur during the summer months, and result in gastroenteritis. Cryptosporidium oocysts can remain infectious for more than 10 days in chlorine concentrations typically mandated in swimming pools, thus contributing to the role of Cryptosporidium species as the leading cause of treated recreational water-associated outbreaks. Recreational water use is an ideal means of amplifying pathogen transmission within a community because of extremely chlorine-tolerant pathogens, coupled with low infectious doses, high pathogen-excretion concentrations, and poor swimmer hygiene (eg, 1Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. As a result, one or more swimmers ill with diarrhea can contaminate large volumes of water and expose large numbers of swimmers to pathogens, particularly if pool disinfection is inadequate or the pathogen is chlorine tolerant. Control Measures Swimming continues to be a safe and effective means of physical activity. Pediatricians should counsel families: Do not go into recreational water (eg, swim) when ill with diarrhea. Toilet use and diaper changing should occur away from the recreational water source and food preparation activities. Recommendations for responding to fecal incidents in treated recreational water ven1 ues have been published. Recreational water activities, showering, and bathing can introduce water into the ear canal, wash away protective ear wax, and cause maceration of the thin skin of the ear canal, predisposing the ear canal to bacterial infection. Topical agents that have the potential for ototoxicity (eg, gentamicin, neomycin, agents with a low pH, hydrocortisone-neomycin-polymyxin) should not be used in children with tympanostomy tubes or a perforated tympanic membrane. Commercial ear-drying agents are available for use as directed, or a 1:1 mixture of acetic acid (white vinegar) and isopropanol (rubbing alcohol) may be placed in the external ear canal after swimming or showering to restore the proper acidic pH to the ear canal and to dry residual water. Otic drying agents should not be used in the presence of tympanostomy tubes, tympanic membrane perforation, acute external ear infection, or ear drainage. However, disease transmission between animals and humans is possible for children who interact with pets or other domestic or wild animals. Infants and children also come in contact with animals at many venues outside the home, including agricultural fairs, farms, zoos, petting zoos, schools or child care centers, hospitals, and animal swap meets. Examples of nontraditional pets and animals commonly encountered in public settings are listed in Table 2. Children younger than 5 years also are at increased risk of injury from animals because of their size and behavior. Some nonnative animals are brought into the United States illegally, thus bypassing rules established to reduce introduction of disease and potentially dangerous animals. In addition, as an animal matures, its physical and behavioral characteristics can result in an increased risk of injuries to children. Compendium of measures to prevent disease associated with animals in public settings, 2011. Among nontraditional pets, reptiles, amphibians, and poultry pose a particular risk because of high asymptomatic carriage rates of Salmonella species, the intermittent shedding of Salmonella organisms in their feces, and persistence of Salmonella organisms in the environment. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis infections also have been described as a result of contact with pet rodents (eg, hamsters). Infectious diseases, injuries, and other health problems can occur after contact with animals in public settings. Individual cases and outbreaks associated with Salmonella species, Escherichia coli O157:H7, and Cryptosporidium species are most commonly reported. Many recent outbreaks of enteric zoonoses have been linked to contact with ruminant livestock (cattle, sheep, and goats); poultry, including chicks, chickens, and ducks; reptiles, especially small turtles; amphibians; and rodents. Direct contact with animals (especially young animals), contamination of the environment or food or water sources, and inadequate hand hygiene facilities at animal exhibits all have been implicated as reasons for infection in these public settings. Indirect contact with animals can also be a source of illness to people, including water in a reptile or amphibian tank or contaminated barriers or fencing. Rabies has occurred in animals in a petting zoo, pet store, animal shelter, and county fair, necessitating prophylaxis of adults and children. However, many pet owners and people in the process of choosing a pet are unaware of the potential risks posed by pets. Additionally, most people are unaware that animals that appear healthy may carry pathogenic microbes. Pediatricians, veterinarians, and other health care professionals are in a unique position to offer advice on proper pet selection, to provide information about safe pet ownership and responsibility, and to minimize risks to infants and children. Acquisition and ownership of nontraditional pets should be discouraged in households with young children or other high-risk individuals. Young children should always be supervised closely when in contact with animals at home or in public settings, including child care centers or schools, and children should be educated about appropriate human-animal interactions. Parents should be made aware of recommendations for prevention of human diseases and injuries from exposure to pets, including nontraditional pets and animals in the home, animals in public settings, and pet products including food and pet treats (Table 2. Pets and other animals should receive appropriate veterinary care from a licensed veterinarian who can provide preventive care, including vaccinations and parasite control, appropriate for the species. Guidelines for Prevention of Human Diseases From Exposure to Pets, Nontraditional Pets, and Animals in Public Settings,a,b continued Consult with parents or guardians to determine special considerations needed for children who are immunocompromised or who have allergies or asthma Animals not recommended in schools, child-care settings, hospitals, or nursing homes include nonhuman primates; inherently dangerous animals (lions, tigers, cougars, bears, wolf/dog hybrids), mammals at high risk of transmitting rabies (bats, raccoons, skunks, foxes, coyotes, and mongooses), aggressive animals or animals with unpredictable behavior; stray animals with unknown health history; venomous or toxin-producing spiders, insects, reptiles, and amphibians; and animals at higher risk for causing serious illness or injury, including reptiles, amphibians, or chicks, ducks, or other live poultry; and ferrets. Additionally, children younger than 5 years should not be allowed to have direct contact with these animals. Compendium of measures to prevent disease associated with animals in public settings, 2013. Cervicofacial is most common, often occurring after tooth extraction, oral surgery, other oral/facial trauma, or even from carious teeth. Thoracic disease most commonly is secondary to aspiration of oropharyngeal secretions but may be an extension of cervicofacial infection. It occurs rarely after esophageal disruption secondary to surgery or nonpenetrating trauma. Thoracic presentation includes pneumonia, which can be complicated by abscesses, empyema, and rarely, pleurodermal sinuses. Focal or multifocal mediastinal and pulmonary masses may be mistaken for tumors. Abdominal actinomycosis usually is attributable to penetrating trauma or intestinal perforation. Intra-abdominal abscesses and peritoneal-dermal draining sinuses occur eventually. Chronic localized disease often forms draining sinus tracts with purulent discharge. Other sites of infection include the liver, pelvis (which, in some cases, has been linked to use of intrauterine devices), heart, testicles, and brain (which usually is associated with a primary pulmonary focus). Infection is uncommon in infants and children, with 80% of cases occurring in adults. Specimens must be obtained, transported, and cultured anaerobically on semiselective (kanamycin/vancomycin) media. Amoxicillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, doxycycline, and tetracycline are alternative antimicrobial choices.
Buy on line piroxicam
Humira is used to treat severe plaque psoriasis in children and adolescents aged 4 to 17 years in whom topical therapy and phototherapies have either not worked very well or are not suitable arthritis medication weight gain cheap piroxicam 20 mg amex. Adolescent hidradenitis suppurativa Hidradenitis suppurativa (sometimes called acne inversa) is a chronic and often painful inflammatory skin disease. Humira is used to treat hidradenitis suppurativa in adolescents from 12 years of age. Paediatric uveitis Non-infectious uveitis is an inflammatory disease affecting certain parts of the eye. Humira is used to treat children from 2 years of age with chronic non-infectious uveitis with inflammation affecting the front of the eye. This inflammation may lead to a decrease of vision and/or the presence of floaters in the eye (black dots or wispy lines that move across the field of vision). What you need to know before your child uses Humira Do not use Humira If your child is allergic to adalimumab or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). It is important that you tell your doctor if your child has symptoms of infections. These infections may be serious and include tuberculosis, infections caused by viruses, fungi, parasites or bacteria, or other opportunistic infections and sepsis that may, in rare cases, be life-threatening. It is very important that you tell your doctor if your child has ever had tuberculosis, or if he/she has been in close contact with someone who has had tuberculosis. Tuberculosis can develop during therapy even if your child has received preventative treatment for tuberculosis. If symptoms of tuberculosis (persistent cough, weight loss, listlessness, mild fever), or any other infection appear during or after therapy tell your doctor immediately. If you received Humira while you were pregnant, your baby may be at higher risk for getting such an infection for up to approximately five months after the last dose you received during pregnancy. It is important to tell your doctor if your child has had or has a serious heart condition. If your child develops a fever that does not go away, bruises or bleeds very easily or looks very pale, call your doctor right away. If your child takes Humira the risk of getting lymphoma, leukemia, or other cancers may increase. On rare occasions, a specific and severe type of lymphoma, has been observed in patients taking Humira. Tell your doctor if your child is taking azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine with Humira. In addition cases of non-melanoma skin cancer have been observed in patients taking Humira. Your child should not take Humira with medicines containing the active substances anakinra or abatacept due to increased risk of serious infection. Driving and using machines Humira may have a minor influence on the ability to drive, cycle or use machines. Children and adolescents with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis Children and adolescents from 2 years of age weighing 10 kg to less than 30 kg the recommended dose of Humira is 20 mg every other week. Children and adolescents from 2 years of age weighing 30 kg or more the recommended dose of Humira is 40 mg every other week. Children, adolescents and adults from 6 years of age weighing 30 kg or more the recommended dose of Humira is 40 mg every other week. Children and adolescents with psoriasis Children and adolescents from 4 to 17 years of age weighing 15 kg to less than 30 kg the recommended dose of Humira is an initial dose of 20 mg, followed by 20 mg one week later. Children and adolescents from 4 to 17 years of age weighing 30 kg or more the recommended dose of Humira is an initial dose of 40 mg, followed by 40 mg one week later. Adolescents with hidradenitis suppurativa from 12 to 17 years of age, weighing 30 kg or more the recommended dose of Humira is an initial dose of 80 mg (as two 40 mg injections in one day), followed by 40 mg every other week starting one week later. Children and adolescents from 6 to 17 years of age weighing 40 kg or more the usual dose regimen is 80 mg (as two 40 mg injections in one day) initially followed by 40 mg two weeks later. Do not attempt to give your child an injection until you are sure that you understand how to prepare and give the injection. After proper training, the injection can be self-administered or given by another person, for example a family member or friend. Failure to perform the following steps as described may cause contamination which may lead to infection of your child. If there is a second box in the carton for a future injection, place it back in the refrigerator immediately. Excess liquid may come out of the needle while the white plunger rod is being pushed. If you use more Humira than you should If you accidentally inject a larger amount of Humira liquid, or if you inject Humira more frequently than told to by your doctor, call your doctor and tell him/her that your child has taken more. Always take the outer carton or the vial of the medicine with you, even if it is empty. If you forget to use Humira If you forget to give your child a Humira injection, you should inject the Humira dose as soon as you remember. The symptoms described above can be signs of the below listed side effects, which have been observed with Humira. Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people) injection site reactions (including pain, swelling, redness or itching); respiratory tract infections (including cold, runny nose, sinus infection, pneumonia); headache; abdominal pain; nausea and vomiting; rash; musculoskeletal pain. Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people) serious infections (including blood poisoning and influenza); intestinal infections (including gastroenteritis); skin infections (including cellulitis and shingles); ear infections; oral infections (including tooth infections and cold sores); reproductive tract infections; urinary tract infection; fungal infections; joint infections, benign tumours; 344 skin cancer; allergic reactions (including seasonal allergy); dehydration; mood swings (including depression); anxiety; difficulty sleeping; sensation disorders such as tingling, prickling or numbness; migraine; nerve root compression (including low back pain and leg pain); vision disturbances; eye inflammation; inflammation of the eye lid and eye swelling; vertigo; sensation of heart beating rapidly; high blood pressure; flushing; haematoma; cough; asthma; shortness of breath; gastrointestinal bleeding; dyspepsia (indigestion, bloating, heart burn); acid reflux disease; sicca syndrome (including dry eyes and dry mouth); itching; itchy rash; bruising; inflammation of the skin (such as eczema); breaking of finger nails and toe nails; increased sweating; hair loss; new onset or worsening of psoriasis; muscle spasms; blood in urine; kidney problems; chest pain; oedema; fever; reduction in blood platelets which increases risk of bleeding or bruising; impaired healing. Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people) opportunistic infections (which include tuberculosis and other infections that occur when resistance to disease is lowered); neurological infections (including viral meningitis); eye infections; bacterial infections; diverticulitis (inflammation and infection of the large intestine); cancer; 345 cancer that affects the lymph system; melanoma; immune disorders that could affect the lungs, skin and lymph nodes (most commonly presenting as sarcoidosis); vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels); tremor; stroke; neuropathy; hearing loss, buzzing; sensation of heart beating irregularly such as skipped beats; heart problems that can cause shortness of breath or ankle swelling; heart attack; a sac in the wall of a major artery, inflammation and clot of a vein; blockage of a blood vessel; lung diseases causing shortness of breath (including inflammation); pulmonary embolism (bloackage in an artery of the lung); pleural effusion (abnormal collection of fluid on the pleural space); inflammation of the pancreas which causes severe pain in the abdomen and back; difficulty in swallowing; facial oedema; gallbladder inflammation, gallbladder stones; fatty liver; night sweats; scar; abnormal muscle breakdown; systemic lupus erythematosus (including inflammation of skin, heart, lung, joints and other organ systems); sleep interruptions; impotence; inflammations. These include: Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people) low blood measurements for white blood cells; low blood measurements for red blood cells; increased lipids in the blood; elevated liver enzymes. What the Humira vial looks like and contents of the pack Humira 40 mg solution for injection in vials is supplied as a sterile solution of 40 mg adalimumab dissolved in 0. One pack contains 2 boxes, each containing 1 vial, 1 empty sterile syringe, 1 needle, 1 vial adapter and 2 alcohol pads. Humira has been shown to slow down the damage to the cartilage and bone of the joints caused by the disease and to improve physical function. Humira is used to treat polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children and adolescents aged 2 to 17 years and enthesitis-related arthritis in children and adolescents aged 6 to 17 years.
Syndromes
- Hypothermia -- warmth (rewarming should be carefully monitored)
- Renal tubular acidosis, proximal
- Coronary artery disease may develop earlier in people with alkaptonuria.
- Passing little or no stools or gas
- Restlessness
- Severe stress
- Staining of the skin (turns brown)
- Teething
- Heart disease
- Age 19 and older: 4.7 g/day

Buy 20mg piroxicam with visa
It is recommended to have the mother take the antithyroid drug after breastfeeding (Marx arthritis nos icd 9 purchase piroxicam online, 2009). One of the serious, rare side effects of thioamides is agranulocytosis, presenting with a fever, sore throat and an absolute granulocyte count of less than 500 per cubic millimeter. Other side effects include leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, hepatitis, and vasculitis. Cross reactivity to thioamide-induced adverse events between the two agents may be as high as 50% (Garcia-Mayor, 2010). Hyperthyroidism is the second most common endocrine disorder that occurs during pregnancy, following only diabetes mellitus (Mestman, 1998). After 12 weeks gestation, the fetal thyroid gland concentrates iodine and synthesizes thyroid hormone and continues fetal brain development (Morreale, 2000; Inoue, 2009; Abalovich, 2007). Significant fetal and maternal complications can occur if the condition is left untreated. Low birth weight has been reported to occur nine times as often compared to pregnancies not complicated by hyperthyroidism (Millar, 1994). The highest complications were associated with the poorest control and the best control was associated with the least complications (Abalovich, 2007). Surgery is reserved for patients who require large doses of antithyroid drugs, or those who demonstrate poor medication adherence and continue to remain hyperthyroid (Cooper, 2005; Miehle &Paschke, 2003; Mestman, 2004; Mestman, 1998; Glinoer, 2003; Karabinas & Tolis, 1998; Masiukiewicz &Burrow, 1999; Atkins, Cohen & Phillips, 2000). If surgery is necessary, surgery is preferred during the second trimester to decrease the risk of spontaneous abortion (Galofre, 2009). It is important not to overtreat because it may result in maternal or fetal hypothyroidsm (Casey, 2006). Throughout the rest of the world, methimazole and carbimazole, are widely used to treat hyperthyroidism in pregnant women (Mandel, 2001; Dwarakanath, 1999). An evaluation of 49,091 live births estimated the incidence of aplasia cutis in the general population to be 0. No increased incidence of spontaneous or induced abortions or major congenital anomalies was reported in the methimazole cohort (DiGianantonio, 2001). However, only one case has been reported of neonatal hepatitis secondary to transplacental propylthiouracil (Hayashida, 1990). It was originally thought that the placental transfer of levothyroxine would prevent fetal hypothyroidism. However, the necessary dose of the antithyroid drug is much higher when given with levothyroxine that fetal goiter and fetal hypothyroidism may still occur. Furthermore, the risk of fetal hypothyroidism is increased because the antithyroid medications but not levothyroxine cross the placenta (Rosenfeld, 2009). Diagnosis of hyperthyroidism was based on history, physical exam, thyroid-stimulating hormone, free thyroxine index, and free triiodothyronine index. Potential limitations to the study were mostly due to the retrospective design; unrandomized, unblinded, and non-placebo controlled. The trial appeared to be well designed and utilized a direct measure of fetal thyroid status at birth. Potential bias may have existed as medication selection was based solely on provider preference. The authors identified 23 children, ages 3 to 11 years, of mothers who were treated with methimazole during pregnancy and 30 children, ages 3 to 11 years, of mothers who were not treated with methimazole during pregnancy. All mothers delivered at term and there were no congenital malformations in either group. Other limitations to this study were a small sample size and low exposure dose of methimazole. Thyroid function and intellectual development of children of mothers taking methimazole during pregnancy. Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of Thyrotoxicosis: Management Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. Thyroid 2011:21:593-646 Barbero P, Valdez R, Rodriguez H, Tiscornia C, Mansilla E, Allons A, Coll S, & Liascovich R. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody levels in a pregnant woman taking propylthiouracil. Carbimazole embryopathy-bilateral choanal atresia and patent vitello-intestinal duct: a case report and review of the literature. Successful treatment with carbimazole of a hyperthyroid pregnancy with hepatic impairment after propylthiouracil administration: a case report. Is neuropsychological development related to maternal hypothyroidism or to maternal hypothyroxinemiafi Pregnancy outcome, thyroid dysfunction and fetal goiter after in utero exposure to propylthiouracil: a controlled cohort study. Dysfunction of the maternal thyroid in pregnancy adversely affects the course of pregnancy and the psychomotor development of the offspring (Haddow 1999, Morreale de Escobar 2004). Impairment of neuronal differentiation leads to inadequate development of the central nervous system with resulting mental retardation. These changes are most prominent in untreated congenital hypothyroidism (cretinism). Moderate thyroid hormone deficit may lead to less pronounced neurocognitive dysfunction. The new guidelines introduce age over 30 years and body-mass index over 40 kg/m2 among the risk factors. In our opinion, this form of screening is likely to be neglected due to practical reasons. It has been shown that the case-finding approach may miss up to one half of pregnant women in comparison with universal screening (Vaidya 2007, Horacek 2010, Jiskra 2011a); and it may be difficult to implement in the routine practice (Vaidya 2002). Number of women screened Total 5520 Positive in screening (at least one parameter) 822 (14. Results of universal screening for thyroid disorders among Czech pregnant women in the 9th to 11th gestational weeks. However, due to the different analytical methods, these results cannot be directly compared. Cooperation with gynaecologists wasnfit always optimal despite the fact that they were provided with all necessary information well in advance. On the other hand, laboratories analysed the samples promptly, and many of them took part in providing publicity and further information to other cooperating health care professionals. In conclusion, the Pilot Project study showed that implementation of universal screening for thyroid disorders in pregnancy would be feasible in the Czech Republic, although the general knowledge on importance of correct thyroid function in pregnancy needs to be improved among practical gynaecologists. Between 2006 and 2009, we performed thyroid ultrasound in 186 pregnant women positively screened for thyroid disorders in the first trimester of pregnancy; i. Therefore, the present pregnant women are already the third generation who live in iodine-sufficient conditions. We regarded women as high-risk if they had any of the following risk factors: family and/or personal history of thyroid disease (including presence of goitre and signs and symptoms suggestive for thyroid dysfunction), family and/or personal history for autoimmune disease, history of neck irradiation, previous miscarriages and preterm deliveries). After exclusion of transient gestational hyperthyroidism, only 74/159 (47 %) women were classified as high-risk for thyroid disease according to their history.
Order piroxicam on line amex
The swelling started at the ankles but now his legs arthritis pain everywhere order piroxicam 20mg online, thighs and genitals are swollen. He had hypertension diagnosed 13 years ago, and a myocardial infarction 4 years previously. He continues to smoke 30 cigarettes a day, and drinks about 30 units of alcohol a week. Examination On examination there is pitting oedema of the legs which is present to the level of the sacrum. His apex beat is not displaced, and auscultation reveals normal heart sounds and no murmurs. The liver, spleen and kidneys are not palpable, but ascites is demonstrated by shifting dullness and fluid thrill. Unilateral oedema is most likely to be due to a local problem, whereas bilateral leg oedema is usually due to one of the medical conditions listed above. Pitting oedema needs to be distinguished from lymphoedema which is characteristically non-pitting. If the oedema is pitting, an indentation will be present after pressure is removed. The major differential diagnoses are cardiac failure, renal failure, nephrotic syndrome, right heart failure (cor pulmonale) secondary to chronic obstructive airways disease or decompensated chronic liver disease. The frothy urine is a clue to the diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome and is commonly noted by patients with heavy proteinuria. The patient has signs of bilateral pleural effusions which may occur in nephrotic syndrome, if there is sufficient fluid retention. The bruising and peri-orbital purpura is classically seen in patients with nephrotic syndrome secondary to amyloidosis. The normochromic, normocytic anaemia is typical of chronic disease and is a clue to the underlying diagnosis of amyloidosis. Patients with amyloidosis may have raised serum transaminase levels due to liver infiltration by amyloid. The patient should have a renal biopsy to delineate the cause of the nephrotic syndrome. The exception is the patient with long-standing diabetes mellitus, with concomitant retinopathy and neuropathy, who almost certainly has diabetic nephropathy. A bone marrow aspirate showed the presence of an excessive number of plasma cells, consistent with an underlying plasma cell dyscrasia. Patients with amyloidosis should have an echocardiogram to screen for cardiac infiltration, and if the facilities are available a serum amyloid P scan should be arranged which assesses the distribution and total body burden of amyloid. The initial treatment of this patient involves fluid and salt restriction, and diuretics to reduce the oedema. He should be anticoagulated to reduce the risk of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolus. Definitive treatment is by chemotherapy supervised by the haematologists to suppress the amyloidogenic plasma cell clone. Patients with nephrotic syndrome secondary to amyloidosis usually progress to end-stage renal failure relatively quickly. The man has recently retired, and returned 2 weeks ago from a coach trip to Eastern Europe and Russia. Staphylococcal food poisoning occurs within a few hours and typically presents abruptly and may be severe but short-lived. Campylobacter, Salmonella and Shigella cause more severe symptoms than viral gastroenteritis. The incubation period for giardiasis is typically about 2 weeks, but varies from 3 days to 6 weeks. Giardia lamblia infects the small intestine and causes a watery, yellow, foul-smelling diarrhoea. The history should try to distinguish between the smalland large-bowel origin of the diarrhoea. Large-bowel diarrhoea tends to be maximal in the morning, pain is relieved by defaecation, and blood and mucus may be present. By contrast diarrhoea of small-bowel origin does not occur at any particular time, and pain is not helped by defaecation. Typically a pale fatty stool without blood or mucus occurs in small-bowel disease. Other pathogens which cause small-bowel diarrhoea include Campylobacter, rotavirus, Cryptosporidia and Strongyloides. If small-bowel-type diarrhoea persists, other non-infective causes of malabsorption should be considered such as tropical sprue, coeliac disease, and chronic pancreatitis. Giardia lamblia occurs worldwide especially in the tropics but also is endemic in Russia, and infection occurs commonly in visitors to St Petersburg. Poor sanitation and untreated water supplies are important factors in transmission. Outbreaks can occur in residents of nursing homes, and giardiasis is a common cause of diarrhoea in homosexuals. If stool samples are negative, cysts can be found on jejunal biopsy or by sampling duodenal fluid by asking the patient to swallow the Enterotest capsule. Ideally a stool sample should be examined 6 weeks after treatment to ensure the parasite has been eradicated. This has developed over the past 10 days, and she is now breathless after walking 50 yards. About 2 weeks ago she had a flu-like illness with generalized muscle aches and fever. She feels extremely tired and has noticed palpitations in association with her breathlessness. In addition she has some discomfort in her anterior chest which is worse on inspiration. Profound hypocalcaemia, hypophosphataemia, and hypomagnaesaemia can all cause myocardial depression. The clinical picture of myocarditis is non-specific, but common symptoms include myalgia, fatigue, shortness of breath, pericardial pain and palpitations. Patients usually have a marked sinus tachycardia disproportionate to the slight fever. There may be atrial or, more commonly, ventricular arrhythmias or signs of conducting system defects. Chest X-ray may be normal if the myocarditis is mild, but if there is cardiac failure there will be cardiomegaly and pulmonary congestion. The differential diagnoses in this case include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pericarditis and myocardial ischaemia. Echocardiographic changes may be focal affecting only the right or left ventricle, or global. An endomyocardial biopsy is performed as soon as possible, and will show evidence of myocardial necrosis. Paired serum samples should be taken for antibody titres to Coxsackie B and mumps. Coxsackie virus can be cultured from the throat, stool, blood, myocardium or pericardial fluid. Corticosteroids tend to be used in patients with a short history, a positive endomyocardial biopsy, and the most severe disease. Most cases are benign and self-limiting, and cardiac function will return to normal. However a minority will develop permanent cardiac damage leading to a dilated cardiomyopathy. Four days prior to presentation he felt unwell and complained of muscle aches and headache.
Cheap piroxicam 20 mg with visa
Activation of pro-gelatinase B by endometase/matrilysin-2 promotes invasion of human prostate cancer cells rheumatoid arthritis questions to ask doctor discount piroxicam express. Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is an early event in prostate carcinogenesis. Transurethral prostate vaporization using an oval electrode in 82 cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Growth and development during early manhood as determinants of prostate size in later life. A novel diagnostic test for prostate cancer emerges from the determination of alpha-methylacyl-coenzyme a racemase in prostatic secretions. Medical treatment modalities for lower urinary tract symptoms: what are the relevant differences in randomised controlled trials. Prostate-specific antigen induces proliferation of peripheral blood lymphocytes and cytokine secretion in benign prostate hypertrophy patients. Comparison between two commercially available chromogranin A assays in detecting neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Minimally invasive therapies for benign prostatic hyperplasia in the new millennium: long-term data. The importance of measuring the prostatic transition zone: an anatomical and radiological study. Continent lower urinary tract reconstruction in the cervical spinal cord injured population. Double urinary bladder voiding technique post removal of urethral catheter in renal allograft recipients. Randomized trial of safety and efficacy of transurethral resection of the prostate using contact laser versus electrocautery. Assessment of obstruction in adult ureterocele by means of color Doppler duplex sonography. History of weight and obesity through life and risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Patients with uncontrolled hypertension or concomitant hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Re: Ethanol injection therapy of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia: preliminary report on application of a new technique. Over the past month how None Only a little Some A lot much physical discomfort did any urinary problems cause youfi Over the past month, how None Only a little Some A lot much did you worry about your health because of any urinary problemsfi Overall, how bothersome Not at all bothersome Bothers me some has any trouble with urination been during the Bothers me a little Bothers me a lot past monthfi Over the past month, how None of the time Most of the time much of the time has any A little of the time All of the time urinary problem kept you from doing the kind of Some of the time things you would usually dofi In the classification of diagnostic tests and studies a recommended test should be performed on every patient during the initial evaluation whereas an optional test is a test of proven value in the evaluation of select patients. In general, optional tests are done during a detailed evaluation and performed by a urologist. Physical Examination and Digital Rectal Exam A focused physical examination should be performed to assess the suprapubic area for bladder distention, and motor and sensory function of the perineum and lower limbs. The volumes of small prostates tend to be overestimated and those of large glands tend to be underestimated. Urinalysis Urine should be analyzed using any of the widely available dipstick tests to determine if the patient has hematuria, proteinuria, pyuria or other pathological findings (eg, glucosuria, ketonuria, positive nitrite test, etc). Examination of the urinary sediment and culture is indicated if the results of the dipstick are abnormal. Frequency Volume Charts Frequency volume charts (voiding diary or time and amount voiding charts) should be used when nocturia is the dominant symptom but may also be used in other settings. The time and voided volume are recorded for each micturition during several 24fihour periods and help to identify patients with isolated nocturnal polyuria or excessive fluid intake, which are common in the aging male. It is useful in the initial diagnostic assessment and during or after treatment to confirm response. Despite the noninvasive nature of the test and its clinical value, it is an optional test in the detailed evaluation to be performed before embarking on any invasive therapy. Peak urinary flow (Qmax) is the best single measure to estimate the probability of a patient to be urodynamically obstructed, but a low Qmax does not distinguish between obstruction and decreased detrusor contractility. Because of the intrafiindividual variability and the volume dependency of the Qmax, at least 2 flow rates should be obtained, ideally both with a volume greater than 150 mL voided urine. Residual Urine the determination of post void residual urine is optional in the initial diagnostic assessment of the patient and during subsequent monitoring as a safety parameter. The determination is best performed by noninvasive transabdominal ultrasonography. Because of the marked intrafiindividual variability of residual urine volume, the test should be repeated to improve precision, particularly if the first residual urine volume is significant and suggests a change in the treatment plan. This distinction is made by relating detrusor pressure at maximum urinary flow rate to the maximum flow rate. Prostate Imaging with Transabdominal or Transrectal Ultrasound When residual urine is determined by transabdominal ultrasonography with a machine generating real time Bfimode images, prostate shape, size, configuration and protrusion into the bladder may be simultaneously evaluated. Outside of this context, imaging of the prostate by transabdominal or transrectal ultrasound is optional in selected patients. The success of certain treatments may depend on anatomical characteristics of the prostate gland (eg, hormonal therapy, thermotherapy, or transurethral incision of the prostate). There are treatment alternatives in which success or failure depends on the anatomical configuration of the prostate (eg, transurethral incision of the prostate, thermotherapy, etc). Endoscopy is recommended if considered helpful when such treatment alternatives are contemplated. Among the most important are benign prostatic obstruction, an overactive bladder and nocturnal polyuria. The choice of treatment is reached in a shared decisionfimaking process between the physician and patient. If the patient has predominant significant nocturia and gets out of bed to void 2 or more times per night, it is recommended that the patient complete a frequency volume chart for 2fi3 days. The frequency volume chart will show 24fihour polyuria or nocturnal polyuria when present, the first of which has been defined as greater than 3 liters total output over 24 hours. In practice, patients with bothersome symptoms are advised to aim for a urine output of 1 liter/24 hours. Nocturnal polyuria is diagnosed when more than 33% of the 24fihour urine output occurs at night. If symptoms do not improve sufficiently he can be treated along the same lines as men without predominant nocturia. If the patient has no polyuria and medical treatment is considered, the physician can proceed with therapy based mainly on first altering modifiable factors such as concomitant drugs, regulation of fluid intake especially in the evening, lifestyle changes (avoiding a sedentary lifestyle) and dietary advice (avoiding dietary indiscretions such as excessive intake of alcohol and highly seasoned or irritative foods) (Brown 1997). If treated pharmacologically, it is recommended that the patient be followed to assess treatment success or failure and possible adverse events. The time after initiation of therapy for the assessment of treatment success varies according to the pharmacological treatment prescribed and is usually 2 to 4 weeks for alpha blocker therapy and at least 3 months for a 5fireductase inhibitor. If treatment is successful and the patient is satisfied, followfiup should be repeated approximately once a year by repeating the initial evaluation as previously outlined. The followfiup strategy will allow the physician to detect any changes that have occurred in the last year, more specifically, if symptoms have progressed or become more bothersome, or if a complication has developed creating an indication imperative for surgery. If medical treatment fails and the patient is not satisfied, he should be referred to a urologist (if not already doing so) for further evaluation and possibly interventional treatment. The urologist may use additional testing beyond those tests recommended for basic evaluation.
Purchase piroxicam now
Page 284 of 885 14 rheumatoid arthritis reddit piroxicam 20 mg online. Candidate for surgery or epidural injection after failed conservative therapy as described in A V. Clinical findings and/or symptoms with no red flags; incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks; or a course of oral steroids [One of the following] 1. Atrophy Page 287 of 885 3. Pain in the neck or back Page 288 of 885 m. Diabetes Page 289 of 885 f. Evaluation of scoliosis [One of the following] Page 290 of 885 A. Evidence-based clinical guidelines for multidisciplinary spine care: diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy, North American Spine Society. Spinal epidural abscess: the importance of early diagnosis and treatment, J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 1998, 65:209-212. Page 291 of 885 18. No red flags and incomplete resolution with conservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or a course of oral steroids B. Primary or metastatic bone tumor (Gadolinium not required if there are no neurological signs or symptoms) [One of the following] 1. Paresthesias (tingling) Page 294 of 885 5. Objective weakness in a nerve root distribution on examination which is 3/5 or less B. Repeat advanced diagnostic imaging in spinal cord injury patients with posttraumatic syrinx is not appropriate without evidence of neurological deterioration. For the Clinical Efficacy Assessment Subcommittee of the American College of Physicians and the American College of Physicians/American Pain Society Low Back Pain Guidelines Panel*, Diagnosis and Treatment of Low Back Pain: A Joint Clinical Practice Guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society, Ann Intern Med. Magnetic resonance imaging of the postoperative spine, Sem Musculoskeletal Radiology, 2000; 4:281-291. Magnetic resonance image findings in the early postoperative period after anterior cervical discectomy, Eur Spine J, 2007; 16:27-31. Guidelines for the Management of Acute Cervical Spine and Spinal Cord Injuries, Section on Disorder of the Spine and Peripheral Nerves of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons and the Congress of Neurologic Surgeons. Page 296 of 885 9. Diagnosis and treatment of cervical radiculopathy from degenerative disorders, North American Spine Society Evidence-Based Clinical Guidelines for Multidisciplinary Spine Care. The diagnosis and treatment of metastatic spinal tumor, Oncologist, 1999; 4:459-469. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis and long-term management of multiple sclerosis, Neurology, 2004; 63(Suppl 5):S3-S11. Outcome in patients with cervical radiculopathy: prospective multicenter study with independent clinical review, Spine, 1999; 24:591-597. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and the presence of spinal cord abnormalities: preoperative magnetic resonance imaging analysis, Spine, 1997; 22:2537-3541. Standardized radiologic protocol for the study of common coccygodynia and characteristics of the lesions observed in the sitting position. Page 297 of 885 35. Suspected primary or metastatic tumor of the cervical cord or leptomeninges (For medulloblastoma or ependymoma see below) [One of the following] 1. Pain increased with straining Page 299 of 885 n. Follow-up every 3 months for 2 years then every 6 months for 2 years and then annually if previously known spine involvement C. Follow up intervals at every 3-4 months for a year and then every 4-6 months for year 2 and every 6-12 months thereafter if previously known spine involvement C. Annual follow-up with no change in signs and symptoms Page 300 of 885 7-10 V. Infection (including osteomyelitis and discitis and epidural 11-16 abscess) [One of the following] A. History of penetrating injury or surgery Page 301 of 885 B. Follow-up during therapy for epidural abscess or disc space infection [One of the following] 1. Trauma including birth trauma motor vehicle accident, falls, sports injuries, gunshot injury, overuse of back packs b. Symptoms [One of the following] Page 302 of 885 a. Known syrinx and history or suspicion of spinal trauma, myelitis, or spinal cord tumor [One of the following] 1. Radiculopathy with symptoms lasting at least 6 weeks and a 9,19-27 history of prior surgery with a posterior approach [One of the following] A. Clinical findings and/or symptoms with no red flags; failure to respond to conservative medical management consisting of either treatment with antiinflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks; or a course of oral steroids [One of the following] 1. Candidate for surgery or epidural injection after failed conservative therapy as described in A and one of the symptoms described in A 1-6 X. Clinical findings and/or symptoms with no red flags; incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks; or oral steroids [One of the following] 1. Neck pain lasting at least 6 weeks and with a history of prior 9,19-27 surgery with a posterior approach [One of the following] A. No red flags and failure to respond to conservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or a course of oral steroids B. Advanced diagnostic imaging every three years for life can be performed once non-progression of the syringomyelia is established d. Chiari malformation is not itself familial and family screening of asymptomatic individuals is not appropriate. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis and longterm management of multiple sclerosis, Neurology, 2004; 63(Suppl 5):S3-S11. Neck pain, cervical radiculopathy, and cervical myelopathy, the J Bone & Joint Surg, 2002; 84:1872-1881. Page 306 of 885 20. Evaluation of magnetic resonance myelography in the investigation of cervical spondylotic radiculopathy, the British Journal of Radiology, 2003; 76:525-531. Magnetic resonance image findings in the early post-operative period after anterior cervical discectomy, Eur Spine J, 2007; 16:27-31. Evaluation and treatment of posterior neck pain in family practice, J Am Board Fam Pract, 2004; 17:S13-22. Primary or metastatic bone tumor (contrast not required if there are no neurological signs or symptoms) [One of the following] Page 308 of 885 1. Periodic assessment during chemotherapy, radiation Rx, or surgery for bone tumor 5. Weakness or stiffness of the legs (objective weakness on exam that is 3/5 or less) 8. Spinal stenosis with symptoms for at least 6 weeks (Contrast should be used if there is history of thoracic spine surgery) [One of the following] Presence of red flags waives any conservative management requirements A. Clinical findings and symptoms with no red flags incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or a course of oral steroids injections [One of the following] Page 309 of 885 1. Clinical findings and symptoms with no red flags incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or oral steroids [One of the following] 1. Pain from a weakened or fractured vertebral body that prevents an individual from participating in physical therapy despite 24 hours of analgesic therapy Page 310 of 885 3. If there is a concern for malignancy, imaging can be performed with and without contrast B. Gardner A, Grannum S, Porter K, Thoracic and lumbar spine fractures, Trauma, 2005; 7:77-85.
Buy 20 mg piroxicam amex
Disatolic = chambers cannot expand during diastole constriction or restriction of heart C arthritis icd 9 cheap 20mg piroxicam. Left sided failure because of bad vasular flow or some intrinsic myocardial problem. Renal = lousy perfusion = poor urine output = fluid retention renin angiotensin 6. Clinical picture four basic scenarios, all depend on rate and severity of narrowing 1. Atherosclerosis by far the most common progressive narrowing 223 fixed obstruction material from the plaque may embolize and cause obstruction sudden complete occlusion from thrombosis on surface of plaque or hemorrhage into the plaque matrix. Acute myocardial infarction may result of blood flow is not restored quickly following complete occlusion. Coagulative necrosis of myocardium takes time to develop up to hour, reversible. No visible changes in myocardium 1-2 hrs, irreversible injury Not much to see, maybe a little change in the myofibrils 4-12 hrs, early change of coagulative necrosis 225 pallor grossly micro: edema, hemorrhage, neutrophils start to appear 18-24 hrs; nuclear changes of dead myocardial cells pyknosis more neutrophils 1-3 days hyperemia grossly micro: fully developed coagulative necrosis, glassy pink cytoplasm, many neutrophils. Rupture with death from tamponade (sac fills with blood, therefore the heart cannot fill during diastole) 5. Actually a Pancarditis endocardium myocardium epicardium and pericardium Ref: Robbins, Pathologic Basis of Disease 2. Mitral valve prolapse (Myxomatous degeneration) parachute deformity Ref: Robbins, Pathologic Basis of Disease 233 4. Vegetations of bugs and fibrin on valve margins may embolize septic emboli brain kidney speen Ref: Robbins, Pathologic Basis of Disease 4. Consequences valve scarring and stenosis no valve left = incompetence of a grand scale many small septic emboli and abscesses 235 stroke E. Marantic endocarditis thrombotic hypercoagulation state associated with various types of glandular (adeno) carcinomas sterile vegetations on valves and endocardium 2. Libman-Sachs S L sterile vegetations marked inflammation of valve in some cases fibrosis and deformity may follow Ref: Robbins, Pathologic Basis of Disease 236 F. Clinical presentation is often starting point, says something about pathological pattern. Dilatation and hypertrophy of all four chambers Ref: Robbins, Pathologic Basis of Disease 4. No well understood cause but several conditions are associated T H previous myocarditis pregnancy 5. Either symmetric or asymmetric hypertrophy asymmetric often involves only septum 2. Diastolic filling is impeded because cannot dilate something in muscle or endocardium that prevents relaxation not pericardial sac, this is something different, here we are dealing with things of the heart proper. Most problems are related to restriction of cardiac action or the source of pain B. Other system failure Ref: Robbins, Pathologic Basis of Disease renal failure with pericardial effusion (you have one in your slide set) 242 F. Scarring conditions that lead to adhesive pericarditis complete fibrous obliteration of pericardial space even with calcification post surgical fibrosis Ref: Robbins, Pathologic Basis of Disease X. Three days later he developed persistent mild hemoptysis associated with increasing dyspnea. He failed to respond to treatment, produced increasing amounts of frothy pink fluid and died 10 days later. At autopsy, the mitral valve was found to be thickened by scar tissue and laminated blood clot was noted in the right atrial appendage. What is the most likely explanation for the lesion in the lower lobe of the left lungfi From the information presented above, what are the important factors in the pathogenesis of the lung lesionfi Gross and microscopic examination of the heart would likely reveal what other changesfi She had a prior history of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, and had smoked one pack of cigarettes daily since 16 years of age. One day before she was to be discharged, she suddenly developed severe chest pain and hypotension and her skin was cold and clammy. He has moderate hypertension, for which he treats himself with diuretics and salt restriction. These were kept on for approximately 15 minutes and alternated from one extremity to another. No complications developed, and the subject was discharged on the 4th hospital day. A tracheostomy was performed and he was placed on mechanical ventilatory assistance. His temperature rose to 38 C on the second postoperative day and fluctuated between 38-39 C until his death on the sixth postoperative day. The vascular disease process most likely present in this person would have what histological appearancefi How can there be total occlusion of the internal carotid arteries and this patient not have been dead at the time initial evaluationfi Retinal vessels showed severe arterial narrowing with blurring of the optic discs. What vascular changes in the kidney would reflect the hypertension present in this womanfi How do you think vascular disease of the kidney could contribute to the high blood pressure in this patientfi What other medical conditions might be made worse, or accelerated, by hypertensionfi He had a long history of hypertension with multiple episodes of congestive heart failure. Coarctation of the aorta had been diagnosed 6 months earlier but no surgical repair was attempted because of his longstanding cardiomegaly and heart failure. Later that evening he developed sudden chest pain, cyanosis, hemoptysis and shortness of breath. A 59-year-old woman with a history of rheumatic heart disease presented with an eight-month history of increasing ascites. The patient was treated with serial large-volume paracentesis, and an aggressive diuretic regimen was started. However, she died shortly after admission as a result of newly diagnosed acute myelogenous leukemia. A giant left atrium has been described almost exclusively in rheumatic heart disease due to pancarditis with eccentric dilatation. This vulnerability is attributed to the complex dysregulation of immunity caused by glucocorticoids. A better knowledge of the interplay between glucocorticoid-induced immunosuppression and invasive fungal infections should assist in earlier recognition and treatment of such infections.

