Medrol
Order medrol 4 mg mastercard
Ovary and fimbria arthritis in my fingers and toes medrol 4 mg with visa, rhesus monkey: the majority of the ovary is replaced by an infiltrative cell tumors that arise from neoplasm (dysgerminoma). Ovary, rhesus monkey: Centrally, there is marked edema, apoptosis, with large nuclei, prominent nuclei, and often, clear cytoplasmic and necrosis with dropout (arrows) separate neoplastic cells and cause invaginations into the nucleus (arrows). This would reported in a variety of mammals and non-mammalian shed some light on the molecular pathways involved in species, including humans (girls and women)9; nonthe pathogenesis of this neoplastic condition, which human primates6; domestic animals7; and wildlife, remains to be determined. Ovarian neoplasm is usually unilateral but may be bilateral, dysgerminomas are considered to arise from the relatively soft, with smooth external surface, and may follicular oocytes or testicular homologues within the have cystic structures on cut surface. The the neoplasm is usually diffusely densely cellular with neoplastic cells share ultrastructural similarity to focal cystic and mineralized areas and high mitotic normal fetal oogonia. These neoplasms typically index, and neoplastic cells are round to polygonal with exhibit cytoplasmic and membranous granular cytoplasm. Although not prominent in carcinoma, malignant lymphoma, and granulosa cell this case, some neoplastic germ cells express vimentin tumor. On histopathological the stem cell-related protein Oct-4 mentioned by the examination, differential diagnosis should include any contributor is also positive in embryonal carcinomas, round cell neoplasm, especially lymphosarcoma. Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry, Theranostic are not widely available for veterinary diagnostics; and Genomic Applications. Dysgerminoma in an eastern rosella (Platycercus Dysgerminomas have been reported in related maned eximius exemius). In horses, dysgerminoma has been reported as a cause of hypertrophic osteopathy, which is more commonly associated with concurrent thoracic disease. High prevalence of ovarian tumors in maned wolves (Chrysocyon brachyurus) at the National Zoological Park. Theses monkeys received an amorphous extracellular antigen was evident in areas average inhaled dose of 729 colony-forming units of of necrosis or pyogranulomatous inflammation in Francisella tularensis (F. Organisms were included increases in body temperature, heart rate, readily identified within membrane-bound vacuoles peak cardiac pressure, and mean blood pressure. The bacteria varied in shape but were Gross Pathology: Prominent gross changes in all generally oval or elongate and measured 0. Bacteria contained a thin cell wall, a pale demarcated, necrotic foci present consistently in the central cytoplasm, and a darker rim of cytoplasm near lungs, mediastinal lymph nodes, and spleen but also the cell wall. An outer membrane was present in some seen in the heart, mediastinum, diaphragm, liver, organisms and appeared as an irregular or wavy urinary bladder, urethra, and mesentery. Many mediastinal lymph nodes, and spleen were most cells containing internal bacilli were seen in various severely affected, with as much as 50% of the tissue stages of degeneration characterized by swollen replaced by necrotic foci. Because severe mandibular, mediastinal, mesenteric, axillary, and degeneration and necrosis often hindered recognition inguinal lymph nodes; and in alveolar macrophages. Splenic borders are rounded, Division of Pathology, United States Army Medical Research Institute of indicating marked congestion. Lung, African green monkey: Foci of lytic necrosis (left) transition airways and extend into surrounding tissue. Also, vaccines that with hemorrhage, edema, necrohemorrhagic pleuritis, protect against ingestional or transdermal infection multifocal necrotizing vasculitis, and rare thrombi. The key exists among wildlife, particularly involving rabbits, pathologic features of inhalational tularemia in these hares, and rodents. Humans may become infected monkeys were numerous and widespread necrotizing through arthropod bites, through intact skin by pyogranulomatous lesions that especially targeted the handling infected animal carcasses, by ingesting lungs and lymphoid tissues. Bacteria were present in contaminated food or water, or by inhaling many cell types but were most readily present in contaminated aerosols. Ultrastructural features included the presence constituting an infectious dose, and it can survive for of bacteria within cytoplasmic vacuoles that were long periods in the environment. Lung, African green monkey: Electron micrograph of an alveolar neutrophils exhibit marked immunoreactivity for F. The wavy, lamellated cell membranes are characteristic of this bacterium when phagocytosed. We did not observe granulomas experimental model for investigating the nature of associated with epithelioid macrophages and host-pathogen interactions in macrophages, as well as multinucleated giant cells in the target organs of other aspects involved in the pathogenesis of tularemia. It is possible that the monkeys in this study succumbed to disease before such lesions had There are limited numbers of documented reports of sufficient time to fully develop. Another exception is experimental aerosolized tularemia in rhesus that the kidney is a reported target of human tularemia, macaques, mostly dating back to the 1960s. These yet none of our cases displayed gross or histologic reports describe acute bronchiolitis progressing to changes in the kidney. We did observe, however, that bronchopneumonia, lymphadenitis, splenitis, and most kidneys had positive immunohistochemistry hepatitis with neutrophilic and histiocytic labeling (for bacterial antigen) within glomerular inflammation with intrahistiocytic bacteria. One report did describe expensive and limited in supply in recent years, which histologic changes in the renal glomeruli of rhesus limits their usefulness as a model of tularemia. The tularemic lesions were present in the oral mucosa, tongue, lungs, liver, Our finding that F. It is essential to continue to phagolysosome fusion, and then replicate in these cells characterize the clinical and pathologic changes that is considered a key aspect of its pathogenesis. Experimental tularemia in gross and histologic lesions after exposure to Macaca mulatta: relationship of aerosol particle size to aerosolized F. Tularaemic necrosuppurative, multifocal, severe, with fibrinous pneumonia: pathogenesis of the aerosol-induced pleuritis. The automated bioaerosol Conference Comment: There are three strains that exposure system: preclinical platform development and cause tularemia: Francisella tularensis var tularensis, a respiratory dosimetry application with nonhuman the most virulent and commonly isolated form, F. In: Textbooks of Military Medicine, New World monkeys have been reported in the United Aspects of Biological Warfare. Typical gross findings include Borden Institute, Office of the Surgeon General, pyogranulomatous pneumonia and enteritis; United States Army Medical Department Center and necrosuppurative glossitis and gingivitis; and School; 2007:167-184. Tularemia is difficult to differentiate from other causes Epizootic of tularemia in an outdoor housed group of of gram negative sepsis and often causes lesions cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Serum Vitamin D Vitamin D analysis in serum from 10 pigs reveals no Signalment: 12 week-old male (castrated) and female detectable (<2. Neonate 5-15 40% mortality from weeks 9-12 in the nursery with no 10 days 8-23 response to antimicrobial therapy. Finishing pigs 30-35 Clinical signs included sudden death, seizure like Mature 35-70 activity, lameness with joint enlargement, and At Parturition 35-100 weakness with muscle fasciculations. Gross Pathology: Swollen joints with increased Bone analysis synovial fluid, swollen chondro-costal junctions, Bone Bone multiple fracture calluses on ribs, rib bones were soft IdentificationBone AshBone density Calcium Phosphorus and rubbery and bent 20-30 degrees before breaking. Pig, ribs: Multiple rib fractures (arrows) as well as an enlarged Lung, liver, spleen, and joint fluid; No significant costochondral junction (large arrow) is present in this 12-week-old pig. Hypertrophic chondrocytes are arranged in poorly organized columns and there are multiple islands of retained cartilage within the metaphysis. Long tongues of cartilage remain within the primary spongiosa that are often surrounded by variably thick seams of unmineralized osteoid which are lined by cuboidal osteoblasts. There is disorganization of primary spongiosa with multifocal fractures and areas of hemorrhage and fibrin accumulation. Pig, rib: Tangential section of the costochondral junction in a 12numbers of mesenchymal cells and variable amounts week-old pig. There is multifocal Pathology, 2764 Veterinary Medicine, Iowa State University, Ames, thinning of cortical bone with increased numbers of Iowa 50011. Swine are particularly sensitive to costochondral junction: Failure of endochondral rickets development because of rapid growth and confined facilities. Rickets and osteomalacia current industry practice for diet composition in market are metabolic bone diseases associated with flawed swine is tailored for lean muscle mass growth, not bone mineralization in growing and adult animals, bone formation. The metaphysis is flared, marrow spaces within the metaphysis are filled with collagen rather than marrow, and the cortex is markedly thinned. Dietary supplementation of vitamin D is considered a necessary practice for swine.
Renshen (Ginseng, Panax). Medrol.
- Depression, anemia, fluid retention, stomach inflammation and other digestive problems, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), fibromyalgia, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, skin cancer, fever, bronchitis, cancer, common cold, influenza, and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Diabetes.
- Male impotence (erectile dysfunction).
- Improving mood and sense of well-being.
- What is Ginseng, Panax?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What other names is Ginseng, Panax known by?
- Premature ejaculation when a cream containing ginseng and other ingredients is applied directly to the skin of the penis.
- Thinking and memory.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96961
Cheap medrol 16 mg without prescription
Adverse Effects + Hypokalemia (serum K less than 3 mmol/L) and/or a transient increase in serum creatinine occurs in approximately 16% of treated patients arthritis hand treatment discount medrol 4mg online. Injures tubular epithelium with resultant urinary loss of potassium and magnesium, decreased reabsorption of sodium, and renal tubular acidosis. Special Considerations/Preparation Available as powder for injection in 50-mg vials. Reconstitute with 10 mL of D5W or preservative free sterile water to a concentration of 5 mg/mL, then dilute further using D5W to a concentration no greater than 0. Terminal Injection Site Compatibility Amiodarone, heparin, hydrocortisone, sodium bicarbonate, and zidovudine. Amikacin, aztreonam, calcium chloride, calcium gluconate, cefepime, cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, dopamine, enalaprilat, fluconazole, gentamicin, linezolid, magnesium sulfate, meropenem, penicillin G, piperacillin/tazobactam, potassium chloride, propofol, ranitidine, remifentanil, and tobramycin. If infusion lasts longer than 2 hours, shake the bag to mix the contents every 2 hours. The diluted admixture is stable for 48 hours refrigerated and an additional 6 hours at room temperature [1]. References Adler-Shohet F, Waskin H, Lieberman J M: Amphotericin B lipid complex for neonatal invasive candidiasis. Pharmacology Amphotericin B lipid complex consists of amphotericin B complexed with two phospholipids in a 1:1 drug-to-lipid ratio. Special Considerations/Preparation Available as a suspension containing 100-mg Abelcet in 20-mL (5 mg/mL). Shake the vial gently until there is no evidence of any yellow sediment on the bottom. Dilute the drug with D5W so that the final infusion concentration is 1 to 2 mg/mL. Acts by binding to the sterol component of a cell membrane leading to alterations in the cell wall permeability and death. Special Considerations/Preparation Available as powder for injection in 50 mg vials. Reconstitute by adding 12 mL of sterile water for injection to a yield a concentration of 4 mg/mL. A 1 mg/mL dilution may be made by filtering (using 5 micron filter) 1 mL of reconstituted solution into 3 mL of D5W. Uses Treatment of systemic fungal infections resistant to conventional amphotericin B therapy or in patients with renal or hepatic dysfunction. Pharmacology AmBisome consists of amphotericin B intercalated within a single bilayer liposomal drug delivery system. Adverse Effects Anemia, thrombocytopenia, hypokalemia, nausea/vomiting, and fever/chills. References Juster-Reicher A, Flidel-Rimon O, Amitay M, et al: High dose liposomal amphotericin B in the therapy of systemic candidiasis in neonates. Uses Broad-spectrum antibiotic useful against group B streptococcus, Listeria monocytogenes,and susceptible E coli species. Therapy should be discontinued at 48 hours if the probability of sepsis is low [5]. Clearance is primarily by the renal route and is inversely related to postnatal age. Reconstituted solution must be used within 1 hour of mixing because of loss of potency. Acyclovir, alprostadil, aminophylline, aztreonam, calcium gluconate, cefepime, chloramphenicol, cimetidine, clindamycin, enalaprilat, famotidine, furosemide, heparin, hydrocortisone succinate, insulin, lidocaine, linezolid, magnesium 68 Micormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014 sulfate, metronidazole, milrinone, morphine, phytonadione, potassium chloride, propofol, ranitidine, remifentanil, and vancomycin. Optimal treatment for suspected, early-onset sepsis is broad-spectrum antimicrobial coverage using a combination of ampicillin and an aminoglycoside (usually gentamicin); once a pathogen is identified, therapy should be narrowed unless synergism is required. Pharmacology 70 Micormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014 Ampicillin is a semisynthetic penicillin that is bactericidal. Hypersensitivity reactions (maculopapular rash, urticarial rash, or fever) are rare in neonates. Special Considerations/Preparation Available as powder for injection in 125-, 250-, 500-mg, 1-g, 2-g, and 10-g vials. Acyclovir, alprostadil, aminophylline, aztreonam, calcium gluconate, cefepime, chloramphenicol, cimetidine, clindamycin, enalaprilat, famotidine, furosemide, heparin, hydrocortisone succinate, insulin, lidocaine, linezolid, magnesium sulfate, metronidazole, milrinone, morphine, phytonadione, potassium chloride, propofol, ranitidine, remifentanil, and vancomycin. Terminal Injection Site Incompatibility Amikacin, amiodarone, dopamine, epinephrine, erythromycin lactobionate, fluconazole, gentamicin, hydralazine, metoclopramide, midazolam, nicardipine, sodium bicarbonate, and tobramycin. Duration of therapy for proven infection, without systemic complications, is at least 2 weeks after documented clearance of Candida from the bloodstream and resolution of symptoms [3]. Candida species are the most common cause of invasive fungal infection in humans; mortality in neonates and children from invasive candidiasis is 10% to 15%. Antifungal therapy should be started on all candidemic patients within 24 hours of a blood culture positive for yeast; delays are associated with increased mortality [3]. Despite sensitivity to amphotericin B, fungal peritonitis was not cleared in a full-term neonate until anidulafungin was added to liposomal amphotericin B; Candida albicans had been cultured from the peritoneum while the patient was receiving amphotericin B monotherapy [2]. Contraindications/Precautions Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to other echinocandins [4]. It has demonstrated activity against the 73 Micormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014 biofilms of C. In a single-dose study, less than 1% was recovered in urine and approximately 30% was recovered in the feces over 9 days, of which less than 10% was intact anidulafungin. In a pharmacokinetic and safety study following 3 to 5 days of anidulafungin (n=15; age 2 days to 2 years), neonates (n=8; 6 out of 8 premature) demonstrated a median weight adjusted clearance of 0. Also monitor for signs and symptoms of worsening hepatic function in patients who develop abnormal liver function tests during therapy [4]. Special Considerations/Preparation Available as 50-mg and 100-mg single-use vials of anidulafungin lyophilized powder for solution. Excursions to 25 degrees C (77 degrees F) are permitted for 96 hours; then, vial may be returned to refrigerator [4]. Terminal Injection Site Incompatibility Amphotericin B conventional colloidal, diazepam, ertapenem, magnesium sulfate, nalbuphine, phenytoin, sodium bicarbonate. The determination of compatibility is 75 Micormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014 based on concentrations for administration recommended herein. Candida species are the most common cause of invasive fungal infection in humans; mortality in neonates and children from 76 Micormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014 invasive candidiasis is 10% to 15%. Anidulafungin may be a useful addition or alternative to other antifungal agents for the treatment of infection due to Candida species, based upon safety, pharmacokinetic [1], and limited treatment data [2]. Hepatitis, hepatic failure, and significant hepatic dysfunction have been reported. Anaphylactic reactions, including shock, have also been reported; discontinue use if reactions occur. Infusion-related reactions (eg, rash, urticaria, flushing, pruritus, bronchospasm, dyspnea, and hypotension) have been reported; to reduce occurrence, do not exceed an infusion rate of 1. Pharmacology Anidulafungin, a semi-synthetic echinocandin, is a non-competitive inhibitor of beta(1,3)-D-glucan synthase; this enzyme is responsible for formation of the polysaccharide, beta-(1,3)-glucan, an essential fungal cell wall component [4]. The clinical relevance of these reports is unknown, but the development of drug resistance may be possible. Undergoes slow chemical degradation at physiologic temperature and pH to a ring-opened peptide (inactive). In a single-dose study, less than 1% was recovered in urine and approximately 30% was recovered in 77 Micormedex NeoFax Essentials 2014 the feces over 9 days, of which less than 10% was intact anidulafungin. Adverse Effects Adverse events reported were hypotension (1), adrenal insufficiency (1), abnormal Xray of kidneys, ureter, and bladder (1), death (1), infection (1), pulmonary edema (1), and oliguria or uremia (2) in a safety study of 8 neonates [1]. Monitoring Monitor blood cultures daily or every other day until yeast is cleared [3]. The 50-mg and 100-mg vials also contain fructose (50 mg and 100 mg, respectively) and mannitol (250 mg and 500 mg, respectively). Reconstitute 50-mg and 100-mg vials with 15 mL and 30 mL, respectively, of sterile water for injection (3. Reconstituted solution may be stored up to 24 hours at 25 degrees C (77 degrees F) or less. Diluted solution for infusion may be stored at room temperature, up to 25 degrees C (77 degrees F), for up to 48 hours or frozen for at least 72 hours prior to administration [4]. Uses Multivitamin supplement for infants with cholestasis and other conditions associated with malabsorption of fat soluble vitamins [1]. Sodium phenylacetate/sodium benzoate should be used concomitantly with arginine hydrochloride.
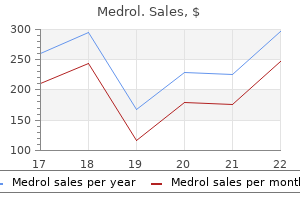
Order medrol with paypal
However osteoarthritis definition order 16mg medrol amex, there are few Eradication of chronic carriage has been achieved with longer dustudies of the in vitro interactions between antimicrobials for Salrations of antimicrobial therapy than are required for managemonella isolates (574, 575). Cholecystectomy can be considered if antimicrobials pregnant women with enteric fever (63, 576). Fluoroquinolones fail, but the surgery can carry risks, and there should be additional have been occasionally used in pregnant patients infected with indications for operation. Animal studies of azithromytion of chronic carriage is increased by giving antimicrobials at the cin have not revealed evidence of fetotoxicity, although there are same time (592). Food and Drug Administration has assigned azithromycin to Evidence Needs for Antimicrobial Management pregnancy category B, indicating that it should be given during Most physicians base their therapeutic choices on international or pregnancy only when benefit outweighs risk. In lowcaution be used when administering azithromycin to nursing resource areas, the diagnosis of invasive Salmonella infection is women. Antimicrobials are easily available without the authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this pubprescription in pharmacies and shops in most developing counlication, and they do not necessarily represent the views, decisions, or tries, and counterfeit or substandard antimicrobials are likely to policies of the U. Many randomized trials have been countries in south and southeast Asia: a systematic review. Invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella disease: an emerging and nefrom existing studies are useful (505, 598). F, Bolliger I, Bonaventure A, Boufous S, Bourne R, Boussinesq M, Braithwaite T, Brayne C, Bridgett L, Brooker S, et al. Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, a high case fatality ratio. Burden of typhoid fever in lowincome and middle-income countries: a systematic, literature-based upvision was needed for contemporary invasive Salmonella infecdate with risk-factor adjustment. Population-based incidence of complicated typhoid fever and may serve as an alternative oral typhoid fever in an urban informal settlement, Nairobi, Kenya: implicadrug in areas where fiuoroquinolone resistance is common. Emergence of Salmonella enterica We thank France Mentre for helpful discussions and Lorna Saint Ange for serotype Paratyphi A as a major cause of enteric fever in Kathmandu, editing. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and is associated with resistance to enteric fever. Helicobacter tibility and clinical outcomes in Toll-like receptor 5-deficient patients pylori infection and typhoid fever in Jakarta, Indonesia. Association between the acquired immunodeficonductance regulator, on the intestinal epithelium. Susceptibility to typhoid fever is associated uninfected adults and adolescents in northern Tanzania. An outpatient, ambulant-design, controlled human disease requiring surgical management. Typhoid fever in African and on clinical features, laboratory findings, and complications of typhoid Indian children in Durban. Salmorovar Typhi from Vietnam: application to acute and relapse cases of nella Typhi meningitis in infants. Community-acquired septicaemia in southern Viet association between typhoid carriage, typhoid infection and subsequent Nam: the importance of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhi. Development and evaluation of an enzyme-linked immuresistant nontyphoidal Salmonella is associated with excess bloodstream nosorbent assay for serum Vi antibodies for detection of chronic Salmoinfections and hospitalizations. Identification of a carrier by using Vi enzyme-linked immunosorin hospitalised adults with community acquired non-typhoidal Salmobent assay serology in an outbreak of typhoid fever in an Indian reservanella gastroenteritis. The decline of typhoid and the rise of non-typhoid salphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Ty21a live oral typhoid vaccine and prevention of Macete E, Nhamposa T, Machevo S, Aide P, Bassat Q, Bardaji A, paratyphoidfevercausedbySalmonellaentericaserovarParatyphiB. MicrobiologSalmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium infections in children in ical analysis of nontyphoidal Salmonella strains causing distinct synFrance: a national case-control study. Invasive non-Typhi protection against bacteremia caused by nontyphoidal strains of SalmoSalmonella disease in Africa. Salmonella infections in immunocompromised Lack of clonal relationship between non-typhi Salmonella strain types adults. Invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella Typhilomatous disease: the European experience. Bacteremia in febrile Malawian children: clinical and microbiantibody-mediated phagocytosis and cell-free killing of invasive African ologic findings. Non-typhoidal salmonellae: a manageacquisition of T cells and antibodies to nontyphoidal Salmonella in Mament challenge for children with community-acquired invasive disease lawian children. Severe febrile illness in adult hospital admissions in clinical differentiation of malaria and typhoid: a preliminary communiTanzania: a prospective study in an area of high malaria transmission. Nadjm B, Amos B, Mtove G, Ostermann J, Chonya S, Wangai H, cases at presentation in outpatient clinics in Jakarta, Indonesia. Searching for the elusive typhoid typhoidal Salmonella meningitis in Malawian children, 1997-2006. Factors infiuencing the results of blood pneumonia caused by nontyphoidal Salmonella in a Malawian child. Hung C-C, Hung M-N, Hseuh P-R, Chang S-Y, Chen M-Y, Hsieh S-M, in areas of endemicity. Study on blood cultures and bacteria counts in the the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy and an increasing trend of blood of paratyphoid fever A patients. Arch Intern Non-typhoidal Salmonella bacteraemia: clinical features and risk factors. Trends in bloodstream infections among human immunodefication of Salmonella Typhi within 18 hours of specimen acquisition by ciency virus-infected adults admitted to a hospital in Nairobi, Kenya, culture of the mononuclear cell-platelet fraction of blood. A relationship between counts and clinical features, transmissibility, and reduction in adult blood stream infection and case fatality at a large antibiotic resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci stream infections in adults: how many blood cultures are neededfi Immunity to salmoBactec Peds Plus/F and Bactec lytic/10 anaerobic/F media for isolation of October 2015 Volume 28 Number 4 Clinical Microbiology Reviews cmr. Widal agglutination test 100 years later: sodium polyanethanol sulfonate as a blood culture additive for recovery still plagued by controversy. Streptokinase clot culture compared with whole treatment Widal test in suspected enteric fever cases in the Philipblood culture for isolation of Salmonella typhi and S. Value of a single-tube Widal test in diagnosis Diagnostic yield of blood clot culture in the accurate diagnosis of enteric of typhoid fever in Vietnam. Summary of an international workshop typhoid fever by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay determination of on typhoid fever. Systemic and intestinal immunities after natural typhoid infecbiotic susceptibility testing of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi isolated tion. Detection of antibodies against Salmonella Typhi bone marrow, blood, stool and duodenal contents cultures for bacteriologicconfirmationoftyphoidfeverinchildren. Serology kinase clot culture and 8 mL 1:10 blood-to-broth ratio blood culture for of typhoid fever in an area of endemicity and its relevance to diagnosis.
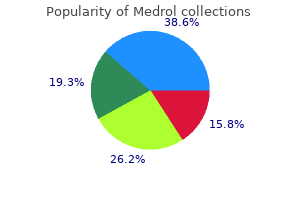
Order medrol no prescription
This quesuseful to provide the references on mold tionnaire can be completed either independently remediation zeel rheumatoid arthritis order 4 mg medrol mastercard. In addition, as stated earlier, we suggest this tool would be instructive with the third group of patients (those who are concerned generally over a potential mold exposure). A Public Health Model: the Sentinel Case Management and Remediation Once a building relationship is established, the healthcare provider is encouraged to exclude Medical Management and Follow-up a more general public health problem related Patient care for the treatment of buildingto the building. Without requesting names, the provider should ask whether other individuals related illnesses include (1) removal from the in the building have similar symptoms. In all states, if frequently, the first two are ignored and only multiple individuals are involved, the treating the underlying condition is emphasized. It is espeevaluate the building to identify the cause of cially important in conditions that may become the illness. Sources of water intrusion and irreversible, such as asthma and hypersensitivity mold amplification need to be identified and pneumonitis. Y N Better Worse Same Better Worse Same Runny, blocked, or stuffy Y N Better Worse Same Better Worse Same nosefi Y N Better Worse Same Better Worse Same Feelings of unsteadiness Y N Better Worse Same Better Worse Same when walkingfi This makes timely recognition of the condition and removal of the patient from expoA Note on the Use sure important. After remediation, clinical follow-up is critical in evaluating the success of the intervention. Frequently, the offending mold can be decreased to a tolerable level, but once an individual is sensitized, this may not always be possible. Unfortunately, current methods of mold detection are not sensitive or quantitative enough to be able to determine if the exposure has been sufficiently decreased. The only assessment for someone very sensitized to mold is to allow the individual to return to the environment and monitor his or her condition carefully to determine if there is an exacerbation of symptoms. Once an individual has developed asthma, the asthma may not subside completely, even when exposure to the original agent has ceased (Chan-Yeung and Lam 1986, Chan-Yeung and Malo 1995). So, one must monitor the severity of asthmatic symptoms and the quantity and type of medications that are required for asthma control. At that point, the patient may be returned, on a trial basis and with careful oversight to detect exacerbation, to the remediated building. The medical management of allergic and irritant syndromes is no different for those related to mold exposure than for other types. Antihistamines, inhaled nasal corticosteroids, and inhaled pulmonary corticosteroids can be prescribed as needed. The clinician needs to be aware of the possibility that symptoms are suppressed in the setting of ongoing exposure to pertinent agents, particularly antigens. This may result in greater morbidity over the long term because removal from the environment of concern may not occur. Concomitant use of medical therapy during evaluation and remediation of an environment is, however, not only acceptable but important in the recovery of the individual. Table E: Environment Intervention Guidance (Selected World Wide Web Resources) United States Environmental Protection Agency Indoor Air-Mold. Fungal Contamination in Public Buildings: A Guide to Recognition and Management, June 1995; Federal-Provincial Committee on Environmental and Occupational Health; Health Canada. Microorganisms in Home and Indoor Work Environments: Diversity, Health Impacts, Investigation and Control, 2001; Ed: Flannigan, Samson and Miller; Taylor & Francis; London and New York. An assessment of mold in the environment may become especially important for patients with specific symptoms and syndromes (see Table A in chapter 5) or for patients with other common symptoms and syndromes (see Table B and Grid D in chapter 5) that are worse in a particular environment. The reader should note that the authors do not advocate air sampling to initially address concerns over mold in the indoor environment. This is in part because air test results are often not representative of the biological exposures a patient may face and, therefore, can be misleading and not helpful. Because the health provider may be given reports and information that includes air-sampling results, this chapter provides guidance on planning an indoor air assessment for mold and on interpreting air-sampling results. Consultant Selection and Staff Training Patients may bring healthcare providers reports with contributions from different types of professionals, including specialists in ventilation, industrial hygiene, environmental science, architecture and building physics, occupational and environmental medicine, mycology, and public health. To evaluate and then use the information in these assessments, it is critical to know the context of the assessment and the background and credentials of the individuals who performed them. For the healthcare provider who may look to suggest an outside environmental assessment, the following paragraphs briefly discuss three categories of professionals who will most likely bring a learned approach to the challenge of assessing the environment for exposures to bioaerosols: industrial hygienists, indoor environmental quality consultants, and environmental health professionals. Although not as common, other professionals may provide assessments or specialized expertise to address indoor environments. Experience conducting environmental assessments with a focus on bioaerosols is a key qualification for any of these professionals. Mycologists knowledgeable about indoor-mold-contamination issues bring a critical perspective to designing sampling programs and interpreting results. Building scientists (usually architects or engineers who have specialized expertise) bring helpful skills and an understanding of the movement of moisture and air in the building, which are often instrumental in finding and remediating moisture intrusion. Industrial Hygienists In the broadest sense, an industrial hygienist focuses on exposures that affect the health and wellbeing of workers. These individuals are well versed in measuring and assessing occupational hazards. Certified Industrial Hygienists have the training to develop the broad perspective required to address mold in the environment. However, because (1) exposure to bioaerosols is not readily identified by standard air-monitoring methods, (2) home and A qualitative assessment that office environments are different than industrial sites, and (3) the biology of mold is complex, an identifies factors that support the assessment is best completed by an industrial hygienist experienced with mold assessment. Individuals who practice as indoor environthese factors provides helpful mental/air quality consultants come from many different backgrounds (engineering, basic sciences, guidance for the healthcare planning, and design) and different professions provider and the patient. Occupational and environmental medicine physicians and nurses, as well as public health professionals (Masters in Public Health and graduate-level epidemiologists), bring relevant background to environmental assessment. The patterns and locations where occupants experience symptoms help direct where to look for mold sources. Moreover, the local health director or state official is not infrequently the person who directs or orders an environmental assessment in a public building, such as a school, when poor indoor environmental quality is suspected because of a high level of health complaints. Patient or Family Member as Investigator of Environment the patient or a family member may assess the environment for mold. One caution: if you suspect mold is present and may be playing a role in illness and you direct your patient to investigate his or her environment beyond the home checklist, it would be prudent to suggest that the patient use care when exploring his or her environment. If the individual develops symptoms while investigating, he or she should be cautioned to ask someone else to explore for and clean up mold contamination if needed. Guidance on personal protection and how to remediate mold contamination is addressed in the next chapter of this book. Qualitative Approach to Environmental Site Assessment A qualitative assessment that identifies factors that support the growth of indoor fungi and makes recommendations for correcting these factors provides helpful guidance to the healthcare provider. The environmental assessor seeks to identify sources of mold growth (reservoirs) and to define the pathways in the environment that may bring mold and any associated toxins into contact with the building occupants (Burge and Otten 1999). The objective is to find areas where mold is amplified (growing) and then disseminated into the breathing space. A moldy odor or visible evidence of mold colonies or mildew on materials indicates the presence of mold. Interview and Walk-through Assessment the assessor gathers qualitative data by interviewing the occupants and taking a walk-through site tour. If the assessor is the patient, noting where in the home environment and under what conditions (such as heat on or off) he or she experiences symptoms will indicate where to look. The walk-through will explore the immediate outside environment and the physical structure of the home or building; note water or moisture incursion from past and present leaks, spills, and condensation; review ventilation and 48 note apparent mold, mildew, and areas with moldy, musty odors. Likely places where moisture may accumulate, such as crawlspaces, should be noted.
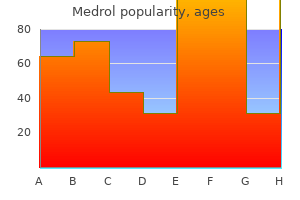
Purchase medrol now
All have an indirect life cycle that utilizes ants arthritis treatment knuckles cheap medrol 16 mg, beetles and flies as the intermediate hosts. Diagnosis: Diagnosis is made by accurate identification of the parasite during necropsy and by identifying proglottides in feces. Treatment: Broad spectrum benzimidazoles are effective for treatment of infestations of this tapeworm. Prevention: Improve sanitary practices and apply approved insecticides to the soil or litter on the premises. Endoparasites:Syngamus trachea (nematode) Other names: Gapeworm, red worm, forked worm. The bird may cough and perform gaping movements when the worms clog and obstruct the airways. It is bright red in color, and both sexes are in permanent procreative conjunction. When the female gapeworm lays her eggs in the trachea of an infected bird, the eggs are coughed up, swallowed, and then defecated. When birds consume the eggs found in the feces or an intermediate host such earthworms, slugs and snails, they become infected with the parasite. Diagnosis: Diagnosis is based on clinical signs, characteristic eggs in the feces, and finding the worms in the airways at post-mortem. Microscopically, they cause dilatation of proventricular glands, and compression and necrosis of glandular epithelial cells. Cause, transmission, and epidemiology: this nematode worm has been reported in North America and Africa. Diagnosis: Definitive diagnosis is reached at post mortem through identification of the worm. Endoparasites: Trematodes There are many trematodes reported in birds, represented in the genera Brachylaemus, Echinostoma, Echinoparyphlum, Hypoderaeum, Notocotylus, Cattropis, and Postharmostomum. Prosthogonimus pellucidus has been reported in Kenya and Brachylaemus commutatus from Uganda. Prosthogonimus ovatus has been found in geese in Africa, Europe, Asia, and North and South America. Adult worms measure 8-9 mm long and 4-5 mm wide, and are broader at the posterior end than the anterior end. Birds infected by Prosthogonimus species have a tendency to sit on the nest, have a milky discharge from the cloaca, and lay eggs with soft or no shells. Endoparasites: Trichostrongylus tenuis (nematode) Clinical signs and lesions: this species is associated with severe weight loss and anemia, and the caecal wall is congested and thickened. Clinical signs and lesions: Many infected wild birds and poultry flocks have transient alphaviral infections and show no clinical signs, but antibodies can be demonstrated in their sera. Sick poultry flocks (especially captive game birds) show marked signs of disease of central nervous system. Signs often include ataxia, paresis, paralysis, inability to stand or hold up the neck, circling, and tremors. Microscopic lesions occur in the brain of most clinically ill birds, but are not specific or definitive indicators of the disease. Cause, transmission, and epidemiology: Equine encephalitis viral infection is an acute disease of pheasants, chukar partridges, turkeys, ducks, pigeons, or wild birds caused by one of a number of alphaviruses. The viruses multiply in the arthropod and are transmitted when they bite susceptible vertebrates. Certain mosquitoes, primarily Culiseta melanura, feed on the viremic birds and become infected with virus, oftentimes for life. Infected mosquitoes then transmit the infection to other susceptible birds while feeding on them. Birds are the major source of infection for the mosquitoes, because they carry a higher titer of virus than most mammals. Cannibalism of viremic, sick, or dead birds by other susceptible birds is an important method of transmission of virus within infected flocks. Certain biting insects (gnats, deerflies, horseflies, etc) may transmit the virus mechanically. Diagnosis: In flocks with clinically ill birds, the signs are suggestive of central nervous system disease. Specific identification is usually made via virus neutralization or complement fixation tests. Prevention: Protect birds against mosquitoes by the use of screens, sprays, or other mosquito control methods. Practice known methods of preventing cannibalism, including avoiding overcrowding and maintaining temperature controls. Recovery: There is no residual risk of infection after a case has occurred based on environmental contamination. However, if the conditions which resulted in the initial infection (presence of mosquitoes, presence of a reservoir host) are not corrected, then new birds may be infected. Clinical signs and lesions: Favus is a skin mycotic infection found primarily in gallinaceous birds. Favus is rare in commercial poultry, but occasionally found in hobby and backyard flocks, and game birds. Lesions include white, scaly crusting on the comb and wattles that can extend to the feathered portion of the skin of the head and neck, with loss of feathers. The fungus infects the epidermis, which is thickened with degeneration, and neutrophils mixed with fungal mycelia. Differential diagnosis: Other skin infections and causes of feather loss (ectoparasites and trauma). Cause, transmission, and epidemiology: Microsporium gallinae is the agent most often isolated, although M. The infection is contagious and is transmissible to man, as are the majority of dermatophytes that form ringworm. It is reported in chickens, turkeys, ducks, quail, and canaries, and is a primary pathogen. Favus spreads slowly through a flock by direct contact or contact by contaminated cages or transport coops. Histological examination of Gridley stained tissue will show characteristic hyphae. Treatment: There is no approved treatment, but topical treatment with Nystatin has been effective on individual bird. Application of a 2% quaternary ammonium disinfectant, 1% tincture of iodine, or 5% formalin will eliminate the infection. Transport crates and other equipment should be thoroughly decontaminated and disinfected to prevent lateral transmission of the agent. Recovery: Complete recovery requires that all individuals in a flock are cured of infection and that none of the causative agents remain in the environment. Recovery may be prolonged if treatment is incomplete or if the environment is not decontaminated. Fowl Cholera Other names: avian pasteurellosis, cholera, avian hemorrhagic septicemia. Clinical signs and lesions: Fowl cholera usually strikes birds older than 6 weeks of age. Fever, reduced feed consumption, mucoid discharge from the mouth, ruffled feathers, diarrhea, and labored breathing may be seen. As the disease progresses birds lose weight, become lame from joint infections, and develop rattling noises from exudate in air passages. As fowl cholera becomes chronic, chickens develop abscessed wattles and swollen joints and foot pads. Differential diagnosis: Fowl cholera must be differentiated from swollen head syndrome, Mycoplasmosis, avian influenza and Newcastle disease.
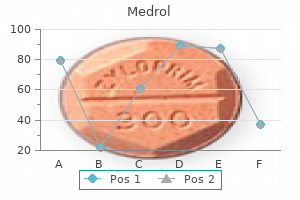
Purchase medrol 16 mg without a prescription
Typically it affects younger birds and presents Definitive diagnosis requires recognition of pathognomic as paralysis (Figure 82) with perineuritis or as lymphoid tumours intranuclear inclusion bodies in the gizzard epithelium (Figure in organs such as liver or kidney gouty arthritis diet list order medrol with mastercard. Clinically birds are often very thin and present with severe bilateral conjunctivitis, swollen eyelids and conjunctival sacs distended with inspissated pus. Mortality tends to be low with the dry form and greater with the wet form of the disease. Culling sick birds with typical lesions may help limit the spread of fowl pox but all-in/all-out rearing practices, with disinfection between batches, is required to eradicate the disease. Typically an egg is Internal and external parasites are common, though clinical retained within the oviduct (egg bound) and fibrinosuppurative disease is not always present. Lice and red mites cause feather seen in aged layers, in which there is often serosal implantation damage and anaemia. Ectoparasites can usually be detected by of the tumour on the intestines and other organs. Usually, a chronic disease of older birds, the typical granulomatous lesions, with acid fast bacteria, are most commonly found in the intestines and liver; pulmonary lesions are less common. Figure 85: Fowl pox lesions in the oral cavity of a chicken identified Figure 86: A sub adult harbour seal showing a characteristic during post-mortem examination (Photo: Jim O Donovan). The injuries are considered case basis and hope to agree a protocol with the State consistent with seals being drawn through a ducted propeller Laboratory and the National Parks and Wildlife Service in 2011 such as a Kort nozzle or some types of Azimuth thrusters, which which will put this work on a more formal footing. Three stateare common means of propulsion and manoeuvre in a variety supported reintroduction projects have been managed by the of coastal and sea-going vessels. Golden Eagle Trust, a private charity (Red Kites in Wicklow and Dublin, Golden Eagles in Donegal, and White-tailed Eagles in Suspected cases of wildlife poisoning in Ireland Co. In all cases it was believed that the raptors were accidentally poisoned by people targeting other species (mainly foxes, crows), and the Golden Eagle Trust has undertaken an education programme, including a leaflet on the safe and legal control of foxes and crows at lambing time. The purpose of this scheme is to investigate deaths of wildlife and occasionally pets where there is evidence that pesticide poisoning may have occurred. The results of these investigations are used to monitor pesticide use and to enforce legislation on the protection of humans, animals, food and the environment from pesticides. Figure 89: A map of the island of Ireland showing the locations where foxes were collected for the Trichinella surveys in 2010 (n=653). Subsequent toxicological examination of tissue samples confirmed death was due to carbofuran poisoning (Photo: Micheal Casey). A further fifteen thousand one hundred and ninety five samples from specific locations in the body (cheek, forelimb, samples were examined for rumen fluke eggs and five thousand tongue and diaphragm) were collected from each fox and these six hundred and seventy nine (37. The were analysed microscopically for the presence of Trichinella frequency of detection was remarkably similar for both liver spiralis larvae following a pepsin digestion procedure. Figure 91 illustrates the change in the proportion were found to be positive for Trichinella spiralis larvae. As an example of this, Figure 90 shows detection in cattle decreased progressively from the first to the the rise in bovine faecal sample numbers submitted for liver fourth quarter. This trend differs considerably from that fluke egg examination in the years 2006 to 2010. Figure 93 illustrates the change in the proportion eggs in a faecal sample needs careful examination. On the other hand, a In 2010, a combined total of fourteen thousand nine hundred large proportion of those animals with positive rumen fluke and fifteen bovine and three thousand one hundred and twenty results show few if any clinical signs of disease. A strongyle burden of greater In terms of mortality, liver fluke infestation is a much more than five hundred eggs per gram of faeces is considered clinically serious threat to livestock (see Diseases of cattle on page7) than significant. The clinical significance of paramphistomosis (rumen fluke 30% infestation) has only become apparent in recent years and accurate data on its true prevalence and economic impact is 25% lacking. Heavy infestation can lead to illthrift but mortality 20% attributable to paramphistomosis is uncommon in 2010 in Northern Ireland one bovine post-mortem examination 15% Bovine Ovine recorded paramphistomosis as the cause of death while in 10% Ireland it was not recorded as the cause of death in any bovine post-mortem examination performed. There may be a number of reasons 30% for this, such as inherent resistance, age profile of the animals 25% sampled, type of pasture grazed etc. A further one thousand seven hundred and of animals to be tested by practitioners in Northern Ireland. Figure 96 illustrates the trend by and rumen fluke eggs between the laboratories may be due, in quarter. However the majority of these positive samples (66 per cent) contained very small numbers of coccidial oocysts and are unlikely to have been solely responsible for significant disease. The results of faecal coccidial oocyst counts in cattle and sheep should be interpreted with caution. Only two (Eimeria bovis and Eimeria zuernii) out of twelve species of bovine coocidia and three (Eimeria crandallis, Eimeria ovinoidalis and Eimeria ahsata) Figure 95: A photomicrograph of a bovine bronchus showing a out of twelve ovine coccidia species are pathogenic. These 4% species can also produce dense focal lesions containing large 4% numbers of oocysts in the small intestine which are visible on 3% post-mortem examination. Large numbers of oocysts can be 3% produced daily from these focal lesions without any clinical 2% effect on the host. As oocysts are prevalent in faeces of sheep 2% of all ages, coccidiosis cannot be diagnosed based solely on the 1% finding of oocysts and the clinical presentation and history 1% should also be considered. The between batches or the mixing of different age groups during farmer normally purchased weanlings and store cattle in the housing. One of the animals (animal A) began to lose its hair over Not Detected Positive 86. An ivermectin pour-on product was administered to the group but did not appear to remedy the situation. Figure 97: the percentage of bovine faecal samples positive for coccidial oocysts (n=12,750). Animal A did not recover however, and died one on the day of the farm investigation (Figure 98). The other animals did respond well and the scratching and licking reduced dramatically over the following weeks. However an assumption was made that animal A was the original source of the infestation. This animal had been purchased at the mart from a farmer who was involved in the business of purchasing, storing and selling sheep wool each year. One theory considered during this investigation was that the animal had come into contact with some stored wool from a sheep infected with sheep scab. Figure 98: Extensive hair loss in a bullock (Animal A) with psoroptic mange (Photo: Alan Johnson). Anthelmintic resistance in Ireland Other animals affected had localised lesions of moist dermatitis and hair loss (Figure 99), mostly on the dorsal parts of the trunk. Currently the returns from a new and extensive Northern Ireland wide questionnaire are being analysed, and studies on the efficacy of anthelmintic regimes used by farmers to control gastrointestinal nematode infestations and liver fluke on over one hundred sheep and cattle farms throughout the province are being carried out. A detailed comparative field study on anthelmintic efficacy against nematodes and fluke is Figure 99: Moist dermatitis and hair loss in a bullock with psoroptic also in progress on a limited number of selected sheep farms mange (Photo: Alan Johnson). A diagnosis of psoroptic mange of anthelmintic resistance, to develop effective protocols for was made following microscopic examination of the scrapings rapid diagnosis in nematode and fluke infestations and to and identification of Psoroptes ovis mites (Figure100). Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles Resistance to antimicrobials is a serious concern in human and veterinary medicine. Increasing resistance within microbial populations to commonly used antibiotics is a global problem. Some resistant bacteria have zoonotic potential, and furthermore, as similar bacteria are found in humans and animals, resistance mechanisms developed by bacterial populations in animals may be transmitted to their counterparts in humans. The ability of micro-organisms to adapt to their environment, Figure 100: Psoroptes ovis mite seen in a skin scraping taken from together with the widespread usage of antibiotics has meant that Animal A (Photo: Brendan Crowe). Information is provided to veterinary practitioners Ampicillin in the form of in vitro resistance profiles for particular bacterial AmxCla isolates on a case by case basis to allow effective therapeutic Cefoxitin decisions to be made. The results indicate the in vitro susceptibility of specific isolates in laboratory conditions, and it is important to note that these in vitro results may not directly correlate with clinical efficacy in field situations.
Syndromes
- The name of the product (ingredients and strengths, if known)
- Coronary angiography
- Penile ultrasound to check for blood vessel or blood flow problems
- In heart failure, fluid collects in the lungs, liver, blood vessels, and body tissues because the heart does a poor job of pumping it to the kidneys where it can be eliminated.
- Change in development
- Antithyroid medications
- Shock
Buy cheap medrol 16mg on-line
There characteristic gross lesion caused by this mite is were similar 1 mm diameter tan nodules within numerous 2 mm tan to white cystic dermal the hairless patches of the dorsum and face arthritis pain wikipedia buy medrol online from canada. The cysts resemble comedones and the face, pinnae, and dorsum are multifocally histologically are characterized by dilated follicles dilated and contain abundant arthropods (mites) 1,5 plugged with abundant mites and keratin debris. The microns in diameter with a chitinous exoskeleton, presence of mites in hair follicles of the pinnae, as multiple jointed appendages, skeletal muscle, and was seen in this case, is a less common a reproductive tract containing basophilic 1 presentation. Similar mites are embedded in sides of the pinna and may need to be hyperkeratotic surface epithelium. There are 1 differentiated from notoedric ear mange, in multifocal 40 60 micron diameter basophilic which the lesion tends to be more superficial and eggs. Rare sections contain subcutaneous proliferative with mites embedded in the stratum inflammation characterized by lymphocytes, 4 corneum. Haired skin, mouse: There are numerous cross sections of follicles containing abundant keratin debris (comedones) (black arrows) arthropod parasites (mites) lining the wall of the comedone. External ear canal, mouse: There is a focal area of epidermal chitinous exoskeleton, obvious jointed appendages, and striated muscle. We receive few wild mice at contact1 and gravid females enter the hair follicles our laboratory but in our experience P. Pinna: Otitis externa, h y p e r k e r a t o t i c a n d lymphohistiocytic, diffuse, moderate, with infundibular adult mites and eggs. Conference Comment: For an institution with thousands of animals comprising hundreds of different species, this case serves as a reminder of the importance in monitoring the health of wildlife pests in addition to exhibit animal population. Psorergates simplex mites were once prevalent in laboratory mice but are now only readily recognized among wild and 4-5. Hair follicles, mouse: Centrally within the comedones, there are moderate numbers of yeasts and pet mice. Nidification of a mite participants discussed the finding of some (Psorergates simplex Tyrell, 1883: Myobiidae) in sections of mites which appeared to be larger the skin of mice. New for the fauna of Several species of mites are relatively common in Poland species of Psorergates spp. Upon histochemical staining, we are unable to determine the specific species of this fungus though we do not believe this morphology is consistent with Malassezia sp. The lack of inflammation associated with the dilated follicles was curious, as neither the mites nor fungi seemed to elicit a response from the host. In some slides, sections of ear pinna were identified which appeared to be the only area where lymphocytes and macrophages were recruited. We elected to include a third diagnosis for this location, though it is worth mentioning the mites seemed to be concentrated in larger numbers in these sections. Contributing Institution: Wildlife Disease Laboratories, Institute for Conservation Research, San Diego Zoo Global: Approximately 200 History: Chronic ascites; suspected neoplastic or ml of blood-tinged, watery fluid was present in inflammatory infiltrate in the liver. Histopathologic Description: Liver: the normal liver architecture is almost completely replaced Gross Pathologic Findings: the liver lobes by coalescing, variably dense aggregates of were diffusely enlarged, pale and rubbery, with a ductules and tubules separated by variably broad trabeculae of fibrous connective tissue in which are scattered capillaries. Ductules are lined by a single layer of cuboidal cells with light eosinophilic cytoplasm and central round to oval nuclei having uniformly granular chromatin, with 1-2 nucleoli. Golden-brown, granular pigment is present in the cytoplasm of some ductal epithelial cells, scattered macrophages and hepatocytes (hemosiderin). Scattered throughout the parenchyma are small foci of ducts with shrunken, hypereosinophilic cells, pyknotic nuclei and karyorrhectic debris (necrosis). Liver, iguana: the hepatic architecture is diffusely altered and replaced by a bright pink, hypocellular material. Cholangiocarcinomas can have a massive or m u l t i l o b u l a r appearance, are often u m b i l i c a t e d a n d protrude from the l i v e r c a p s u l. Pseudocarcinomatous biliary hyperplasia must also be differentiated from biliary hamartoma and cholangioma. In human and veterinary medicine, biliary hamartomas are rare and consist of ducts of varying caliber, unique cystic cavity f o r m a t i o n a n d 1-2. Liver, iguana: At higher magnification, hepatocytes are diffusely replaced by proliferating bile ducts separated 15,17 by a dense collagenous stroma. I n domestic animals, capsule are mildly to moderately thickened by cholangiomas are fibrous connective tissue. In L i v e r: S e v e r e, d i f f u s e, c h r o n i c, one retrospective study, 31% of all primary pseudocarcinomatous biliary hyperplasia with neoplasms in lizards affected the liver versus other organ systems,16 with malignant biliary marked interstitial fibrosis. Aflatoxins are excreted in the bile, two previously reported cases in female green causing periportal necrosis and inflammation in iguanas. With chronic exposure, there is bile biliary ductules replace the majority of normal duct hyperplasia and fibrosis, as described with chronic active hepatitis. Mild cellular atypia, the hyperplasia has been reported in an alpaca in absence of mitotic figures, and lack of invasion of association with parasitic ova of Fasciola hepatica,8,14 and hepatic coccidiosis. These include granular receptor can be involved in epithelial hyperplasia, cell tumors,2 anaplastic large cell lymphoma,12 wound healing and tumorigenesis. The acini, clinical pathologic findings in this case to those which completely replace hepatic parenchyma in previously reported to assist in determining most sections, certainly appear to be biliary ducts whether the abdominal fluid is related to the and in our view, lack malignant characteristics as hepatic lesion. Oral granular cell variety of liver insults,5 many of which are tumors: An analysis of 10 new pediatric and mentioned by the contributor. Courville P, Wechsler J, Thomine E, Vergier differentiate into either biliary epithelium or B, Fonck Y, Souteyrand P, Beylot-Barry M, Bagot hepatocytes proliferate, as also may occur in M, Joly P, and the French Study Group On severe hepatic injury. Severe biliary fibrosis, which develops around hepatic venules, hyperplasia associated with liver fluke infection is termed periacinar fibrosis and occurs in an adult alpaca. Bile duct obstruction is not a prerequisite for type I biliary epithelial cell hyperplasia. Pseudocarcinomatous epithelial hyperplasia in the bladder unassociated with prior irradiation or chemotherapy. Solitary biliary hamartoma with cholelithiasis in a domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Multiple biliary hamartomas: magnetic resonance features with histopathologic correlation. Analysis of the pathomorphology of the intraand extrahepatic biliary system in biliary atresia. In some sections of lung, Signalment: Southern hairy nosed wombat, alveoli are filled by hemorrhage and alveolar Lasiorhinus latifrons. Lung: Multifocal alveolar hemorrhage and examination for a wombat health investigation congestion. Moderate multifocal dorsal and lateral walled non-budding non-replicating adiaspores in alopecia with mild seborrhoea and tissue and elicit granulomatous inflammatory exudative dermatitis reactions in the host. Free the brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula),9 within alveolar lumina or more commonly within most likely secondary to co-habitation of the multinucleated alveolar macrophages there are opossum with introduced British mammals (otter, many large spherical organisms (yeasts). Occasionally, subepithelial connective tissues of bronchioles are infiltrated by Wombats are large herbivorous burrowing aggregates of foamy macrophages forming small marsupials native to Australia, of which there are granulomas with intralesional yeasts. Lung, wombat: Alveoli contain moderate numbers of foamy macrophages and neutrophils with fewer multinucleated giant cell macrophage admixed with fibrin and cellular debris. The Aleuriospores of Emmonsia are ubiquitous and southern hairy nosed wombat is native to South soil borne, and on inhalation form thick-walled Australia and it is estimated that up to 100,000 non-replicating adiaspores in host tissues which remain in the wild. Infection of wombats case was culled and examined as part of a larger is thought to occur when they are pouch young, study examining skin disease and poor body and a linear increase in Emmonsia spherule size condition in wombats in the Murrayland region of with increasing wombat age has been observed. Pulmonary adiaspiromycosis was the habitat and burrowing habits of the wombat observed in all wild wombats culled concurrently is thought to render them prone to infections.
4 mg medrol fast delivery
Often patients cise diagnosis may require more specialized laboratory with polycythemia are detected through an incidental tests arthritis ribs buy genuine medrol on-line, such as hemoglobin electrophoresis or a screen for finding of elevated hemoglobin or hematocrit levels. Acquired defects in red cell survival are cern that the hemoglobin level may be abnormally high is often immunologically mediated and require a direct or usually triggered at 170 g/L (17 g/dL) for men and indirect antiglobulin test or a cold agglutinin titer to 150 g/L (15 g/dL) for women. Hematocrit levels >50% in detect the presence of hemolytic antibodies or complemen or >45% in women may be abnormal. Rarely, in the acute setting, anemia may be so experience symptoms related to the increased red cell severe that red cell transfusions are required before a mass or an underlying disease process that leads to specific diagnosis is made. The dominant symptoms acute or gradual onset, the selection of the appropriate from increased red cell mass are related to hyperviscosity treatment is determined by the documented cause(s) of and thrombosis (both venous and arterial) because the the anemia. Often, the cause of the anemia may be blood viscosity increases logarithmically at hematocrits multifactorial. Manifestations range from digital ischemia to rheumatoid arthritis who has been taking anti-infiamBudd-Chiari syndrome with hepatic vein thrombosis. Neuroassociated with chronic infiammation as well as chronic logic symptoms such as vertigo, tinnitus, headache, and blood loss associated with intermittent gastrointestinal visual disturbances may occur. Transfusion is discussed in Patients may have easy bruising, epistaxis, or bleeding Chap. Splenomegaly favors polycythemia vera as Therapeutic options for the treatment of anemias the diagnosis (Chap. Increased blood transformed the lives of patients with chronic renal failviscosity raises pulmonary artery pressure; hypoxemia ure on dialysis and made some improvements in the can lead to increased pulmonary vascular resistance. Those who cannot stop smoking require (>36 mL/kg in men, >32 mL/kg in women), serum phlebotomy to control their polycythemia. The procoagulant forces include platelet adhesion and Platelet adhesion results in subsequent platelet activaaggregation and fibrin clot formation; anticoagulant tion and aggregation. This process is enhanced and forces include the natural inhibitors of coagulation and amplified by humoral mediators in plasma. Under normal circumstances, hemostasis is nephrine, thrombin); mediators released from activated regulated to promote blood fiow; however, it is also platelets. The major components of which they secrete contents that further promote aggrethe hemostatic system, which function in concert, are gation and inhibit the naturally anticoagulant endothelial (1) platelets and other formed elements of blood, such cell factors. During platelet aggregation (platelet-platelet as monocytes and red cells; (2) plasma proteins (the interaction), additional platelets are recruited from the coagulation and fibrinolytic factors and inhibitors); and circulation to the site of vascular injury, leading to the (3) the vessel wall itself. This receptor is the key mediator of platelet the high levels of shear stress that would tend to detach aggregation, so it has become an effective target for them with the fiow of blood. Thromand activation through the classic extrinsic pathway but bin is a multifunctional enzyme that converts soluble with critically important amplification through elements plasma fibrinogen to an insoluble fibrin matrix. The critical cell membrane compocomponents of the vessel wall, such as smooth-muscle nents, acidic phospholipids, are not normally exposed cells and fibroblasts. However, when microparticles, presumably shed from cells including platelets, monocytes, and endothelial cells are activated monocytes and platelets. Coagulation requires calcium (not bin formation and subsequent conversion of fibrinogen to shown) and takes place on phospholipid surfaces, usually the fibrin. Fibrinogen is a trinoduPlasma lar structure consisting of 2 D domains and 1 E domain. These mechanisms operate to preserve blood increases by a factor of several thousand in the presence fluidity and limit blood clotting to specific focal of heparin. Endothelial cells have many other activated clotting factors occurs physiologically on antithrombotic effects. They also activate fibProtein C is a plasma glycoprotein that becomes an antirinolytic mechanisms through the production of tissue coagulant when it is activated by thrombin. The thrombinplasminogen activator 1, urokinase, plasminogen activainduced activation of protein C occurs physiologically on tor inhibitor, and annexin-2. This reaction is accelerated by forming a complex between the active site of the a cofactor, protein S, which, like protein C, is a glycoproenzyme and the reactive center of antithrombin. The tein that undergoes vitamin K-dependent posttranslarate of formation of these inactivating complexes tional modification. Quantitative or qualitative deficiencies of protein C or protein S, or resistance to the action of generate the active enzyme plasmin. The sites of plasmin cleavage of fibrin are the same as those in Any thrombin that escapes the inhibitory effects of the fibrinogen. However, when plasmin acts on covalently physiologic anticoagulant systems is available to convert cross-linked fibrin, D-dimers are released; hence D-dimers fibrinogen to fibrin. In response, the endogenous fibrican be measured in plasma as a relatively specific test of nolytic system is then activated to dispose of intravascufibrin (rather than fibrinogen) degradation. D-Dimer lar fibrin and thereby maintain or reestablish the assays can be used as sensitive markers of blood clot forpatency of the circulation. Physiologic regulation of fibrinolysis occurs primarily Figure 3-4 shows the general scheme of fibrinolysis. Any free plasmin is complexed with History of Bleeding A history of bleeding is the most -antiplasmin (Pl). In evaluating a 2 2 26 patient for a bleeding disorder, a history of at-risk to minor trauma. The latter has been termed senile situations, including the response to past surgeries, purpura. Does the patient have a history Epistaxis is a common symptom, particularly in of spontaneous or trauma/surgery-induced bleedchildren and in dry climates, and it may not refiect an ingfi Bleeding with eruption of primary shows the disorders affecting primary hemostasis. It trauma is normal; however, an exaggerated response is uncommon in children with mild bleeding disorto trauma may be an indication of an underlying ders. Ecchymoses presenting without (platelet adhesion) do have increased bleeding after known trauma, particularly on the trunk, and espedental cleanings and other procedures that involve cially large ecchymoses, >2 in. The introMenorrhagia is defined quantitatively as a loss of duction of medications or nutritional supplements >80 mL of blood per cycle, based on blood loss with platelet inhibitory activity often enhance bruisrequired to produce iron-deficiency anemia. A coming and bleeding in a patient with an underlying plaint of heavy menses is subjective and has a poor bleeding disorder. Predictors of medical conditions in which there is no identifiable menorrhagia include bleeding resulting in iron-deficoagulopathy; instead, the conditions are caused by an ciency anemia or a need for blood transfusion, excesabnormality of blood vessels or their supporting tissive pad or tampon use, menses lasting >8 days, passues. In Ehlers-Danlos syndrome there may be sage of clots, bleeding through protection, or fiooding posttraumatic bleeding and a history of joint hyperat night. Defects of platelet secretion Women with a history of postpartum hemorrhage Decreased cyclooxygenase activity have a high risk of recurrence with subsequent Drug-induced (aspirin, nonsteroidal pregnancies. Rupture of ovarian cysts with intraanti-infiammatory agents) abdominal hemorrhage has also been reported in Inherited women with underlying bleeding disorders. Granule storage pool defects Inherited Tonsillectomy is a major hemostatic challenge Acquired because intact hemostatic mechanisms are essential to Nonspecific drug effects prevent excessive bleeding from the tonsillar bed. Uremia Bleeding may occur early after surgery or after fi7 days Platelet coating. Muscle and soft tissue bleeds are also common Meadowsweet (Filipendula ulmaria) Willow (Salix spp. Bleeding into a joint Coumarin-Containing Herbs results in severe pain and swelling, as well as loss of Motherwort (Leonurus cardiaca) function, but is rarely associated with discoloration Chamomile (Matricaria recutita, Chamaemelum mobile) from bruising around the joint. Life-threatening sites Horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) of bleeding include bleeding into the oropharynx, Red clover (Trifolium pratense) where bleeding can obstruct the airway, into the cenFenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) tral nervous system, and into the retroperitoneum. Central nervous system bleeding is the major cause of bleeding-related deaths in patients with severe congenital factor deficiencies. The aspirin effect on presenting complaint in liver disease, severe renal platelet function as assessed by aggregometry can perimpairment, hypothyroidism, paraproteinemias or sist for up to 7 days, although it has frequently amyloidosis, and conditions causing bone marrow returned to normal by 3 days after the last dose. This situation is often comMany herbal supplements can impair hemostatic pounded by thrombocytopenia from splenomegaly function (Table 3-2).
Discount medrol 16 mg otc
In all cases arthritis pain relief in knuckles order generic medrol, the role of the commander is to ensure Soldiers do not violate their profiles and are assigned duties that they can perform without undue risk to health and safety. Medical guidance is critical in advising commanders of potential problems, physical limitations and potential situations that could be harmful to the Soldier or detrimental to the mission. Some Soldiers, because of certain medical conditions, may require administrative consideration when assigned to combat areas or certain geographic areas. The counseled Soldiers will be advised that they will not violate their profiles and will perform duties assigned by the commander which they can perform without undue risk to health and safety. The following medical conditions must be reviewed carefully by the medical provider before making a recommendation as to whether the Soldier can deploy to duty in a combat zone or austere isolated area where medical treatment may not be readily available. If found fit for duty, the Soldier should not deploy to areas where insulin cannot be properly stored (stored above freezing level but at less than 86 degrees Fahrenheit) or appropriate medical support cannot be reasonably assured. Deployment should only follow predeployment review and recommendation by an endocrinologist. If after an evaluation by a cardiovascular specialist, the Soldier is found to meet medical retention standards, the Soldier must remain at a location with access to echocardiography and medical monitoring for 6 months from the date myocarditis was diagnosed. If it is determined that the Soldier can be returned to duty, the Soldier should not deploy if he/she cannot wear protective gear, has experienced recent emergency room visits, or requires repetitive use of oral corticosteroids. Soldiers with any recent musculoskeletal injury or surgery that prevents necessary mobility or firing a weapon should not deploy. If found fit for duty, the Soldier may be deployed unless he/she cannot function in the specific environment in which he/she is being assigned. Soldiers with a psychiatric disorder in remission or whose residual symptoms do not impair duty performance may be considered for deployment duties. The commander makes the ultimate decision to deploy after consulting with the treating physician or other privileged provider. The availability, accessibility, and practicality of a course of treatment or continuation of treatment in theater or austere environment should be consistent with clinical practice standards. If there are any questions on the safety of psychiatric medication, a psychiatrist must be consulted. The potential for deterioration must be evaluated considering potential environmental demands and individual vulnerabilities. Antipsychotics used to control psychotic, bipolar, and chronic insomnia symptoms; lithium and anticonvulsants to control bipolar symptoms; 2. Medications that require special storage considerations, for example, refrigeration; 3. Medications that require laboratory monitoring or special assessments, including lithium, anticonvulsants, and antipsychotics; 4. Medication prescribed within 3 months prior to deployment that has yet to demonstrate efficacy or be free of significant impairing side effects. Decisions to deploy personnel on such medications should be balanced with necessity for such medication in order to effectively function in a deployed setting, susceptibility to withdrawal symptoms, ability to secure and procure controlled medications, and potential for medication abuse. If there is any evidence of significant heat intolerance, the Soldier should not deploy to warm austere climates. Soldiers with a history of cancer who have been returned to duty but have a requirement for periodic monitoring every 6 months or less should not deploy. Soldiers with recently treated moderate or severe dysplasia may only be deployed to austere environments if coordination is arranged via the unit commander and theater surgeon to ensure follow-up evaluation 7 to 9 months after initial evaluation and treatment. Soldiers with history of malignant hyperthermia should not be assigned to areas where complete anesthesia services are unavailable or to austere environments. Soldiers taking medications should not automatically be disqualified for any duty assignment. Medications used for serious and/or complex medical conditions are not usually suitable for extended deployments. The medications on the list below are most likely to be used for serious and/or complex medical conditions that could likely result in adverse health consequences. This is not an all-inclusive listing of medications that may render an individual non-deployable but is provided as a guideline to be used during pre-deployment medical screening. Because some medications are used for multiple reasons, any medical screening should take into account whether the drug is being used for a serious and/or complex medical condition or another use that might be appropriate for a deploying Soldier. Examples of areas where altitude is an important consideration are La Paz, Bolivia; Quito, Ecuador; Bogota, Columbia; and Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Date of medical incapacitation is the date a disqualifying medical condition was definitively diagnosed by history, examination, or test. The effective date of medical termination from aviation service is based on this date. Selected and eligible aircrew members may be referred to the tertiary aeromedical consultative services of the U. This physical is valid for up to 24 months to allow completion of the Flight Training programs. It will be performed within 90 days before the end of the birth month in the year it is due. It will be performed within 90 days before the end of the birth month and is valid until the end of the next birth month. If retiring, the period of validity will extend to 18 months past the birth month. Army aeromedical standards from chapters 2 and 4 for the determination of medical fitness for flying duty. All others (that is, new disqualifications or not meeting annual waiver requirements) must be reviewed and co-signed by the supervising flight surgeon for submission. Consultations may be obtained at Government expense when authorized as stated below. The tests and consultations are conducted only to the extent required to determine medical fitness for flying duties and not for the treatment or correction of disqualifying conditions. In no case will the originals be given to the applicant or other individuals not in the procurement chain of command. Waiver and suspension recommendation and approval letters will be filed in the individual health record and flight record. If a disqualifying medical condition is found, a waiver must be granted by the appropriate authority before further flying duties are performed. Treatment means any medical treatment or procedure performed by a non-aeromedical health care provider, and includes, but is not limited to , the following: (1) Any medical or dental procedure requiring use of medications after treatment. Examples include ankle sprain, acute rhinitis, gastroenteritis, and simple closed fracture. The immediate commander will set the date of medical incapacitation and impose the temporary medical suspension.
Generic medrol 4mg amex
Across both trials arthritis back diet purchase medrol with mastercard, the most common adverse reactions (fi20%) were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite. The trial excluded patients with active autoimmune disease, medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression, or with symptomatic interstitial lung disease. The most frequent (fi2%) serious adverse reactions were pneumonia, dyspnea, pneumonitis, pleural effusion, and dehydration. The most common (fi20%) adverse reactions were fatigue, decreased appetite, musculoskeletal pain, dyspnea, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and cough. The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in fi1% of patients were pneumonia, infusionrelated reaction, pyrexia, colitis or diarrhea, pleural effusion, pneumonitis, and rash. The most common adverse reactions (fi20%) among all patients were upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, diarrhea, pyrexia, musculoskeletal pain, rash, nausea, and pruritus. After an immune-mediated adverse reaction, reactions following nivolumab rechallenge were included if they occurred up to 30 days after completing the initial nivolumab course. Twenty-eight patients (11%) had new-onset peripheral neuropathy and 3 patients had worsening of neuropathy from baseline. Other common findings (fi10%) included increased creatinine, electrolyte abnormalities, and increased amylase. Forty-six percent (46%) of patients had a dose interruption for an adverse reaction. The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in fi2% of patients were urinary tract infection, sepsis, diarrhea, small intestine obstruction, and general physical health deterioration. Treatment was discontinued in 13% of patients and delayed in 45% of patients for an adverse reaction. The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of patients were pyrexia, ascites, back pain, general physical health deterioration, abdominal pain, pneumonia, and anemia. Based on the design of the study, the data below cannot be used to identify statistically significant differences between the cohorts summarized below for any adverse reaction. The trial excluded patients who were refractory or intolerant to taxane therapy, had brain metastases that were symptomatic or required treatment, had autoimmune disease, used systemic corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, had apparent tumor invasion of organs adjacent to the esophageal tumor or had stents in the esophagus or respiratory tract. There was no evidence of altered pharmacokinetic profile or increased incidence of infusion-related reactions with anti-nivolumab antibody development. There was no evidence of increased incidence of infusion-related reactions with anti-nivolumab antibody development. Nivolumab administration resulted in a non-dose-related increase in spontaneous abortion and increased neonatal death. In surviving infants (18 of 32 compared to 11 of 16 vehicle-exposed infants) of cynomolgus monkeys treated with nivolumab, there were no apparent malformations and no effects on neurobehavioral, immunological, or clinical pathology parameters throughout the 6-month postnatal period. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were reported between elderly patients and younger patients. In elderly patients with intermediate or poor risk, no overall difference in effectiveness was reported. The predicted exposure of nivolumab after a 30-minute infusion is comparable to that observed with a 60-minute infusion. Nivolumab clearance does not decrease over time in patients with completely resected melanoma, as the geometric mean population clearance is 24% lower in this patient population compared with patients with metastatic melanoma at steady state. In 1-month and 3-month repeat-dose toxicology studies in monkeys, there were no notable effects in the male and female reproductive organs; however, most animals in these studies were not sexually mature. The trial excluded patients with autoimmune disease, medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression, ocular melanoma, active brain metastasis, or a history of Grade 4 ipilimumab-related adverse reactions (except for endocrinopathies) or Grade 3 ipilimumab-related adverse reactions that had not resolved or were inadequately controlled within 12 weeks of the initiating event. Of 38 patients with responses, 87% had ongoing responses with durations ranging from 2. The trial population characteristics were: median age was 65 years (range: 18 to 87), 59% were male, and 99. Patients underwent imaging for tumor recurrence every 12 weeks for the first 2 years then every 6 months thereafter. Patients with treated brain metastases were eligible if neurologically returned to baseline at least 2 weeks prior to enrolment, and either off corticosteroids, or on a stable or decreasing dose of <10 mg daily prednisone equivalents. Study treatment continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for up to 24 months. Tumor assessments were performed every 6 weeks from the first dose of study treatment for the first 12 months, then every 12 weeks until disease progression or study treatment was discontinued. Treatment could continue beyond disease progression if a patient was clinically stable and was considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator. Efficacy results from the prespecified interim analysis when 351 events were observed (87% of the planned number of events for final analysis) are presented in Table 36. The trial excluded patients with autoimmune disease, medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression, symptomatic interstitial lung disease, or untreated brain metastasis. All patients received prior therapy with a platinum-doublet regimen and 99% of patients had tumors of squamous-cell histology. Prior therapy included platinum-doublet regimen (100%) and 40% received maintenance therapy as part of the first-line regimen. The majority of patients (77%) were treated with one prior anti-angiogenic therapy. Across the trial population, 28% (101/361) of patients had nonquantifiable results. In pre-specified exploratory subgroup analyses, the hazard ratio for survival was 0. Tumor response assessments were conducted every 8 weeks for the first 48 weeks and every 12 weeks thereafter. Twenty-seven percent had non-bladder urothelial carcinoma and 84% had visceral metastases. Thirty-four percent of patients had disease progression following prior platinum-containing neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy. Eighteen percent of patients had a hemoglobin <10 g/dL, and twenty-eight percent of patients had liver metastases at baseline. Treatment in both cohorts continued until unacceptable toxicity or radiographic progression. The median age was 53 years (range: 26 to 79) with 23% fi65 years of age and 5% fi75 years of age, 59% were male and 88% were White. The median age was 58 years (range: 21 to 88), with 32% fi65 years of age and 9% fi75 years of age; 59% were male and 92% were White. Prior treatment history included surgical resection (66%), radiotherapy (24%), or locoregional treatment (58%). Prior cancer treatment history included surgery (74%), radiotherapy (29%), or local treatment (59%). The trial excluded patients who were refractory or intolerant to taxane therapy, had brain metastases that were symptomatic or required treatment, had autoimmune disease, used systemic corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, or had apparent tumor invasion of organs adjacent to the esophageal tumor or had stents in the esophagus or respiratory tract. The tumor assessments were conducted every 6 weeks for 1 year, and every 12 weeks thereafter. These problems can sometimes become serious or life-threatening and can lead to death. These problems may happen anytime during treatment or even after your treatment has ended. Call or see your healthcare provider right away if you develop any symptoms of the following problems or these symptoms get worse: Lung problems (pneumonitis). Talk to your healthcare provider about birth control methods that you can use during this time. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare providers and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Your healthcare provider will determine if you will also need to receive chemotherapy every 3 weeks for 2 cycles.

